全双工加扰的非可信中继系统的渐近性能分析
赵睿,谭星,李元健,贺玉成,李春国
全双工加扰的非可信中继系统的渐近性能分析
赵睿1,谭星1,李元健1,贺玉成1,李春国2
(1. 华侨大学厦门市移动多媒体通信重点实验室,福建 厦门 361021;2. 东南大学信息科学与工程学院,江苏 南京 210096)
在物理层安全领域,协作中继技术因具备提升网络容量和扩展网络覆盖范围等优点,受到学术界广泛关注。但是,协作中继在某些时候可能存在非可信情形。基于此,在瑞利衰落信道下,为提升非可信中继系统安全性能,提出一种多天线全双工目的节点加扰(FDJ, full-duplex destination jamming)策略。为最大化系统安全容量,针对多天线目的节点提出一种切换分离式最优天线选择(OAS, optimal antenna selection)方案,并设计出信源和目的节点功率分配优化方案,给出相应的安全性能指标闭合表达式。在大规模天线下,推导出FDJ-OAS策略的遍历可达安全速率和瞬时安全容量下最优功率分配因子闭合表达式。在不同的渐近条件下,推导出FDJ-OAS策略的安全中断概率的渐近线闭合表达式。仿真结果显示,理论分析与蒙特卡洛仿真曲线十分吻合,FDJ-OAS策略的安全分集阶数与天线数呈正比,可实现天线全分集,凸显了FDJ-OAS策略的性能优越性。
物理层安全;全双工目的节点加扰;最优天线选择;遍历可达安全速率;安全中断概率
1 引言
无线协作中继网络技术不仅能提升系统容量、增大信号覆盖范围,还能充分利用无线信道空间和时变特性,从物理层保证安全通信[1-3]。但是,实际中的中继不总是有利于安全通信的,有时可能存在不可信中继场景,即中继在辅助转发信源信息时,也扮演着一个被动的窃听者的角色[4-11],这导致通信内部存在安全隐患。而且,当信源与信宿较远且中继节点使用解码转发(DF, decode and forward)时,中继会比目的节点获得更多的保密信息。因此在非可信中继网络中,研究者们通常使用放大转发(AF, amplify and forward)协议转发信息[5]。
在非可信中继网络系统中,为提升安全速率和防止内部窃听保密信息,研究者们探索出各种安全传输策略,例如,目的节点加扰(DBJ, destination based jamming)[5-8]、多天线选择[6]、协作最优中继选择(ORS, optimal relay selection)[5,7]、最优功率分配(OPA, optimal power allocation)[10-11]等策略。文献[5]提出了DBJ策略,即目的节点发送噪声信号干扰中继窃听,以保证获得正安全容量。文献[6]针对多天线中继系统,采用天线选择和最大比合并技术分析安全中断概率(SOP, secrecy outage probability)指标,得出中继的天线数越多系统安全性能越差的结论。文献[7]分析了多个非可信中继网络的渐近安全性能,推导了分布式波束成形和ORS这2种策略的上下界平均安全容量计算式,并进一步分析了安全分集阶数(SDO, secrecy diversity order)。文献[8]探索能量采集技术下的非可信中继网络,中继将接收到的有用信息和噪声信息的一部分转换成能量,用于转发信息所需的能量。文献[9]针对3种不同信道状态信息下的用户选择准则,推导了其SOP的闭合表达式和渐近表达式。为最大化系统的安全容量,文献[10-11]在大规模多输入多输出(MIMO, multiple input and multiple output)系统下推导出瞬时安全速率下的最优功率分配因子,并根据OPA策略去分析遍历安全容量和SOP。针对MIMO系统,文献[12-13]运用大数定理的极限形式近似各信道参数,简化分析AF和DF协议下的SOP;文献[14]运用最大值定理的极限形式分析了系统的吞吐量渐近表达式。
全双工(FD, full duplex)技术以同时收发信息来成倍提升安全速率和频谱效率,并已广泛地运用于下一代通信系统中。当FD技术与目的节点加扰技术相结合时,称之为全双工目的节点加扰(FDJ, full-duplex destination jamming)策略,并在文献[15-17]中已应用。例如,在二层分散的无线异构网络中,文献[15]研究了FDJ策略在物理层安全领域具备一定优势;在多窃听MIMO信道中,分布有多个全双工目的节点和窃听节点,文献[16]研究了联合信源和信宿人工噪声预编码算法来优化系统的瞬时安全容量;文献[17]针对目的节点已知瞬时窃听信道状态信息(ECSI, eavesdropping channel state information)和统计ECSI这2种情况,提出了全双工目的节点加扰的收发天线模式自适应切换算法,从而优化安全速率。然而,在非可信中继网络中,目前存在的DBJ仅仅运用在半双工(HD, half duplex)模式下,且不考虑直达路径的理想情况。针对此问题,本文考虑更为实际的情形,即信源与目的节点之间存在直达路径、目的节点分配多根天线且工作于FDJ模式下[15],采用自由切换分离式天线选择技术选择收发天线[18-19],并通过信源和目的节点的总功率合理分配来分析安全通信问题。
针对上述讨论,本文研究了一种最优天线选择(OAS, optimal antenna selection)策略下的FDJ的非可信中继系统。为了对比分析,还研究了与OAS策略结合的2种HD策略,即半双工目的节点加扰(HDJ, half-duplex destination jamming)和无加扰(NJ, non-jamming)。本文主要贡献有以下3点.
1) 推导出大规模天线数下3种策略的近似遍历可达安全速率(EASR, ergodic achievable secrecy rate)闭合表达式,并通过Matlab仿真对比分析2种半双工策略以及全双工自干扰(SI, self-interference)的影响、文献[20]中的信源节点加扰(SBJ, source- based jamming)策略和文献[21]中的全双工中继传输策略的系统性能,得出FDJ-OAS策略的性能优越性。
2) 通过合理的近似化简,推导出大规模天线下FDJ-OAS策略瞬时安全容量的OPA方案,并进一步分析了高信噪比下的OPA方案。
3) 在3种不同的渐近条件下,推导出3种策略的SOP渐近线闭合表达式,并分析了3种策略的SDO和安全阵列增益。
2 系统模型
本节详细地介绍了非可信中继网络模型以及FDJ和最优天线选择策略。
2.1 非可信中继系统模型
非可信中继系统模型架构如图1所示。

图1 非可信中继系统模型架构
2.2 全双工目的节点加扰
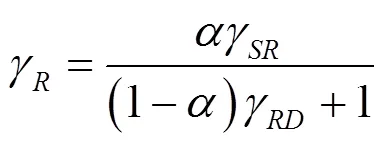


针对FDJ策略模型,由于中继为非可信中继,则系统的瞬时安全容量可表示为

2.3 最优天线选择方案


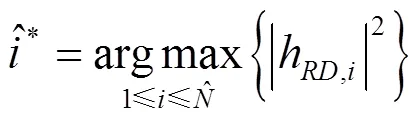
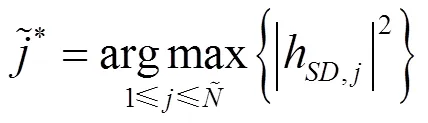

2.4 2种半双工策略
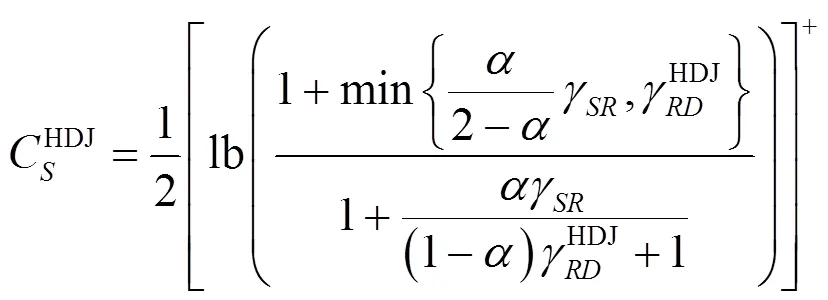

3 大规模天线的遍历可达安全速率
根据文献[29-30]的描述,将遍历安全容量(ESC, ergodic secrecy capacity)定义为可达平均通信速率的最大值。在非可信中继系统中可表示为

3.1 统计量的概率分布
在瑞利衰落信道中,各信道参数均服从指数分布,根据前面的天线选择方案,它们的累积分布函数和概率分布函数可以分别写为
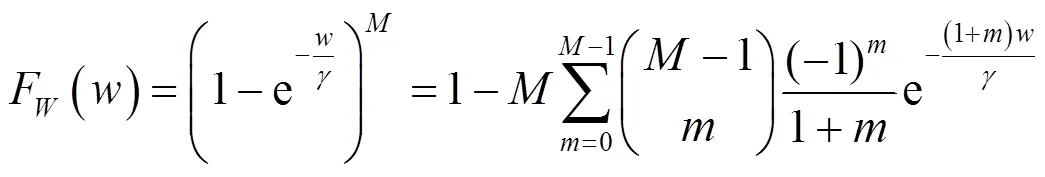

3.2 大规模天线下的遍历可达安全速率分析




利用式(11)和式(12),并引用文献[31]中的式(4.337.1)和式(4.337.2),通过简单的数学积分,求得式(15)和式(16)的闭合解,分别为

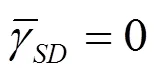
3.3 功率分配方案分析
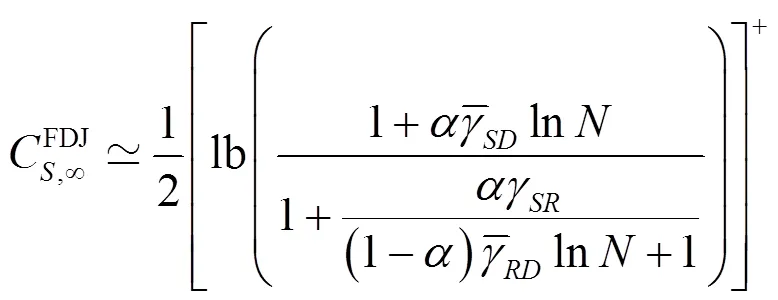

证毕。
根据上述定理,在高下给出简化的FDJ-OAS的OPA因子。

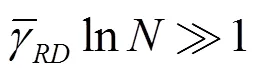
证毕。
4 渐近安全中断概率分析
在非可信中继网络中,为解释天线选择是否对系统有利,并参考文献[6-7]的分析,本文给出了3种策略下3种情形的渐近性能分析。
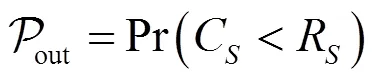
对于NJ-OAS而言,其的闭合表达式如下。
引理3 根据式(22),可得NJ-OAS的为
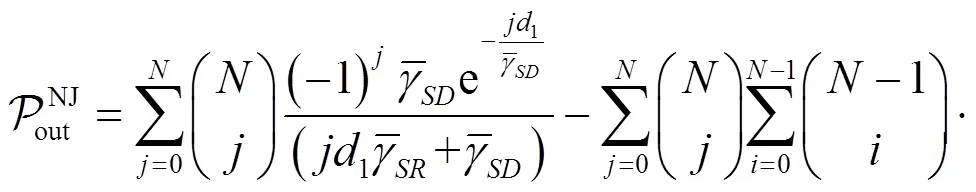

证明略。
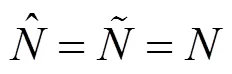

证明过程详见文献[6]中引理1的证明。

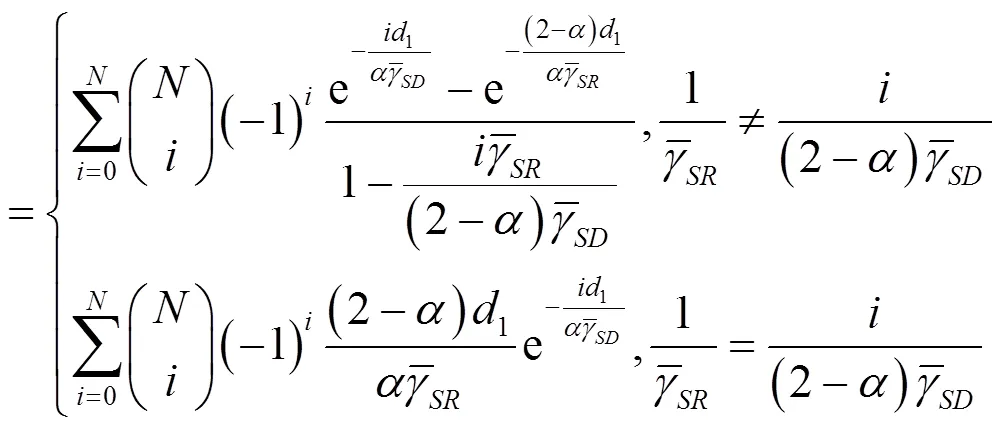
证明略。
同理,运用式(8)和式(22),HDJ-OAS的渐近线闭合表达式为

引用式(23),可得NJ-OAS的可化简为
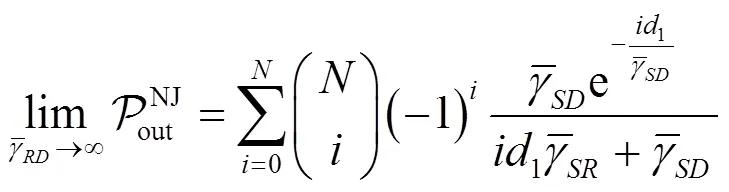



证明略。
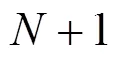

5 仿真结果与讨论

图2 3个节点位置变化拓扑结构

图3 5种策略下EASR随着功率P的变化曲线

图4 3种策略下EASR随N的变化趋势

图5 不同PA方案下EASR随N的变化趋势

图6 在不同的和下3种策略的SOP曲线变化
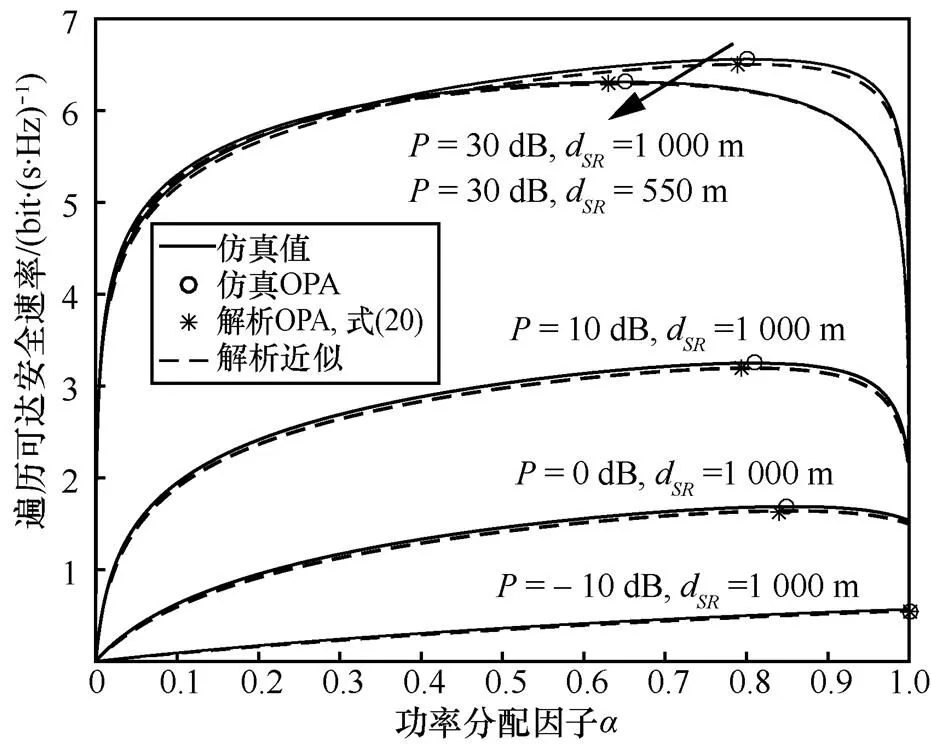
图7 FDJ-OAS策略EASR在不同的P和dSR下的曲线

图8 3种策略的SOP随着dRD的曲线变化
6 结束语
[1] DONG L, HAN Z, PETROPULU A P, et al. Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1875-1888.
[2] ZHAO R, HUANG Y, WANG W, et al. Ergodic achievable secrecy rate of multiple antenna relay systems with cooperative jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(4): 2537-2551.
[3] ZHAO R, YUAN Y, FAN L, et al. Secrecy performance analysis of cognitive decode and-forward relay networks in nakagami fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(2): 549-563.
[4] JEONG C, KIM I M, KIM D I. Joint secure beamforming design at the source and the relay for an amplify-and-forward MIMO untrusted relay system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(1): 310-325.
[5] SUN L, ZHANG T, LI Y, et al. Performance study of two-hop amplify-and-forward systems with untrustworthy relay nodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2012, 61(8): 3801-3807.
[6] HUANG J, MUKHERJEE A, SWIND L A L. Secure communication via an untrusted non-regenerative relay in fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(10): 2536-2550.
[7] KIM J B, LIM J, CIOFFI J M. Capacity scaling and diversity order for secure cooperative relaying with untrustworthy relays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(7): 3866-3876.
[8] KALAMKAR S S, BANERJEE A. Secure communication via a wireless energy harvesting untrusted relay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(3): 2199-2213.
[9] 邓单, 周雯. 不可信无线中继网络中基于用户选择的安全通信研究[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(7): 1593-1600.
DENG D, ZHOU W. Secure selection for decode-and-forward cooperative networks with untrusted relay[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(7): 1593-1600.
[10] KUHESTANI A, MOHAMMADI A. Destination-based cooperative jamming in untrusted amplify-and-forward relay networks: resource allocation and performance study[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(1): 17-23.
[11] WANG L, ELKASHLAN M, HUANG J, et al. Secure transmission with optimal power allocation in untrusted relay networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2014, 3(3): 289-292.
[12] CHEN X, CHEN J, LIU T. Secure transmission in wireless powered massive MIMO relaying systems: performance analysis and optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(10): 8025-8035.
[13] CHEN X, LEI L, ZHANG H, et al. Large-scale MIMO relaying techniques for physical layer security: AF or DF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(9): 5135-5146.
[14] SHARIF M, HASSIBI B. On the capacity of MIMO broadcast channels with partial side information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(2): 506-522.
[15] ZHENG T X, WANG H M, YANG Q, et al. Safeguarding decentralized wireless networks using full-duplex jamming receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(1): 278-292.
[16] MASOOD M, GHRAYEB A, BABU P, et al. A minorization-maximization algorithm for maximizing the secrecy rate of the MIMOME wiretap channel[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(3): 520-523.
[17] LI Y, ZHAO R, FAN L, et al. Antenna mode switching for full-duplex destination-based jamming secure transmission[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 9442-9453.
[18] YANG K, CUI H, SONG L, et al. Efficient full-duplex relaying with joint antenna-relay selection and self-interference suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(7): 3991-4005.
[19] ZHOU M, SONG L, LI Y, et al. Simultaneous bidirectional link selection in full duplex MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(7): 4052-4062.
[20] LV L, CHEN J, YANG L, et al. Improving physical layer security in untrusted relay networks: cooperative jamming and power allocation[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(3): 393-399.
[21] 李博轮, 梁涛, 鲍丽娜. 基于全双工非可信中继的物理层安全性能分析[J]. 军事通信技术, 2016, 37(4): 29-33.
LI B L, LIANG T, BAO L N. Analysis of physical layer secure scheme for untrusted full-duplex relay system[J]. Military Communications Technology, 2016, 37(4): 29-33.
[22] LI C G, ZHANG S, LIU P, et al. Overhearing protocol design exploiting intercell interference in cooperative green networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(1): 441-446.
[23] 吴飞, 邵士海, 唐友喜. 一种基于多天线波束成形的全双工自干扰抵消算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(1): 8-15.
WU F, SHAO S H, TANG Y X. A novel self-interference cancellation algorithm using multi-antenna beamforming in full-duplex system[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(1): 8-15.
[24] ZHANG Z, CHAI X, LONG K, et al. Full duplex techniques for 5G networks: self-interference cancellation, protocol design, and relay selection[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2015, 53(5): 128-137.
[25] GUO T, WANG B, WU W, et al. Secrecy-oriented antenna assignment optimization at full-duplex receiver with self-interference[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, PP(99):1.
[26] LI L, CHEN Z, ZHANG D, et al. A full-duplex Bob in the MIMO Gaussian wiretap channel: Scheme and performance[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(1): 107-111.
[27] CHEN D, CHENG Y, YANG W, et al. Physical layer security in cognitive untrusted relay networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 7055-7065.
[28] CIRIK A C, BISWAS S, VUPPALA S, et al. Beamforming design for full-duplex MIMO interference channels-QoS and energy efficiency considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(11): 4635-4651.
[29] BLOCH M, BARROS J, RODRIGUES M R D, et al. Wireless information-theoretic security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(6): 2515-2534.
[30] ZHAO R, LIN H, HE Y C, et al. Secrecy performance of transmit antenna selection for MIMO relay systems with outdated CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(2): 546-559.
[31] GRADSHTEYN I S, RYZHIK I M. Table of integrals, series, and products[M].Manhattan: Academic Press, 2007.
[32] HUANG J, SWINDLEHURST A L. Cooperative jamming for secure communications in MIMO relay networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(10): 4871-4884.
[33] 王伟, 安立源, 章国安, 等. 能量受限全双工双向中继系统的波束成形设计[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(2): 43-52.
WANG W, AN L Y, ZHANG G A, et al. Beamforming design for energy-constrained full-duplex two-way relaying system[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(2):43-52.
[34] WANG R, TAO M, LIU Y. Optimal linear transceiver designs for cognitive two-way relay networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(4): 992-1005.
Asymptotic performance analysis of untrusted relay system with full-duplex jamming destination
ZHAO Rui1, TAN Xing1, LI Yuanjian1, HE Yucheng1, LI Chunguo2
1. Xiamen Key Laboratory of Mobile Multimedia Communications, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China 2. School of Information Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
The cooperative relay technique in the field of physical layer security is widely concerned by the academic community, due to the advantages of increasing the network capacity and expanding the network coverage. However, cooperative relays may play as untrusted nodes in some certain circumstances. Based on this, to enhance the secrecy performance of untrusted relay systems, a novel full-duplex destination jamming (FDJ) scheme was proposed in the Rayleigh fading channel. In order to maximize the system’s secrecy capacity, a switchable split-optimal antenna selection (OAS) scheme was proposed for a multiple-antenna destination, the power allocation optimization scheme between the source and destination was designed, and the corresponding closed-form expressions of secrecy performance were given. In the large-scale antennas analysis, the closed-form expressions of the ergodic achievable secrecy rate and the optimal power allocation factor of instantaneous secrecy capacity for the FDJ-OAS scheme were derived. Furthermore, based on different asymptotic cases, the asymptotic analyses of secrecy outage probability for the FDJ-OAS scheme were significantly analyzed. Simulation results show that the analytical curves match well with the Monte-Carlo simulation results. It is concluded that the diversity order of the FDJ-OAS scheme is proportional to the number of antennas and antenna diversity can be achieved, which reveals the advantages of the proposed FDJ-OAS scheme.
physical layer security,full-duplex destination jamming, optimal antenna selection, ergodic achievable secrecy rate, secrecy outage probability
TN92
A
10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2018155
赵睿(1980−),男,江苏扬州人,博士,华侨大学教授,主要研究方向为无线通信信号处理、协作通信和物理层安全等。

谭星(1993−),男,重庆人,华侨大学硕士生,主要研究方向为物理层安全技术、协作中继通信技术等。
李元健(1993−),男,山东德州人,华侨大学硕士生,主要研究方向为无线通信信号处理、物理层安全技术等。

贺玉成(1964−),男,山西太原人,博士,华侨大学教授,主要研究方向为无线通信信号处理、深空通信和信道编码等。
李春国(1983−),男,山东胶州人,博士,东南大学教授、博士生导师,主要研究方向为新一代移动通信技术、MIMO-OFDM技术、协作通信和水下无线通信技术等。

2018−03−22;
2018−07−15
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No.61401165, No.61671144);华侨大学中青年教师科研提升资助计划(No.ZQN-PY407)
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61401165, No.61671144), The Promotion Program for Young and Middle-aged Teacher in Science and Technology Research of Huaqiao University (No.ZQN-PY407)

