一类带有时滞的SIR模型的稳定性及分支分析
孔建云,刘茂省,王弯弯
(中北大学理学院,山西太原 030051)
一类带有时滞的SIR模型的稳定性及分支分析
孔建云,刘茂省,王弯弯
(中北大学理学院,山西太原 030051)
为了研究饱和发生率和时滞对传染病模型动力学性态的影响,建立了一类具有饱和发生率和指数出生且带有时滞的SIR模型,通过对模型特征方程的分析,判定了系统的地方病平衡点的稳定性,并找到了系统发生分支的临界值,通过数值模拟验证了理论分析结果的正确性。结果表明:当时滞小于临界值时,地方病平衡点是局部渐近稳定的;当时滞大于临界值时,地方病平衡点不稳定,并产生了Hopf分支。研究结果对解释传染病的周期性暴发、预防和控制传染病的传播具有借鉴作用。
稳定性理论;SIR模型;时滞;饱和发生率;Hopf分支
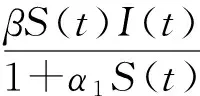
1 模型的建立
考虑了下面一类具有饱和发生率且含有因病死亡和指数出生的时滞SIR模型:
(1)

关于系统(1)的平衡点性质,有下面的定理。
定理1 当R0<1时,系统(1)存在解
(S(t),I(t),R(t))→(∞,0,0),t→∞。
当R0>1且满足α1(R0-1)[μ(μ+ρ+δ)-b(μ-ρ)]-α2μ(b-μ)>0时,系统(1)存在唯一地方病平衡点:
证明 首先该系统在非负初值情况下解满足存在唯一性。对于I(t)而言,零初值对应零解,正初值对应正解,所以当t→∞,分I(t)=0和I(t)>0的情况进行讨论。
在R0<1的情况下,
当I(t)=0时,由系统的第3个方程可以得到R(t)=0, 代入第1个方程可以得到:
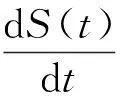
当t→∞时, 可以得到S(t)→∞,即系统恒存在1个解:(S(t),I(t),R(t))→(∞,0,0)。
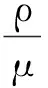
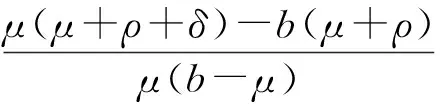

即在R0>1时,得到地方病平衡点:
由于S(t),I(t),R(t)均要求为非负的,因此还需满足:
α1(R0-1)[μ(μ+ρ+δ)-b(μ+ρ)]-
α2μ(b-μ)>0。
2 稳定性分析
令λ为特征方程的特征根,
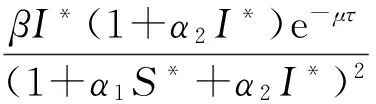
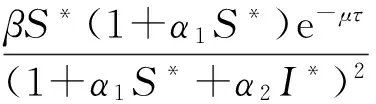
通过计算Jacobian矩阵,可以得到系统(1)的特征方程为
f1(λ)= (λ3+p1λ2+p2λ+p3)+
(q1λ2+q2λ+q3)e-λτ,
(2)
其中:
p1=3μ+ρ+δ-b,
q1=A-B,
p2=3μ2+2μ(ρ+δ)-2bμ-b(ρ+δ),
q2=(2μ-b)(A-B)+(ρ+δ)A,
p3=μ3+μ2(ρ+δ)-μ2b-μb(ρ+δ),
q3=[μ(μ+ρ+δ)-b(μ+ρ)]A+μ(b-μ)B。
通过分析系统的特征方程来判断地方病平衡点P*的稳定性,有如下定理。
定理2 假设2μ-b>0,且当R0>1成立时,存在一个τ*>0。当τ∈⎣0,τ*)时,地方病平衡点P*是局部渐近稳定的;当τ>τ*时,地方病平衡点P*不稳定,即在τ=τ*处,产生Hopf分支。
证明 在地方病平衡点P*处,当τ=0时,特征方程可变形为f(λ)=λ3+b1λ2+b2λ+b3,经过计算可以得到:
b1=p1+q1=
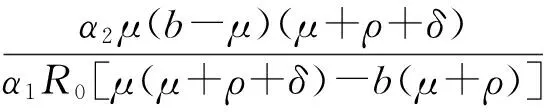
b2=p2+q2=
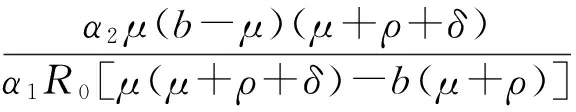
(μ+ρ+δ-b)A+
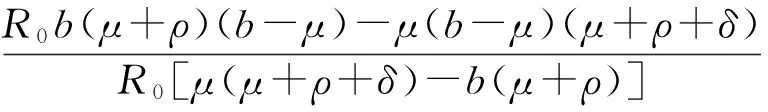
b3=p3+q3=

根据Hurwitz判据,当R0>1时,b1b2-b3>0,所以在R0>1的情况下,当τ=0时,地方病平衡点P*是局部渐近稳定的。当τ>0时,假设存在纯虚根iω(其中ω>0),代入式(2)后通过分离实部和虚部,可得:
ω3-ωp2=ωq2cos(ωτ)+
(ω2q1-q3)sin(ωτ),
(3)
ω2p1-p3=ωq2sin(ωτ)+
(-ω2q1+q3)cos(ωτ),
(4)
整理得:
ω6+a4ω4+a5ω2+a6=0,
(5)

在这里,假设z=ω2,则式(5)可变形为
z3+a4z2+a5z+a6=0。
(6)
通过计算可以得到:
a6=p3-q3=(p3-q3)(p3+q3)<0 ,
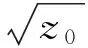
下面使用τ作为分支参数,分析分支的存在情况。用含变量τ的解来研究式(2)的分支存在情况。假设λ(τ)=γ(τ)+iω(τ)是式(2)的一个根,且γ(0)=0,ω(0)=ω0。通过式(3)和式(4)可以得到:
3 数值模拟
当τ=0时,选取如下的参数:b=0.8;μ=0.7;ρ=0.2;δ=0.7;β=0.3;α1=0.5;α2=0.4。通过图1,可以观察到当R0<1时,系统存在解:
(S(t),I(t),R(t))→(∞,0,0),
随着易感者的人数逐渐增加,趋向于无穷大,而染病者和恢复着的人数逐渐减少且趋近于零。
图1 当t→∞时,系统(1)的解(S(t),I(t),R(t))→(∞,0,0)Fig.1 When t→∞, the solutions of system (1) (S(t),I(t),R(t))→(∞,0,0)
在图2中,分别在τ=0和τ=0.8的情况下,进行地方病平衡点的稳定性及分支存在性的数值模拟。参数的选取如下:b=0.8;μ=0.7;ρ=0.2;δ=0.7;β=0.3;α1=0.01;α2=0.01。
通过图2可以看出,在τ=0时,地方病平衡点是稳定的;在τ=0.8时,地方病平衡点是不稳定的。图3模拟出了在S-I相平面上分支的情形,图4给出了在τ=0.8时系统在S-I-R相空间中分支的情形,可以看出系统存在周期解,即产生了Hopf分支。
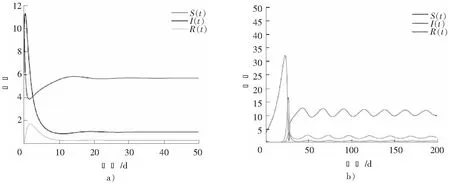
图2 系统(1)在τ=0和τ=0.8时的解曲线Fig.2 When τ=0 and τ=0.8,the solution of system (1)

图3 当τ=0.8时,系统(1)在S-I相平面上分支Fig.3 When τ=0.8,the bifurcation of system (1) on S-I phase plane
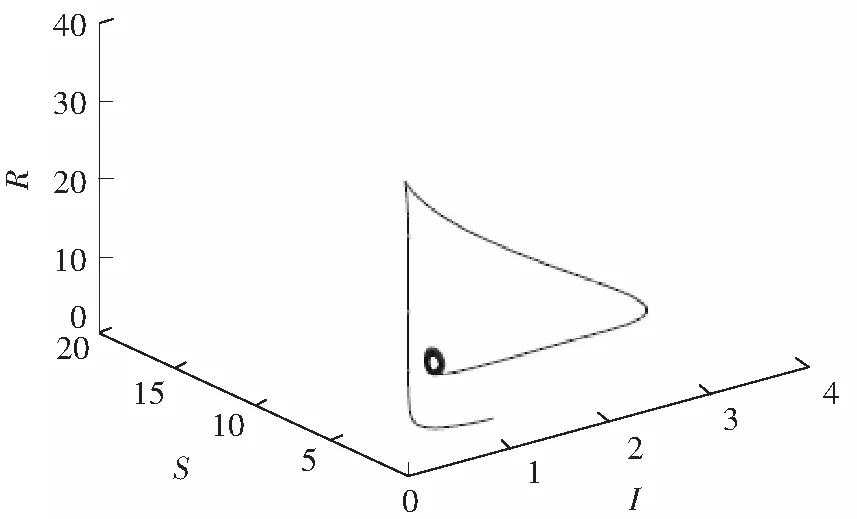
图4 当τ=0.8时,系统(1)在S-I-R相空间上分支Fig.4 When τ=0.8,the bifurcation of system (1) on S-I-R phase space
4 结 论
本文所研究的一类带有时滞的SIR模型是具有饱和发生率和指数出生的,通过分析得到了系统的地方病平衡点的稳定性,并找到系统发生分支的临界值,通过数值模拟验证了理论分析结果的正确性。通过特征方程的方法分析了系统的Hopf分支,以及关于系统其他类型的分支,今后会做更深入的分析。另外,在研究方法的应用上,整篇文章都是以传染病的传播为例进行分析,实际上,这些结果也可以应用于对计算机病毒以及信息传播的分析,另外,还可以研究网络上的SIR模型。本文研究的结果对研究整体的动力学行为具有一定的参考价值。
/References:
[1] 马知恩, 周义仓, 王稳地, 等. 传染病动力学的数学建模与研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.
[2] 董亚丽,乔志琴.两种基因类型的丙肝传染病混合模型的动力学分析[J].河北工业科技,2017,34(1):1-6. DONG Yali, QIAO Zhiqin. Dynamic analysis of mixture model about Hepatitis C Virus with two genetic types[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2017,34(1):1-6.
[3] 秦文惠, 张菊平. 具有交叉感染的两菌株对逼近模型的分析[J]. 河北工业科技, 2017,34(2):103-109. QIN Wenhui, ZHANG Juping. Analysis of pair approximation model of two strains with the cross infection[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2017,34(2):103-109.
[4] 李梁晨,徐瑞. 一类具有细胞感染年龄和一般饱和感染率的病毒感染动力学模型的稳定性分析[J]. 河北科技大学学报,2016,37(4):349-356. LI Liangchen, XU Rui. Stability analysis of a viral infection dynamics model with infection age of cells and general satu-rated infection rate[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology,2016,37(4):349-356.
[5] 王建军, 张晋珠, 靳祯. 具有饱和发生率的SIR模型的持久性和稳定性[J]. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 29(6): 479-485. WANG Jianjun, ZHANG Jinzhu, JIN Zhen. Analysis of permanence and stability for SIR model with saturation incidence[J]. Journal of North University of China(Natural Science Edition), 2008,29(6): 479-485.
[6] 赵仕杰,袁朝晖. 一类时滞SIR传染病模型的稳定性与Hopf分岔分析[J]. 经济数学, 2010,27(3): 16-23. ZHAO Shijie, YUAN Zhaohui. Stability and Hopf bifurcation of a delayed SIR epidemic model[J]. Mathematics in Economics, 2010, 27(3): 16-23.
[7] XU Rui, MA Zhien, WANG Zhiping. Global stability of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with saturation incidence and temporary immunity[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2010, 59(9): 3211-3221.
[8] XU Rui, MA Zhien. Stability of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2009,41(5): 2319-2325.
[9] KADDAR A. On the dynamics of a delayed SIR epidemic model with a modified saturated incidence rate[J]. Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, 2009, 2009(133): 3665-3677.
[10]SUN Chengjun, HSIEH Y H. Global analysis of an SEIR model with varying population size and vaccination[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2010,34(10): 2685-2697.
[11]ROST G, HUANG S Y, SZEKELY L. On a SEIR epidemic model with delay[J]. Dynamic Systems & Applications, 2012,21(21): 33-48.
[12]JIANG Zhichao, WEI Junjie. Stability and bifurcation analysis in a delayed SIR model[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2008, 35(3):609-619.
[13]ANDERSON R M, MAY R M. Regulation and stability of Host-Parasite population interactions: I. Regulatory processes[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 1978, 47(1):219-247.
[14]ZHANG Jinzhu, JIN Zhen, YAN Jurang, et al. Stability and Hopf bifurcation in a delayed competition system[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications, 2009, 70(2): 658-670.
[15]WEI Huiming, LI Xuezhi, MARTCHEVA M. An epidemic model of a vector-borne disease with direct transmission and time delay[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2008,342(2): 895-908.
[16]HASSARD B D, KAZARINOFF N D, WAN Y H. Theory and Applications of Hopf Bifurcation[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
Analysis of stability and bifurcation of a delayed SIR model
KONG Jianyun, LIU Maoxing, WANG Wanwan
(School of Science, North University of China, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030051,China)
In order to analyze the effects of saturation incidence and time delay on the dynamics of epidemic model, a delayed SIR model with a saturated incidence rate and exponential birth is constructed. By considering the characteristic equation of the system, the stability of the endemic equilibrium is analyzed, and the critical value of the bifurcation is found. The theoretical analysis results are verified by numerical simulations. The result shows that when the delay is less than the critical value, the endemic equilibrium is locally asymptotically stable; When the delay is larger than the critical value, the endemic equilibrium is unstable and there exists a Hopf bifurcation. The results of this study can be used to explain the periodic outbreaks of infectious diseases, and guide the prevention and control of the spread of the disease.
stability theory; SIR model; delayed; saturated incidence rate; Hopf bifurcation
1008-1534(2017)03-0167-05
2017-02-25;
2017-04-18;责任编辑:张 军
山西省自然科学基金(2015011009,201601D021015);山西省留学回国人员科技活动择优资助项目;山西省留学回国人员科研资助项目(2016-086)
孔建云(1991—),男,山西忻州人,硕士研究生,主要从事传染病动力学方面的研究。
刘茂省教授。E-mail:liumaoxing@126.com
O175.13
A
10.7535/hbgykj.2017yx03003
孔建云,刘茂省,王弯弯.一类带有时滞的SIR模型的稳定性及分支分析[J].河北工业科技,2017,34(3):167-171. KONG Jianyun,LIU Maoxing,WANG Wanwan. Analysis of stability and bifurcation of a delayed SIR model[J].Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2017,34(3):167-171.

