生物信息学方法分析前列腺癌组织及细胞系中LMNA基因第七外显子点突变
左灵坤 阳荣辉 马 慧 周 萍 孔 璐*
(1.首都医科大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学系,北京 100069;2.首都医科大学生物医学工程学院生物医学信息学系,北京 100069)
·基础研究·
生物信息学方法分析前列腺癌组织及细胞系中LMNA基因第七外显子点突变
左灵坤1阳荣辉1马 慧1周 萍2*孔 璐1*
(1.首都医科大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学系,北京 100069;2.首都医科大学生物医学工程学院生物医学信息学系,北京 100069)
目的探讨前列腺癌中核纤层蛋白A/C(lamin A/C,LMNA)基因第七外显子点突变与LMNA 表达差异的相关性。方法采用高通测序分析了永生化正常前列腺上皮细胞(RWPE-1)、低侵袭力前列腺癌上皮细胞(PC-3M-2B4)及高侵袭力前列腺癌上皮细胞(PC-3M-1E8)LMNA基因的12个外显子,识别出在RWPE-1与PC-3M-1E8细胞系中C.1159C>CA(p.L387LI)点突变,定位在1号染色体156106006。为了验证点突变在前列腺癌患者中的分布情况,PubMed GEO数据库下载了3组数据,分别是100例前列腺癌患者石蜡包埋标本的总RNA测序数据、20例前列腺癌和10例配对正常组织的转录组数据及21种前列腺正常及癌细胞株的测序数据。在1号染色体上选取156105950到156106055范围,设置比对序列CTACGCCTG或者NTACGCCTGTCCCCCAGCCC,每次分析比对长度为50 nt。同时,利用GEO数据库分析了突变点周围序列的特点与功能。最后,转染突变质粒,蛋白质电泳分析LMNA点突变对LMNA蛋白质表达的影响。结果在所有分析的样品中,1号染色体LMNA外显子7从156106006到156106011的区域内,存在2种错义突变形式:C/CA (p.L387LI)、C/CG (p.L387LV)和4种同义突变形式:C/CT (p.L387L)、 C/CA (p.R388R)、C/CT (p.R388R)、C/CG (p.R388R)。前列腺癌按格里森(Gleason score,GS)评分系统分组,错义突变的总发生率分别占40%(正常)、11%(GS 5-6)、2%(GS 7)和6%(GS 8-10)。在16种前列腺癌细胞系和5种前列腺良性细胞系中,错义突变的总发生率分别占31% 和60%。此外,还发现1号染色体上从156106008到156106066是转录因子结合位点,常见转录因子为 PAX5、HEN1 (NHLH1)、HTF、P53、MIF1、COMP1 和 NGFIC (NGF4)。通过功能聚类分析,这些转录因子的功能主要集中在染色质重组及调控、RNA代谢过程的正向调节、组蛋白修饰的调控以及程序性细胞死亡的负调节等方面。高表达突变LMNA的细胞系LMNA及磷酸化LMNA蛋白质表达下调。结论156106006位点突变多发生在前列腺正常组织和前列腺良性细胞株,与LMNA蛋白质表达密切相关,可能是lamin蛋白质异源性表达的机制之一。
前列腺癌; 核纤层蛋白A/C;突变;生物信息分析
前列腺癌(prostate cancer,PCa)是威胁男性健康的最常见肿瘤之一,在发达国家中其发病率居男性肿瘤的首位;病死率居男性癌症病死率第二,仅次于肺癌[1]。核纤层蛋白A/C(lamin A/C,LMNA)是核壳结构蛋白(又称核纤层)的主要组成成分。它由LMNA基因编码,其中编码区域约24 kb,有12个外显子[2]。正常情况下,通过选择性剪切拼接,LMNA基因可以编码产生4 种A型核纤层蛋白(A、A△10、C、C2),其中核纤层蛋白A 和C 是主要的异构体。Lamin A/C 的中部是一个α-螺旋的杆状结构域,由7 个重复的疏水氨基酸序列组成,两端则由球状的氨基端和羧基端组成。LaminA/C 的分布具有显著的组织特异性,T淋巴细胞及B淋巴细胞几乎不表达,一般多表达于平滑肌及上皮性细胞。LaminA/C 在DNA复制、染色质锚着、核孔复合体(nuclear pore complexes)的空间定位、核膜蛋白的结合及核稳定中的作用已得到文献[3]证实。LMNA基因及编码蛋白质异常可引起一组人类遗传病-核纤层蛋白病(laminopathies)[4]。前期研究[5]显示laminA/C 可增加前列腺癌细胞迁移及侵袭力;下调时可增加前列腺癌细胞的凋亡率;在前列腺癌组织中表达显著差异。目前,尚不知道LMNA表达差异性的意义。推测它的表达差异可能由基因变异引起。本研究中,在采用高通量测序方法分析3种恶性程度及侵袭力差异的3种前列腺细胞系(RWPE-1、PC-3M-1E8、PC-3M-2B4)LMNA基因变异的基础上、进一步分析临床样品LMNA基因的突变,为揭示LMNA表达差异性提供实验数据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
永生化正常前列腺上皮细胞(RWPE-1)、低侵袭力前列腺癌上皮细胞(PC-3M-2B4)及高侵袭力前列腺癌上皮细胞(PC-3M-1E8)细胞系购自协和细胞库,RPMI1640、K-SFM培养基及胎牛血清均购自美国Gibco公司,抗生素购自上海碧云天公司,Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂购自美国Invitrogen 公司,LMNA(ab169532)、磷酸化LMNA多克隆抗体(ab58528)购自美国Abcam公司,蛋白质浓度试剂盒购自美国Thermo公司,β-actin抗体购于上海依科赛公司,二抗(来源于兔和羊)购自美国Sigma-Aldrich公司,增强型化学发光(enhanced chemiluminescence,ECL)液购自美国Milipore公司,LMNA(p.L387LI)点突变质粒购自上海生物工程有限公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
RWPE-1培养在K-SFM培养基[含有0.05 mg/mL牛垂体素,5 ng/mL表皮生长因子,2%(体积分数)胎牛血清],PC-3M-1E8和PC-3M-2B4培养在RPMI1640培养基[10%(体积分数)胎牛血清],所有培养均添加100 U/mL 青霉素、100 μg/mL 链霉素,置于 37 ℃、5% (体积分数) CO2细胞培养箱中培养。
1.2.2 生物信息学分析点突变的方法
1)数据下载:从PubMed GEO数据库中下载3组数据:石蜡包埋前列腺癌RNA测序数据(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE54460)、前列腺癌及配对正常组织的RNA测序数据 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE22260)及前列腺癌细胞系转录组测序数据(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE25183)。所有下载数据中reads的比对序列为:CTACGCCTG或NTACGCCTGTCCCCCAGCCC。

3)氨基酸及蛋白质序列比较分析:在临床的数据中,有两个突变位点存在(比细胞系多一个),如GAGGAGAGGC(156106006) TACGC(156106011) CTGTCCCCCAGCCCT序列中的灰色显示。将该序列与编码氨基酸序列比对,确认氨基酸变异位点分别为L或者R:LDMEIHAYRKLLEGEEERLRLSPSPTSQRSRGRASSHSSQTQGGGSVTKKRK。
1.2.3 质粒转染
取接种于6 孔板中对数生长期2 × 105的PC-3M-2B4细胞进行突变质粒转染。细胞融合达 50%~60% 时,操作按Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂说明书,取对照质粒、突变质粒及无突变质粒0.5 μg进行转染,6 h 后换成完全培养基,继续培养48 h 后收集细胞。
1.2.4 Western blotting
用蛋白裂解液冰上裂解细胞30 min,在 4 ℃用13 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清即为细胞总蛋白质。蛋白质定量后,调整浓度为一致,加入5×上样缓冲液,95 ℃煮沸5 min,于-20 ℃保存。取50 μg蛋白质样品聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,转至聚偏氟乙烯膜,将膜在含有5%(质量分数)脱脂牛奶的PBST中室温封闭1 h,随后分别加入兔抗LMNA和磷酸化LMNA一抗(均为1∶3 000),4 ℃孵育过夜,PBST洗涤后加入相应二抗(1∶10 000),室温孵育1 h,PBST洗涤后用化学发光试剂检测结果。
1.3 统计学方法

2 结果
2.1 细胞系中LMNA点突变(p.L387LI)结构分析
测序识别出在RWPE-1与PC-3M-1E8中有一个很低的突变峰,显示在图1A蓝色框内。计算机与氨基酸序列比对,发现突变序列位于LMNA剪接位点结构域和氨基酸成分低复杂性区域(amino acid low compositional complexity region,LCR,http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/),详见图1B、1C和1D。LMNA突变 p.L387LI 刚好发生在靠近磷酸化修饰区域(图1E)。
2.2 分析GEO 下载的3组数据中LMNA点突变(p.L387LI)
在分析chr1:156105950-156106055的数据中,发现存在2种错义突变形式:C/CA (p.L387LI)、C/CG (p.L387LV) 和4种同义突变形式:C/CT (p.L387L)、 C/CA (p.R388R)、C/CT (p.R388R)、C/CG (p.R388R)。依据前列腺癌Gleason分级系统,调查LMNA点突变与癌症恶性程度的关联性。有趣的是,恶性程度越高,错义突变率反而降低,如错义突变的总发生率分别占40%(正常)、11%[格里森(Gleason score,GS)5~6]、2%(GS 7)和 6%(GS 8~10)(表1),采用Pearsonχ2检验组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.001);GS 5~6与正常组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.074)。GS 7与正常组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.001);GS 8~10与正常组比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.028),和细胞系发生的趋势是一致的,在16种前列腺癌细胞系和5种前列腺良性细胞系中,错义突变的总发生率分别占31% 和 60%(表2),但2类细胞系的χ2检验差异无统计学意义(P=0.248)。
2.3 对突变位点附近结合的转录因子进行功能聚类分析
在前列腺数据中检查到常见的2个突变位点,156106006和156106011,其中156106006距离转录因子结合位点仅有一个碱基的距离。因此,进一步分析了结合转录因子的种类,详见图2。这些转录因子主要负调控程序性细胞死亡及组蛋白修饰等。
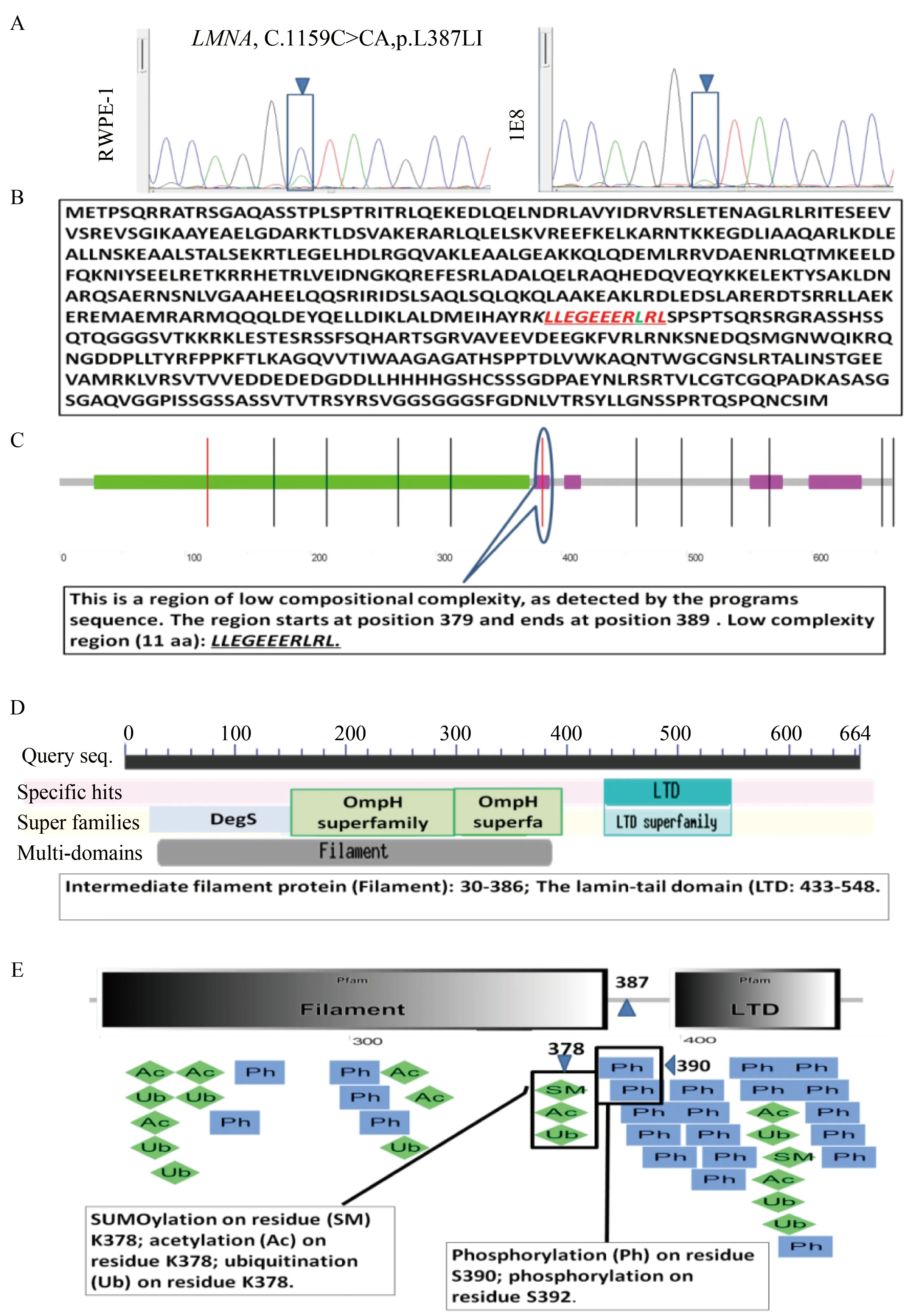
图1 LMNA突变位点的分析Fig.1 LMNA mutation in p.L387LI was identified
A:Mutation peak picture of sequence analysis of PCR products generated from RWPE-1 and 1E8.B:Amino acid sequence ofHomosapienslamin A/C from NCBI/nucleotide,sequence ID: ref(NM_170707.3).C:p.387 ofLMNAlocated on the amino acid low complexity region by analysis at http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/.D:Low complexity region of p.387 is connected to the region between two major domains of the LMA protein,indexed by CDD tools from the Conserved Domain Database of NCBI.Parameters were set in CDD version 3.11.Expected value of threshold: 0.01.E: LMNA mutation p.L387LI occurred near phosphorylated regions from http://ptmcode.embl.de/index.cgi.LMNA:lamin A/C.
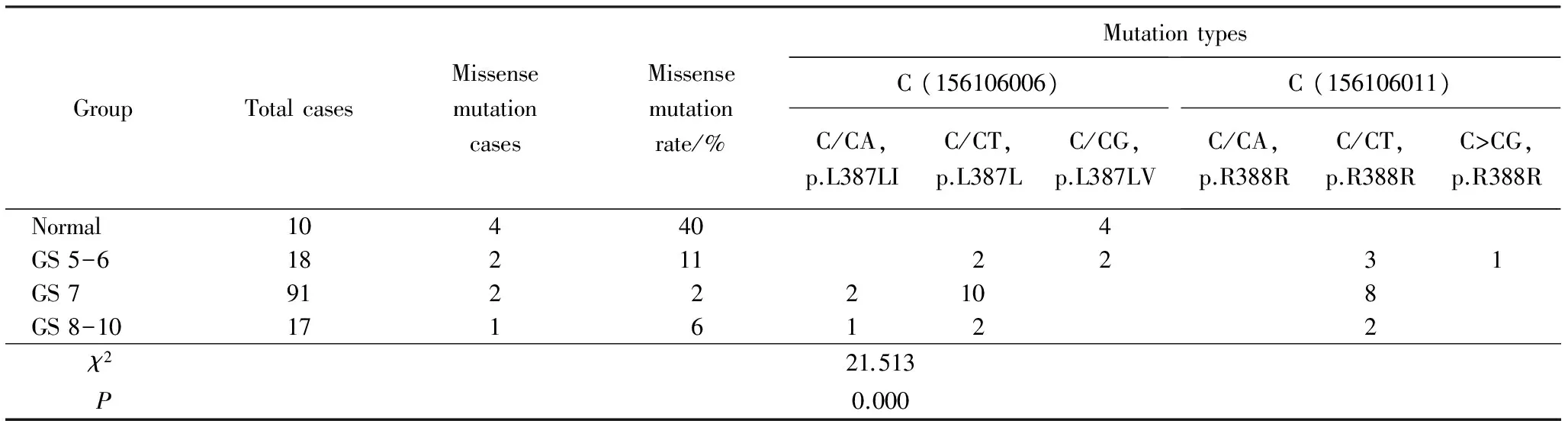
表1 突变位点(chr1:156105950~156106055) 与前列腺癌GS分级关联性研究Tab.1 The association analysis between mutation site (chr1:156105950~156106055) and GS
GS:Geason score;Rate of missense mutation=total missense mutation cases/total cases.
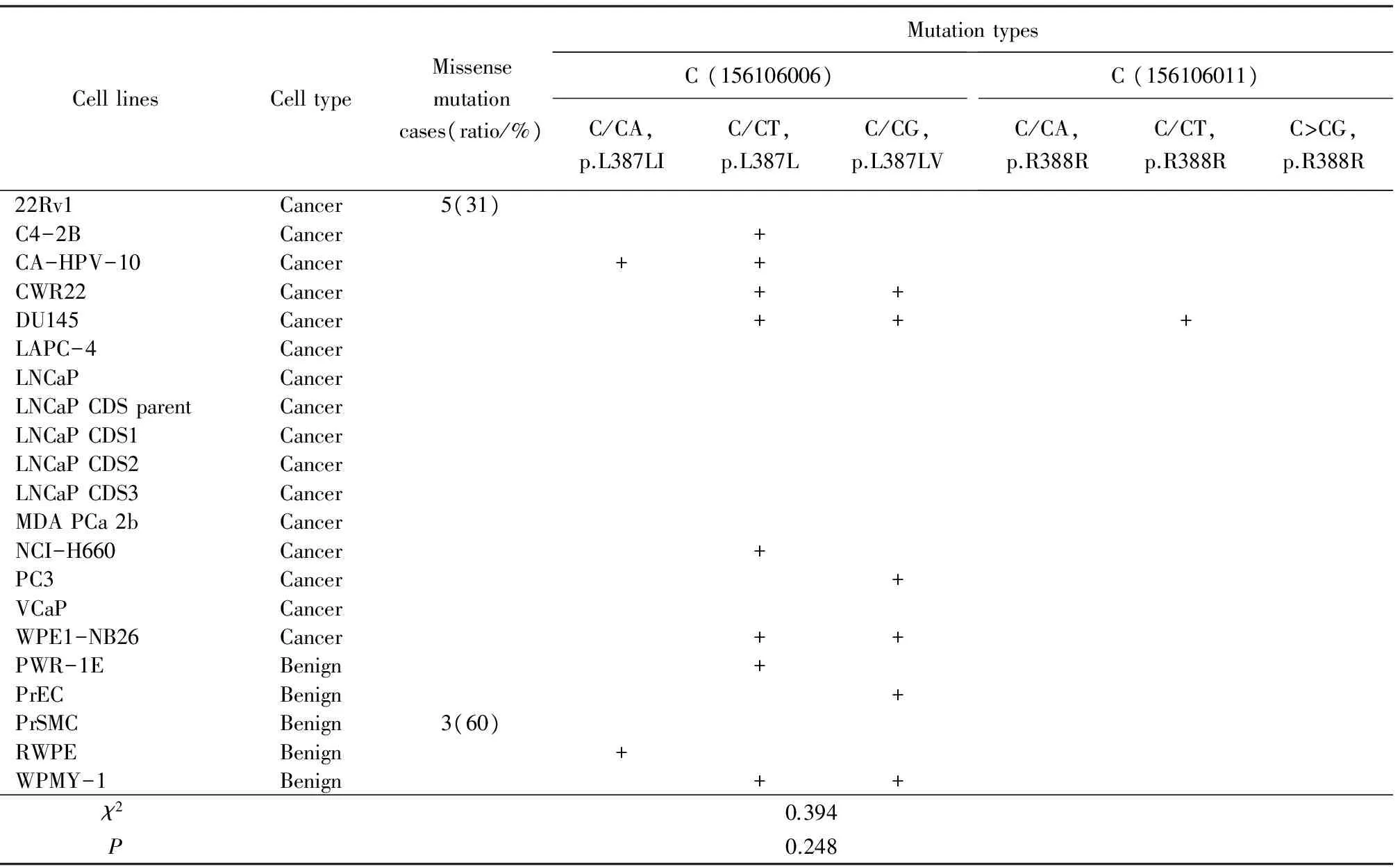
表2 细胞系前列腺细胞系突变位点 (chr1:156105950~156106055) 分析Tab.2 Cell lines mutation site (chr1:156105950-156106055) analysis
+: mutation.
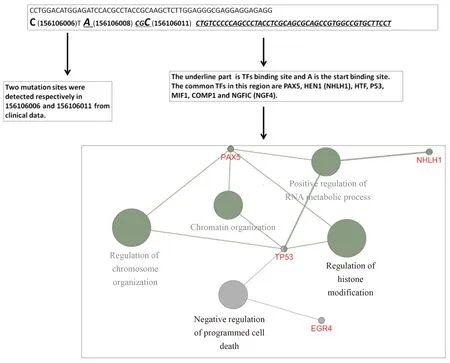
图2 分析结合在突变位点附近的转录因子及功能聚类Fig.2 Functional cluster analysis of the transcription factor (TF) near mutation sequence
A (156106008) is TF start binding site;there is only 1 base for a TF binding start site away from the mutation C site (156106006).The common TFs in this region are PAX5,HEN1 (NHLH1),HTF,P53,MIF1,COMP1 and NGFIC (NGF4).By functional cluster analysis,the functions of these TFs focus on chromatin organization,positive regulation of RNA metabolic process,regulation of histone modification,regulation of chromosome organization and negative regulation of programmed cell death.
2.4 LMNA点突变(p.L387LI)降低了LMNA及磷酸化LMNA的表达水平
在PC-3M-2B4转染了带绿色荧光蛋白(green fluorescence protein,GFP)的质粒,用LMNA和GFP抗体共同孵育,显示100 000左右的突变质粒表达的蛋白,70 000野生型的LMNA蛋白,突变显示转染效率达到50%左右(图3A)。Western blotting显示突变组LMNA蛋白及磷酸化蛋白表达均下调(图3B)。
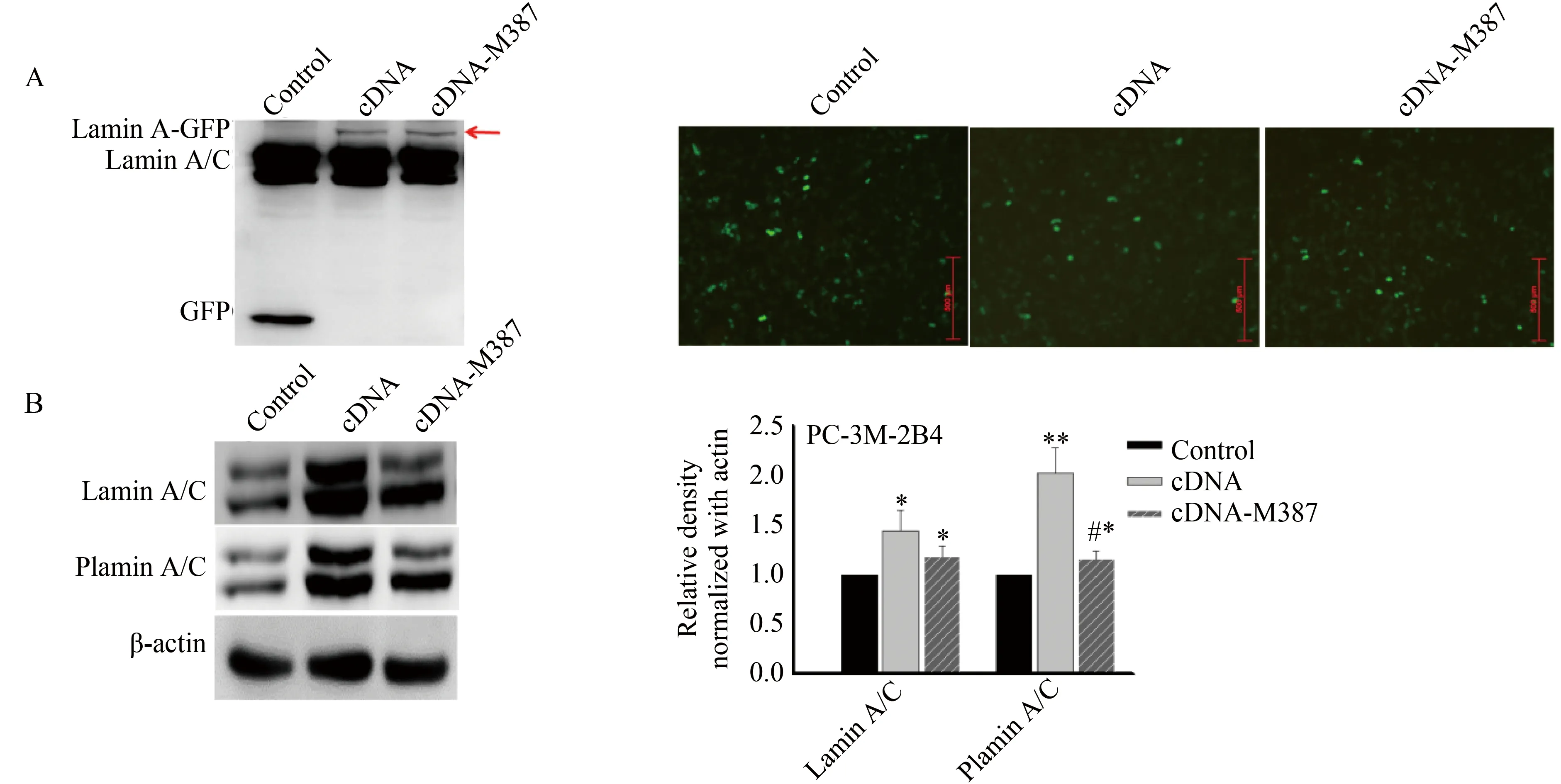
图3 PC-3M-2B4细胞中LMNA p.387 突变对蛋白表达的影响Fig.3 Expression effects of LMNA p.387 mutation in PC-3M-2B4 cells
A:PC-3M-2B4 cells in 6-well plates were transiently transfected withLMNAcDNA M387-GFP plasmid or LMNA cDNA-GFP,and negative control GFP tag vector for 48 hours and transfection efficiency was evaluated by Western blotting analysis with a monoclonal antibody raised against GFP (left) and fluorescence microscopy (right).B:LMNAp.387 mutation affects the expression of endogenous lamin A/C,plamin A/C in PC-3M-2B4 cells detected by Western blotting.The right side shows semi-quantification results plot by Image J software.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrols;#P<0.05vsLMNAcDNA-GFP;LMNA:lamin A/C.
3 讨论
前列腺癌发现晚,并且难以治疗的根本原因在于其生物学行为高度异质性,癌变不同阶段分子生物学特征差异明显,难以准确预测。因此研究前列腺癌异质性的分子机制,鉴定前列腺癌始发、转移的标志分子,是准确预测前列腺癌发生、发展的核心。除了早期报道LMNA表达异常可能是胃癌[6]、结肠癌[7]、肺癌[8]等的风险标志物[9],2016年最新报道,LMNA的缺失及剪接体的异常改变还可能是宫颈癌[10]、乳腺癌[11]的风险标志物。本课题组自前期研究[5]中,采用免疫组织化学方法分析了376 例前列腺上皮增生及前列腺癌的组织芯片,发现有趣的现象:LMNA在不同的前列腺组织中表达明显差异性,即前列腺增生的上皮组织中高表达;Gleason 评分低的癌组织中低表达;Gleason 评分高的癌组织中高表达,并且集中高表达于肿瘤区域的被膜下、神经管周围、腺管周围、转移至精囊及淋巴结的癌组织,肿瘤团块的中央区域表达却明显减少,这种异质性表达的原因直到目前尚未清楚。
LMNA基因缺失或者突变与人类一些遗传性疾病相关,被称为核纤层异常病(laminopathies)。除此,日本科学家[12]报道,LMNA启动子-1030 的C/T多态性与日本人动脉粥样硬化,LMNA 1908 的C/T多态与脑血管病密切相关。因此,在本课题组实验中设计了高通测序方法研究了3种细胞系中LMNA基因的改变情况。结果表明,在 RWPE-1 和1E8 细胞中发现了 LMNA 突变 p.L387LI,而1E8 中显示了微弱的突变峰值。为了获得这个突变位点更有意义的临床价值,在随后大数据样品的分析中,笔者发现p.387 位于 LMNA 的剪接结构域 与氨基酸组成低复杂区 (low complexity regions,LCRs),两个主要结构域之间的连接区域。而且,距离磷酸化结构域仅有5个氨基酸的距离。另外,这个位点距离最近的转录因子结合起始位点只有1个碱基的距离,这些转录因子的功能主要集中在调控染色质及表观调控和细胞生长等重要细胞功能上。LCRs这种区域在蛋白质中是普遍存在的。迄今为止,关于人类 LCRs 功能的研究很少。据报道[13],LCRs 可导致人类免疫缺陷病毒gp120蛋白(HIV-1 gp120 protein)高度可变。Lamin A的分布受蛋白不同区域特殊位点的磷酸化影响[14]。LMNA磷酸化则是促进核有丝分裂破裂的关键事件。1993年,Haas等[15]报道了LMNA氨基酸残基Thr-19/Ser-392 和 Ser-22/Ser-392位点共同磷酸化调节有丝分裂中LMNA的解离,但当在磷酸化结构域侧翼区核定位信号中的Ser-403/Ser-404两个位点突变,64%的细胞则出现抑制突变的LMNA运输回到细胞核内。因此,提出了LMNA磷酸化与核定位相关。基于上述,笔者推断,在前列腺组织中在LMNA中这个区域很重要,然而这个区域存在很多可变位点。有趣的是,在dbSNP数据库中笔者发现LMNA 387或388突变实际上是一个单核苷酸变异(single nucleotide variation,SNV,序列号:rs267607562 和 rs58133342)。PolyPhen-2软件预测387位点突变是有危害性的。
最为有趣的是,从chr1中156105950~156106055范围,仅有105 bp的区域内,在前列腺组织与细胞中,就发现了6种变异形式,2种错义突变C/CA (p.L387LI)、C/CG (p.L387LV) 和4种同义突变C/CT (p.L387L)、 C/CA (p.R388R)、C/CT (p.R388R)、C/CG (p.R388R)。尽管错义突变高发在正常前列腺组织及良性细胞系,也不能否认它在癌变机制中的作用,而且错义突变可以影响到LMNA和磷酸化LMNA蛋白的表达,从而影响其功能,同样也不能否认同义突变的意义,这需要未来临床研究中进一步功能验证。
[1] Buyyounouski M K,Choyke P L,McKenney J K,et al.Prostate cancer-major changes in the American joint committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2017,67(3):245-253.
[2] Wang X,Zabell A,Koh W,et al.Lamin A/C cardiomyopathies: current understanding and novel treatment strategies[J].Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine,2017,19(3):21.
[3] Guglielmi L,Nardella M,Musa C,et al.Lamin A/C is required for ChAT-Dependent neuroblastoma differentiation[J].Mol Neurobiol,2017,54(5):3729-44.
[4] Dutta S,Bhattacharyya M,Sengupta K.Implications and assessment of the elastic behavior of lamins in laminopathies[J].Cells,2016,5(4):E37.
[5] Kong L,Schäfer G,Bu H,et al.Lamin A/C protein is overexpressed in tissue-invading prostate cancer and promotes prostate cancer cell growth,migration and invasion through the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway[J].Carcinogenesis,2012,33(4):751-759.
[6] Kermorgant S,Cadiot G,Lewin M J,et al.Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor,C-Met in human digestive tissues and different gastric and colonic cancer cell lines[J].Gastroenterol Clin Biol,1996,20(5):438-445.
[7] Belt E J,Fijneman R J,van den Berg E G,et al.Loss of lamin A/C expression in stage Ⅱ and Ⅲ colon cancer is associated with disease recurrence[J].Eur J Cancer,2011,47(12):1837-1845.
[8] Kaufmann S H,Mabry M,Jasti R,et al.Differential expression of nuclear envelope lamins A and C in human lung cancer cell lines[J].Cancer Res,1991,51(2):581-586.
[9] Sartore-Bianchi A,Ardini E,Bosotti R,et al.Sensitivity to entrectinib associated with a novel LMNA-NTRK1 gene fusion in metastatic colorectal cancer[J].J Nat Cancer Inst,2016,108(1).
[10] Capo-chichi C D,Aguida B,Chabi N W,et al.Lamin A/C deficiency is an independent risk factor for cervical cancer[J].Cell Oncol,2016,39(1):59-68.
[11] Aljada A,Doria J,Saleh A M,et al.Altered lamin A/C splice variant expression as a possible diagnostic marker in breast cancer[J].Cell Oncol,2016,39(2):161-174.
[12] Akasaka H,Katsuya T,Saitoh S,et al.A promoter polymorphism of lamin A/C gene is an independent genetic predisposition to arterial stiffness in a Japanese general population (the Tanno and Sobetsu study)[J].J Atheroscler Thromb,2009,16(4):404-409.
[13] Maria Velasco A,Becerra A,Hernandez-Morales R,et al.Low complexity regions (LCRs) contribute to the hypervariability of the HIV-1 gp120 protein[J].J Theor Biol,2013,338:80-86.
[14] Kochin V,Shimi T,Torvaldson E,et al.Interphase phosphorylation of lamin A[J].J Cell Sci,2014,127(Pt 12):2683-2696.
[15] Haas M,Jost E.Functional analysis of phosphorylation sites in human laminA controlling lamin disassembly,nuclear transport and assembly[J].Eur J Cell Biol,1993,62(2):237-247.
Bioinformaticsanalysisaboutpointmutationofexon7inLMNAinprostatetissuesandcelllines
Zuo Lingkun1,Yang Ronghui1,Ma Hui1,Zhou Ping2*,Kong Lu1*
(1.DepartmentofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,SchoolofMedicalSciences,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100069,China;2.DepartmentofBioinformatics,BiomedicalEngineeringInstitute,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100069,China)
ObjectiveOur research focuses on investigating the associations between point mutation of exon 7 inLMNAand its expression in prostate cancer.MethodsA lamin A/C (LMNA) genomic missense variation C.1159C>CA (p.L387LI,located chr1: 156106006),identified by DNA sequencing for all 12 exons ofLMNA,in HPV-immobilized normal epithelium(RWPE-1)and high-invasive prostate cancer cell line(PC-3M-1E8)models was recognized.To verify these point mutations in prostate cancer patients,we downloaded three group data from PubMed GEO datasets,respectively from global RNA sequencing data,paraffin-embedded (FFPE) prostatectomy samples from 100 patients,from the transcriptome (polyA+) data of 20 prostate cancer tumors and 10 matched normal tissues and from sequencing data from 21 prostate cell lines.All reads were selected on the range from 156105950 to 156106055 on chr1 and these reads were aligned with CTACGCCTG or NTACGCCTGTCCCCCAGCCC.The length of reads analyzed is 50 nt for one time.Further,we analyzed the function of the sequence around the mutation point using GEO database.At last,we analyzed the effects ofLMNAmutation by Western blotting in transfected mutation plasmid cells.ResultsWe found that missense mutation has two forms of C/CA (p.L387LI) and C/CG (p.L387LV),however same-sense mutation has four forms of C/CT (p.L387L),C/CA (p.R388R),C/CT (p.R388R) and C/CG (p.R388R) in the range from 156106006 to 156106011 of exon 7 of chr1 inLMNAfrom samples or cell lines.However,the incidence of missense mutation accounted for respectively 40%,11%,2% and 6% in normal,Gleason score 5-6,7 and 8-10 of patient samples.In 16 prostate cancer cell lines and 5 prostate benign cell lines,the incidence of missense mutation accounted for respectively 31% and 60% in cancer and benign cell lines.In addition,this sequence from 156106008 to 156106066 on chr1 was transcription factors (TFs) binding site;The common TFs in this region were PAX5,HEN1 (NHLH1),HTF,P53,MIF1,COMP1 and NGFIC (NGF4).By functional cluster analysis,the function of these TFs focuses on chromatin organization,positive regulation of RNA metabolic process,regulation of histone modification,regulation of chromosome organization and negative regulation of programmed cell death.Mutation led to a downregulation of in LMNA and phosphor-LMNA expression levels.ConclusionMissense mutation incidence of 156106006 on chr1 in both prostate cancer tissues and prostate cancer cell lines is lower than that of prostate normal tissue and prostate benign cell lines.It is possible to have relationship between the mutation and expression level or a heterogeneous expression pattern of LMNA.
prostate cancer;lamin A/C (LMNA);mutation;bioinformatics analysis
国家自然科学基金(81272406,81672834),北京市教育委员会科技计划面上项目(KM201510025009)。This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(81272406,81672834),Scientific Research Program of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KM201510025009).
*Corresponding authors,E-mail:konglu@ccmu.edu.cn,wjzpwyz@163.com
时间:2017-12-13 21∶25
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.R.20171213.2125.056.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.06.021]
R329.2
2017-07-12)
编辑 孙超渊

