Low-Gradient, Low Ejection Fraction SevereAortic Stenosis: Still a Management Conundrum
Blase A. Carabello, MD
1East Carolina Heart institute, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC, USA
Introduction
A 78-year-old patient cannot walk 50 feet to collect the morning newspaper without stopping to relieve dyspnea. His exercise tolerance has p rogressively worsened during the past 2 years. He also notes two-to-three pillow orthopnea and occasional ankle edema but no angina or syncope.
–Medication: furosemide, 80 mg/day.
– Physical examination: pulse 80; blood pressure 100/76 mmHg.
– Central venous pressure 9 cmH2O; carotid upstrokes mildly delayed and low in volume.
– Chest: clear.
–COR: grade 2/6 mid-late peaking systolic ejection murmur. S2physiologically split.
–Extremities: +1 ankle edema.
–Echocardiogram: poorly mobile heavily calcified aortic valve.
–Peak jet velocity 2.8 m/s, mean gradient 20 mmHg.
–Ejection fraction (EF): 0.22; aortic valve area(AVA) 0.7 cm2; B-type natriuretic peptide 480 pg/mL; STS 3.8.
Discussion
The patient has low-gradient, low- flow, low-EF aortic stenosis (AS). In normal individuals the 3.0-cm2aortic ori fice area accommodates normal systolic flow with virtually no pressure gradient between the left ventricle (LV) and the aorta. Even when the AVA is reduced by half (1.5 cm2), the pressure gradient is usually less than 10 mmHg. However, further reduction in AVA leads to progressively greater transvalvular gradients, so an AVA of 1.0 cm2produces a pressure gradient of 25–40 mmHg, an AVA of 0.75 cm2causes a pressure gradient of 50–70 mmHg,and an AVA of 0.5 cm2causes a pressure gradient of more than 100 mmHg when LV stroke volume is normal. Wall stress (σ) is an indicator of the afterload on the LV, and is represented as σ =P×r/2th,wherePis LV pressure,ris LV radius, and th is LV thickness. As AS increases the pressure term in the numerator, concentric hypertrophy (LV hypertrophy)can increase the thickness term in the denominator,maintaining normal afterload [1]. In some cases,LV hypertrophy is inadequate to normalize stress,afterload increases, impairing ejection, and EF is reduced [2]. However, in the case presented here,the peak LV pressure (systolic blood pressure plus peak gradient) is only about 120 mmHg; thus afterload is not likely to be excessive nor the cause of the profoundly impaired EF. Instead, EF is depressed because of severe LV contractile dysfunction, as the result of either long-standing pressure overload or a secondary cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease, or some combination of the three [2]. Such patients pose a difficult clinical challenge; while most patients undergo aortic valve replacement(AVR) at a low operative risk, low-gradient, low-EF patients have an operative risk many times greater than that of high-gradient patients [3]. Poor prognosis in low-gradient, low-EF patients accrues from severe LV dysfunction that often does not abate after AVR. However, some low-gradient, low-EF patients do improve after AVR, and the clinical challenge is predicting this improvement after AVR.
Does Our Patient Have Severe Aortic Stenosis?
Severe AS is usually de fined by an AVA of 1.0 cm2or less, a peak transaortic jet velocity of 4.0 m/s or greater, and/or a mean transvalvular pressure gradient of 40 mmHg or more [4]. However, as can be seen in Figure 1, these measures are often incongruous with each other [5]. Indeed, in a recent “real world” experience, 38% of patients had a mean gradient of less than 40 mmHg, consistent with the data presented in Figure 1. This discordance is especially true in low- flow states. In the presented case here,only the AVA fits the de finition of severe AS, and the physical examination, which is key in such cases, is less than reassuring because several of the features of severe AS (late peaking murmur, single S2) are lacking. However, the immobility and heavy calci fication of the valve supports the diagnosis of severe AS [6].
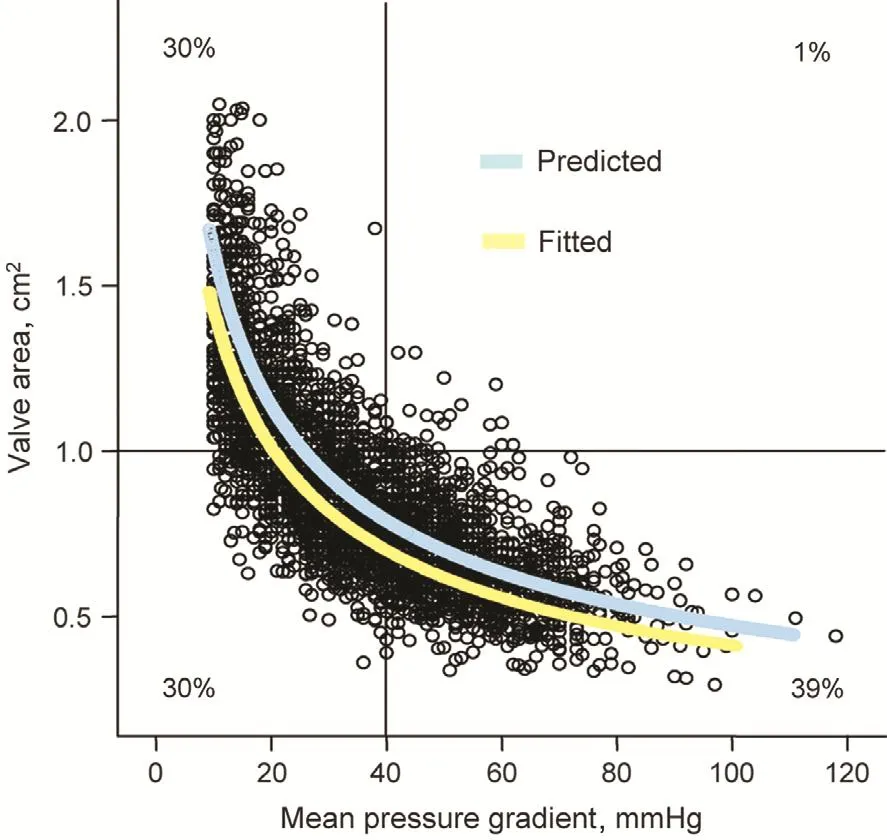
Figure 1 The Relationship of Aortic Valve Area and Mean Pressure Gradient for More Than 3400 Patients with Aortic Stenosis.
Very Low Gradient
The de finition of low-gradient, low- flow, low-EF is somewhat arbitrary. Prognosis worsens when stroke volume index is less than 35 mL/m2, but obviously stroke volume is a continuous not a dichotomous variable [7]. The value of 35 mL/m2is most useful in de fining study populations and less useful in clinical decision making. Because a mean gradient of 40 mmHg and/or an aortic valve peak jet velocity of 4 m/s have been used to de fine severe AS[4], values less than these in the face of an AVA of 1.0 cm2or less are often de fined as corresponding to a low gradient. Both low flow in some studies [6]and a low gradient in others independently predict poor outcome [8]. However, prognosis is dramatically worse in patients with very low EF (<0.30)and very low mean gradient of 20 mmHg or less where LV dysfunction is extraordinarily severe [9].
Inotropic Reserve
Assessment of inotropic reserve is the best proven technique in helping to risk stratify low-gradient,low-EF patients for AVR [10]. Patients demonstrating an increase in stroke volume of 20% or more during dobutamine infusion have an approximately 10% operative risk (depending on other comorbidities) compared with three times that risk for patients without inotropic reserve. The test also helps separate patients with true AS from those with pseudo-AS. This latter condition is one in which a small AVA is calculated at low flow but in which AVA increases substantially at high flow ( flow increases far more than gradient), presumably because greater flow opens a moderately but not severely stenotic valve to a wider aperture [11]. Because the valve is not severely stenotic, it seems unlikely that AVR would be of bene fit, although it is possible that in such severely dysfunctional ventricles that even modest afterload reduction might be bene ficial. It is likely that inotropic incompetence also impairs hemodynamic support in the immediate postoperative period, predisposing to low-output state. It is important to note that while lack of inotropic reserve impairs prognosis, some such patients do improve following AVR, making judgment about surgery in this group all the more difficult [12].
Myocardial Architecture
Assessment of myocardial composition and architecture may also be useful in stratifying risk in this group of patients. Extensive scarring from previous myocardial infarction or extensive fibrosis from long-standing pressure overload represents a void of contractile elements that cannot respond to afterload reduction from AVR. LV midwall fibrosis detected by late gadolinium enhancement during cardiac MRI helps predict a poor outcome in this group of patients [13].
Biomarkers
Biomarkers have been helpful in aiding prognosis in asymptomatic AS patients, and high levels of natriuretic peptides and troponin predict a poor prognosis in general. However, the group of lowgradient, low-EF patients invariably have heart failure, where the levels of biomarkers are inevitably elevated, making them less useful in prognosis for this group of AS patients.
Balloon Valvotomy
While dense calci fication of the aortic valve in AS prevents balloon valvotomy (BAV) from providing durable increases in AVA in most patients, it does offer temporary relief in most. While the increase in AVA and decrease in gradient is only modest, in some patients this modest improvement may cause a signi ficant although only temporary clinical improvement. Accordingly BAV is used in some cases as a trial bridge to de finitive AVR [14]. While evidence for this technique is not robust, many investigators report substantial improvement following BAV that is then used as a bridge to AVR. BAV has been used both in profoundly ill inoperable patients who became operable after BAV-induced improvement and as a test to see whether de finitive AVR was justi fied.
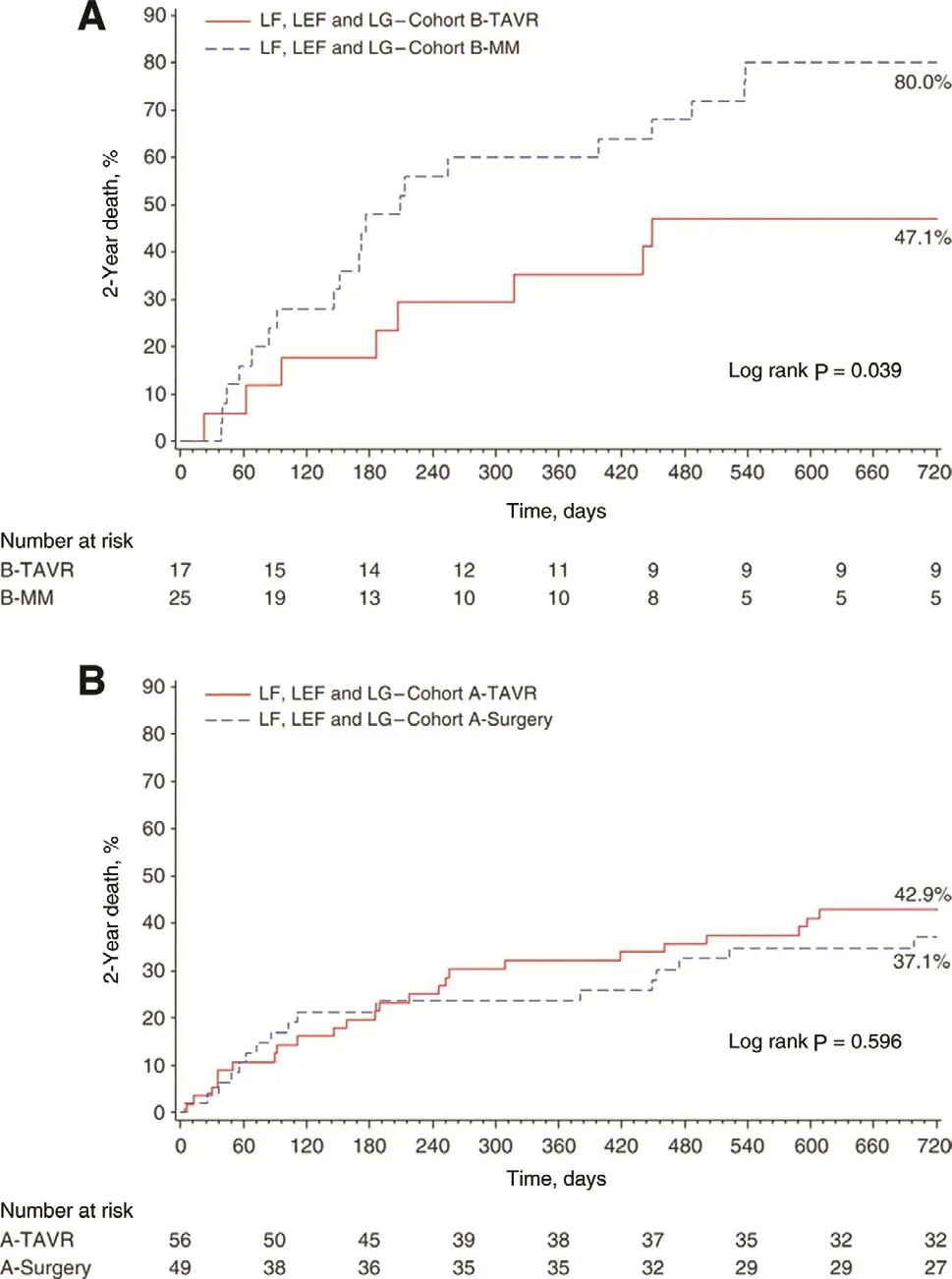
Figure 2 Survival rates.(A) The survival of patients with inoperable low-gradient (LG),low- flow (LF), low ejection fraction (LEF) aortic stenosis treated with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR; solid line) versus medical management (MM; dotted line), where TAVR is superior to MM. (B) Similar outcome for TAVR (solid line) and surgical aortic valve replacement (dotted line) for high-risk surgical patients. From Herrmann et al. [7].
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Transcatheter AVR (TAVR) could be an attractive therapy in low-gradient, low- flow, low-EF patients because it avoids the negative effects of the trauma of surgery and of requiring extracorporeal circulation. Data from a subset of the PARTNERS randomized trial found that low- flow AS patients had worse survival than normal- flow patients shown in Figure 2 [7]. However, low- flow AS patients had substantially better survival with TAVR than with so-called medical therapy, while survival was similar between surgical AVR and TAVR (Figure 2)[7]. Of interest would be a trial involving very low gradient (<20 mmHg) AS patients that randomized them to receive TAVR versus conservative therapy.
Our Patient
Our patient underwent a dobutamine infusion,achieving a peak jet velocity of 4.1 m/s. He subsequently underwent TAVR. He required brief inotropic support, but improved rapidly, going home on the fifth post-TAVR day. His predischarge echocardiogram found an EF of 0.40.
Conclusion
When low- flow, low-EF AS is due to a high gradient and thus high afterload, the results following AVR are good because AVR relieves the afterload excess immediately, improving LV performance.However, low-gradient, low- flow, low-EF AS is indicative of severe myocardial dysfunction. In some cases, function improves after AVR, in others it does not. Proof that AS is truly severe, that the gradient exceeds 20 mmHg, that there is inotropic reserve, and that there is minimal myocardial fibrosis leans toward a favorable outcome of AVR in AS patients. However, the next step in assessing this group of patients will be understanding the intrinsic myocardial properties that are responsible for myocardial recovery or its lack following relief of the AS-induced pressure overload.
REFERENCES
1. Grossman W, Jones D, McLaurin LP. Wall stress and patterns of hypertrophy in the human left ventricle. J Clin Invest 1975;56:56–64.
2. Carabello BA, Green LH, Grossman W, Cohn LH, Koster JK, Collins JJ Jr. Hemodynamic determinants of prognosis of aortic valve replacement in critical aortic stenosis and advanced congestive heart failure.Circulation 1980;62:42–8.
3. Connolly HM, Oh JK, Schaff HV,Roger VL, Osborn SL, Hodge DO,et al. Severe aortic stenosis with low transvalvular gradient and severe left ventricular dysfunction: result of aortic valve replacement in 52 patients. Circulation 2000;101:1940–6.
4. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP,Guyton RA, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease:executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63(22):2438–88.
5. Minners J, Allgeier M, Gohlke-Baerwolf C, Kienzle RP, Neumann FJ, Jander N. Inconsistencies of echocardiographic criteria for the grading of aortic valve stenosis.Eur Heart J 2008;29(8):1043–8.
6. Tastet L, Enriquez-Sarano M,Capoulade R, Malouf J, Araoz PA, Shen M, et al. Impact of aortic valve calci fication and sex on hemodynamic progression and clinical outcomes in AS. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;69(16):2096–8.
7. Herrmann HC, Pibarot P,Hueter I, Gertz ZM, Stewart WJ,Kapadia S, et al. Predictors of mortality and outcomes of therapy in low- flow severe aortic stenosis:a placement of aortic transcatheter valves (PARTNER) trial analysis.Circulation 2013;127(23):2316–26.
8. Baron SJ, Arnold SV, Herrmann HC, Holmes DR Jr, Szeto WY,Allen KB, et al. Impact of ejection fraction and aortic valve gradient on outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;67(20):2349–58.
9. Levy F, Laurent M, Monin JL,Maillet JM, Pasquet A, Le Tourneau T, et al. Aortic valve replacement for low- flow/low-gradient aortic stenosis operative risk stratification and long-term outcome:a European multicenter study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51(15):1466–72.
10. Monin JL, Quéré JP, Monchi M,Petit H, Baleynaud S, Chauvel C,et al. Low-gradient aortic stenosis:operative risk strati fication and predictors for long-term outcome: a multicenter study using dobutamine stress hemodynamics.Circulation 2003;108:319–24.
11. Nishimura RA, Grantham JA,Connolly HM, Schaff HV, Higano ST, Holmes DR Jr. Low-output,low-gradient aortic stenosis in patients with depressed left ventricular systolic function: the clinical utility of the dobutamine challenge in the catheterization laboratory.Circulation 2002;106(7):809–13.
12. Quere JP, Monin JL, Levy F,Petit H, Baleynaud S, Chauvel C, et al. In fluence of preoperative left ventricular contractile reserve on postoperative ejection fraction in low-gradient aortic stenosis. Circulation 2006;113(14):1738–44.
13. Dweck MR, Joshi S, Murigu T,Alpendurada F, Jabbour A, Melina G, et al. Midwall fibrosis is an independent predictor of mortality in patients with aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58:1271–9.
14. Kefer J, Gapira JM, Pierard S, De Meester C, Gurne O, Chenu P,et al. Recovery after balloon aortic valvuloplasty in patients with aortic stenosis and impaired left ventricular function: predictors and prognostic implication. J Invasive Cardiol 2013;25(5):235–41.
 Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications2018年1期
Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications2018年1期
- Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications的其它文章
- Mitral Stenosis: A Review
- Functional Tricuspid Regurgitation and Ring Annuloplasty Repair
- Misdiagnosed Aortic Intramural Hematoma and the Role of Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging in Detection of Acute Aortic Syndrome: A Case Report
- Management of Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient Contemplating Pregnancy
- An Asymptomatic Patient with Severe Mitral Regurgitation
- Clinical Evaluation of a Patient with Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
