CIDE B/C基因多态性与高三酰甘油血症相关性研究*
刘 莉,平智广,詹芳芳,戚敏杰,黄 忻
(郑州大学:1.基础医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室; 2.公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学教研室,郑州 450001)
CIDE B/C基因多态性与高三酰甘油血症相关性研究*
刘莉1,平智广2△,詹芳芳2,戚敏杰2,黄忻1
(郑州大学:1.基础医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室; 2.公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学教研室,郑州 450001)
[摘要]目的通过分析CIDE B/C基因多态性的人群分布特征,探明CIDE B/C基因多态性与中国河南汉族人群血三酰甘油(TG)水平的关系。方法选取528例无亲缘关系研究对象,男198例,女330例,平均年龄(52.23 ±13.41)岁,以1.70 mmol/L为TG界值,将研究对象分为高三酰甘油血症(HTG)组(181例)和正常三酰甘油组(NTG组,347例)。检测CIDE B/C基因的7个SNP,采用SHEsis进行基因单倍型研究,分析两种基因的单倍型与TG的关系。结果分析显示rs2144492、rs2281472、rs2144493位点与TG有关,其中rs2144492的A等位基因、rs2281472和rs2144493的C等位基因具有保护作用,携带上述等位基因的个体TG水平相对较低。CIDE B基因的ATCC单倍型在NTG组比例较高,具有保护作用,OR及其95%CI为0.698 (0.490~0.992)。结论CIDE B/C基因多态性及CIDE B基因的ATCC单倍型对HTG的发生风险存在一定作用。
[关键词]甘油三酯类;CIDE;基因多态性;单倍型
慢性代谢性疾病已成为影响生命质量和增加各国财政负担的全球性重要公共卫生问题[1]。高三酰甘油血症(hypertriglyceridemia,HTG)作为患病率很高的代谢异常,已成为冠心病、高血压、2型糖尿病、非酒精性肝病等的主要危险因素之一[2]。大量研究证实,遗传因素在HTG的发生、发展中确实起着重要作用[3-5],虽有单位点突变导致的少数病例,但大多数研究显示HTG是由多个基因共同作用的结果。
CIDE (cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor 45-like effector)家族包括CIDE A、CIDE B和CIDE C[小鼠中CIDE C被称为脂肪特异性蛋白27 (fat special protein 27,FSP27)][6]主要分布于棕色脂肪组织(brown adipose tissue,BAT),肝脏和白色脂肪组织(white adipose tissue,WAT)[7]。该家族最初被认为与哺乳动物的细胞凋亡有关[6,8]。近来研究发现CIDE蛋白在脂质贮存、脂滴形成、脂质分解等脂质代谢过程中发挥重要作用,并与肥胖、糖尿病、脂肪肝等疾病的发生、发展有关[9-11]。然而,迄今为止,关于CIDE家族与血三酰甘油(triglyceride,TG)的研究主要集中在动物实验和细胞水平,而人群中CIDE基因多态性与TG的关系仍未被揭示。
由于HTG是多基因遗传的复杂性疾病,发病往往为多个微效基因共同作用所致,而且单倍型致病研究是探索基因多态性与疾病关系的一个重要途径[12]。因此,本研究将对人群CIDE B和CIDE C基因的7个多态性位点及单倍型与TG水平的关系进行了分析。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料通过现场横断面调查获得528例无亲缘关系汉族个体,其中男198例,女330例,平均年龄(52.23±13.41)岁。根据TG水平将研究对象分为HTG组(TG≥1.70 mmol/L)和正常TG组(NTG组,TG<1.70 mmol/L)[13]。HTG组181例,男62例,女119例,平均年龄(53.41±11.22)岁;NTG组347例,男136例,女211例,平均年龄(51.62±14.39)岁。两组间性别、年龄比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2方法
1.2.1单核苷酸多态性(SNP)检测所有调查对象抽取肘静脉血2 mL,血清用于测量TG水平,白细胞用于提取DNA并检测SNP。
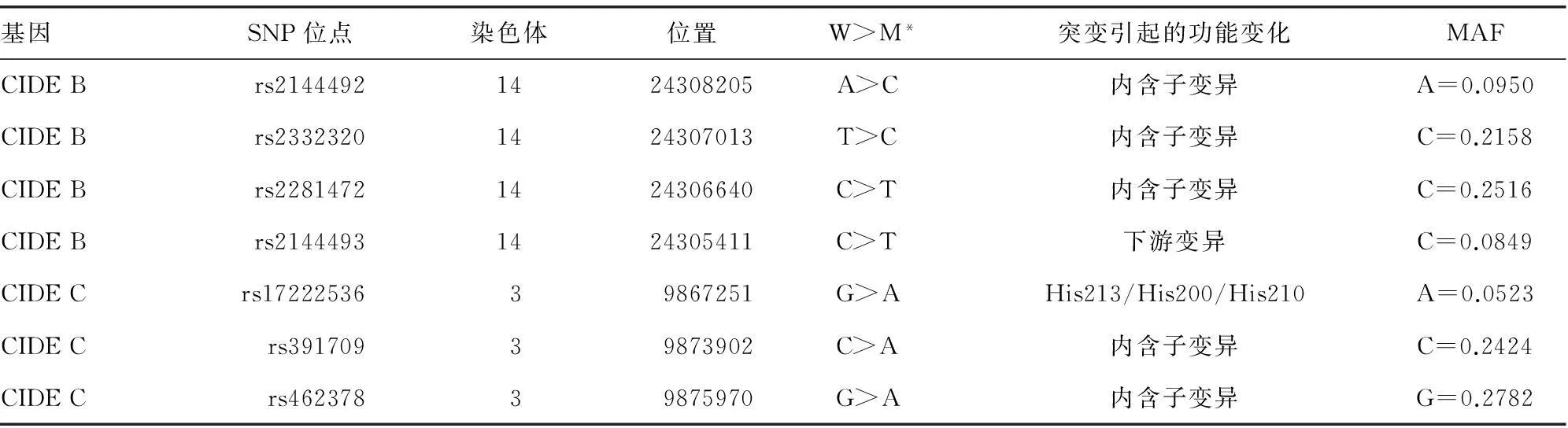
表1 CIDE B和CIDE C基因7个SNP位点信息
*W:野生型等位基因;M:突变型等位基因。

表2 CIDE B和CIDE C基因7个SNP位点引物信息
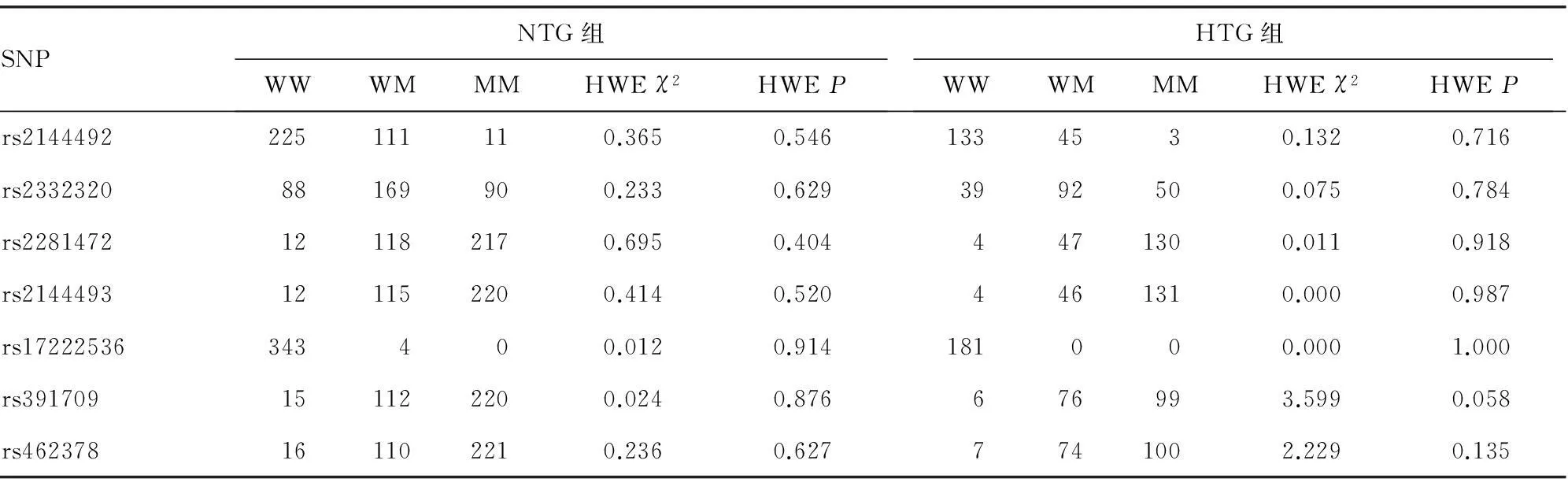
表3 两组CIDE B和CIDE C基因SNP位点等位基因、基因型分布
1.2.2SNP的选择在CIDE B和CIDE C基因上分别选择了4个和3个SNP,筛选依据为满足下列条件之一:(1)已报道与TG或代谢异常有关;(2)具有杂合性且最小等位基因频率(minor allele frequency,MAF)>0.05;(3) 所在基因片段能够引起功能性改变。所选SNP位点的详细信息见表1。
1.2.3基因分型采用Promega公司的基因组DNA提取试剂盒按说明书操作提取DNA,并采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA质量。采用snapshot或连接酶技术(ligase detection reaction,LDR)进行SNP分型。引物信息见表2。

2结果
2.1两组SNP分布特征CIDE B和CIDE C基因分型在NTG组和HTG组的分布见表3。各位点均满足哈温平衡(Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,HWE),差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。

表4 SNP单位点与TG水平的Logistic回归结果
2.2SNPs单位点与TG水平的关系采用Logistic回归按加性遗传模式对各位点与高TG的关系进行分析,结果见表4。rs2144492、rs2281472、rs2144493位点与TG水平的关系差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),其中rs2144492的A等位基因、rs2281472和rs2144493的C等位基因具有保护作用,携带上述等位基因的个体TG水平相对较低。rs17222536位点因A等位基因频率较低,估计误差较大,故其OR值及其95%CI未列出。
2.3单倍型与TG的关系采用SHEsis在线软件分别估算CIDE B、CIDE C基因SNP的连锁不平衡系数(表5、6),根据D′和r2可知CIDE B、CIDE C基因的SNPs位点存在连锁不平衡,进而估计各基因的单倍型及其频率,计算相应的频数,整理结果见表7。CID E/B基因常见单倍型为CCTT(50.38%)、CTTT(30.78%)和ATCC(17.23%),CIDE C基因常见单倍型为GAA(77.94%)和GCG(21.12%)。结果显示,CIDE B基因的ATCC单倍型在组间存在差异,其在HTG组的比例较低,具有保护作用,OR及95%CI为0.698(0.490~0.992)。

表5 CIDE B 各SNP的连锁不平衡参数
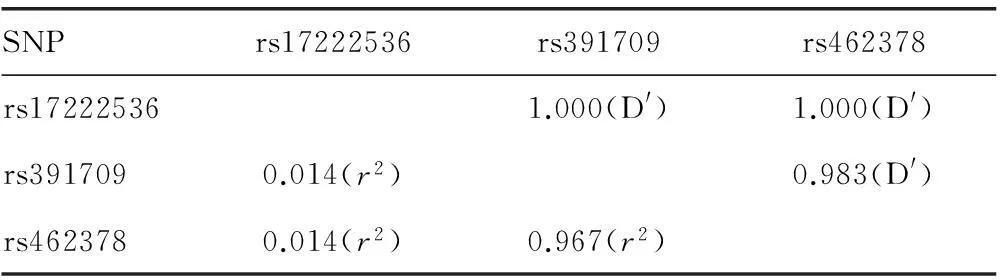
表6 CIDE C 各SNP的连锁不平衡参数
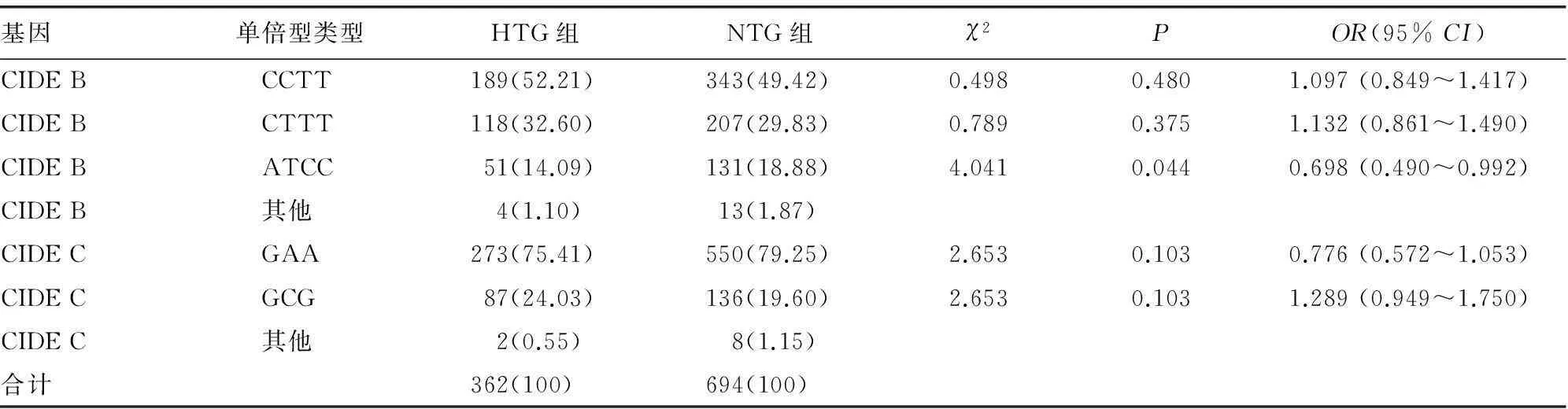
表7 CIDEB、CIDEC单倍型组间分布频率[n(%)]
3讨论
本研究检测了CIDE B/C基因的多态性,并分析了基因多态性、单倍型与TG水平的关系。研究发现,rs2144492、rs2281472、rs2144493位点与TG水平具有统计学关联,其中rs2144492的A等位基因、rs2281472和rs2144493的C等位基因具有保护作用,那么,rs2144492的G等位基因、rs2281472和rs2144493的T等位基因则是危险等位基因。此前虽未见有关多态性与HTG风险之间的相关报道,但本研究的结果依然得到了有关CIDE B/C的功能研究的支持。
CIDE家族包括3种蛋白:CIDE A、CIDE B和CIDE C(或称Fsp27),其在哺乳动物中,分别主要表达于棕色脂肪、肝脏和白色脂肪[15]。考虑到成人体内棕色脂肪较少,因此本研究重点研究了CIDE B和CIDE C基因。近年研究表明,CIDE蛋白与脂质代谢调节密切相关[16]。CIDE家族所有成员都在脂滴的聚集、融合中发挥重要作用[17-20]。研究表明CIDE B在能量储存和消耗中发挥重要作用,CIDE B缺失小鼠表现出能耗升高,血浆TG水平降低,胰岛素敏感性和血游离脂肪酸增加[21]。其原因是VLDL包裹TG是在CIDE B的介导下完成的,CIDE B可调控TG和胆固醇水平[22]。CIDE C属脂滴相关蛋白,可抑制脂肪分解,从而导致TG在脂肪细胞中的积累[23]。即使在非脂肪细胞中,CIDE C依然可以在诱导小脂滴融合为大脂滴的过程中发挥至关重要的作用,其分泌不足可导致小鼠脂滴分散、脂肪分解率升高[24]。而纯合子无义突变可致人体部分性脂肪代谢障碍,以及含多个小脂滴的脂肪细胞的出现[25]。这些结果均表明,CIDE C在脂质代谢、能量贮存及血TG水平调节中发挥重要作用。遗憾的是,之前的研究多为动物实验或细胞水平的研究,尚少见CIDE B/C人群基因多态性与血TG水平之间关系的研究。因此,本研究的结果将为明确CIDE B、CIDE C基因与TG水平的关系并将相应的遗传因素作为防治脂质代谢紊乱疾病的分子靶点提供理论依据。
虽然目前少见这7个多态性位点与HTG关系的研究供对比。但已有报道:PGC-1、PPAR和PLIN等重要的脂滴相关蛋白,其基因多态性均与HTG相关,而与细胞内脂质代谢关系密切的CIDE B/C,其与PGC-1、PPAR和PLIN等蛋白极其密切的关系亦渐渐被揭示,这些研究间接支持了本研究结果。PGC-1在将细胞质中的TG装配入VLDL分泌小室并促进VLDL分泌中起着重要的作用,而该功能是通过诱导CIDE B行使的[26]。Kim等[23]研究发现在调节脂肪细胞中脂质代谢及脂质贮存方面举足轻重的PPARγ2是通过诱导CIDE C而发挥作用的。FSP27与PLIN在调节脂肪细胞中脂滴的大小方面发挥协同作用[27]。目前,已有多项研究表明PGC-1[28]、PPAR[2]、PLIN[29]等的基因多态性与脂代谢有关。本研究亦证实与PGC-1、PPAR、PLIN关系密切的CIDE B/C基因多态性也与TG相关。
综上所述,本研究通过检测中国河南汉族人群CIDE B/C多态性并通过单位点和单倍型分析证实了CIDE B/C多态性与TG水平有关。另外,CIDE B/C与其他脂代谢相关基因的交互作用也值得进一步研究。
参考文献
[1]Shah A,Rader DJ,Millar JS.The effect of PPAR-alpha agonism on apolipoprotein metabolism in humans[J].Atherosclerosis,2010,210(1):35-40.
[2]Gu SJ,Liu MM,Guo ZR,et al.Gene-gene interactions among PPARα/δ/γ polymorphisms for hypertriglyceridemia in Chinese Han population[J].Gene,2013,515(2):272-276.
[3]Aguilar-Salinas CA,Tusie-Luna T,Pajukanta P.genetic and environmental determinants of the susceptibility of amerindian derived populations for having hypertriglyceridemia[J].Metabolism,2014,63(7):887-894.
[4]Rosenthal EA,Ranchalis J,Crosslin DR,et al.Joint linkage and association analysis with exome sequence data implicates SLC25A40 in hypertriglyceridemia[J].Am J Hum Genet,2013,93(6):1035-1045.
[5]Behar DM,Adler L,Basel-Vanagaite L.Severe hypertriglyceridemia in an infant of Arab descent[J].Isr Med Assoc J,2013,15(1):53-54.
[6]Ito M,Nagasawa M,Omae N,et al.Differential regulation of CIDEA and CIDEC expression by insulin via Akt1/2- and JNK2-dependent pathways in human adipocytes[J].J Lipid Res,2011,52(8):1450-1460.
[7]Gong J,Sun Z,Li P.CIDE proteins and metabolic disorders[J].Curr Opin Lipidol,2009,20(2):121-126.
[8]Liang L,Zhao M,Xu Z,et al.Molecular cloning and characterization of CIDE-3,a novel member of the cell-death-inducing DNA-fragmentation-factor (DFF45)-like effector family[J].Biochem J,2003,370(Pt 1):195-203.
[9]Li JZ,Ye J,Xue B,et al.Cideb regulates diet-induced obesity,liver steatosis,and insulin sensitivity by controlling lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation[J].Diabetes,2007,56(10):2523-2532.
[10]Kim JY,Liu K,Zhou S,et al.Assessment of fat-specific protein 27 in the adipocyte lineage suggests a dual role for FSP27 in adipocyte metabolism and cell death[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2008,294(4):E654-667.
[11]Li YH,Lei T,Chen XD,et al.Molecular cloning,chromosomal location and expression pattern of porcine CIDEa and CIDEc[J].Mol Biol Rep,2009,36(3):575-582.
[12]Crawford DC,Nickerson DA.Definition and clinical importance of haplotypes[J].Annu Rev Med,2005,56:303-320.
[13]中国成人血脂异常防治指南制订联合委员会.中国成人血脂异常防治指南[J].中华心血管病杂志,2007,35(5):390-419.
[14]Li ZQ,Zhang Z,He ZD,et al.A partition-ligation-combination-subdivision EM algorithm for haplotype inference with multiallelic markers:update of the SHEsis [J].Cell Res,2009,19(4):519-523.
[15]Wu C,Zhang Y,Sun Z,et al.Molecular evolution of Cide family proteins:novel domain formation in early vertebrates and the subsequent divergence[J].BMC Evol Biol,2008,8:159.
[16]Barneda D,Frontini A,Cinti S,et al.Dynamic changes in lipid droplet-associated proteins in the “browning” of white adipose tissues[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1831(5):924-933.
[17]Xu L,Zhou L,Li P.CIDE proteins and lipid metabolism[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2012,32(5):1094-1098.
[18]Christianson JL,Boutet E,Puri V,et al.Identification of the lipid droplet targeting domain of the Cidea protein[J].J Lipid Res,2010,51(12):3455-3462.
[19]Singaravelu R,Lyn RK,Srinivasan P,et al.Human serum activates CIDEB-mediated lipid droplet enlargement in hepatoma cells[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2013,441(2):447-452.
[20]Gong J,Sun Z,Wu L,et al.Fsp27 promotes lipid droplet growth by lipid exchange and transfer at lipid droplet contact sites[J].J Cell Biol,2011,195(6):953-963.
[21]Li JZ,Lei Y,Wang Y,et al.Control of cholesterol biosynthesis,uptake and storage in hepatocytes by Cideb[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2010,1801(5):577-586.
[22]Zhang LJ,Wang C,Yuan Y,et al.Cideb facilitates the lipidation of chylomicrons in the small intestine[J].J Lipid Res,2014,55(7):1279-1287.
[23]Kim YJ,Cho SY,Yun CH,et al.Transcriptional activation of Cidec by PPARgamma2 in adipocyte[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2008,377(1):297-302.
[24]Jambunathan S,Yin J,Khan W,et al.FSP27 promotes lipid droplet clustering and then fusion to regulate triglyceride accumulation[J].PLoS One,2011,6(12):e28614.
[25]Rubio-Cabezas O,Puri V,Murano I,et al.Partial lipodystrophy and insulin resistant diabetes in a patient with a homozygous nonsense mutation in CIDEC[J].EMBO Mol Med,2009,1(5):280-287.
[26]Chen Z,Norris JY,Finck BN.Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) stimulates VLDL assembly through activation of cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector B (CideB)[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(34):25996-26004.
[27]Grahn TH,Zhang Y,Lee MJ,et al.FSP27 and PLIN1 interaction promotes the formation of large lipid droplets in human adipocytes[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2013,432(2):296-301.
[28]Ambye L,Rasmussen S,Fenger M,et al.Studies of the Gly482Ser polymorphism of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) gene in Danish subjects with the metabolic syndrome[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2005,67(2):175-179.
[29]王姣锋.PLIN 14995(A/T)多态性与肥胖、血脂、血糖及血压水平的关系[D].郑州:郑州大学,2007.
doi:论著·临床研究10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.15.010
*基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(81001280,81202277);河南省科技攻关项目(112102310198)。
作者简介:刘莉(1977-),副教授,硕士,主要从事慢性非传染性疾病分子学发病机制研究。△通讯作者,E-mail:ping_zhg@163.com。
[中图分类号]R589.2
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1671-8348(2016)15-2061-04
(收稿日期:2015-11-18修回日期:2016-01-07)
The relation between gene polymorphisms of CIDE B/C and hypertriglyceridemia*
Liu Li1,Ping Zhiguang2△,Zhan Fangfang2,Qi Minjie2,Huang Xin1
( 1.TeachingandResearchSectionofHistologyandEmbryology,BasicMedicalCollege;2.TeachingandResearchSectionofEpidemiologyandHealthStatistics,CollegeofPublicHealth,ZhengzhouUniversity,Zhengzhou,Henan450001,China)
[Abstract]ObjectiveTo determine the possible effect of CIDEB/C gene polymorphism and haplotypes on hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) in Han group.Methods528 unrelated subjects were selected (198 males,330 females) with the mean age of 52.23±13.41 years old.According to the criteria of triglyceride (TG) ≥1.70 mmol/L(150 mg/dl),181 persons were arranged into HTG (hypertriglyceridemia) group and 347 persons were in NTG(normal triglyceride) group.A total of 7 SNPs in CIDEB and CIDEC genes were detected.The relationship between these ten SNPs and TG were analyzed under additive inheritance pattern by logistic regression.SHEsis online were used to get the haplotypes and their effects on TG.Resultsrs2144492,rs2281472 and rs2144493 were associated with TG.The frequency of ATCC,haplotype of CIDEB,was higher in NTG group.OR and its 95% confidence interval was 0.698[0.490~0.992].ConclusionATCC of CIDE B/C gene polymorphism may be related to the occurrence of HTG.
[Key words]triglycerides;CIDE;gene polymorphism;haplotype

