蔓荆子总黄酮抑制肝细胞癌球形成与激活AMPK抑制AKT相关
李 辉,陈 碧,邹 辉,舒 玲,曹建国,张坚松
(1.郴州市第一人民医院药学部,郴州423000;2.湖南师范大学医学院,长沙 410013)
蔓荆子总黄酮抑制肝细胞癌球形成与激活AMPK抑制AKT相关
李辉*1,陈碧*1,邹辉2,舒玲2,曹建国2,张坚松2
(1.郴州市第一人民医院药学部,郴州423000;2.湖南师范大学医学院,长沙410013)
【摘要】目的:研究蔓荆子总黄酮(FVTF)抑制人肝细胞癌自我更新作用及其机制是否涉及AMPK/Akt信号传导。方法:肿瘤球形成法测定FVTF对肝细胞癌SMMC-7721和MHCC97H细胞系球形成率的影响。Westernblot分析FVTF处理SMMC-7721细胞AMPK和Akt磷酸化水平。结果:FVTF显著降低SMMC-7721和MHCC97H细胞系球形成率,呈浓度依赖性。不同浓度FVTF(1.0、2.0、4.0μg/mL)处理SMMC-7721细胞24h,AMPK磷酸化水平增高;Akt磷酸化水平下降。结论:FVTF抑制肝细胞癌自我更新作用与其激活AMPK抑制Akt活性相关。
【关键词】蔓荆子总黄酮;肝细胞癌;自我更新;AMPK;Akt
1997年Bonnet等首次从急性髓系白血病患者骨髓中分离并证实肿瘤干细胞(cancerstemcells,CSCs)的存在以来,越来越多的证据表明肿瘤中存在一小群具有干细胞特征的细胞,表现出自我更新、多向分化和高致瘤性的特性,是维持肿瘤发生、生长和肿瘤转移、复发的根源[1,2]。蔓荆子为马鞭草科植物单叶蔓荆VitextrifoliaL.v.ar1simplicifoliaCham.或蔓荆Vitextrifolia L.的干燥成熟果实,是载入中国药典的一种传统中药,具有消热解表、利湿解毒、止咳祛痰、缓解支气管痉挛等症状的作用[3]。蔓荆子总黄酮(FructusViticisTotal Flavonoids,FVTF)是自主创制的一种具有靶向抑制肿瘤干细胞作用的蔓荆子有效部位(国家发明专利号:ZL201210591146.9)。本文的研究目的是检测FVTF抑制人肝细胞癌自我更新作用并探讨其机制是否涉及AMPK/Akt信号传导。
1 资料与方法
1.1试剂和细胞系蔓荆子总黄酮(FVTF)根据专利说明书(国家发明专利号:ZL201210591146.9)从蔓荆子中提取和制备。FVTF的性状为棕褐色粉末。FVTF按干燥品计算,总黄酮量以芦丁计等于53%。高糖DMEM培养基、DMEM/F12培养基、胎牛血清、0.25%胰蛋白酶(含EDTA)和磷酸缓冲液(PBS)购自美国Hyclone公司。抗AMPK、p-AMPK、Akt和p-Akt抗体均系美国Cell signaling公司产品。抗β-actin抗体来自美国Sigma Aldrich公司。人肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞系和MHCC97H细胞系分别购自中国科学院细胞库(中国上海市)和上海复祥生物科技有限公司(中国上海市)。细胞在含10%胎牛血清、100IU/mL青霉素G和100μg/mL链霉素的高葡萄糖DMEM细胞培养基中,置37°C、饱和湿度的5% CO2培养箱中单层贴壁生长。
1.2球形成率测定按照先前文献[4,5]描述的方法测定不同浓度FVTF(1.0、2.0、4.0μg/mL)处理48h的球形成率。
1.3Westernblot按照先前发表文献[5]的方法进行westernblot分析。
1.4统计学分析各组实验数据录入Spss15.0for windowsevaluation软件建立数据库,数据用均数±标准差(Mean±SD)表示。采用OneWayANOVA方差分析;首先进行方差齐性检验,在方差齐性时,多组均数比较采用LSD法;在方差不齐时,多组均数间比较采用Tukey's检验。P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1FVTF对肝细胞癌细胞自我更新能力的影响球形成率测定结果显示,FVTF以浓度依赖方式降低人肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞(图1A)和MHCC97H细胞(图1B)的肿瘤球形成率(P<0.05)。
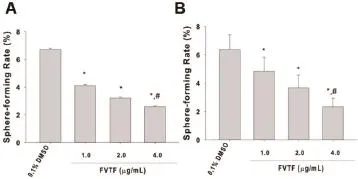
图1 FVTF抑制肝细胞癌肿瘤球形成(Mean±SD,n=3)A:肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞;B:肝细胞癌MHCC97H细胞。与溶媒对照组比较,*P<0.05;与1.0 μg/mL FVTF处理组比较,#P<0.05。
2.2FVTF对肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞AMPK磷酸化的影响免疫印迹分析结果发现,FVTF增高人肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞AMPK蛋白磷酸化水平。
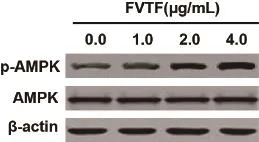
图2 FVTF增高SMMC-7721细胞AMPK蛋白磷酸化水平
2.3FVTF对肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞Akt蛋白磷酸化水平的影响免疫印迹分析结果证明,FVTF降低人肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞Akt蛋白磷酸化水平。

图3 FVTF降低SMMC-7721细胞Akt蛋白磷酸化水平
3 讨论
FVTF是我们创制的一种具有靶向抑制肿瘤干细胞作用的蔓荆子有效部位(国家发明专利号:ZL201210591146.9)。为了验证FVTF是否具有抑制人肝细胞癌干细胞样细胞特性作用,在本研究中,我们采用球形成率测定法检测不同浓度FVTF(1.0、2.0、4.0μg/ mL)对人肝细胞癌SMMC-7721和MHCC97H细胞系细胞肿瘤球形成的影响。结果证实:FVTF以浓度依赖方式降低上述两种细胞系球形成率。从而说明FVTF具有抑制体外培养肝细胞癌自我更新作用。
鉴于FVTF中的有效成分紫花牡荆素能通过促进多种肿瘤细胞活性氧生成诱导细胞凋亡[6-8],我们推测FVTF可能通过变动肝细胞癌干细胞特有的有氧糖酵解代谢性质发挥抑制肝细胞癌细胞自我更新作用。最近的研究表明,靶向肿瘤细胞代谢是一种可供选择的肿瘤治疗方法。AMPK是一个关键性的能量传感器,调控正常细胞和肿瘤细胞的新陈代谢[9,10]。据此,我们寻求检测FVTF是否通过激活AMPK抑制肝细胞癌细胞自我更新作用。本文的Westernblot分析结果发现,FVTF能有效增高AMPK蛋白磷酸化水平。这些结果建议FVTF抑制体外培养肝细胞癌肿瘤球形成至少部分是由于其增强AMPK活性所致。
有研究报道AMPK是调节二甲双胍抗肿瘤作用的关键分子,并认为AMPK介导抑制Akt起关键作用[11,12]。在本研究中,我们的实验结果还证实,不同浓度FVTF(1.0、2.0、4.0μg/mL)处理,在增高AMPK蛋白磷酸化水平的同时,伴随着Akt蛋白磷酸化水平的逐渐下降。这些结果首次表明AMPK/Akt信号传导级联在FVTF抑制肝细胞癌球形成中的作用。现在仍不明确AMPK/Akt信号传导级联是否仅在FVTF抗肝细胞癌或肝癌干细胞中起作用,要明确这一点需要进一步研究,并描述该信号级联在其他人肿瘤干样细胞和非干样细胞中是否起作用。
参考文献
[1] Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell[J]. Nat Med, 1997, 3(7): 730-737.
[2] Dick JE. Stem cell concepts renew cancer research[J]. Blood, 2008, 112(13): 4793-4807.
[3] 王雪莉, 曹晓诚, 盛习锋, 等. 紫花牡荆素对宫颈癌HeLa细胞系干细胞样细胞自我更新的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学学报: 医学版, 2013(3): 11-14.
[4] Quan MF, Xiao LH, Liu ZH, ET AL. 8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin inhibits properties of liver cancer stem cells via downregulation of β-catenin[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(43): 7680-7695.
[5] Ren KQ, Cao XZ, Liu ZH, ET AL. 8-bromo-5-hydroxy-7-methoxychrysin targeting for inhibition of the properties of liver cancer stem cells by modulation of Twist signaling[J]. Int J Oncol, 2013, 43(5): 1719-1729.
[6] Chen D, Cao J, Tian L, et al. Induction of apoptosis by casticin in cervical cancer cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial signaling pathways[J]. Oncol Rep, 2011, 26(5): 1287-1294.
[7] Zeng F, Tian L, Liu F, Cao J, et al. Induction of apoptosis by casticin in cervical cancer cells: reactive oxygen species-dependent sustained activation of Jun N-terminal kinase[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2012, 44(5): 442-449.
[8] He L, Yang X, Cao X, et al. Casticin induces growth suppression and cell cycle arrest through activation of FOXO3a in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncol Rep, 2013, 29(1): 103-108.
[9] Kim YH, Liang H, Liu X, et al. AMPKalpha modulation in cancer progression: multilayer integrative analysis of the whole transcriptome in Asian gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 13(10): 2512-2521.
[10] Din FV, Valanciute A, Houde VP, et al. Aspirin inhibits mTOR signaling, activates AMP-activated protein kinase, and induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Gastroenterology. 2012, 13(7): 1504-1515.
[11] Aljada A, Mousa SA. Metformin and neoplasia: Implications and indications[J]. PharmacolTher. 2012, 133: 108-115.
[12] Sato A, Sunayama J, Okada M, et al. Glioma-initiating cell elimination by metformin activation of FOXO3 via AMPK[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2012, 1(11): 811-824.
【中图分类号】R734.2
【文献标识码】A
【文章编号】1673-016X(2016)03-0005-03
收稿日期:2016-01-10
基金项目:国家自然科学青年基金项目(No.30760248);湖南省科技厅社发领域科技重点研发计划(2015SK2066);郴州市科技局科学技术研究计划项目(No.cz2015007)
通讯作者:张坚松,E-mail:jwc_zjs@126.com
Inhibition of sphere-forming rate of hepatocellular carcinoma cellsby FructusViticis Total Flavonoids is associated with activation of AMPK and suppression of Akt
Li Hui1, Chen Bi1, Zou Hui2, Shu Ling2, Cao Jian-guo2, Zhang Jian-song2
(1. Department of pharmacy, The First People Hospital of Chenzhou, Changsha 432000, China;2. Medical College, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410013, China)
[Abstract]Objective To investigate FructusViticis Total Flavonoids(FVTF) inhibits self-renewal capability of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and the mechanism by which is involved in regulation of AMPK/Akt signaling. Methods Tumorsphere formation assay was used to determine the effects of FVTF on sphere forming rate of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 and MHCC97H cell lines. Western blot was emploied to analyze the phosphorylation levels of AMPK and Akt proteins of SMMC-7721 cells treated with FVTF. Results FVTF significantly lowered the sphere forming rates of SMMC-7721 and MHCC97H cell lines, in a concentration-dependent manner. Treatment with various concentrations of FVTF(1.0、2.0 、4.0 μg/mL) for 24 h, the phosphorylation level of AMPK was elevated and the phosphorylation level of Akt was reduced in SMMC-7721 cells. Conclusion FVTF inhibits self-renewal capability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells is associated with activation of AMPK and suppression of Akt.
[Key words]fructus viticis total flavonoids; hepatocellular carcinoma; self-renewal; AMPK; Akt

