阿魏酸对脂多糖损伤的PC12细胞和大鼠海马神经元细胞的保护作用
黄 浩,马增春,王宇光,高 月(1.北京工业大学生命科学与生物工程学院,北京 10014;.军事医学科学院放射与辐射医学研究所,北京 100850)
阿魏酸对脂多糖损伤的PC12细胞和大鼠海马神经元细胞的保护作用
黄浩1,2,马增春2,王宇光2,高月2
(1.北京工业大学生命科学与生物工程学院,北京 100124;2.军事医学科学院放射与辐射医学研究所,北京 100850)
目的 探讨阿魏酸(FA)对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的PC12细胞和大鼠海马神经元损伤的保护作用,并探讨其可能的作用机制。方法 体外实验:FA 2.5~40 μmol·L-1与PC12细胞预处理12 h,加入LPS 0.15 g·L-1继续培养8 h,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活力;ELISA法检测细胞培养上清中肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)的释放;激光共聚焦显微镜检测细胞骨架蛋白F肌动蛋白的表达。体内实验:FA 25,50和100 mg·kg-1ip给予SD大鼠,每天1次,连续35 d。给药第29天时ip给予LPS 0.2 mg·kg-1,每天1次,连续7 d,运用免疫组织化学法观察大鼠海马神经元磷酸二酯酶4B(PDE4B)蛋白表达的变化;Western蛋白质印迹法检测cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(CREB)和磷酸化CREB(p-CREB)表达。结果 体内实验:与LPS组细胞比较,FA 10,20和40 μmol·L-1预处理组细胞活力明显升高(P<0.05),炎性因子TNF-α和IL-1β的释放显著减少(P<0.05),细胞骨架蛋白F肌动蛋白的分布和结构明显改善。体内实验:HE染色结果显示,预先给予FA 50和100 mg·kg-1可以减轻LPS诱导的大鼠海马神经元损伤;免疫组织化学实验结果显示,FA 50和100 mg·kg-1能够显著降低LPS诱导的大鼠海马神经元PDE4B蛋白表达水平的升高(P<0.05);Western蛋白印迹实验结果表明,FA 50和100 mg·kg-1可逆转LPS对CREB和p-CREB蛋白表达的抑制作用(P<0.05)。结论 FA对LPS诱导的PC12细胞和大鼠海马神经元细胞损伤有保护作用,FA抗神经炎症的作用可能与抑制PDE4表达、激活cAMP/CREB信号通路相关。
阿魏酸;磷酸二酯酶4B;脂多糖;cAMP反应元件结合蛋白
DOl:10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2016.04.005
阿魏酸(ferulic acid,FA)是当归、川芎和升麻等中药的有效成分之一,具有抑制炎症介质形成和释放、疏通微循环和改善血液流变的作用,还可改善免疫功能、清除和抑制自由基等[1]。FA可以透过血脑屏障,提高脑组织超氧化物歧化酶活性,显著降低丙二醛含量,通过抗氧化应激的作用发挥其神经保护作用[2-5]。FA对小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤有一定程度的保护作用,对于β淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素转基因小鼠也具有保护作用[6],并能够破坏已形成的β-样淀粉小纤维,减缓阿尔茨海默病的病理过程[7],从而改善阿尔茨海默病的症状。进一步研究发现,FA可以拮抗β-淀粉样蛋白所致的神经细胞毒性、细胞内活性氧升高以及细胞内钙离子超载。大量的动物实验也表明,FA可以逆转神经炎症等引起的小鼠记忆缺失,升高羰基蛋白水平,减轻神经细胞损伤[8-9]。本研究利用脂多糖(lipopolysaccha⁃rides,LPS)诱导PC12细胞损伤的体外模型以及ip给予LPS导致大鼠皮质和海马神经元损伤的体内模型,探讨FA对LPS所致神经细胞损伤的保护作用及机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1药物、细胞、试剂和仪器
细胞实验所用反式FA为白色粉末(相对分子质量为194.18),由中国药品生物制品检定所提供,纯度>99.6%,用二甲亚砜溶解,配置成100 mmol·L-1的母液,用时加RPMI 1640培养基稀释至所需浓度;动物实验用FA和LPS购自美国Sigma公司,前者用二甲亚砜溶解配置成100 mmol·L-1的母液,后者用PBS溶解为3.125 g·L-1母液,用时加RPMI 1640培养基稀释至所需浓度。PC12细胞由中国医学科学院基础医学研究所细胞资源中心提供。RPMI 1640培养基、胰蛋白酶和胎牛血清购自新西兰Gibco公司;CCK-8测定试剂盒购自同仁化学研究所;大鼠白细胞介素1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)ELISA检测试剂盒购自联科生物技术有限公司;罗丹明标记的鬼笔环肽购自上海Invitrogen公司;核蛋白提取试剂盒和BCA蛋白质含量检测试剂盒购自康为世纪生物科技有限公司;磷酸二酯酶4B (phosphodiesteras 4B,PDE4B)(H-56)抗体购自美国Santa Cruz公司;抗cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(cAMP response element-binding protein,CREB)抗体和磷酸化CREB(phospho-CREB,p-CREB)(Ser133)抗体购自美国Cell Signaling Technology公司;山羊抗兔IgG二抗购自柏奥易杰北京科技有限公司。KD-BM生物组织包埋机(中国科迪仪器),RM2016轮转石蜡切片机(德国Leica公司),Nikon E200光学显微镜(日本尼康公司),UltraVIEWVoX Confocal Imaging System激光共聚焦显微镜(美国PerkinElmer公司)。
1.2细胞培养
PC12细胞按其培养要求接种于培养瓶中,加入含10%灭活胎牛血清和5%马血清的RPMI 1640细胞培养液,培养液中加入100 kU·L-1青霉素和100 g·L-1链霉素(1%),置于37°C,5%CO2,饱和湿度条件下培养。将PC12用含2%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养液稀释至1×108L-1细胞,接种于6孔板或96孔板培养24 h,进行以下实验。
1.3CCK-8法检测细胞存活
FA单用对PC12细胞存活的影响:将细胞分为正常对照组、溶剂对照组(0.1%DMSO)和FA 2.5,5.0,10,20和40 μmol·L-1组,每组5孔,每孔200 μL。待细胞贴壁并进入对数生长期后,按照分组换液,培养24 h。每孔加入CCK-8试剂10 μL,37°C孵育2 h,酶标仪测定450 nm波长处每孔的吸光度值(A450 nm)。细胞存活率(%)=药物处理组A450 nm/正常对照组A450 nm×100%。
FA对LPS损伤的PC12细胞存活的影响:将细胞分为正常对照组、LPS对照组和LPS+FA 2.5,5.0,10,20和40 μmol·L-1组。FA预处理PC12细胞12 h,然后加入LPS 0.15 g·L-1继续孵育8 h,计算细胞存活率。
1.4ELlSA检测细胞培养上清TNF-α 和lL-1β 的水平
将PC12细胞用FA 2.5,5,10,20和40 μmol·L-1预处理12 h,然后加入LPS 1 g·L-1与PC12细胞继续孵育8 h,诱导细胞产生炎性因子,收集各组细胞上清液,用ELISA试剂盒检测TNF-α和IL-1β水平。
1.5激光共聚焦显微镜检测PC12细胞F肌动蛋白的结构和分布
FA 10,20和40 μmol·L-1预处理PC12细胞12 h,加入LPS 1 mg·L-1继续孵育8 h,收集细胞,用4%的多聚甲醛固定15 min。用PBS洗涤3次;用含0.5%BSA的PBS封闭,0.1%Triton X-100透化10 min;用PBS洗涤3次;室温下用罗丹明标记的鬼笔环肽1 μmol·L-1孵育PC12细胞30 min;PBS洗涤3次,用DAPI染核;PBS洗涤3次,用激光共聚焦显微镜进行检测。罗丹明:激发波长561 nm,吸收波长580~650 nm;DAPI:激发波长405 nm,吸收波长415~475 nm。
1.6动物、模型制备和给药
60只成年雌性SD大鼠,体质量280~320 g,购自中国药品生物制品鉴定所实验动物中心,许可证编号:SCXK(京)2012-0001;大鼠自然昼夜节律光照,适应1周以上开始实验。将大鼠随机分为正常对照组、LPS模型组、FA 25,50和100 mg·kg-1防护组。正常对照组和LPS模型组每天给予等体积生理盐水。FA防护组大鼠ip给予FA,每天1次,连续35 d。于第29天开始,除正常对照组外,其余各组大鼠ip给予LPS 0.2 mg·kg-1,每天1次,连续7 d。第36天,大鼠麻醉后处死,心脏灌流后迅速取大鼠海马组织,分成2份,一份固定于4%甲醛中,常规石蜡包埋,切片,HE染色,在显微镜下观察海马组织病理变化。另一份用无RNA酶水冲洗,液氮速冻,-80°C保存,用于基因或者蛋白表达分析。
1.7免疫组织化学法检测大鼠海马神经元PDE4B蛋白表达
大鼠海马组织切片,经二甲苯梯度脱蜡和乙醇梯度脱水,用PBS洗涤3次,每次5 min;切片浸入EDTA溶液中并放入微波炉以中高火进行抗原修复;切片放入3%双氧水去离子水中常温孵育10 min,以消除内源性过氧化物酶活性,PBS洗涤2次,每次3 min;滴加正常山羊血清工作液室温孵育15 min封闭,倾去,勿洗;随后滴加PDE4B一抗(1∶200),4℃过夜;PBS冲洗3次,每次3 min,滴加二抗,37℃温箱15 min;滴加辣根过氧化物酶标记链霉卵白素工作液(S-A/HRP),放入37℃温箱孵育15 min;PBS冲洗3次,每次3 min;DAB显色剂显色,蒸馏水充分冲洗,复染,脱水,透明,中性树胶封片。用Nikon ECLIPSE E200显微镜连接Tucsen TCH-5.0数码相机拍照,并用Image-Pro Plus 6.0软件分析染色阳性区域积分吸光度(integrated absorbance,IA),表达PDE4B蛋白相对表达水平。
1.8Western蛋白质印迹法检测大鼠海马神经元CREB和p-CREB蛋白表达
按照核蛋白和胞浆蛋白提取试剂盒说明书提取大鼠海马组织核蛋白和胞浆蛋白,必须在蛋白提取液中加入蛋白酶抑制剂和磷酸酶抑制剂。高速离心后收集上清,将胞浆蛋白和核蛋白分别提取收集并放入-80°C冰箱保存备用。经BCA法进行蛋白定量后,每个点样孔加入50 μg蛋白样品,以12% SDS-PAGE进行电泳,用预饱和的PVDF膜进行转膜,Westren蛋白质印迹封闭液(BSA,Tris系统)封闭1 h后,用1∶1000稀释的抗CREB,p-CREB和Histone H3一抗孵育,4°C过夜,次晨用辣根过氧化物酶标记的1∶2000稀释的二抗37°C孵育1 h,ECL显影,用Image J图像分析软件对蛋白条带进行IA分析,以待测蛋白和Histone核蛋白内参条带的IA比值表示待测蛋白相对表达水平。
1.9统计学分析
实验结果数据采用x±s表示,数据经Graphpad Prism5软件统计分析,采用单因素方差分析(oneway ANOVA),P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1FA对LPS损伤PC12细胞存活率的影响
如图1所示,与正常对照组相比,FA 2.5~20 μmol·L-1单独对PC12细胞处理24 h,对PC12细胞存活率无明显影响;FA 40 μmol·L-1处理组细胞存活率有所升高(P<0.05)。LPS 0.15 g·L-1可使PC12细胞存活率降低至正常对照组的约75%;FA 10,20和40 μmol·L-1预处理PC12细胞12 h,对LPS导致的PC12细胞存活率下降有一定的防护作用(P<0.05,P<0.01)。
2.2FA对LPS损伤PC12细胞TNF-α 和lL-1β 释放的影响
如图2所示,与正常对照组相比,LPS组PC12细胞上清液中炎性因子TNF-α和IL-1β的释放量显著增加(P<0.01);FA 2.5~40 μmol·L-1预处理PC12细胞12 h,能显著降低LPS所致TNF-α和IL-1β水平的升高(P<0.05,P<0.01)。
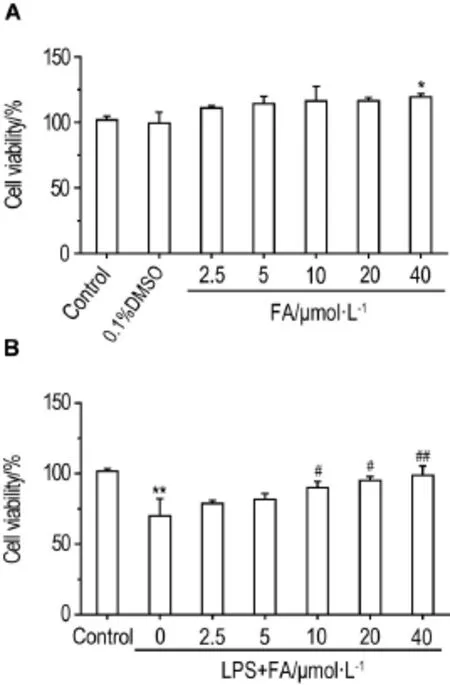
Fig.1 Effect of ferulic acid(FA)alone(A)or in combination with lipopolysaccharides(LPS)(B)on viability of PC12 cells.A:PC12 cells were treated with FA for 24 h;B:PC12 cells were pretreated with FA for 12 h,then exposed to LPS 0.15 g·L-1for 8 h.±s,n=3.*P<0.05,**P<0.01,compared with corresponding control group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with LPS group.

Fig.2 linhibition of FA on generation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α )and interleukin-1β (lL-1β )in PC12 cells injuried by LPS.PC12 cells were pre-incubated with FA for 12 h,then exposed to LPS 1 mg·L-1for 8 h.±s,n=3.**P<0.01,compared with corresponding control group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with LPS group.
2.3FA对LPS损伤PC12细胞骨架蛋白F肌动蛋白的保护作用
激光共聚焦显微镜观察结果(图3)显示,正常对照组PC12细胞内F肌动蛋白染色清晰,骨架完整,在细胞质中分布均匀;LPS模型组PC12细胞骨架排列紊乱,并且集结成束状,细胞轮廓不清晰;FA 10 μmol·L-1组细胞骨架与LPS组比较无明显差异;FA 20 μmol·L-1组细胞骨架形态有所恢复;FA 40 μmol·L-1组细胞骨架良好,F肌动蛋白排列有序,细胞形态完整。表明FA对LPS所致PC12细胞F肌动蛋白骨架的损伤具有保护作用。
2.4FA对LPS导致大鼠海马神经元损伤的保护作用
HE染色结果(图4)显示,正常对照组大鼠海马神经细胞排列整齐,结构完好,未见缺血性神经元改变。LPS模型组海马神经元均有不同程度的局部缺血性改变,海马神经元核固缩、胞浆红染,结构不清。FA 25 mg·kg-1组海马神经元呈局部缺血性改变伴细胞及血管间隙加大,提示有轻度水肿,病理改变均较正常对照组严重。FA 50 mg·kg-1组海马神经元偶见缺血性改变,病理改变均较模型组为轻;FA 100 mg·kg-1组海马神经元之间轻微的病理改变。提示FA 50和100 mg·kg-1对LPS诱导的大鼠海马神经元损伤具有保护作用。
2.5FA对LPS诱导大鼠海马神经元PDE4B表达的影响
如图5所示,正常对照组海马神经元中PDE4B广泛表达,其定位主要是在细胞浆中,成棕黄色。与正常对照组相比,LPS损伤模型大鼠海马神经元内PDE4B表达明显增强(P<0.05);给予FA 25,50 和100 mg·kg-1进行预保护,海马神经元内PDE4B表达较LPS模型组减弱(P<0.05)。
2.6FA对LPS诱导大鼠海马神经元CREB和p-CREB蛋白表达的影响
由图6所示,与正常对照组相比,LPS模型组大鼠海马神经元CREB和p-CREB蛋白表达均明显降低(P<0.01);给予FA 50和100 mg·kg-1进行预保护,其海马神经元内CREB表达较LPS模型组明显增强(P<0.01),同时p-CREB表达亦明显增强(P<0.01)。提示FA可能对PDE4/cAMP/CREB信号通路有明显调节作用。
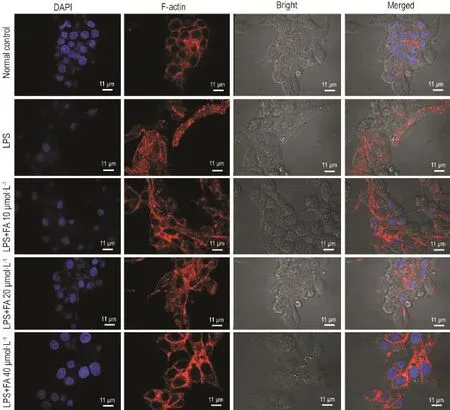
Fig.3 Effect of FA on F-actin in PC12 cells injured by LPS.See Fig.2 for the cell treatment.Fluorescence staining of F-actin with Alexa Fluor 488 rodamine-conjugated phalloidin(red)and with DAPI(blue)to label cell nucleus(blue).

Fig.4 Effect of FA on pathological changes of hippocampus of rats induced by LPS(HE staining,×400).FA was ip given SD rats once a day for 39 d.From the 29th day,LPS 0.2 mg·kg-1was ip given once a day for 7 d.Arrows show histopathological changes.

Fig.5 Effect of FA on phosphodiesteras 4B(PDE4B)expressions in hippocampus of rats induced by LPS (Immunohistochemistry,×200).See Fig.4 for the rat treatment.IA:integrated absorbance.B was semi-quantitative result of A.±s,n=6,#P<0.05,compared with normal control group;#P<0.05,compared with LPS model group.
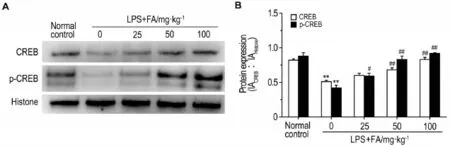
Fig.6 Effect of FA on expression of cAMP response element-binding protein(CREB) and phospho-CREB(p-CREB)protein in hippocampal neuros of rats induced by LPS by Western blotting.See Fig.4 for the rat treatment.B was the semi-quantitative result of A.±s,n=3.**P<0.01,compared with normal control group;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,compared with LPS model group.
3 讨论
LPS具有很强的促炎活性,参与炎症的发生发展。LPS刺激PC12细胞在一定程度上模拟了体内炎症反应过程。本研究结果表明,FA对LPS所致PC12细胞的活性降低具有抑制作用,可显著降低LPS所致TNF-α和IL-1β水平的升高。神经炎症会造成神经元突触功能异常和认知能力下降,过度的神经炎症是阿尔兹海默病等神经退行性疾病发生和发展的中心环节。FA具有良好的抗氧化和抗炎作用[10],对神经系统具有保护作用[11-12]。
F肌动蛋白是细胞骨架的主要成分之一,对细胞起支撑作用,在维持细胞形态、调节细胞黏附、运动、增殖及细胞内外信号转导等过程中起重要作用[13]。激光共聚焦显微镜观察显示,正常对照组细胞内F肌动蛋白排列整齐,分布均匀,基本充满细胞质,尤其胞膜部分F肌动蛋白骨架清晰。LPS模型组细胞F肌动蛋白集结成粗大的束状,提示应力纤维大量形成,有可能导致细胞骨架受损,细胞膜失去支持。FA预处理组的PC12细胞,其F肌动蛋白的形态、排列均有不同程度的改善。本研究结果提示,FA对LPS所致F肌动蛋白损伤具有保护作用。
大鼠腹腔注射LPS可引起大鼠的学习记忆功能减退及海马神经元结构损伤[14-15]。本研究通过腹腔注射LPS诱导大鼠海马神经元损伤,部分胞体有凋亡和坏死改变,核深染且结构不清,有核固缩、碎裂和溶解现象。腹腔注射LPS可诱导大鼠的学习记忆减退大脑皮质及海马神经元受损,与报道一致[20]。FA 50和100 mg·kg-1保护组SD大鼠海马神经元的损伤情况较LPS模型组明显减轻。提示FA在防治中枢神经系统疾病方面具有潜力。
据报道,LPS能够特异性诱导PDE4B及相关炎性因子的表达升高,从而进一步导致记忆和学习能力的下降[16-18]。本研究也发现,FA对LPS诱导的PDE4B表达上调及其下游信号分子CREB和p-CREB下调的对抗作用。很多研究结果表明,PDE4B广泛分布于在哺乳动物脑部的杏仁核、纹状体以及下丘脑,这也提示PDE4B可能作为抗抑郁及抗阿尔茨海默病等神经系统疾病的潜在治疗靶点[19]。CREB作为一种重要的核转录因子,其功能包括调节基因的转录、细胞的发育、成瘾性、抑郁以及学习记忆等[20]。胞外信号通路通过影响CREB的磷酸化激活有关的靶基因转录。CREB在细胞内被相应的激酶磷酸化以后,调节下游基因的表达,表现出相应的功能。CREB的磷酸化受多条信号通路的影响,如cAMP信号通路、Ca2+/钙调蛋白激酶信号通路和Ras/细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路等[21-22]。本研究发现,FA能降低LPS所引起SD大鼠海马神经元PDE4B表达的升高。LPS对PDE4B/cAMP/CREB信号通路的作用机制主要在于cAMP通过激活蛋白激酶A对LPS诱导的信号具有抑制作用。为了克服这种限制,LPS信号需要激活PDE4B基因的转录并积累PDE4B蛋白,在敲除PDE4B基因小鼠模型中不能去除cAMP的限制作用,也就不能对LPS的刺激产生正常的应答[23]。
FA作为一种天然酚酸,本身具有强烈的抗氧化及抗炎作用,并且能够通过血脑屏障[5,24]。本研究结果表明,FA具有抑制LPS诱导PC12细胞损伤的作用;对LPS引起的大鼠海马神经元病理改变发挥保护作用,其机制可能与其对LPS诱导的PDE4B表达上调及其下游信号分子CREB和p-CREB下调的对抗作用密切相关。FA对神经细胞的保护作用是否涉及到其他机制还有待继续研究。
[1]Dong GC,Kuan CY,Subramaniam S,Zhao JY,Sivasubramaniam S,Chang HY,et al.A potent inhibition of oxidative stress induced gene expression in neural cells by sustained ferulic acid release from chitosan based hydrogel[J].Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl,2015,49:691-699.
[2]Sgarbossa A,Giacomazza D,Di Carlo M.Ferulic acid:a hope for alzheimer′s disease therapy from plants[J].Nutrients,2015,7(7):5764-5782.
[3]Barone E,Calabrese V,Mancuso C.Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for agerelated diseases[J].Biogerontology,2009,10(2):97-108.
[4]Cao YJ,Zhang YM,Qi JP,Liu R,Zhang H,He LC. Ferulic acid inhibits H2O2-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via inhibition of the NADPH oxidase and NF-kappa B pathway[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2015,28(2):1018-1025.
[5]Lin TY,Lu CW,Huang SK,Wang SJ.Ferulic acid suppresses glutamate release through inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium entry in rat cerebrocortical nerveterminals[J].JMedFood,2013,16(2):112-119.
[6]Yan JJ,Jung JS,Kim TK,Hasan A,Hong CW,Nam JS,et al.Protective effects of ferulic acid in amyloid precursor protein plus presenilin-1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease[J].Biol PharmBull,2013,36(1):140-143.
[7]Bramanti E,Fulgentini L,Bizzarri RA,Sgarbossa A. β-Amyloid amorphous aggregates induced by the small natural molecule ferulic acid[J].J Phys Chem B,2013,117(44):13816-13821.
[8]Subash S,Essa MM,Braidy N,Awlad-Thani K,Vaishnav R,Al-Adawi R,et al.Diet rich in date palm fruits improves memory,learning and reduces betaamyloidintransgenicmousemodelof Alzheimer′s disease[J].J Ayurveda Integr Med,2015,6(2):111-120.
[9]Nabavi SF,Devi KP,Malar DS,Sureda A,Daglia M,Nabavi SM.Ferulic acid and Alzheimer′s disease:promises and pitfalls[J].Mini Rev Med Chem,2015,15(9):776-788.
[10]Di Domenico F,Perluigi M,Foppoli C,Blarzino C,Coccia R,De Marco F,et al.Protective effect of ferulic acid ethyl ester against oxidative stress mediated by UVB irradiation in human epidermal melanocytes[J].Free Radic Res,2009,43(4):365-375.
[11]Yabe T,Hirahara H,Harada N,Ito N,Nagai T,SanagiT,etal.Ferulicacidinducesneural progenitor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo[J]. Neuroscience,2010,165(2):515-524.
[12]Sultana R, Ravagna A, Mohmmad-Abdul H,Calabrese V,Butterfield DA.Ferulic acid ethyl ester protects neurons against amyloid beta-peptide(1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity:relationship to antioxidant activity[J].J Neurochem,2005,92(4):749-758.
[13]Villanueva J,Torregrosa-Hetland CJ,García-Martínez V,del Mar Francés M,Viniegra S,Gutiérrez LM.The F-actin cortex in chromaffin granule dynamics and fusion:a minireview[J].J Mol Neurosci,2012,48 (2):323-327.
[14]Lee B,Sur B,Park J,Kim SH,Kwon S,Yeom M,et al.Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates lipopolysaccha⁃ride-induced learning and memory impairments by anti-inflammatory activity in rats[J].Biomol Ther (Seoul),2013,21(5):381-390.
[15]Lee JW,Lee YK,Yuk DY,Choi DY,Ban SB,Oh KW,et al.Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharidecausescognitiveimpairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid generation [J].J Neuroinflammation,2008,5:37.
[16]Min SS,Quan HY,Ma JH,Han J,Seol GH. Chronic brain inflammation impairs two forms of long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampal CA1 area[J].Neurosci Lett,2009,456(1):20-24.
[17]Johansson EM,Sanabra C,Cortés R,Vilaró MT,Mengod G.Lipopolysaccharide administration in vivo induces differential expression of cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase 4B mRNA splice variants in the mouse brain[J].J Neurosci Res,2011,89(11):1761-1772.
[18]Reyes-IrisarriE, Perez-TorresS, MiroXA,Puigdomenech P,Palacios JM,Mengod G.Differen⁃tial distribution of PDE4B splice variant mRNAs in rat brain and the effects of systemic administration of LPS in their expression[J].Synapse,2008,62 (1):74-79.
[19]JohanssonEM,Reyes-IrisarriE,Mengod G. Comparison of cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase mRNAs distribution in mouse and rat brain[J]. Neurosci Lett,2012,525(1):1-6.
[20]Giampà C, Middei S, Patassini S,Borreca A,Marullo F,Laurenti D,et al.Phosphodiesterase type IV inhibition prevents sequestration of CREB binding protein,protects striatal parvalbumin inter⁃neurons and rescues motor deficits in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington′s disease[J].Eur J Neurosci,2009,29(5):902-910.
[21]Xi YD,Zhang DD,Ding J,Yu HL,Yuan LH,Ma WW,et al.Genistein inhibits Aβ25-35-inducedsynaptictoxicity and regulates CaMKⅡ/CREBpathway in SH-SY5Y cells[J/OL].Cell Mol Neurobiol,(2015-12-11)[2016-01-29].http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007% 2Fs10571-015-0311-6
[22]Lee WR,Shen SC,Wu PR,Chou CL,Shih YH,Yeh CM,et al.CSE1L Links cAMP/PKA and Ras/ ERK pathways and regulates the expressions and phosphorylations of ERK1/2,CREB,and MITF inmelanoma cells[J/OL].MolCarcinog,(2015-09-01)[2016-01-29].http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/ doi/10.1002/mc.22407/full
[23]Guo J,Lin P,Zhao X,Zhang J,Wei X,Wang Q,et al.Etazolate abrogates the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced downregulation of the cAMP/pCREB/ BDNF signaling,neuroinflammatory response and depressive-like behavior in mice[J].Neuroscience,2014,263:1-14.
[24]Anselmi C,Centini M,Andreassi M,Buonocore A,La Rosa C,Facino RM,et al.Conformational analysis:a tool for the elucidation of the antioxidant properties of ferulic acid derivatives in membrane models[J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2004,35(5):1241-1249.
Corresponding auther:GAO Yue,E-mail:gaoyue@bmi.ac.cn
(本文编辑:齐春会)
Protective effect of furelic acid on lipopolysaccharide induced damage in PC12 cells and hippocampal neurons of rats
HUANG Hao1,2,MA Zeng-chun2,WANG Yu-guang2,GAO Yue2
(1.College of Life Science and Bioengineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China;2.Institute of Radiation Medicine,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Beijing 100850,China)
OBJCTlVE To investigate the protective effect of ferulic acid(FA)on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced damage to PC12 cells and hippocampal neurons in Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats and its potential mechanisms.METHODS① in vitro study:PC12 cells were pretreated with FA 2.5-40 μmol·L-1for 12 h and treated with LPS for another 8 h.CCK-8 kit was used to test PC12 cell viability.Inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α)and interleukin-1β(IL-1β)were de⁃tected by ELISA kits.Laser scanning confocal microscopy was performed to measure F-actin expres⁃sion in the cells.②in vivo study:FA 25,50 and 100 mg·kg-1was ip given to Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats once a day for 35 d,and from the 29th day,ip co-administered with LPS(0.2 mg·kg-1)for 7 d. Immunohistochemistry method was used to determine protein expression of phophodiestera 4B (PDE4B)in the hippocampus of rats.The protein expression of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)and phospho CREB(p-CREB)was determined by Western blotting.RESULTS In the in vitro study,compared with LPS group,cell viability was significantly increased in FA 10,20 and 40 μmol·L-1groups(P<0.05),while the production of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β decreased(P<0.05). The structure and distribution of cytoskeletal protein F-actin were ameliorated markedly in PC12 cells.In the in vivo study,hematoxylin-eosin(HE)staining showed that pretreatment with FA(50 and 100 mg·kg-1)alleviated the damage to the hippocampus induced by LPS in SD rats.Immunohistochemistry showed that FA(50 and 100 mg·kg-1)pretreatment effectively prevented LPS-induced up-regulation of PDE4B expression in the hippocampus of rats(P<0.05).Western blotting analysis showed that the inhibitory effects on the protein expressions of CREB and p-CREB induced by LPS were altered by FA(50 and 100 mg·kg-1)pretreatment(P<0.05).CONCLUSlON FA can protect against LPS induced damage to PC12 cells and hippocampal neurons of rats.The resistant effect on neuron-inflammation of FA may be conferred by inhibiting LPS-induced up-regulation of PDE4B and stimulating signaling pathways of cAMP/CREB.
ferulic acid;phospholiesteras 4B;lipopolysaccharides;cAMP response element binding protein
The project supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(81130067);and National Natural Science Foundation of China(81202936)
R967
A
1000-3002-(2016)04-0330-08
国家自然科学基金(81130067);国家自然科学基金(81202936)
黄 浩,男,博士研究生,主要从事中药药理学研究,Tel:(010)66931225,E-mail:happyhh758@163.com;高 月,博士,研究员,博士生导师,主要从事中药药理学研究;马增春,副研究员,主要从事新药发现与中药药理研究。
通迅作者:高 月,E-mail:gaoyue@bmi.ac.cn
2016-01-29接受日期:2016-04-10)

