MicroRNA 127过表达胆管癌患者预后分析*
魏卫卫 王 超 易继林 杨 镇 李岽健
MicroRNA127过表达胆管癌患者预后分析*
魏卫卫 王 超 易继林 杨 镇 李岽健#
目的分析胆管癌癌组织微小RNA127(miRNA 127)水平变化及不同治疗患者的生存预后。方法47例肝门部胆管癌患者,应用内镜逆行胆管造影(ERCP)采集癌组织样本,依据Bismuth分型和患者全身状况分为手术完全切除治疗组(R0治疗组,n=28)和手术非完全切除组(非R0治疗组,n=19),同期采集的癌旁正常组织作为正常对照组(对照组,n=47),实时定量聚合酶链式反应(qRT-PCR)检测分析各组样本中miRNA 127表达水平和差异,比较R0治疗组、非R0治疗组癌组织miRNA 127过表达和非过表达患者无病生存时间、总生存时间、平均生存时间和5年生存率。结果(1)R0治疗组和非R0治疗组miRNA 127水平均高于对照组(P<0.05),R0治疗组更高(P<0.05),并且R0治疗组miRNA 127过表达患者比例也高于非R0治疗组(P<0.05)。(2)R0治疗组中miRNA 127过表达患者的无病生存时间、平均生存时间和5年生存率均低于非miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.05,P<0.01),非R0治疗组中miRNA 127过表达患者的各种生存时间和5年生存率亦均低于非miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.05)。结论miRNA 127过表达胆管癌患者预后较差,或可将其作为胆管癌预后的评估指标。
胆管癌;微小RNA 127;预后
胆管癌变发生率近年来逐年上升,成为癌症相关死亡的第六大主要原因[1]。胆管癌早期诊断、治疗,复发风险和预后监测一直是临床研究的重要内容。已有研究提示CA19-9(Carbohydrogen Antigen 19-9)可作为胆管癌早期诊断和预测其复发的新的生物标记物,但其临床应用价值尚存争议[2]。微小RNA(MicroRNA,miRNA)是一种含有10-24个核苷酸的非编码小RNA[3],其中很多miRNAs与胰腺癌、食道癌和肝癌[4-6]等胃肠道实体恶性肿瘤有关,如有实验报道miRNA 127在恶性胆管细胞体外增殖中高度过表达[7]。但关于miRNA,包括miRNA 127在临床胆管癌组织的表达及与患者预后的关联性所见报道较少。本文选择47例肝门部胆管癌行内镜下逆行胰胆管造影术(ERCP)时采取的癌和癌旁患者组织标本,检测其miRNA 127水平变化,并分析miRNA 127过表达患者的生存情况。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例及分组
2010-01-2012-12在本院住院的47例患者,均经组织病理学检查确诊为肝门部胆管上皮细胞癌(图1)。其中男26例,女21例,年龄43-87岁,平均61.40±11.20岁。根据Bismuth法分型[8]及患者全身状况分为非R0治疗组(Bismuth IV型,不行根治性手术治疗,n=19),包括15例因广泛浸润和全身情况较差放弃手术治疗,4例因存在淋巴转移但全身情况尚可而采取姑息性术中内引流患者,男11例,女4例,年龄52-87岁,平均64.20±12.45岁。其余患者为R0治疗组(Bismuth I-III型,接受完全切除术,n=28),男15例,女13例,年龄43-79岁,平均55.75±10.33岁。R0治疗组和非R0治疗组患者性别、年龄差异无统计学意义(t=0.281,χ2=1.086,P>0.05)。以两组患者癌旁组织作为对照(对照组,n=47)。

图1 胆管癌患者癌变组织和癌旁组织病理切片 (光学显微镜,×200)
1.2 手术和药物治疗方法
R0治疗组手术方式:肝门部胆管癌Bismuth I型:局部肿瘤切除,同时行肝门、肝外胆管血管骨骼化、区域淋巴脂肪组织的清扫;Bismuth II型:将邻近的尾状叶切除或部分方叶切除,胆管采用整形拼合、高位肝管空肠Roux-en-Y吻合;Bismuth IIIa、IIIb型:肿瘤合并左、右半肝切除。
非R0治疗组即Bismuth IV型,采用胆管空肠Roux-en-Y吻合术或经皮肝穿刺胆管引流术减轻黄疸。
两组患者术后化疗方法相同,采用吉西他滨加顺铂方案(GP方案),按临床常规安排实施治疗。
1.3 癌组织及癌旁组织miRNA 127水平检测
1.3.1组织样本采集及miRNA提取:经ERCP在胆总管处进行样本采集。切开括约肌后,于Vater壶腹部进行内镜活检,分别收集癌变及癌旁正常组织样本,-70℃冻存。检测前将冻存组织在4℃条件下复融后按照mirVANATMmiRNA分离试剂盒(Ambion®,Life Technologies Korea,韩国首尔)说明书进行miRNA的提取。
1.3.2实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测miRNA127水平:逆转录PCR获取的cDNA于-20℃保存。qRT-PCR反应体系10μl,TaqMan探针®5μl,上游引物0.2μl,下游引物0.2μl,模板cDNA 0.5μl,ddH2O 4.1μl,采用荧光定量PCR仪(Bio-Rad)进行检测,35个循环。TaqMan探针®为Applied Biosystems产品,基因编号:Gene ID:406914,引物编号:NM 001134888.2。非编码GAPDH RNA作为内参照。各引物序列及相关信息见表1。以2-△△Ct法表示目的基因相对表达量,统计各组miRNA 127过表达患者(即miRNA 127表达水平超过对照组平均水平的2倍)。


表1 各引物序列及相关信息
1.4 随访
通过门诊或者电话随访两组患者在术后期间(五年)无病生存时间(从手术结束至癌症复发间隔时间)[9]、总生存时间(手术结束至患者因胆管癌死亡时间段)及5年生存率(术后5年胆管癌患者的存活例数与患者总例数之比)。
1.5 统计学处理
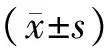
2 结果
2.1 各组miRNA 127表达水平及过表达病例分布比较
各组间miRNA 127的表达水平及miRNA 127过表达比例差异有统计学意义(P均<0.01)。R0治疗组和非R0治疗组miRNA 127表达水平及miRNA127过表达比例均高于对照组(t=2.33、2.05,P<0.05;χ2=1.66、1.74,P<0.05),并且R0治疗组miRNA 127表达水平及miRNA 127过表达比例均高于非R0治疗组患者(t=1.99,P<0.05,χ2=1.86,P<0.05),见表2。
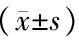
表2 各组miRNA 127表达水平及高表达例数比较
注:与对照组比较,1)P<0.05,与非R0治疗组比较,2)P<0.05
2.2 两组miRNA 127过表达患者预后比较
2.2.1R0治疗组患者生存情况:R0治疗组miRNA 127过表达患者术后平均生存时间短于非miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.05);miRNA 127过表达患者5年生存率亦低于非miRNA 127过表达患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。miRNA 127过表达患者与非miRNA 127过表达患者总生存时间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),但非miRNA 127过表达患者无病生存时间长于miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.05)。见表3、图2、图3。

表3 R0和非R0治疗组患者平均生存时间及5年生存率比较
注:与同组miRNA 127过表达者比较,1)P<0.05,2)P<0.01

图2 R0治疗组患者总生存时间的K-M曲线
2.2.2非R0治疗组患者生存时间:非R0治疗组中miRNA 127过表达患者术后平均生存时间短于非miRNA 127过表达患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);miRNA 127过表达患者与非miRNA127过表达患者5年生存率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。非miRNA 127过表达患者总生存时间显著长于miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.01),无病生存时间亦显著长于miRNA 127过表达患者(P<0.05),见表3、图4、图5。

图3 R0治疗组患者无病生存时间的K-M曲线

图4 非R0治疗组患者总生存时间的K-M曲线

图5 非R0治疗组患者无病生存时间的K-M曲线
3 讨论
胆管癌是指原发于左右肝管汇合部至胆总管下端的肝外胆管恶性肿瘤。近年来由于饮食习惯的变化,胆管癌的发病率呈逐年上升趋势,较高年龄和胆道慢性炎症刺激是胆管癌发生的基础。临床治疗胆管癌常采用手术、放疗、化疗等方法,但其确切的预后判断非常困难[10,11]。近年研究认为miRNA不仅对保持细胞正常生理状态起重要作用,而且对疾病的发生及预后也具有一定的警示作用;不仅已经作为食管癌、胰腺癌及肝癌等胃肠道实体恶性肿瘤的生物标记物[4-6],而且可能是胆管癌预后的候选生物标记物[12,13]。
miRNA 127是miRNA家族成员之一,其生物学功能非常广泛,涉及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、细胞周期的调控、细胞黏附等多个方面[14,15]。有文献报道,相对于非恶性肿瘤,恶性肿瘤组织中miRNA 127过表达[16],其作用可能是miRNA 127上调脂多糖(LPS)诱导下的核因子κB(NF-κB)活性,使NF-κB信号通路激活,从而在恶性肿瘤发生和转移过程中发挥重要作用[17-19]。表明miRNA 127可通过影响肿瘤发生和转移过程中的信号通路参与肿瘤的发生与转移。
本文结果中,所有胆管癌患者癌组织miRNA 127表达水平均明显高于对照组,进一步验证了上述结果和推论。对于胆管癌患者癌组织miRNA 127过表达与其预后的关系尚未见到相关报道,我们的随访研究发现,R0治疗组中miRNA 127过表达患者平均生存时间和5年生存率低于非miRNA 127过表达患者,非R0治疗组中miRNA 127过表达患者平均生存时间和5年生存率也低于非miRNA127过表达患者,提示miRNA 127可作为胆管癌患者预后评估的有效指标。
综上所述,胆管癌患者癌组织miRNA 127水平升高不仅可为其诊断提供生物标记物,也是胆管癌患者预后评估的指标之一。
◀
本文第一作者简介:
魏卫卫(1983-),男,汉族,博士研究生,研究方向:普通外科疾病基础与临床
1 National Cancer Information Center. Cancer information services [Internet]. Goyang: National Cancer Information Center; c2016 [cited 2016 Mar 12]. Available from: http://www.cancer.go.kr/mbs/cancer.2016-05-12.
2 Grunnet M, Mau-Sorensen M. Serum tumor markers in bile duct cancer: a review[J]. Biomarkers, 2014,19(9):437-443.
3 Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2009,10(10):704-714.
4 Halkova T, Cuperkova R, Minarik M, et al. MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: involvement in carcinogenesis and potential use for diagnosis and prognosis[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2015,2015(3):892 903.
5 Schmittgen TD, Jiang J, Liu Q, et al. A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2004,32(4):e43.
6 Lyra-González I, Flores-Fong LE, González-García I, et al. MicroRNAs dysregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma: insights in genomic medicine[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015,7(11):1 530-1 540.
7 Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, et al. Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006,130(7):2 113-2 129.
8 Bismuth H, Nakache R, Diamoned T. Management strategies in resections for hilar cholanglocarcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 1992, 215(15): 31-37.
9 Bortlik M, Duricova D, Machkova N. Discontinuation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a prospective observation[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2016 , 51(2):196-202
10 Schmittgen TD, Jiang J, Liu Q, et al. A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2004,32(4):e43.
11 Blechacz B, Komuta M, Roskams T, et al. Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol ,2011,8(11):512-522.
12 Zhang J, Han C, Wu T. MicroRNA-26a promotes cholangiocar-cinoma growth by activating beta-catenin[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012,143(20):246-256.e8.
13 Meng F, Wehbe-Janek H, Henson R, et al. Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-370 by interleukin-6 in malignant human cholangiocytes[J]. Oncogene, 2008,27(33):378-386.
14 Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, et al. mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis[J]. Oncogene, 2007,26(15):6 133-6 140.
15 Peng F, Jiang J, Yu Y, et al. Direct targeting of SUZ12/ROCK2 by miR-200b/c inhibits cholangiocarcinoma tumourigenesis and metastasis[J]. Br J Cancer, 2013,109(25):3 092-3 104.
16 Tryndyak VP, Ross SA, Beland FA, et al. Down-regulation of the microRNAs miR-34a, miR-127, and miR-200b in rat liver during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by a methyl-deficient diet[J]. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 2009,48(6):479-487.
17 Qiao M, Luo D, Kuang Y, et al. Cell cycle specific distribution of killin: evidence for negative regulation of both DNA and RNA synthesis[J]. Cell cycle, 2015,14(12):1823-1829.
18 Wu Q, Yang Z, Shi Y, et al. MiRNA in human cancers:the diagnostic and therapeutic implications[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2014;20(33):5336-5347.
19 Coornaert B, Baens M, Heyninck K, et al. T cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1 paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20[J]. Nature immunology, 2008,9(3):263-271.
CorrelationBetweenHighExpressionofMicroRNA127andPrognosisinPatientswithCholangiocarcinoma
WEI Wei-wei, WANG Chao, YI Ji-Lin, YANG Zhen, LI Dong-Jian#
Department of General Surgery, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China;#Corresponding author
Objective: To observe the changes of miRNA 127 levels in patients with cholangiocarcinoma and to analyze the surrival prognosis of patients with different treatment methods.Method47 cases of bile duct cancer, according to the Bismuth tying and the body were divided into R0 treatment group (n=28) and non R0 group (n=19), Samples of cancer tissnes were collected by ERCP,and normal tissue adjacent to cancer were collected as antol group(n=47).endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERCP) acquisition of cholangiocarcinoma tissue samples and adjacent normal tissues (normal control group),Useing Real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to detect the expression level of miRNA 127 in carcinoma and adjacent tissues, Analysis the different of R0 group and non R0 treatment with different levels of miRNA 127 expression in cancer tissue in patients with five year survival rate, differences in disease-free survival and overall survival.Results(1)The levels of miRNA 127 in the R0 treatment group and the non R0 treatment group were higher than that in the control group (P<0.05), the R0 treatment group was higher (P<0.01), and the proportion of patients with over expression of miRNA 127 in the R0 treatment group was higher than that in the non R0 treatment group.(2)In the R0 treatment group,the disease free survival,mean surviral time and the five year survival rate in thopa tierts with over expression of is lower than that non-over expression of miRNA 127 patients,And,in the non R0 treat ment group,the drease free surriral,meansurriral time and the five year surriral rabe in patients with high miRNA 127 expreesinon is lower than in patients with non-high miRNA127 expression.ConclusionmiRNA 127 over-expression was correlated with bad prognosis of biliary tract cancer, and miRNA 127 is a potential biomarkers to appraise the prognosis of biliary tract cancer.
Biliary tract neoplasms;MicroRNA 127;Prognosis
10.3969/j.issn.1005-1740.2017.04.007
R657.3
A
1005-1740(2017)04-0034-05
国家自然科学基金 (30901430)
华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院普外科,武汉 430030;#
,E-mail:lidongjian@vip.sina.com
本文2017-03-23收到,2017-06-23修回

