CP466722抑制HepG2细胞增殖并诱导细胞凋亡*
孙 珂, 褚翠英, 郑梦琦, 高 远, 齐由坤, 王凤泽
(泰山医学院生命科学学院, 山东 泰安 271016)
CP466722抑制HepG2细胞增殖并诱导细胞凋亡*
孙 珂, 褚翠英, 郑梦琦, 高 远, 齐由坤, 王凤泽△
(泰山医学院生命科学学院, 山东 泰安 271016)
目的: 研究共济失调毛细血管扩张症突变蛋白(ATM)抑制剂CP466722对人肝细胞癌HepG2细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其可能的分子机制。方法: MTT法检测CP466722对HepG2细胞活力的抑制作用,细胞集落形成实验观察CP466722对细胞增殖的影响,流式细胞术分析细胞周期的变化,TUNEL染色观察CP466722对细胞凋亡诱导作用,Western blotting检测细胞内蛋白的表达水平。结果: CP466722能够剂量依赖性地抑制HepG2细胞活力与细胞增殖;HepG2细胞经CP466722作用24 h后,细胞周期明显阻滞于G2/M期,同时磷酸化细胞分裂周期蛋白2(p-Cdc2)、细胞分裂周期蛋白25 C (Cdc25C)和磷酸化Cdc25C(p-Cdc25C)的蛋白水平下降,而p27的蛋白表达则上调。较高浓度的CP466722诱导HepG2细胞发生凋亡,促进胱天蛋白酶3(caspase-3)和多腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶(PARP)的剪切。此外,CP466722抑制β-联蛋白(β-catenin)及其下游因子生存素(survivin)的表达,上调p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 MAPK)的磷酸化水平。结论: CP466722抑制HepG2细胞增殖并诱导细胞发生凋亡,其机制可能与其抑制β-catenin信号途径和激活p38 MAPK相关。
CP466722; 肝细胞癌; 细胞增殖; 细胞凋亡; p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶; β-联蛋白
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)是全球最常见恶性肿瘤之一,严重威胁人类的生存与健康。中国是全球HCC发病率最高的国家,据统计2015年全国新发病例约47万,新增死亡病例约42万[1]。虽然手术治疗是HCC的主要治疗方法,但由于多数HCC 诊断时即为中晚期,使得化学药物治疗已成为HCC临床治疗的主要手段之一[2-3]。但应注意的是,药物治疗的毒副作用以及化疗药物耐药等复杂情况限制了治疗方案的选择[4]。因此,提高抗肿瘤药物的疗效及寻找新的化疗药物已成为HCC治疗的主要方向之一。
CP466722 (CP)是一种小分子共济失调毛细血管扩张症突变蛋白(ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein,ATM)的可逆抑制剂,能够抑制离子辐射诱导的ATM磷酸化激活,从而增加肿瘤细胞的放疗敏感性[5]。本研究以肝癌细胞HepG2为实验用细胞株,研究CP466722对肝癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,同时初步探索其抑癌活性的分子机制,为CP466722的临床应用以及HCC治疗提供新思路和实验依据。
材 料 和 方 法
1 实验材料
CP466722购自Selleck Chemicals;胎牛血清购自Gibco;MTT和抗β-actin抗体购自Sigma;TUNEL凋亡检测试剂盒购自Roche;ECL试剂盒购自Thermo Scientific Pierce;抗p-Cdc2(Tyr15)、p-Cdc25C(Ser216)、β-catenin、survivin、caspase-3和PARP抗体购自Cell Signaling Technology;抗ERK、p-ERK、p38、p-p38、p27、Cdc2和cyclin B1抗体购自Santa Cruz;抗Cdc25C抗体购自Abcam; II 抗均购自北京中杉金桥。
2 实验方法
2.1 细胞培养 肝癌细胞株HepG2购自中科院上海细胞库,用含有10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基在37 ℃和5% CO2条件下培养。
2.2 细胞活力测定 将HepG2细胞接种于96孔板中,加入不同剂量的CP466722作用24 h。在终止培养前4 h加20 μL (5 g/L)的MTT于各孔中。吸去细胞培养液并加入150 μL的DMSO,室温振荡5~10 min后用酶标仪在490 nm波长下测定吸光度值,并对实验结果进行统计分析。
2.3 细胞集落形成实验 将HepG2细胞以合适密度接种于6孔培养板中,加入不同浓度CP466722进行药物干预。10 d后吸出培养基,PBS洗涤,加入无水甲醇固定细胞20 min。PBS洗涤细胞,加入结晶紫染色10 min,PBS洗涤细胞,倒置显微镜下拍照并计数每孔细胞团数目。
2.4 细胞周期的检测 接种HepG2细胞于6孔培养板中。待细胞贴壁后加入不同浓度的CP466722处理细胞24 h。胰酶消化收集细胞,800 r/min 离心5 min,PBS洗涤后用70% 预冷乙醇固定过夜。离心去除乙醇,加入RNase A于37 ℃作用细胞30 min,然后用碘化丙啶(propidium iodide,PI)避光染色10 min,流式细胞术分析细胞周期。
2.5 细胞凋亡的检测 经CP466722处理24 h的HepG2细胞用PBS洗涤2次后,于4 ℃固定1 h,接着用0.1% Triton X-100 打孔2 min。然后按照TUNEL凋亡检测试剂盒说明书对细胞进行凋亡染色,最后于倒置荧光显微镜下观察TUNEL染色结果并拍照。
2.6 Western blotting检测蛋白表达 细胞用RAPI裂解液(含有蛋白酶抑制剂)冰上裂解20 min,然后4 ℃ 13 000×g离心20 min,收集上清定量。取30~40 μg总蛋白进行SDS-PAGE,电转移至PVDF膜上。采用5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭PVDF膜2 h,接着加入 I 抗室温孵育3 h,PBS洗涤3次后加入 II 抗,室温孵育1 h,PBS洗涤3次后ECL显色试剂盒显影。实验重复3次。
3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 16.0 统计软件对数据进行统计分析。数据用均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示,多组之间比较采用单因素方差分析,应用SNK-q检验进行组间两两比较,以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1 CP466722降低HepG2细胞的存活率
MTT实验的检测结果显示,HepG2细胞经不同浓度CP466722作用24 h后,细胞活力与对照组相比呈下降趋势,且具有明显的浓度依赖性关系,表明CP466722能够剂量依赖性地降低HepG2细胞活力,见图1。
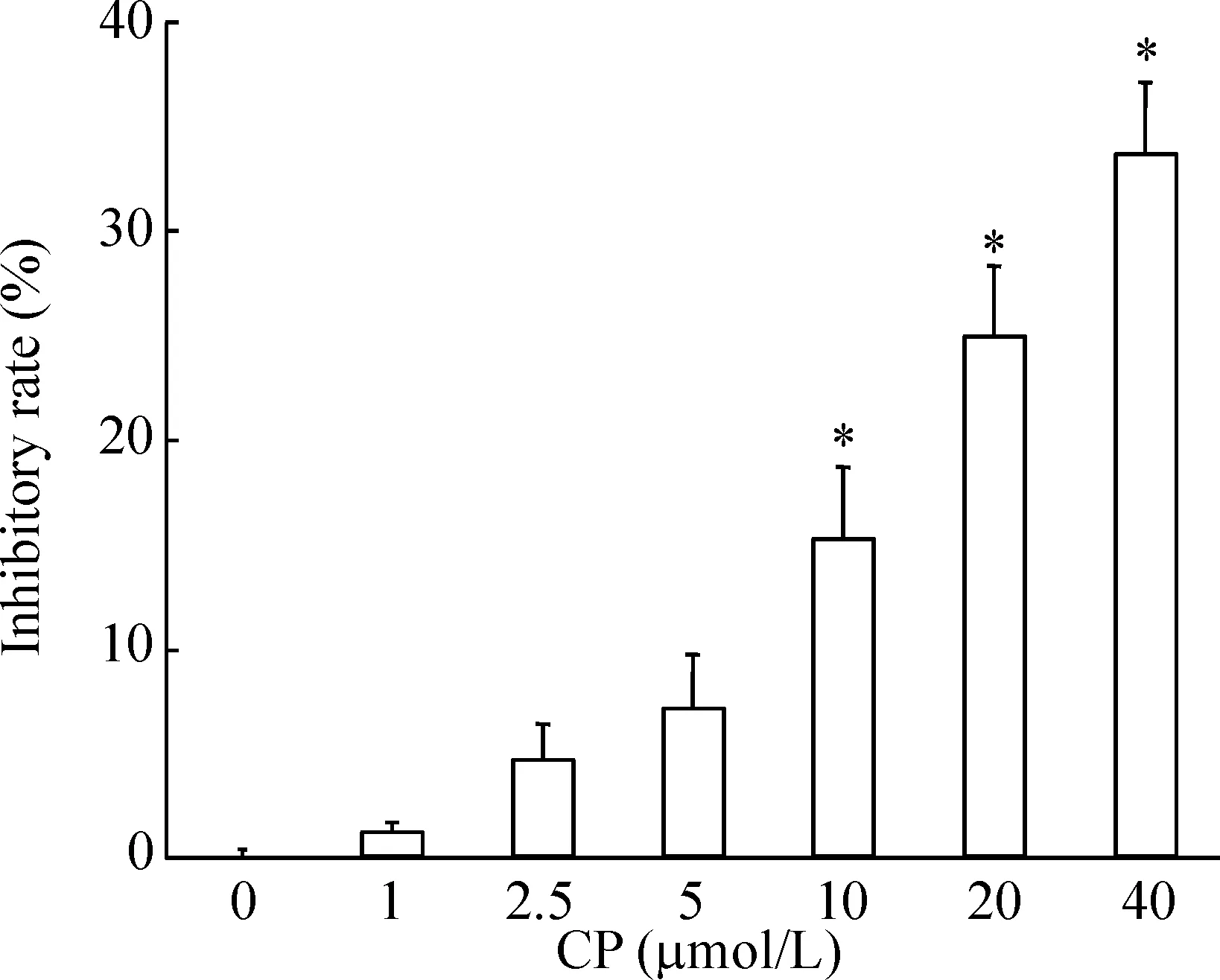
Figure 1.CP466722 reduced the viability of HepG2 cells. The cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of CP466722 for 24 h and then processed for MTT assay. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图1 CP466722降低HepG2细胞活力
细胞集落形成实验的结果显示CP466722对HepG2细胞增殖具有抑制作用,CP466722能明显减少HepG2细胞克隆的形成,抑制了HepG2细胞的增殖,见图2。

Figure 2.CP466722 inhibited the colony formation ability of HepG2 cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图2 CP466722抑制HepG2细胞增殖
2 CP466722阻滞HepG2细胞于G2/M期
PI 法检测CP466722对HepG2细胞周期的影响,结果显示CP466722 作用于细胞24 h后,与对照组相比,G2/M期细胞比例明显升高,而S期的细胞比例则相应减少,提示CP466722能够阻滞肝癌细胞于G2/M期,见图3、表1。

Figure 3.Upon exposure to CP466722 for 24 h, HepG2 cells exhibited G2/M phase arrest.
图3 CP466733诱导HepG2细胞发生G2/M期阻滞
表1 CP466722诱导HepG2细胞周期阻滞于G2/M期
Table 1.Upon exposure to CP466722 for 24 h, HepG2 cells exhibited G2/M phase arrest (%.Mean±SD.n=3)
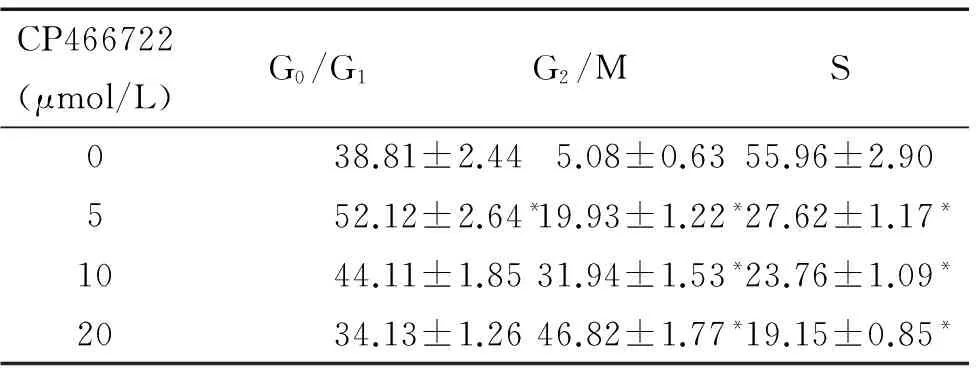
CP466722(μmol/L)G0/G1G2/MS038.81±2.445.08±0.6355.96±2.90552.12±2.64*19.93±1.22*27.62±1.17*1044.11±1.8531.94±1.53*23.76±1.09*2034.13±1.2646.82±1.77*19.15±0.85*
*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
Western blotting结果显示,不同浓度CP466722作用于HepG2 细胞24 h后, p27的蛋白表达增加,而p-Cdc2、Cdc25C和p-Cdc25C的蛋白水平降低,cyclin B1的表达水平未见明显变化,见图4。
3 CP466722诱导HepG2细胞发生凋亡
采用TUNEL染色法观察CP466722对HepG2细胞凋亡的影响,结果显示与对照组相比,较高浓度的CP466722能够诱导HepG2细胞发生凋亡,见图5。
Western blotting结果证实,CP466722促进HepG2细胞中caspase-3的活性剪切,同时也增加PARP的切割,表明胱天蛋白酶家族成员的激活可能与CP466722诱导肝癌细胞凋亡相关,见图6。
4 CP466722激活HepG2细胞中p38 MAPK 的活性
Western blotting结果显示,CP466722作用肝癌细胞后,p38 MAPK的磷酸化水平明显升高,而ERK的磷酸化未见明显变化,见图7。

Figure 4.The effects of CP466722 treatment at different concentrations for 24 h on the protein levels of cell cycle-associated proteins in the HepG2 cells. β-actin served as loading control. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图4 CP466722对细胞周期相关蛋白水平的影响
Figure 5.HepG2 cells were treated with 20 μmol/L of CP466722 for 24 h, and the apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL staining (×400). Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图5 CP466722诱导HepG2细胞发生凋亡
5 CP466722对β-catenin信号通路的抑制作用
如图8所示,HepG2细胞经CP466722作用24 h后,β-catenin的表达水平明显下降,同时其下游因子survivin的蛋白表达也受到抑制。
讨 论
本研究主要探讨CP466722对肝癌细胞增殖的抑制活性及细胞凋亡的诱导作用,同时阐明其可能的内在分子机理。研究结果表明,CP466722能够剂量依赖性地抑制肝癌细胞活力和细胞集落形成能力;较高浓度的CP466722能够激活与细胞凋亡密切相关的caspase-3 发生活性剪切,促进其底物PARP的切割,进而诱导HepG2细胞发生凋亡。
细胞周期调控在肿瘤的发生和治疗中起着重要作用,多种化疗药物均可诱导细胞发生G2/M 期阻滞并促进细胞发生凋亡[6-7]。Cdc2与cyclin B1复合物是G2/M检验点的关键调节因子,而Cdc25C又是调节Cdc2 活性的关键酶,当Ser216位点磷酸化时,Cdc25C与14-3-3蛋白结合并滞留在胞质中,不能进入到细胞核而失去活性[8-9]。本研究发现,CP466722作用于HepG2细胞24 h 后,G2/M期的细胞数目明显增多,而处于S期的细胞比例则相应下降,表明CP466722抑制HepG2细胞增殖与诱导G2/M 期阻滞有密切关系。Western blot结果显示,CP466722对细胞周期的调控可能与其下调Cdc25C和p-Cdc25C表达水平进而抑制Cdc2的磷酸化相关,其上调p27蛋白表达也可能参与该过程。
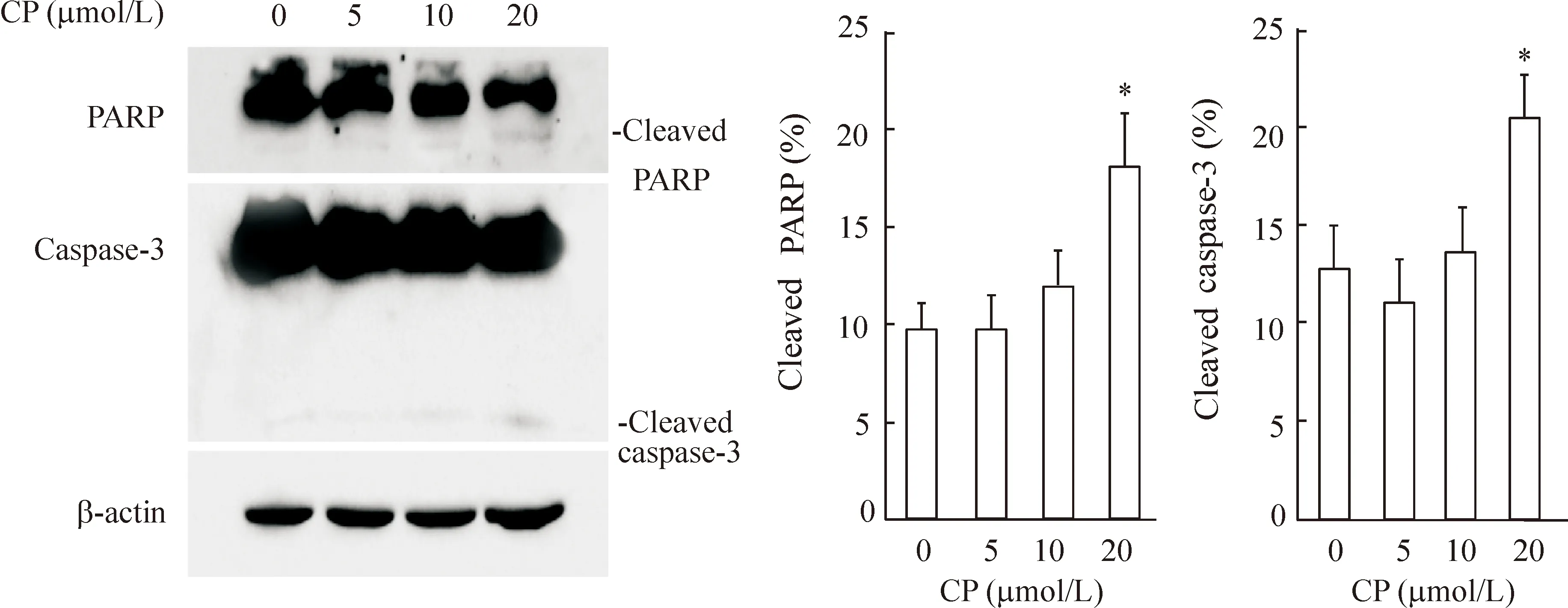
Figure 6.HepG2 cells were exposed to indicate concentrations of CP466722 for 24 h and cleavages of caspase-3 and PARP were estimated by Western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图6 CP466722促进caspase-3 和PARP的剪切
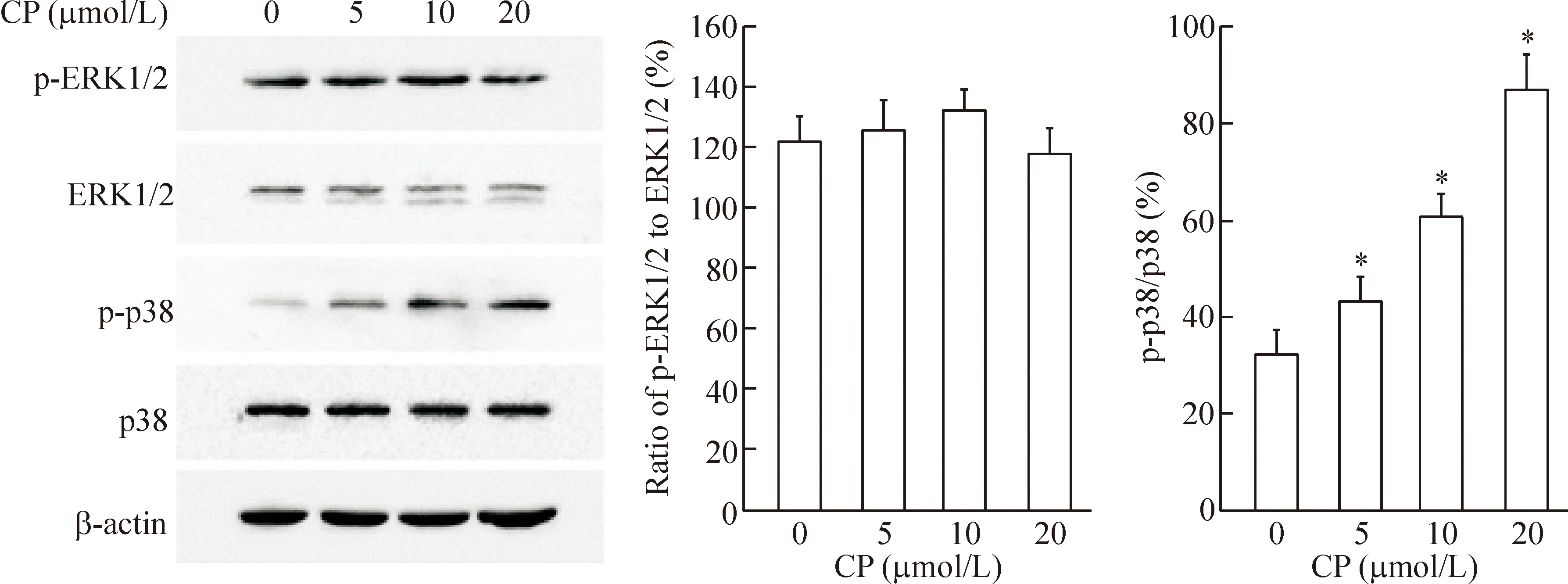
Figure 7.CP466722 increased the activation of p38 in the HepG2 cells. The cells were exposed to CP466722 for 24 h, and the protein levels of p-ERK1/2, p-p38, ERK1/2 and p38 were identified by Western blotting. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图7 CP466722 促进p38 MAPK磷酸化

Figure 8.CP466722 inhibited the expression of β-catenin and survivin in the HepG2 cells. The cells were exposed to CP466722 for 24 h, and the levels of β-catenin and survivin were measured by Western blotting. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μmol/L.
图8 CP466722抑制β-catenin和survivin的表达
MAPK 家族蛋白参与调节细胞增殖、凋亡及分化等生理病理过程,在细胞的各种生命活动中均发挥着重要作用[10]。因此,本研究检测了MAPK家族因子ERK和p38 MAPK是否参与CP466722调控HepG2细胞增殖和凋亡的过程。实验结果表明,CP466722能够促进肝癌细胞中p38 MAPK的磷酸化水平,提示p38 MAPK可能与CP466722的抗肿瘤活性相关。
此外,CP466722显著抑制HepG2 细胞中β-catenin及其下游因子survivin的蛋白水平。Wnt/β-catenin 信号途径能够促进肿瘤细胞的增殖、迁移并抑制细胞凋亡,该信号通路的异常活化与多种肿瘤发生过程密切相关,而抑制该信号通路则可减缓肿瘤细胞生长及诱导肿瘤细胞发生凋亡[11-12]。由此推测,CP466722抑制Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路可能参与调控HepG2细胞增殖和诱导细胞凋亡的过程。
综上所述,CP466722能够显著抑制HepG2细胞增殖,促进细胞发生G2/M期阻滞,同时诱导细胞发生凋亡。其可能机制与CP466722 促进p38 MAPK的磷酸化及抑制β-catenin和survivin的表达水平密切相关。
[1] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2):115-132.
[2] Tsurusaki M, Murakami T. Surgical and locoregional the-rapy of HCC: TACE[J]. Liver Cancer, 2015, 4(3):165-175.
[3] Deng GL, Zeng S, Shen H. Chemotherapy and target the-rapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: new advances and challenges[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7(5):787-798.
[4] Moriguchi M, Umemura A, Itoh Y. Current status and future prospects of chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2016, 9(4):184-190.
[5] Rainey MD, Charlton ME, Stanton RV, et al. Transient inhibition of ATM kinase is sufficient to enhance cellular sensitivity to ionizing radiation[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(18):7466-7474.
[6] 彭晓丹, 诸梦露, 高绿芬, 等. FK228和雷帕霉素协同促进人乳腺癌细胞凋亡和细胞周期阻滞[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2015, 31(4):577-584.
[7] Wang FZ, Fei HR, Cui YJ, et al. The checkpoint 1 kinase inhibitor LY2603618 induces cell cycle arrest, DNA damage response and autophagy in cancer cells[J]. Apoptosis, 2014, 19(9):1389-1398.
[8] Ma YC, Su N, Shi XJ, et al. Jaridonin-induced G2/M phase arrest in human esophageal cancer cells is caused by reactive oxygen species-dependent Cdc2-tyr15 phosphorylation via ATM-Chk1/2-Cdc25C pathway[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2015, 282(2):227-236.
[9] Wei D, Parsels LA, Karnak D, et al. Inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A radiosensitizes pancreatic cancers by modulating CDC25C/CDK1 and homologous recombination repair [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(16):4422-4432.
[10]来丽娜, 宋丽华, 张晓京, 等. ROS/PKC/p38 MAPK途径在山茱萸多糖抑制心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤的作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2014, 30(12): 2201-2205.
[11]Chen Y, Liu ZH, Xia J, et al. 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of KG-1a cells through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Oncol Rep, 2016, 36(1):137-146.
[12]Qi HH, Bao J, Zhang Q, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an important role in the protective effects of FDP-Sr against oxidative stress induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cell [J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2016, 26(19):4720-4723.
(责任编辑: 林白霜, 罗 森)
CP466722 inhibits proliferation and triggers apoptosis of HepG2 cells
SUN Ke, CHU Cui-ying, ZHENG Meng-qi, GAO Yuan, QI You-kun, WANG Feng-ze
(SchoolofLifeSciences,TaishanMedicalUniversity,Tai’an271016,China.E-mail:wfz221@sina.com)
AIM: To investigate the effect of CP466722, an inhibitor of ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein (ATM), on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. METHODS: The cell viability was detected by MTT assay. The cell growth inhibition was measured by colony formation assay. The effect of CP466722 on the cell cycle distribution of the HepG2 cells was examined by flow cytometry. The cell apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL staining. The protein expression was examined by Western blotting. RESULTS: CP466722 inhibited the cell viability and cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. In CP466722-treated HepG2 cells, the cell cycle was arrested in G2/M phase, and the protein levels of phosphorylated cell division cycle protein 2 (p-Cdc2), cell division cycle protein 25C (Cdc25C) and phosphorylated Cdc25C (p-Cdc25C) were inhibited, whereas the protein expression of p27 was up-regulated. CP466722 triggered the apoptosis of HepG2 cells through cleavages of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). In addition, CP466722 increased the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) and suppressed the expression of β-catenin and survivin in the HepG2 cells. CONCLUSION: CP466722 inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of HepG2 cells, which may be related to activating p38 MAPK and inhibiting the expression of β-catenin and survivin.
CP466722; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Cell proliferation; Cell apoptosis; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; β-catenin
1000- 4718(2017)04- 0655- 06
2016- 11- 08
2016- 12- 19
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. 81272683); 国家级大学生创新创业训练计划项目(No. 201510439067; No. 201610439275)
R730.23
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000- 4718.2017.04.013
△通讯作者 Tel: 0538-6231086; E-mail: wfz221@sina.com

