肝脏瞬时弹性成像和门静脉血流动力学指标检测对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化的诊断意义
徐晓鸾,孟繁坤,孙丽娟
肝脏瞬时弹性成像和门静脉血流动力学指标检测对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化的诊断意义
徐晓鸾,孟繁坤,孙丽娟
目的探讨瞬时弹性成像(TE,Fibroscan)R技术测量肝脏硬度值(LSM)和超声检测门静脉血流动力学参数对慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者肝脏纤维化分级的效能。方法91例CHB患者和41例正常人经Fibroscan-502仪测定LSM;使用彩色多普勒超声诊断仪检测门静脉主干内径(PVD)、最大流速(PVVmax)和平均流速(PVVmean);CHB患者在超声引导下行肝脏穿刺,对穿刺组织进行病理学检查。结果CHB患者LSM、PVD、PVVmax和PVVmean分别为(9.40±0.95)kPa、(11.63±0.12)mm、(35.40±0.94)cm/s和(29.82±0.84)cm/s,均显著高于正常人[分别为(4.45±0.20)kPa、(10.85±0.12)mm、(26.10±1.07)cm/s和(21.94±0.73)cm/s,P<0.01];CHB患者肝组织纤维化病理分期为S0者LSM、PVD、PVVmax和PVVmean分别为(5.46±0.33)kPa、(11.36±0.24)mm、(40.99±1.46)cm/s和(34.42±1.29)cm/s,S1期者为(6.06±0.31)kPa、(11.33±0.16)mm、(34.09±1.43)cm/s和(28.90±1.31)cm/s,S2期者为(9.87±1.15)kPa、(12.14±0.31)mm、(33.51±1.59)cm/s和(27.78±1.73)cm/s,S3期者为(15.48±2.16)kPa、(12.42±0.26)mm、(33.01±2.11)cm/s和(28.48±2.05)cm/s,和S4期者为(31.85±8.38)kPa、(12.50±0.34)mm、(28.42±2.78)cm/s和(24.58±2.91)cm/s],差异有统计学意义(F=29.13、F=4.52、F=5.98和F=4.36,P均<0.01);CHB患者LSM与PVD、PVVmax和PVVmean存在相关性(r=0.362、r=-0.364、r=-0.345,P<0.01)。结论综合应用LSM及门静脉血流动力学指标对临床无创评估CHB患者肝纤维化有一定的诊断意义。
慢性乙型肝炎;肝纤维化;瞬时弹性成像;门静脉血流动力学;诊断
本研究使用瞬时弹性成像仪(Transient elastography,TE,Fibroscan)检查肝脏硬度值(Liver stiffness mearsurement,LSM),同时使用彩色多普勒超声获得门静脉血流动力学参数,并与肝脏穿刺活检所得病理学检查结果相对照,观察上述指标与肝纤维化分期的相关性,探讨其应用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1研究对象收集2011年8月至2014年8月在我院就诊的CHB患者91例,男38例,女53例,年龄16~61岁,平均年龄(32.9±11.6)岁。CHB诊断标准:参照“慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2010年版)”,既往有乙型肝炎病史或HBsAg阳性超过6个月,现HBsAg和(或)HBV DNA仍为阳性者,除外合并其他病毒性肝炎、药物性肝损伤、自身免疫性肝病、肝豆状核变性、有肝脏穿刺禁忌证或不能成功完成Fibroscan检查者。正常体检者41例,男22例,女19例,年龄20~51岁,平均年龄(32.1±9.3)岁。
1.3彩色多普勒超声检查在检查前,禁食8~12小时。取样的容积大小为管腔内径l/3时进行测量,获得受试者门静脉主干内径(Inner diameters of portal vein,PVD)、最大流速(Max blood flow velocity of portal vein,PVVmax)和平均流速(Mean blood flow velocity of portal vein,PVVmean)。
1.4病理学检查91例CHB患者均签署肝穿刺知情同意书。于多普勒超声及FibroscanR检测当日行超声引导下肝组织穿刺活检术。
1.5统计学处理应用SPSS 19.0统计学软件,对数据进行统计学分析,计量资料以(±s)表示,两组计量资料的比较采用t检验,相关性分析采用Spearman相关分析法,各病理分组之间检测值的比较采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),所有统计分析采用双侧检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1CHB患者肝组织病理学表现在91例行肝活检术的CHB患者中,S0期28例(30.77%),S1期31例(34.07%),S2期14例(15.38%),S3期12 (13.19%),S4期6例(6.59%)。
2.2肝弹性检测值和门静脉血流动力学指标检测结果本组CHB患者LSM范围为3.4 kPa~75.0 kPa。S0期为(5.46±1.76)kPa,S1期为(6.06±1.73)kPa,S2期为(9.87±4.31)kPa,S3期为(15.48±7.48)kPa,S4期为(31.85±20.53)kPa(图1~5,表1、表2)。CHB患者LSM、PVD、PVVmax、PVVmean与正常人差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);不同肝纤维化分期CHB患者LSM、PVD、PVVmax、PVVmean存在显著统计学差异(F值分别为29.13、4.52、5.98、4.36,P<0.01);CHB患者LSM与PVD、PVVmax和PVVmean存在显著性相关(r=0.437、-0.364、-0.345,P<0.01)。
3 讨论
目前,肝脏穿刺病理组织活检仍然是评价肝脏纤维化程度的“金标准”[1~4],但由于肝穿组织标本体积有限,以及肝纤维化分布的不均匀性,导致肝穿活检存在抽样误差(10%~45%)[5],同时肝脏穿刺活体组织检查也存在病理医师的主观差异。另外,肝组织活检因其有创性可能给患者带来痛苦及一些并发症甚至死亡(有报道称致死率为0.01%~0.1%)[6],因而不能被患者广泛的接受,也不便于临床医生对患者病情进行动态的观察。有学者应用超声造影进行肝纤维化分级,结果显示超声造影对诊断S3和 S4期肝纤维化具有一定的价值,但对诊断S≤2期的肝纤维化准确性不高[7]。
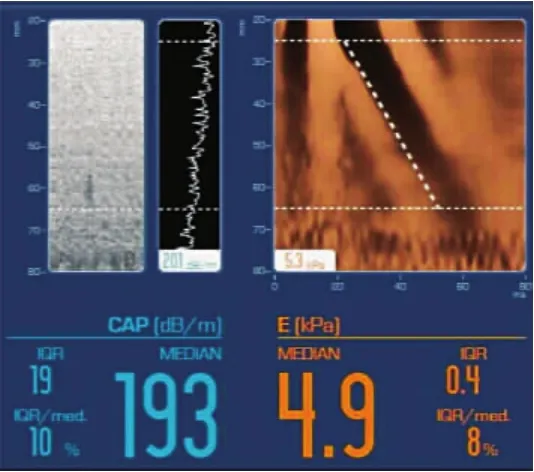
图1 肝纤维化S0期(LSM=4.9kPa)

图2 肝纤维化S1期(LSM=6.4kPa)
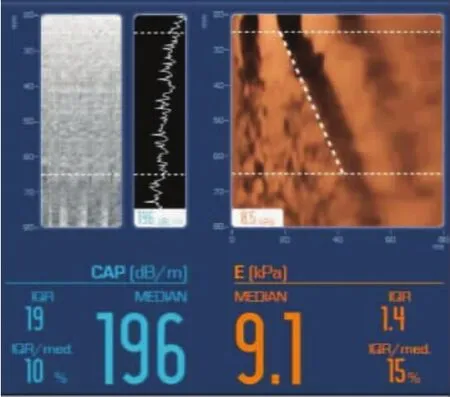
图3 肝纤维化S2期(LSM=9.1kPa)

图4 肝纤维化S3期(LSM=14.1kPa)
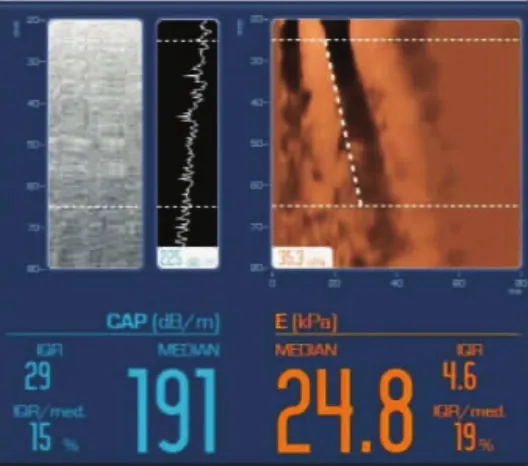
图5 肝纤维化S4期(LSM=24.8kPa)
表1 两组肝脏弹性值和门静脉血流动力学参数(±s)比较

表1 两组肝脏弹性值和门静脉血流动力学参数(±s)比较
例数LSM(kPa)PVD(mm)PVVmax(cm/s)PVVmean(cm/s)正常人414.45±0.2010.85±0.1226.10±1.0721.94±0.73乙型肝炎919.40±0.9511.63±0.1235.40±0.9429.82±0.84 t值3.4794.5565.9165.884 P值0.0010.0000.0000.000
表2 不同肝纤维化患者肝脏弹性值和门静脉血流动力学参数(±s)比较
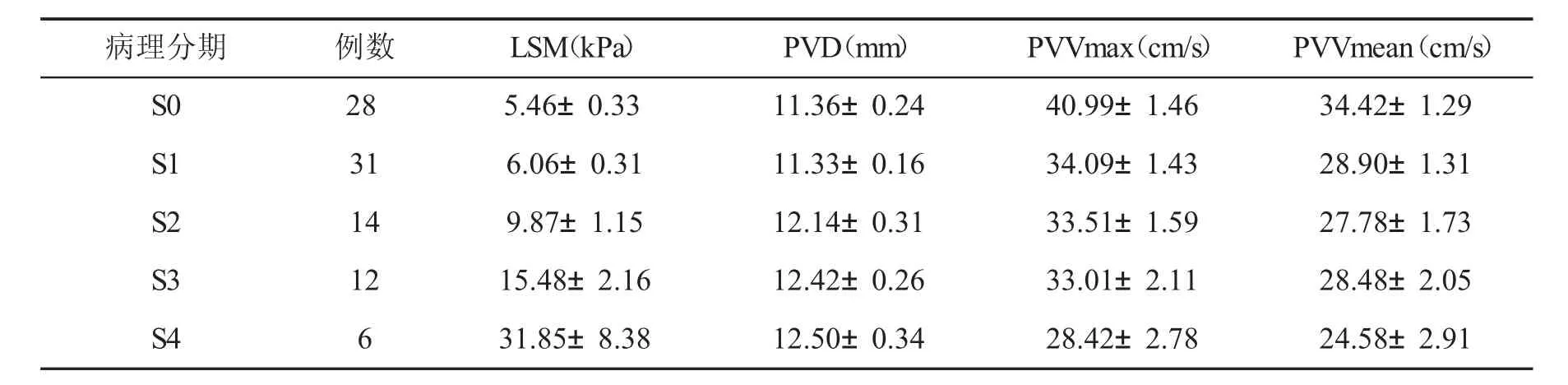
表2 不同肝纤维化患者肝脏弹性值和门静脉血流动力学参数(±s)比较
病理分期例数LSM(kPa)PVD(mm)PVVmax(cm/s)PVVmean(cm/s)S0285.46±0.3311.36±0.2440.99±1.4634.42±1.29 S1316.06±0.3111.33±0.1634.09±1.4328.90±1.31 S2149.87±1.1512.14±0.3133.51±1.5927.78±1.73 S31215.48±2.1612.42±0.2633.01±2.1128.48±2.05 S4631.85±8.3812.50±0.3428.42±2.7824.58±2.91
彩色多普勒超声是非侵入性的诊断,而且血管内径和血流速度等指标具有客观性,检查的可重复性较好,可作为评估肝脏纤维化程度的手段。本组各纤维化分期慢性乙型肝炎患者LSM、PVD、PVVmax、PVVmean存在统计学差异,LSM与PVD呈正相关,与PVVmax或PVVmean呈负相关。分析原因如下:随着肝纤维化进程的发展肝脏LSM逐步增加。肝组织纤维化程度越高,声波在组织内传播的速度越快,经过转换得出的硬度值也就越大。肝炎病毒长期刺激,肝纤维化逐步进展,纤维组织增生,正常的肝小叶结构被破坏,肝窦内血流阻力增高。另外,血浆内源性缩血管物质增加,静脉管壁内的平滑肌细胞收缩,静脉回流受阻,导致门静脉阻力增加。此外,由于肝纤维化可导致肝内小血管间形成吻合支,部分压力较高的肝动脉血流向门静脉,进一步使门静脉内压力升高,门静脉内径增加[18,19]。
本研究有着以下的不足之处,由于病例数量的限制,S4期病例仅6例,需要后续研究进一步扩大病例数,进行大样本研究。
综上所述,肝纤维化早期,门静脉血流动力学改变已经出现,并随着纤维化的进展逐渐明显,使用彩色多普勒超声检测门静脉血流动力学改变,对临床简便、无创、客观地评价肝纤维化有一定的指导意义。
[1]吴春晓,周晓蕾,陈燕鸿,等.乙型肝炎相关性原发性肝癌发生的危险因素分析.实用肝脏病杂志,2015,18(3):306-307.
[2]韩莹,丁惠国.抗病毒治疗乙型肝炎肝硬化的过去、现在和将来.实用肝脏病杂志,2015,18(5):453-456.
[3]中华医学会肝病学分会和感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2010年版).实用肝脏病杂志,2011,14(2):81-89.
[4]中华医学会传染病与寄生虫病学分会、肝病学分会.病毒性肝炎防治方案.中华肝脏病杂志,2000,8(6):324-329.
[5]Lupsor M,Badea R,Stefanescu H,et a1.Analysis of histopathological changes that influence liver stiffness in chronic hepatitis C.Results from a cohort of 324 patients.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis,2008,17(2):155-163.
[6]Cadranel JF,Rufat P,Degos F.Practices of liver biopsy in France:resultsofaprospectivenationwidesurvey.Forthe Group of Epidemiology of the French Association for the Study of the Liver(AFEF).Hepatology,2000,32(3):477-481.
[7]张舒眉,黄春旺,钟健,等.超声造影对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝组织纤维化分级的诊断价值.实用肝脏病杂志,2012,15(2):117-119.
[8]张琪,戴琳,陈永鹏,等.FibroScan弹性值测定在HBV感染所致肝衰竭患者中的应用价值.中国康复,2009,24(2):120-122.
[9]张纯林,罗福成,童清平.超声弹性成像在肝脏疾病中的应用.实用肝脏病杂志,2010,13(6):456-460.
[10]Takemoto R,Nakamuta M,Aoyagi Y,et al.Validity of FibroScan values for predicting hepatic fibrosis stage inpatients with chronic HCV infection.J Dig Dis,2009,10(2):145-148.
[11]Ogawa E,Furusyo N,Toyoda K,et al.Transient elastography for patientswithchronichepatitisBandCvirusinfection:Non-invasive,quantitativeassessmentofliverfibrosis.Hepatol Res,2007,37(12):1002-1010.
[12]程小飞,梁雄波,熊晓红,等.超声多普勒测定肝硬化患者门脉系统参数与Fibroscan得分的相关性分析.实用肝脏病杂志,2013,16(2):111-112.
[13]Sandrin L,Fourquet B,Hasquenoph JM,et a1.Transient elastography:anew noninvasivemethodforassessmentofhepatic fibrosis.Ultrasound Med Biol,2003,29(12):1705-1713.
[14]Castera L,Vergniol J,Foucher J,et al.Prospective comparison of transient elastography,Fibrotest,APRI,and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C.Gastroenterology,2005,128(2):343-350.
[15]FraquelliM,RigamontiC,Casazza G,etal.Reproducibility of transientelastography intheevaluationof liverfibrosisin patients with chronic liver disease.Gut,2007,56(7):968-973.
[16]Stefanescu H,Griqorescu M,Lupsor M,et al.Spleen stiffness measurement using Fibroscan for the noninvasive assessment of esophageal varices in liver cirrhosis patients.J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2011,26(1):164-170.
[17]Millonig G,Reimann FM,Friedrich S,et al.Extrahepatic cholestasis increases liver stiffness(FibroScan)irrespective of fibrosis. Hepatology,2008,48(5):1718-1723.
[18]Searle J,Mendelson R,Zelesco M,et a1.Non-invasive prediction of the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C using an ultrasound contrast agent.A pilot study.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol,2008,52(2):1440-1673.
[19]Tang A,Kim TK,Heathcote J,et a1.Does hepatic vein transit time performed with contrast-enhanced ultrasound predict the severity of hepatic fibrosis.Ultrasound Med Biol,2011,37(12):1963-1969.
(收稿:2016-02-23)
(本文编辑:陈从新)
ObjectiveTo investigate the efficacy of hemodynamic indexes of portal vein and liver stiffness measure(LSM)in diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B(CHB).MethodsA total of 91 patientswithCHB and41healthy personswererecruitedinthisstudy.Allsubjectswereexaminedby Fibroscan-502 to obtain the LSM,and color Doppler ultrasound were applied for the detection of inner diameters of portal vein(PVD),max blood flow velocity of portal vein(PVVmax)and mean blood flow velocity of portal vein (PVVmean).All CHB patients underwent liver biopsy for evaluation of liver fibrosis staging.ResultsThe LSM,PVD,PVVmax and PVVmean in patients with CHB[(9.40±0.95)kPa,(11.63±0.12)mm,(35.40±0.94)cm/s and(29.82±0.84)cm/s]were much higher than those in healthy persons[(4.45±0.20)kPa,(10.85±0.12)mm,(26.10±1.07)cm/s and(21.94±0.73)cm/s,respectively,P<0.01];the LSM,PVD,PVVmax and PVVmean in patients with S0fibrosis were(5.46±0.33)kPa,(11.36±0.24)mm,(40.99±1.46)cm/s and(34.42±1.29)cm/s,in patients with S1were(6.06±0.31)kPa,(11.33±0.16)mm,(34.09±1.43)cm and(28.90±1.31)cm/s,in patients with S2were(9.87±1.15)kPa,(12.14±0.31)mm,(33.51±1.59)cm/s and(27.78±1.73)cm/s,in patients with S3were(15.48±2.16)kPa,(12.42±0.26)mm,(33.01±2.11)cm/s and(28.48±2.05)cm/s,and in patients with S4 were(31.85±8.38)kPa,(12.50± 0.34)mm,(28.42±2.78)cm/s,and(24.58±2.91)cm/s,significantlydifferentamongthefivegroups (F=29.13,F=4.52,F=5.98andF=4.36,P<0.01);the correlationsbetweenLSMandPVD,PVVmax,and PVVmeaninpatientswithCHBwerestatistically significant(r=0.362,r=-0.364,r=-0.345,P<0.01).ConclusionsThe combination detection of hemodynamic indexes of portal vein and LSM of liver may be valuable in determining liver fibrosis in a noninvasive way in patientswith CHB.
Chronic hepatitis B;Liver fibrosis;Transient elastography;Portal vein hemodynamics;Diagnosis
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2016.04.012
100069北京市首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院超声与功能诊断中心
徐晓鸾,女,34岁,硕士研究生,医师。主要从事超声影像、介入和超声弹性成像诊断研究。E-mail:xuxiaoluan168@126. com
Application of transient elastography and portal hemodynamics indexes in diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis inpatients withchronichepatitis BXu Xiaoluan,Meng Fankun,Sun Lijuan.Ultrasonic and Functional Diagnosis Center,Youan Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100069,China

