基于GA-SVR模型预测多环芳香烃在超临界CO2中的溶解度
陈 静,张 倩,卞小强,韩 兵
(1.西南石油大学 应用技术学院,四川 南充 637001;2.西南石油大学 油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室,四川 成都 610500)
基于GA-SVR模型预测多环芳香烃在超临界CO2中的溶解度
陈 静1,张 倩2,卞小强2,韩 兵2
(1.西南石油大学 应用技术学院,四川 南充 637001;2.西南石油大学 油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室,四川 成都 610500)
针对有机固体溶质在超临界CO2(SCCO2)中的溶解度实验耗时费力问题,采用基于支持向量机和遗传算法建立了多环芳香烃(PAH)在SCCO2中的溶解度模型(GA-SVR),利用PAH在SCCO2中的467个实验溶解度数据对GA-SVR模型进行了训练和预测,并基于帽子矩阵和William plot 理论,建立了一种检测GA-SVR模型异常点的方法。实验结果表明,新模型预测PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度精度较高,绝对相对偏差最小为5.42%,最大7.77%,平均为5.94%,对所有数据点进行了异常点检测,发现新建模型没有出现异常数值。该研究成果为溶质在超临界流体中的溶解度计算提供了一种新方法。
溶解度;支持向量机;遗传算法;多环芳香烃;超临界CO2
超临界流体(SCF)在石油化工中主要应用于超临界萃取技术,如超临界流体萃取多环芳香烃(PAH)。PAH是分子中含有两个或两个以上并环苯环结构的烃类化合物[1]。而在超临界萃取过程中,PAH在SCF中的溶解度是进行萃取参数选择和设备操作的关键。超临界CO2(SCCO2)是SCF中最常见的一种流体,无毒、不可燃、不爆炸、价格相对低廉。目前,确定PAH在SCCO2中溶解度的方法主要有实验法[2]、状态方程法[3]、缔合模型[4-6]和智能模型[7]。实验测定溶解度较准确,但耗时费力、成本较高。状态方程法需要溶质的临界参数[5],很多情况下溶质的临界参数并不清楚。缔合模型无需溶质的临界参数,计算相对简单,但其预测能力较差[5,8]。近年来,神经网络能够较好模拟PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度,也无需考虑溶质的临界参数,但神经网络需要大量的实验数据,方法本身易出现局部最优、泛化能力较差、网络结构参数选择难[9]等问题。
本工作采用支持向量机(SVM)和遗传算法(GA)相结合的方法,建立了PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度模型(记为GA-SVR模型)。该模型输入变量:温度、压力、SCCO2的密度,输出变量为PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度。利用PAH在SCCO2中的467个溶解度数据对GA-SVR模型进行了训练和预测,基于帽子矩阵和William plot理论方法,开展了所有数据点(467个)的异常点检测,为有机固体溶质在SCCO2中溶解度的准确预测提供了一种有效的新方法。
1 理论基础
1.1 支持向量机
SVM是一种创新型机器学习算法,具有理论性强、泛化能力好等特点,能有效避免BP神经网络等方法中常出现的局部最优、泛化能力差[9-10]等问题。
SVM非线性回归模型(SVR)的基本思想是通过一个非线性映射将低维空间的非线性回归问题转为高维特征空间的线性回归问题[9]。给出一个训练样本集{(xi,yi),i=1,2,…,N},其基本回归函数f(x):

SVM回归中所用的结构风险函数R(f):
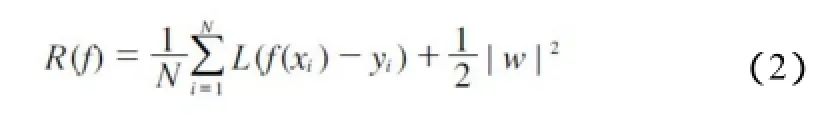
式(2)中损失函数为:

将方程(3)代入式(2)并引入松弛变量ξ和ξ*可得目标函数:

方程(4)引入Lagrange函数并进行对偶处理:

联立式(6)和(7),可得SVM回归模型:

对于内积问题,常用Radial basis function(RBF)核函数进行代替:
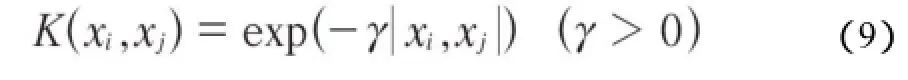
最终,SVM回归模型:

其中,ε为损失函数的损失因子;ξ和ξ*为松弛变量;C为惩罚因子;αi和为每个样本对应的Lagrange乘子对;γ为核函数的宽度参数[9]。
1.2 遗传算法
GA是一种具有自适应能力、全局性的概率搜索[11]算法。GA求解问题的核心过程包括:编码(二进制)、遗传操作(选择、交叉、变异)、适应度函数。针对SVM存在的参数有C,γ,ε。首先对参数进行二进制编码,确定初始种群,对新模型进行训练,再利用遗传算法计算出适应度函数,进行全局最优解判断,如果满足条件,确定C,γ,ε,反之迭代重新计算[12]。在参数寻优的过程中,惩罚因子C的值对ε-SVR回归模型的准确度影响最大[13]。
2 GA-SVR预测模型的建立
常见的核函数有Linear,Polynomial,RBF,Sigmoid核函数[14]。本工作采用RBF核函数,训练时采用ε-SVR函数模型。利用Matlab(2014a)软件和LIBSVM工具箱进行扩展编程,选用GA作为模型的优化算法,建立GA-SVR模型。GA-SVR模型预测PAH在SCCO2中溶解度的优化参数,结果见表1。模型具体的计算流程见图2。
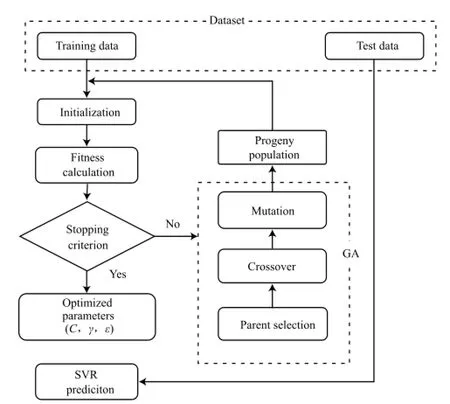
图2 GA-SVR模型流程图Fig.2 Flowchart of the proposed GA-SVR model.

表1 GA-SVR模型的优化参数Table 1 Optimized parameters of the GA-SVR model
2.1 数据选择
应用SVM,建立预测PAH在SCCO2中溶解度模型,确保数据的多样性和有效性。本工作选取了6种典型的多环芳香烃类固体溶质(467个数据点),如表2所示。选取表2中每一组溶质数据的70%作为训练,用以建立GA-SVR模型,选取剩余的数据作为测试,以检验GA-SVR模型的准确性。
由于实验数据数量级不一致,为了提高预测精度,采用mapminmax函数对数据进行归一化和反归一化处理[9]。函数所采用的映射见式(11):
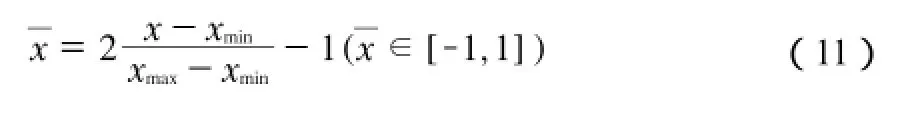
2.2 参数优化
训练过程中利用GA对模型中涉及的参数(C,γ,ε)进行优化。每种溶质相对应的最优C,γ,ε见表3。
3 模型训练和预测分析结果
GA-SVR模型训练和预测的结果分别见图3和图4。由图3和4可知,GA-SVR模型训练和预测值大多均匀分布在45°线附近,相关系数分别为0.995 3和0.995 2。

图3 GA-SVR模型训练结果Fig.3 Comparison of experimental data and training data from the GA-SVR model.
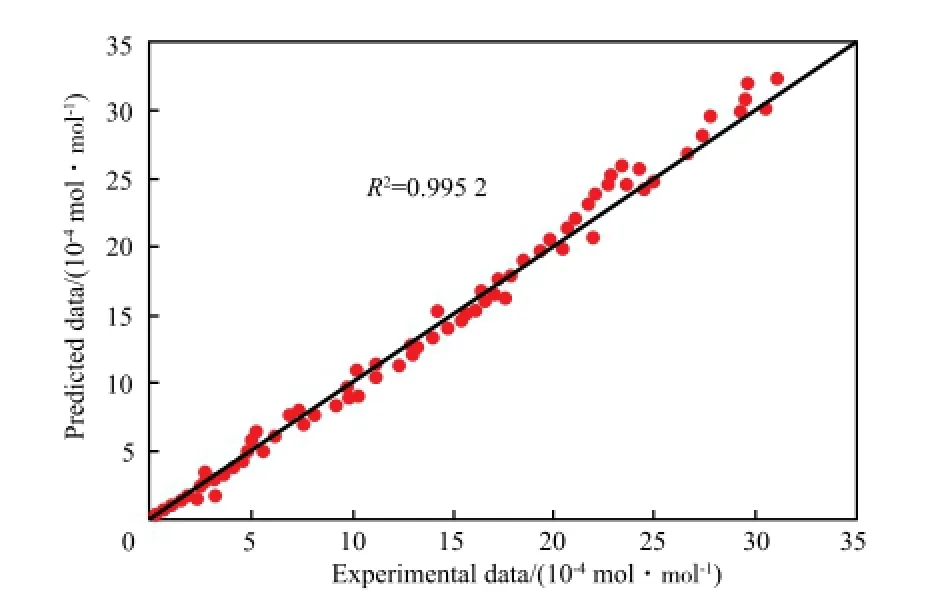
图4 GA-SVR模型预测结果Fig.4 Comparison of the experimental data and data predicted by the GA-SVR model.
为定量评价模型,定义平均绝对相对偏差(AARD):

表4为每种物质对应的AARD。由表4可知,GA-SVR模型能较好地预测PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度;除Triphenylene的预测AARD超过7.0%外,其余训练和预测值均在7.0%以下,预测AARD最小为5.42%,最大值为7.77%,平均为5.94%。

表4 不同溶质的GA-SVR模型的AARDTable 4 AARD of the proposed GA-SVR model for each solute
4 异常点的检测
基于帽子矩阵和Williams plot 理论,对所有的数据点进行异常点检测,鉴别GA-SVR模型的有效性[18]。帽子矩阵见式(13):

式中,X是一个二维矩阵,此矩阵由数据点和模型参数的个数决定,Xt为矩阵的转置。设定H*为H的杠杆值,将其定义为:

式中,m是模型输入变量的个数。经计算每种溶质相对应的H*分别是0.103 5,0.134 8,0.125 0,0.137 9,0.279 1,0.307 7,H*的有效范围是0≤H≤H*。
SVM模型标准化残差(SR)定义为:

其中,Hii为第i个数据点帽子矩阵的对角线元素。一般的选择SR有效范围为-3≤SR≤3。
运用上述方法计算GA-SVR模型的H值和SR,以H和SR为横纵坐标,作异常点检测图,结果见图5。

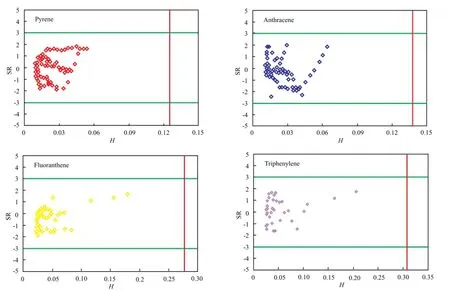
图5 溶质异常点检测图Fig.5 Outlier data detection and applicability domain of the GA-SVR model for the prediction of the solubility of PAH in supercritical carbon dioxide(SCCO2).
由图5可知,所有的数据点均分布在0≤H*≤H和-3≤SR≤3控制的区域内,说明GASVR模型没有出现异常值现象,进一步说明了模型的可靠性和准确性。
5 结论
1)采用GA和SVM法,建立了一种预测PAH在SCCO2中的GA-SVR模型。
2)采用467个PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度文献数据对新建GA-SVR模型进行检验,结果表明新模型预测PAH在SCCO2中的溶解度精度较高,预测和训练的相关系数分别为0.995 3和0.995 2,AARD最小为5.42%,最大7.77%,平均为5.94%。
3)基于帽子矩阵和William plot理论,建立了一种检测GA-SVR模型异常点的方法,经检验建立的新模型没出现异常值现象。
符 号 说 明

AARD 平均绝对相对偏差,%b偏移量

C惩罚因子H帽子矩阵Hii第i个数据点帽子矩阵的对角线元素H*H的杠杆值m模型输入变量的个数N样本个数n每组溶质相对应的数据点总数p压力,MPaR2相关系数SR 模型的标准化残差T温度,kw权重X二维矩阵Xt矩阵的转置xx1,x2,…xN的集合体xi第i个学习样本输入值yy1,y2,…yN的集合体yi第i个学习样本输出值yprei第i个数据点的预测值yexpi第i个数据点的实验值αi,α*i,αj,α*j每个样本对应的Lagrange乘子对

γ核函数的宽度参数ε损失函数的损失因子ξ,ξ*松弛变量ρ密度,kg/m3
[1] 任伟伟. 原油荧光光谱特性及分析技术研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2010.
[2] Miller D J,Hawthorne S B,Clifford A A,et al. Solubility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in supercritical carbon dioxide from 313 K to 523 K and pressures from 100 bar to 450 bar[J].J Chem Eng Data,1996,41(4):779-786.
[3] Vitu S,Privat R,Jaubert J N,et al. Predicting the phase equilibria of CO2+ hydrocarbon systems with the PPR78 model(PR EOS andkijcalculated through a group contribution method)[J].J Supercrit Fluid,2008,45(1):1-26.
[4] Bian Xiaoqiang,Zhang Qian,Du Zhimin,et al. A fiveparameter empirical model for correlating the solubility of solid compounds in supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria,2016,411:74-80.
[5] 卞小强,杜志敏,汤勇. 改进密度模型计算溶质在超临界CO2中的溶解度[J].石油化工,2011,40(5):536-540.
[6] Bian Xiaoqiang,Li Jing,Chen Jing,et al. A combined model for the solubility of different compounds in supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Chem Eng Res Des,2015,104:416-428.
[7] Khayamian T,Esteki M. Prediction of solubility for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in supercritical carbon dioxide using wavelet neural networks in quantitative structure property relationship[J].J Supercritl Fluid,2004,32(1):73-78.
[8] Mehdizadeh B,Movagharnejad K. A comparison between neural network method and semi empirical equations to predict the solubility of different compounds in supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria,2011,303(1):40-44.
[9] 卞小强,韩兵,杜志敏. 基于支持向量机的酸性天然气水合物生成条件预测[J].中国科技论文,2016,11(9):1017-1020.
[10] Boyle B H. Support vector machines:Data analysis,machine learning,and applications[M].New York:Nova Science Publishers Inc,2012.
[11]Holland J H. Adaptation in natural and artificial systems:An introductory analysis with applications to biology,control,and artificial intelligence[M].Michigan:U Michigan Press,1975.
[12] 臧淑英,张策,张丽娟,等. 遗传算法优化的支持向量机湿地遥感分类——以洪河国家级自然保护区为例[J].地理科学,2012,32(4):434-441.
[13] Bian Xiaoqiang,Han Bing,Du Zhimin,et al. Integrating support vector regression with genetic algorithm for CO2-oil minimum miscibility pressure(MMP) in pure and impure CO2streams[J].Fuel,2016,182:550-557.
[14] Vapnik V. The nature of statistical learning theory[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media,2013.
[15] Bartle K D,Clifford A A,Jafar S A. Measurement of solubility in supercritical fluids using chromatographic retention:The solubility of fl uorene,phenanthrene,and pyrene in carbon dioxide[J].J Chem Eng Data,1990,35(3):355-360.
[16] Anitescu G,Tavlarides L L. Solubilities of solids in supercritical fl uids I. New quasistatic experimental method for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs)+ pure fluids[J].J Supercrit Fluid,1997,10(3):175-189.
[17] Yamini Y,Bahramifar N. Solubility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in supercritical carbon dioxide[J].J Chem Eng Data,2000,45(1):53-56.
[18] Eslamimanesh A,Gharagheizi F,Mohammadi A H,et al. Assessment test of sulfur content of gases[J].Fuel Process Technol,2013,110:133-140.
(编辑 平春霞)
Prediction of the solubility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in supercritical CO2by the GA-SVR model
Chen Jing1,Zhang Qian2,Bian Xiaoqiang2,Han Bing2
(1. College of Applied Technology,Southwest Petroleum University,Nanchong Sichuan 637001,China;2. State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu Sichuan 610500,China)
Aimed at the expensive and time-consuming problems in the experimental determination of the solubility of solid organic compounds in supercritical carbon dioxide(SCCO2) under different temperature and pressure,a solubility model(GA-SVR) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAH) in SCCO2was established based on the support vector machine model and the genetic algorithm. Training and prediction for the GA-SVR model were carried out based on 467 data experimental data for the solubility of PAH in SCCO2. A detection method for the outliers of the GA-SVR model was established by means of the Hat matrix and the Williams plot theory. It was showed that the predictions of the proposed model were in excellent agreement with the experimental data,with the minimum average absolute relative deviation(AARD) of 5.42%,the maximum AARD of 7.77% and the average AARD of 5.94%. It was indicated that presented GA-SVR model for predicting the solubility of PAH in SCCO2was correct without any outliers.
solubility;support vector machine;genetic algorithm;polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons;supercritical carbon dioxide
1000-8144(2017)03-0321-06
TQ 013.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2017.03.010
2016-09-19;[修改稿日期]2016-12-03。
陈静(1980—),女,内蒙古自治区乌海市人,硕士,助教,电邮 569127901@qq.com。联系人:卞小强,电话 13438945103,电邮 bxqiang3210_88@163.com。
国家自然科学基金青年科学基金资助项目(51404205)。

