双水平气道正压通气和经鼻持续正压通气治疗足月儿呼吸窘迫综合征的差异分析
杜佩珍+林多华+孙世兰+廖沛娜+潘文中

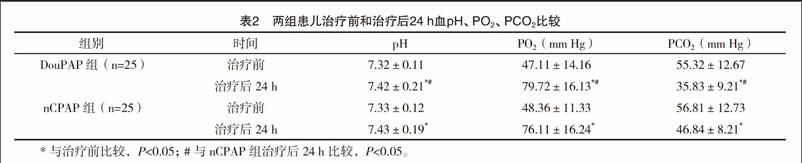

【摘要】 目的:研究双水平气道正压通气(double-level positive airway pressure,DuoPAP)和经鼻持续正压通气(nasal contin-uous positive airway pressure,nCPAP)治疗足月儿呼吸窘迫综合征(Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome,NRDS)的差异,为NRDS的治疗提供更好的方案。方法:选取2015年
4月-2016年12月在本院治疗的足月儿RDS患儿50例,采取随机对照分组法分为DouPAP组(n=25)和nCPAP组(n=25)。两组患者均采用常规的NRDS治疗方案,在此基础上分别给予DuoPAP和nCPAP治疗,記录两组患儿治疗后24 h的二氧化碳分压(PCO2)、血氧分压(PO2)及血pH,与治疗前的情况进行分析比较。分析记录整个治疗过程中的持续通气时间及治疗后24 h吸入氧浓度(FiO2)、通气治疗失败的比例以及通气后出现不良反应的比例情况。结果:两组患者治疗后24 h血pH、PO2、PCO2较治疗前均明显改善(P<0.05);DouPAP组治疗后24 h PO2明显高于nCPAP组,PCO2明显低于nCPAP组(P<0.05);DouPAP组治疗后24 h FiO2和持续通气时间均低于nCPAP组(P<0.05);DouPAP组治疗后通气失败率明显低于nCPAP组(P<0.05);两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:双水平气道正压通气对足月儿呼吸窘迫综合征的治疗效果明显优于经鼻持续正压通气,且安全性较好,可以在临床上推广。
【关键词】 足月儿; 呼吸窘迫综合征; 正压通气
【Abstract】 Objective:To study the differences of double-level positive airway pressure (DuoPAP) and nasal continuous positive pressure ventilation (nCPAP) in the treatment of newborns respiratory distress syndrome,provide a good treatment for neonatal RDS treatment.Method:Selected 50 full-term infants with RDS into the hospital treatment from April 2015 to December 2016,randomized control grouping was divided into DouPAP group(n=25) and nCPAP group(n=25).Two groups of patients were treated with conventional NRDS regimen,on this basis,respectively given DuoPAP and nCPAP treatment,recorded the partial pressure of carbon dioxide(PCO2),partial pressure of oxygen(PO2) and the pH of the blood after treatment for 24 h,and compared with the situation before treatment,analysis of the duration of ventilation,after 24 h inhalation oxygen concentration(FiO2)and the incidence of ventilation failure and adverse reactions after ventilation.Result:The pH,PO2 and PCO2 were significantly improved in the two groups after 24 h of treatment(P<0.05),the PO2 of DouPAP group after treatment with 24 h was significantly higher than that of nCPAP group,and the PCO2 was significantly lower than that of nCPAP group(P<0.05).After treatment with 24 h,FiO2 and the duration of ventilation in the DouPAP group were lower than those in the nCPAP group(P<0.05).The failure rate of ventilation after treatment in DouPAP group was lower than that in nCPAP group(P<0.05),there was no significant difference in adverse reactions between the two groups(P>0.05).Conclusion:DouPAP in the treatment of neonatal RDS was significantly better than nCPAP,and the security is better than it too,it is worthy of clinical promotion.
【Key words】 Term infant; Respiratory distress syndrome; Positive pressure ventilationendprint

