600例老年骨折病史的调查分析
宋洪光
北华大学第一临床医学院,吉林吉林132013
600例老年骨折病史的调查分析
宋洪光
北华大学第一临床医学院,吉林吉林132013
目的调查并分析该院2015年间收治的600例老年患者的骨折情况。方法选取2015年1—12月间在该院骨科就诊或行体检的600例老年人为研究对象。根据老年群体特点设计调查问卷,并根据相关的预后调查对问卷进行修改。分析患者骨折时的年龄、骨折部位和骨折原因。结果600例老年患者中有206例有骨折史,占34.33%,其中178例患者发生1次骨折,26例患者发生2次骨折,2例患者发生3次骨折,骨折总发生次数为236次。在236次骨折中,出现在60岁之前的62次,占25.42%;骨折发生在60岁及以后的共174次,占74.58%。老年骨折病史的患者中60岁之前骨折的次数明显低于60岁及以后的骨折次数,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。60岁之前骨折部位分布情况和60岁及以后之间不一致,其中60岁之前骨折部位多集中在足骨、腕骨、腰椎;60岁及以后骨折部位多集中在腰椎、腕骨、股骨近端。60岁之前骨折原因分布情况和60岁及以后之间不一致,其中60岁之前骨折原因多集中在跌倒、高处坠落、车祸;60岁及以后骨折原因多集中在跌倒、车祸、高处踩空。结论老年人主要骨折部位为足骨、腕骨、腰椎,主要原因为跌倒、车祸、高处踩空。
老年人;骨折;调查研究
骨折多发于意外事件,对日常生活造成不良影响。随着我国人口老龄化的加剧,降低老年群体骨折发生率受到社会各界的广泛关注。老年人由于机体行动能力处于不断退化过程,如不及时给予针对性的干预措施,骨折发生风险很高[1]。相关研究显示,老年近股骨端骨折患者中,一年内出现各种并发症最终引发死亡的比例高达15%[2],在存活的患者中也有50%以上终生残疾[3],日常生活无法自理,严重影响了生活质量,给家庭和社会带来严重负担。该研究选取2015年1—12月间在该院骨科就诊或行体检的600例老年人,采用问卷调查方式分析老年群体骨折多发部位和主要原因,为相关干预措施的制定提供参考,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2015年1—12月间在该院骨科就诊或行体检的600例老年人为研究对象。筛选标准:①年龄≥60岁,自愿参与该次研究;②表达较为清晰,无意识或精神障碍。其中男性357例,女性243例;年龄60~76岁,平均(67.35±5.27)岁。
1.2 方法
该次研究根据老年群体特点设计调查问卷,并根据相关的预后调查对问卷进行修改。问卷内容包括:年龄、性别、是否存在骨折史、骨折部位、骨折原因、骨折时年龄。研究开始前对调查人员进行集中培训,问卷填写前由调查人员向受试者讲解问卷各项内容,并介绍填写格式和方法,调查时间控制在60 min以内调查人员进行详细记录。收集600例受调查者问卷后进行统计分析。
1.3 统计方法
应用SPSS15.0统计软件进行处理,该研究均为计数资料,以百分比表示,进行χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 入选该次调查研究患者的基本情况
该次调查的600例老年患者中有206例有骨折史,占34.33%,其中178例患者发生1次骨折,26例患者发生2次骨折,2例患者发生3次骨折,骨折总发生次数为236次。在236次骨折中,出现在60岁之前的62次,占25.42%;骨折发生在60岁及以后的共174次,占74.58%。老年骨折病史的患者中60岁之前骨折的次数明显低于60岁及以后的骨折次数,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。
2.2 患者60岁前后骨折部位和原因
该次调查的600例老年患者中,其中60岁之前骨折部位多集中在足骨、腕骨、腰椎;60岁及以后骨折部位多集中在腰椎、腕骨、股骨近端,见表1。60岁之前骨折原因分布情况和60岁及以后之间不一致,其中60岁之前骨折原因多集中在跌倒、高处坠落、车祸;60岁及以后骨折原因多集中在跌倒、车祸、高处踩空,见表2。
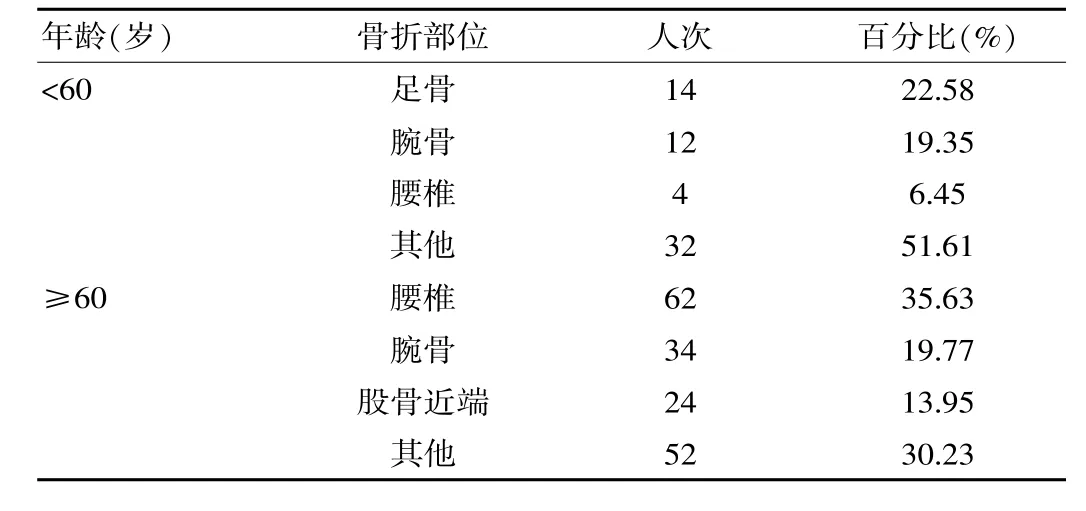
表160 岁前后骨折部位分布情况
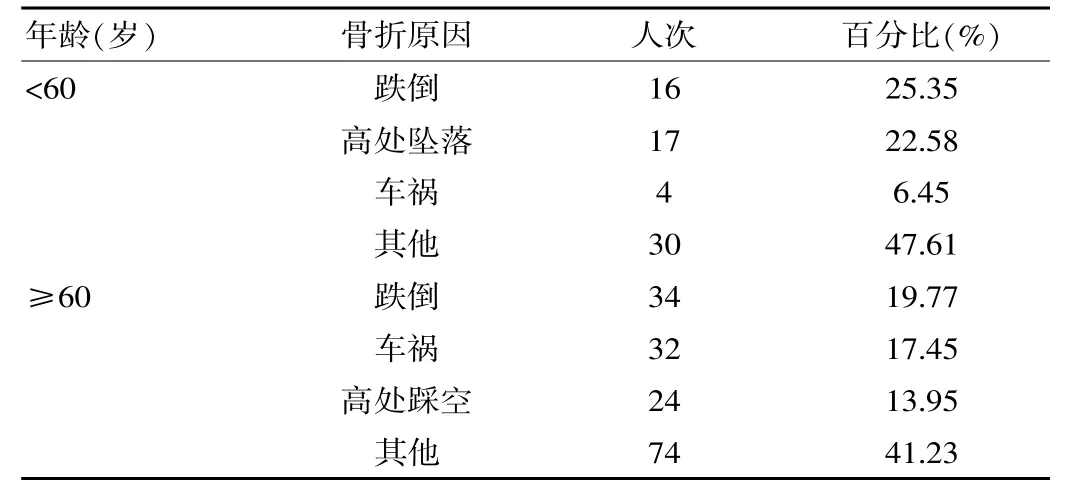
表260 岁前后骨折原因分布情况
3 讨论
该次调查研究数据分析显示,60岁之后骨折发生率明显高于60岁之前,说明随着年龄的增大,骨折发生风险逐渐增加。其原因与随着年龄增加,下肢关节活动能力逐步退化,肌肉呈逐渐萎缩的趋势,同时骨量的降低和骨骼微结构破坏,导致老年人机体骨骼的脆性增加[4-6]。老年人应针对上述因素有针对性地补充钙元素,科学进行锻炼,延缓骨骼退化。
60岁之前骨折多发生在足骨、腕骨、腰椎,而60岁及之后骨折多发生在腰椎、腕骨、股骨近端。说明随着年龄增加,骨折高发部位在不断改变,其原因与老年人机体骨量不断降低的过程中,普遍存在骨质疏松,而腰椎、腕骨、股骨是机体日常活动频率较高的部位,易出现骨折[7-8]。60岁之前骨折原因跌倒、车祸、高处踩空,以上骨折原因多会对患者足部造成一定影响,导致老年患者易发生足部骨折。
该次研究提示,60岁之后和60岁之前患者骨折最主要的原因均为跌倒,因此给予积极的干预措施防止跌倒是预防老年骨折的重要手段。社会相关部门应当加强符合老年基本生活习惯的基础设施建设。日常生活中应建议老年人选取科学的运动方式,如散步、慢跑、太极拳等,运动时节奏应缓慢,幅度不宜过大[9-10]。重点注意避免腰椎、腕骨、股骨近端骨折的发生。随着我国人口老龄化的逐渐加剧,老年骨折问题逐渐引起相关领域的重视,因此分析我国老年人骨折的流行规律和危险因素,对制定相关干预措施,降低老年骨折发生率具有重要意义。
[1]陈文远,张寿,丁晓莉,等.海口地区老年人骨质疏松患病率及骨折发生率的调查[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(6):824-826.
[2]Nurminen J,Puustinen J,Piirtola M,et al.Opioids,antiepileptic and anti cholinergicdrugs and the risk of fractures in patients 65 years of age and older:A prospective populationbased study[J].Age and Ageing:The Journal of the British Geriatrics Society and the British Society for Research on Ageing,2013,42(3):318-324.
[3]Hao Y,Ma Y,Wang X,et al.Short-term muscle atrophy caused by botulinum toxin-A local injection impairs fracture healing in the rat femur[J].Journal of orthopaedic research,2012,30 (4):574-580.
[4]Gao G,Zhang ZL,Zhang H et al.Hip axis length changes in 10,554 males and females and the association with femoral neck fracture[J].Journal of clinical densitometry,2008,11(3): 360-366.
[5]陈明光.AO可塑形双钢板置入内固定修复老年肱骨远端骨折:效果的影响因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015(31): 5016-5020.
[6]Edgren J,Rantanen T,Heinonen A,et al.Effects of progressive resistance training on physical disability among older community-dwelling people with history of hip fracture[J].Aging clinical and experimental research,2012,24(2):171-175.
[7]Ostrowski C,Ronan L,Sheridan R,et al.An osteoporotic fracture mimicking cervical dystonia in idiopathic parkinson's disease[J].Age and Ageing:The Journal of the British Geriatrics Society and the British Society for Research on Ageing,2013,42(5):658-659.
[8]Kenneth Cheng,Sandy Montgomery,Sarah Housley et al.Clinical Risk Factors for Hip Fracture in Young Adults Under 50 Years Old[J].European journal of trauma and emergency surgery,2009,35(1):40-42.
[9]K.Huang<,D.Department of Petroleum Engineering,Texas A&,M University,College Station,TX 77843,U.S.A.et al.Modeling three-dimensional hydraulic fracture propagation using virtual multidimensional internal bonds[J].International journal for numerical and analytical methods in geomechanics,2013,37(13):2021-2038.
[10]Keunhwan Pack,Kwanghyun Ahn,Hoon Huh et al.Fracture modelling of DP780 sheets using a hybrid experimentalnumerical method and two-dimensional digital image correlation[J].International journal of materials&product technology,2014,48(1/4):34-46.
Analysis of the Senile Fracture History of 600 Cases
SONG Hong-guang
First Clinical Medical College of Beihua University,Jilin,Jilin Province,132013 China
ObjectiveTo investigate and analyze the fracture of 600 cases of senile patients admitted and treated in our hospital in 2015.Methods600 cases of senile patients in the department of orthopaedics in our hospital from January 2015 to December 2015 were selected as the research objects and the questionnaires were designed according to the senile group features,and corrected according to the related prognosis survey,and the fracture age,site and cause of patients were analyzed.ResultsIn 600 cases of senile patients,there were 206 cases with fracture history,accounting for 34.33%,1 fracture was in 178 cases,2 fractures was in 26 cases,3 fractures was in 2 cases,and 236 fractures occurred,62 fractures occurred before 60 years old,accounting for 25.42%,174 fractures occurred at and after 60 years old,accounting for 74.58%,and the difference had obvious statistical significance,P<0.01,and the distribution of fracture site of patients before 60 years old was not consistent with patients at and after 60 years old,and the fracture site of patients before 60 years old focused on foot bone,wrist and lumbar,and of patients at and after 60 years old focused on lumbar spine,wrist and proximal femur, and the distribution cause of fracture site of patients before 60 years old was not consistent with patients at and after 60 years old,the causes of patients before 60 years old were falling,falling from a height and car accident,and of patients at and after 60 years old were falling,traffic accident and making a misstep on high.ConclusionThe main fracture site of senile patients is foot bone,wrist and lumbar,and the main cause is falling,traffic accident and making a misstep on high.
Senile patients;Fracture;Investigation
R274.1
A
1672-5654(2017)01(a)-0149-03
10.16659/j.cnki.1672-5654.2017.01.149
2016-10-17)
宋洪光(1981.12-),男,吉林通化人,在读研究生,主治医师,研究方向:骨折手术治疗。

