响应面法优化木质素基选择性吸附树脂的皂化条件*
姚庆鑫,王 蓓,阳后桂,谢建军
(中南林业科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410004)
响应面法优化木质素基选择性吸附树脂的皂化条件*
姚庆鑫,王 蓓,阳后桂,谢建军
(中南林业科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410004)
采用响应面法研究了膨润土/木质素磺酸钠接枝丙烯酰胺选择性吸附树脂(BLPAM)的皂化实验。以氢氧化钠溶液浓度、皂化温度、皂化时间为影响因素,以Pb2+吸附量、Cu2+吸附量、Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数、Pb2+去除率、Cu2+去除率为响应值建立Box-Behnken数学模型,通过响应面分析得到针对各响应值的主次因素和优化皂化条件。采用组合赋权法确定各响应值的权重,获得最终的优化皂化条件。结果表明,BLPAM的优化皂化条件为:氢氧化钠溶液浓度1.45 mol/L、皂化温度98 ℃、皂化时间2.90 h,所得皂化BLPAM树脂在二元Pb2+/Cu2+溶液中对Pb2+吸附量为1.772 mmol/g,Cu2+吸附量为1.719 mmol/g,Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数为1.604,Pb2+去除率为96.062%,Cu2+去除率为93.864%。
木质素;吸附树脂;皂化;选择性吸附; 组合赋权法; 响应面法
0 引 言
近年来,水体中重金属离子污染日趋严重,其治理已经成为人类亟待解决的重要问题。在重金属离子的处理方法中,吸附法被广泛用于去除水体中重金属离子,其操作简便、效果显著、运行成本较低廉[1-2]。在吸附过程中,吸附材料起了至关重要的作用。目前,开发低成本、高性能的重金属离子吸附材料已经引起人们的广泛关注。其中,木质素是自然界中第二大天然有机物,其基本结构中含有芳香基、羟基、甲氧基等多种活性官能团,可以用作重金属离子吸附材料[3-4]。为了提高木质素基吸附材料的重金属离子吸附性能,通常采用化学方法对木质素进行改性,如接枝共聚、Mannich反应、缩合反应等,在木质素骨架上引入具有良好吸附性能的基团如酰胺基、羧基、季铵基等[5-6]。
传统实验设计中通常采用单因素方法来探索实验优化条件,然而单因素方法实验设计工作量大、耗费时间以及原料成本,且不能得到各影响因素之间的相互作用。响应面优化法是一种实验条件寻优的方法,它通过建立连续变量曲面模型,对影响因素及其交互作用进行评价,寻求最佳组合条件[7]。响应面法的优势在于:实验条件寻优过程中,响应面优化法所需的实验数相对较少,且可连续的对实验各水平进行分析[8]。
皂化法是提高树脂吸附性能的一种简便而有效的后处理方法,它可改变树脂中吸附基团的种类及其比例,提高吸附树脂对重金属离子的吸附性能。膨润土/木质素磺酸钠接枝丙烯酰胺复合吸附树脂(BLPAM)的结构中含有大量的活性官能团-CONH2,但由于其吸附溶胀性差,内部大量活性基团不能外露而有效参与重金属离子吸附,导致BLPAM的综合吸附性能较差。故本文采用皂化法进一步处理BLPAM,并结合运用响应面法优化BLPAM的皂化条件。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要原料
膨润土/木质素磺酸钠接枝丙烯酰胺复合吸附树脂(BLPAM),该树脂为本文自制,制备过程参考文献[9]。BLPAM树脂在浓度为2.0 mmol/L的二元Pb2+/Cu2+溶液中的基本吸附性能为对Pb2+的吸附量为0.0613 mmol/g,对Cu2+的吸附量为0.0582 mmol/g,Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性系数为1.295,对Pb2+的去除率为1.211%,对Cu2+的去除率为0.013%。
NaOH,分析纯(AR),湖南汇虹试剂有限公司;硝酸铅(Pb(NO3)2)、硝酸铜(Cu(NO3)2),AR,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 皂化与吸附实验
皂化、吸附实验的操作方法及金属离子的吸附量(以q表示)和Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性系数(以α表示)的计算参考文献[10],金属离子去除率(R)计算参考文献[11]。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 响应面法优化实验设计
在前期探索实验的基础上,根据响应面实验设计原理(Box-Behnken模型),对BLPAM选择性吸附树脂的皂化后处理进行3因素3水平实验设计,以氢氧化钠浓度(A)、皂化温度(B)、皂化时间(C)为主要考察因素,以树脂在二元Pb2+/Cu2+溶液中对Pb2+吸附量(qPb)、Cu2+吸附量(qCu)、Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数(α)、Pb2+去除率(RPb)、Cu2+去除率(RCu)为响应值进行响应面实验,实验因素水平如表1所示。响应面实验设计共17个实验点,其中12个析因点,5个中心点,实验设计及结果见表2所示。
表1 响应面实验设计的因素与水平
Table 1 Experimental design of factors and levels of Box-Beheken response surface method

因素编码水平-101C(NaOH)/mol·L-1A0.501.252.00Temperature/℃B7085100Time/hC0.501.252.00
表2 Box-Beheken优化实验设计与结果
Table 2 Experimental design and results of Box-Beheken response surface method

No.ABCqPb/mmol·g-1qCu/mmol·g-1αRPb/%RCu/%11.25702.001.8081.7653.99396.41487.08721.25851.251.7831.7901.75595.64188.97031.25851.251.7731.5921.92393.49979.17042.001001.251.7971.7683.35295.87787.38251.251002.001.8661.8933.42499.02893.24961.25700.501.4090.9153.55273.17342.50671.25851.251.7401.7851.69993.74489.20080.50701.251.3940.9233.37872.76343.44192.00850.501.5901.3512.74384.08365.642102.00701.251.6731.6641.91390.72883.679112.00852.001.8471.9582.09498.59397.156120.50852.001.6421.4283.03087.78470.343130.501001.251.6331.3503.28686.19165.283140.50850.501.2820.8173.20967.66038.739151.25851.251.7541.7921.73792.60887.791161.25851.251.7121.6862.11592.35983.359171.251000.501.6071.3672.98686.16267.333
2.2 各响应值的优化皂化条件
首先,以Pb2+吸附量(qPb)为响应值,采用Design Expert 8.0软件对表2实验结果进行二次多项式拟合,得到Pb2+吸附量对3因素的多元二次回归方程为
(1)
由表3的方差分析可知,回归模型P<0.0001,表明该二次方程模型显著性高,可用于指导BLPAM皂化实验设计。各因素对Pb2+吸附量的影响由大到小依次为A>C>B。

表3 回归模型的方差分析
图1散点为实验所得Pb2+吸附量,表明实验值与模型预测值的偏离程度,该模型的失拟项不显著;且相关系数R2=0.9880,表明预测值和实验值之间的相关性很好。为增加模型预测的可靠性,将R2给予适当的修正Radj2=0.9725,仅有2.75%的响应值的总变异不能用该模型表示。
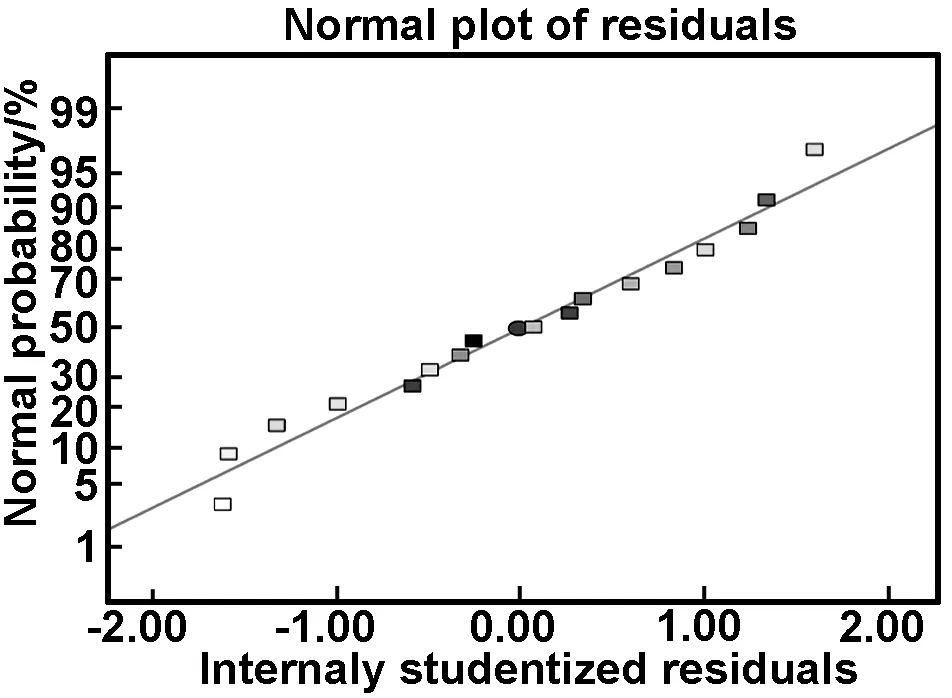
图1 Pb2+吸附量的回归模型预测值与实验值的比较
Fig 1 Comparation between predicted and experimental adsorption capacity of Pb2+
为了考虑各因素及其交互作用对Pb2+吸附量的影响,采用Design Expert 8.0软件辅助分析,得到响应面三维图和等高线图见图2~4。

图2 氢氧化钠浓度和皂化温度对Pb2+吸附量影响的响应面图及等高线图
Fig 2 Response surface plotted and contour map for the adsorption capacity of Pb2+under differentC(NaOH) and temperatures
由图2,3可知,该响应面坡度比较陡峭,说明氢氧化钠浓度对Pb2+吸附量影响显著;随着氢氧化钠浓度增加,Pb2+吸附量先增大后减小。由图4可知,该响应面坡度相对平缓,说明皂化温度和皂化时间对Pb2+吸附量影响较小。
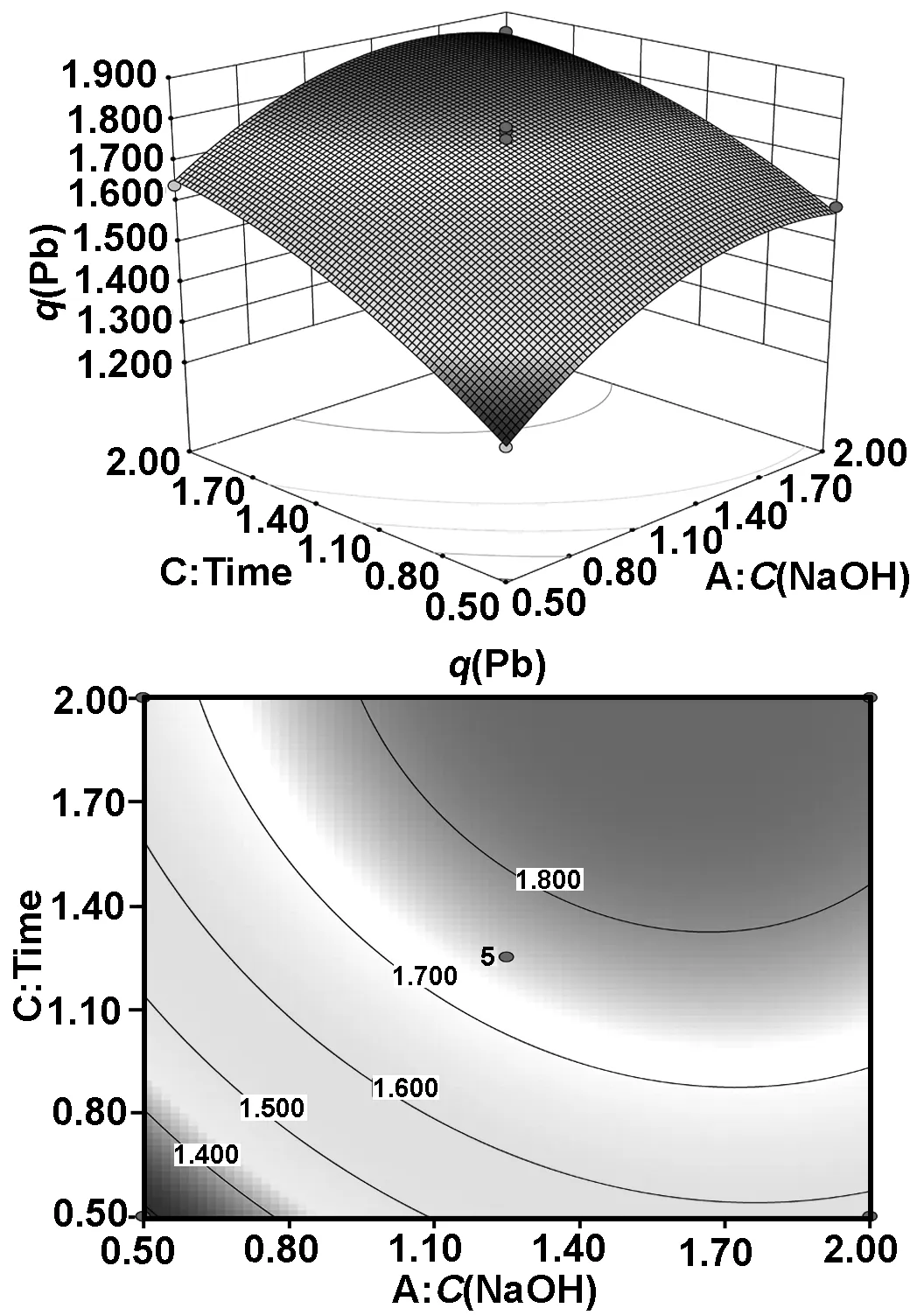
图3 氢氧化钠浓度和皂化时间对Pb2+吸附量影响的响应面图及等高线图
Fig 3 Response surface plotted and contour map for the adsorption capacity of Pb2+under differentC(NaOH) and times

图4 皂化温度和时间对Pb2+吸附量影响的响应面图及等高线图
Fig 4 Response surface plotted and contour map for the adsorption capacity of Pb2+under different temperatures and times
另外,由图可知A、B、C存在最大极值点,为取得最佳值,对回归方程做一阶偏导数等于零并求解,得到响应值为Pb2+吸附量的最佳皂化条件为氢氧化钠浓度为1.51 mol/L、皂化温度与时间分别为94.04 ℃、2.10 h。根据实际情况,将BLPAM优化皂化条件修正为:氢氧化钠浓度为1.51 mol/L、皂化温度为94 ℃、皂化时间为2.10 h。
同理,用软件对Cu2+的吸附量(qCu)、Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数(α)、Pb2+的去除率(RPb)、Cu2+的去除率(RCu)等响应值进行多元拟合,分别得到不同响应值的多元二次回归方程分别为
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
对回归方程(2)~(5)做一阶偏导数等于零并求解,即得各个响应值的最佳皂化条件,且根据实际情况,得到具体优化皂化条件,见表4所示。

表4 各响应值的优化皂化条件
2.3 组合赋权法优化BLPAM的皂化条件
对于多指标实验设计,由于涉及多个参考指标,因而对各项指标得到的优化条件往往各不相同。因此,需要全方面分析,兼顾各项指标的综合效应,最终综合确定优化实验条件。如表4可知,每一个响应值都会对应一个优化皂化条件,且各优化皂化条件之间相差较大,这给实际工业生产带来不便。为此,本文首先采用文献中的专家评分法[12]、对比排序法[13]、熵权法[14]、CRITIC法[15]等单一赋权法分别对各个指标进行赋权,结果见表5。然后根据文献[16]中提到的组合赋权法综合考虑,得到qPb、qCu、α、RPb、RCu的权重系数分别为0.267,0.177,0.171,0.241和0.143。
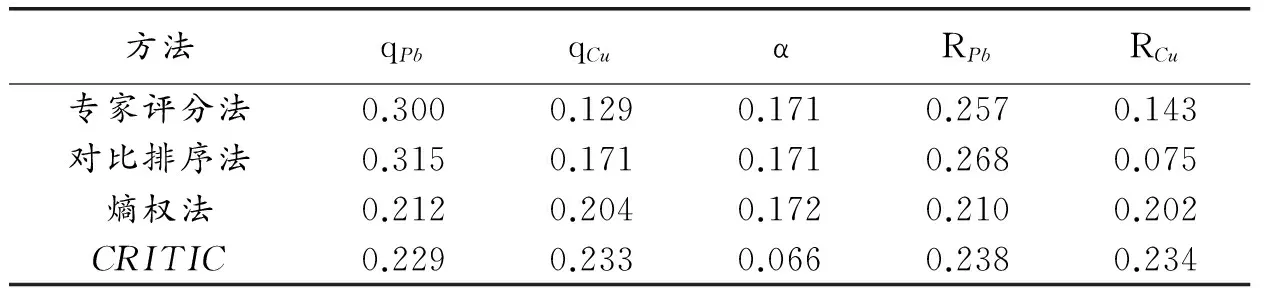
表5 不同单一赋权法得到的权重系数
对方程(1)~(5)进行线性组合得到综合回归方程,为
(6)
对方程(6)做一阶偏导数等于零并求解,即得各因素的最佳条件,为A=1.45、B=97.93、C=2.91。根据实际情况,将BLPAM皂化最优条件修正为:氢氧化钠浓度为1.45 mol/L、皂化温度为98 ℃、皂化时间为2.90 h。进行3组平行验证实验,得到皂化BLPAM树脂在浓度为2.0 mmol/L的二元Pb2+/Cu2+溶液中的吸附性能为对Pb2+的吸附量为1.772 mmol/g,对Cu2+的吸附量为1.719 mmol/g,Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数为1.604,Pb2+去除率为96.062%,Cu2+去除率为93.864%。对比可知,皂化可显著提高BLPAM的吸附性能。
3 结 论
(1) 氢氧化钠浓度、皂化温度、皂化时间对各响应值的影响显著性依次为:氢氧化钠浓度>皂化时间>皂化温度;响应曲面设计预测并根据实际情况得出针对各响应值的优化皂化条件。
(2) 通过组合赋权法得到BLPAM的优化皂化条件为:氢氧化钠浓度为1.45 mol/L、皂化温度为98 ℃、皂化时间为2.90 h。最优条件下的皂化BLPAM树脂在2.0 mmol/L二元Pb2+/Cu2+溶液中的吸附性能为:对Pb2+的吸附量为1.772 mmol/g,Cu2+的吸附量为1.719 mmol/g,Pb2+对Cu2+的选择性吸附系数为1.604,Pb2+去除率为96.062%,Cu2+去除率为93.864%。
[1] Modenes A N, Espinoza-Quinones F R, Colombo A, et al. Inhibitory effect on the uptake and diffusion of Cd2+onto soybean hull sorbent in Cd-Pb binary sorption systems [J]. J Environ Manag, 2015, 154: 22-32.
[2] Pal P, Banat F. Comparison of heavy metal ions removal from industrial lean amine solvent using ion exchange resins and sand coated with chitosan [J]. J Natur Gas Sci Eng, 2014, 18: 227-236.
[3] Duval A, Lawoko M. A review on lignin-based polymeric, micro-and nano-structured materials [J]. React Funct Polym, 2014, 85: 78-96.
[4] Yao Q X, Xie J J, Liu J X, et al. Adsorption of lead ions using a modified lignin hydrogel [J]. J Polym Res, 2014, 21: 1-16.
[5] Yao Qingxin, Xie Jianjun, Zeng Nian, et al. Preparation and adsorption property of BLAMA adsorbent composites [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2014, 45(2): 02129-02133.
姚庆鑫, 谢建军, 曾 念, 等. BLPAM复合吸附树脂制备与吸附性能[J]. 功能材料, 2014, 45(2): 02129-02133.
[6] Ge Y Y, Li Z L, Kong Y, et al. Heavy metal ions retention by bi-functionalized lignin: synthesis, applications, and adsorption mechanisms [J]. J Ind Eng Chem, 2014, 20(6): 4429-4436.
[7] Sun L, Wan S G, Yu Z B, et al. Optimization and modeling of preparation conditions of TiO2nanoparticles coated on hollow glass microspheres using response surface methodology [J]. Sep Purif Techn, 2014, 125: 156-162.
[8] Zhu Junren, Zheng Huaili, Zhang Zhi, et al. Synthesis and characterization of composite flocculant PAFS-CPAM by response surface methodology [J]. CIESC J, 2012, 63(12): 4019-4027.
朱俊任, 郑怀礼, 张 智, 等. 响应面法优化制备PAFS-CPAM复合混凝剂及其表征[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(12): 4019-4027.
[9] Yao Q X, Liu J X, Tang L P, et al. Preparation of adsorbent composites based on bentonite/sodium lignosulfonate-g-AM [J]. Appl Mechan Mater, 2014, 628: 12-15.
[10] Yao Q X,Xie J J, Liu J X. Saponification of adsorbent BLPAMA [J]. Adv Mater Res, 2013, 721: 20-23
[11] Lei Li, JinYinjia, Wang Ting, et al. Simultaneous removal of Cd(Ⅱ) and phenol by titanium dioxide-titanate nanotubes composite nanomaterial synthesized through alkaline-acid hydrothermal method [J]. Environ Sci, 2015, 36(7): 2573-2580.
雷 立, 晋银佳, 王 婷, 等. 碱热-酸热法合成二氧化钛-钛酸纳米管复合纳米材料对Cd(Ⅱ)和苯酚的同步去除[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7): 2573-2580.
[12] Rao R V, Patel B K. A subjective and objective integrated multiple attribute decision making method for material selection [J]. Mater Design, 2010, 31(10): 4738-4747.
[13] He Qing, Gu Hong, Guo Xiaojin, et al. Application of multiple methods for weight of technology strength assessment indicators [J]. Chinese J Health Stat, 2013, 30 (1): 27-30.
何 倩, 顾 洪, 郭晓晶, 等. 多种赋权方法联合应用制定科技实力评价指标权重[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2013, 30(1): 27-30.
[14] Wang Hui, Chen Li, Chen Ken, et al. Multi-index comprehensive weighing method and the selection for weights of attributes [J]. J Guangdong Coll Pharm, 2007, 23(5): 583-589.
王 晖, 陈 丽, 陈 垦, 等. 多指标综合评价方法及权重系数的选择[J]. 广东药学院学报, 2007, 23(5): 583-585.
[15] Zhang Yu, Wei Huabo. Integrated weighting method of multiple attribute decision based on CRITIC method [J]. Stat Decis, 2012, 16: 75-77.
张 玉, 魏华波. 基于CRITIC的多属性决策组合赋权方法[J]. 统计与决策, 2012, 16: 75-77.
[16] Zeng Xianbao. New exploration in the integrated weighing method [J]. Forecast, 1997, 5: 69-72.
曾宪报. 组合赋权法新探[J]. 预测, 1997, 5: 69-72.Optimization for saponification of lignin-based selective adsorbent by response surface methodology
YAO Qingxin,WANG Bei,YANG Hougui,XIE Jianjun
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha 410004, China)
The saponification hydrolysis of adsorbent composites comprising of bentonite/sodium lignosulfonate graft-polymerized with acrylamide (BLPAM) were investigated by response surface methodology (RSM). In the process, the concentration of NaOH, saponification temperature and saponification time were used as response variables and the adsorption capacity of lead ions, the adsorption capacity of copper ions, the selective coefficient of lead to copper ions, the removal ratio of lead ions and the removal ratio of copper ions were studied. The Box-Behnken mathematical relational model between response variables and response values was established and the saponification conditions were optimized. Then, combination weighting method was applied to determine the index weights and the optimized saponification conditions considering all response values were obtained. Results have shown that the optimized saponification conditions of BLPAM were as follows: the concentration of sodium hydroxide is 1.45 mol/L, the saponification temperature is 98℃, the saponification time is 2.90 h. The adsorption capacities of the saponified BLPAM for Pb2+and Cu2+in Pb2+/Cu2+binary solution are 1.772 and 1.719 mmol/g, respectively, the selective coefficient of Pb2+to Cu2+is 1.604, and the removal ratios of Pb2+and Cu2+are 96.062% and 93.864%, respectively.
lignin;adsorbent;saponification;selective adsorption; combination weighing method;response surface methodology
1001-9731(2016)11-11215-05
国家自然科学基金资助项目(31270603);湖南省研究生科技创新基金资助项目(CX2015B285)
2015-10-25
2016-06-08 通讯作者:谢建军,E-mail: xiejianjun12@sina.com
姚庆鑫 (1987-),男,河北唐山人,在读博士,师承谢建军教授,从事功能高分子材料、水处理材料研究。
TB34;TQ028.14;O647.314
A
10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2016.11.042

