自适应性统计迭代重建在颈动脉CTA中的应用研究
夏伟委 薛蕴菁 刘元芬 江少凡 段青
[摘要] 目的 探讨自适应统计迭代重建算法在颈动脉CTA的可行性,比较权重50% ASIR重建算法相对于常规滤波反投影重建算法对图像质量的影响。 方法 随机选取64例受检者在能谱CT上行颈动脉CTA检查。采用管电压120kVp,管电流480mA,320mgI/mL碘佛醇5mL/s团注。将所得原始数据传输至GE AW4.5工作站,行影像重建分析。每组原始数据运用两类重建方法重建,分别获得对应两组数据,A组采用常规FBP重建算法对原始数据重建分析;B组运用权重50% ASIR重建算法对原始数据进行影像重建分析。分别记录两组影像颈部血管各分支CT值,噪声值及背景CT值,计算和比较图像对比噪声比(CNR),信噪比(SNR),行统计学分析。 结果 B组血管噪声值(11.5±2.38)低于A组(16.70±2.98)(P<0.01);B组CNR(61.14±22.38)高于A组(38.19±11.57)(P<0.01);B组SNR(48.16±18.26)也高于A组(30.03±9.49)(P<0.01)。两组血管CT值和背景CT值均无统计学意义。 结论 颈动脉CTA结合权重50% ASIR重建算法不仅可以很好保证影像质量,还能有效降低影像噪声,提高影像信噪比和对比噪声比。
[关键词] 体层摄影术;X线计算机;颈动脉CTA;自适应性统计迭代重建;信噪比
[中图分类号] R816.1 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 2095-0616(2016)09-151-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore and discuss the feasibility of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction algorithm in the carotid artery CTA.To compare the image quality effectS between weight 50% ASIR reconstruction algorithm and conventional filter back projection reconstruction algorithm. Methods 64 patients were randomly selected for carotid artery CTA examination in the CT spectrum,which utilized 120kVp tube voltage,480mA tube current and 320mgI/mL ioversol in 5mL/s bolus injection.The original data were transferred to the GE AW4.5 workstation for image reconstruction analysis. The original data of each group utilized two reconstruction algorithms to obtain two sets of data correspondingly.The group A adopted routine FBP reconstruction algorithm for reconstruction analysis of the original data,while the group B utilized weight 50% ASIR reconstruction algorithm for image reconstruction analysis of the original data.The CT value of image neck vessels branches,noise value and background CT value of the two groups were recorded respectively,the image contrast noise ratio (CNR) and signal to noise ratio (SNR) were calculated and compared,which had statistical analysis. Results The vascular noise value of the group B was (11.5±2.38),which was lower than the (16.70±2.98) of the group A (P<0.01).The CNR of the group B was (61.14±22.38),which was higher than the (38.19±11.57) of the group A (P<0.01).The SNR of the group B was (48.16±18.26),which was also higher than the (30.03±9.49) of the group A (P<0.01).There were no statistical differences between two groups vascular CT value and background CT value. Conclusion The carotid artery CTA combined weight 50% ASIR reconstruction algorithm could not only ensure the image quality,but also effectively reduce the image noise and improve the image signal to noise ratio and contrast to noise ratio.
[Key words] Tomography;X-ray computer;Carotid artery CTA;Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction;Signal-to-noise ratio
随着物质水平的提高和精神压力的增加,心脑血管疾病已成为常见病,多发病,越来越为人类所关注[1-2]。CT技术迅猛发展,颈动脉CTA也以其强大优势获得广泛认可。为获得较好影像质量,颈动脉CTA往往需要较大的辐射剂量[3]。因此,在降低辐射剂量的同时,如何保证图像质量,这是放射医学工作者一直关注的问题[4-5]。常规降低辐射剂量的方法有降低管电流,管电压,这些处理方式往往伴随影像噪声的提高。较少有运用影像重建技术降低辐射剂量的报道。随着能谱CT的应用和普及,自适应性统计迭代重建算法(adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction,ASiR)逐渐被人们认识。通过同组原始数据运用两种不同影像学方法重建分析,进而探讨权重50%ASIR重建相对于常规FBP重建算法的优势是此次研究的目的。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2014年6月~2015年6月期间,在美国GE能谱CT(GE Discovery CT 750 HD)上行颈动脉CTA检查的受检者共64例。其中,男36例,女28例。所得原始数据分别采用两种不同重建方法进行重建分析:A组采用常规FBP重建算法对原始数据重建分析;B组采用权重50%ASIR重建算法对同一原始数据进行影像重建分析。
1.2 仪器与方法
采用能谱CT(GE Discovery CT 750 HD),常规检查前准备,所有受检者均被告知相关检查风险并签署知情同意书。患者取仰卧位,头稍后仰,下颌支与床台面垂直,两外耳孔与台面等距,矢状面与台面垂直。双手平行放置于身体两侧,固定患者头部并告知其制动重要性。扫描范围自主动脉弓下水平至颅内海绵窦水平。扫描参数;管电压120kVp,管电流480mA,旋转时间0.5S,螺距1.375:1,重建层厚及间隔0.625mm,采用Medrad双筒高压注射器,320mgI/mL碘伏醇(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司,15122346),生理盐水,对比剂团注流速5mL/s。
1.3 数据测量及分析
所得数据传输至AW4.5工作站,分别测量两组影像头臂干动脉,左颈总动脉,左锁骨下动脉,颈动脉近、中、远段及下颌部脂肪的CT值及噪声值,每组测量3次,取均值。记录每组背景CT值,背景噪声值,SNR,CNR。由2位高年资的医师对图像进行双盲法评分。采用5分法进行评分:5分,图像显示清晰,噪声小,能很好满足影像诊断要求;4分,图像显示较清楚,噪声尚可。完全满足影像诊断要求;3分,图像显示欠佳,噪声较大,可以满足影像诊断要求;2分,图像显示不清,噪声大,不能满足影像诊断要求;1分,图像显示不清,有较大伪影,噪声大,完全无法达到影像诊断要求。
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS19.0统计软件分析处理,采用t检验;采用Mann-Whitney U非参数检验;以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般资料
64例患者,其中男36例,占56.25%,女28例,平均(55.4±10.9)岁。见表1。
2.2 影像质量统计结果
采用权重50%ASIR重建算法的B组血管噪声值低于常规FBP重建的A组,差异具有统计学意义;在SNR、CNR上,B组均高于A组,差异具有统计学意义。两组影像主观评分差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
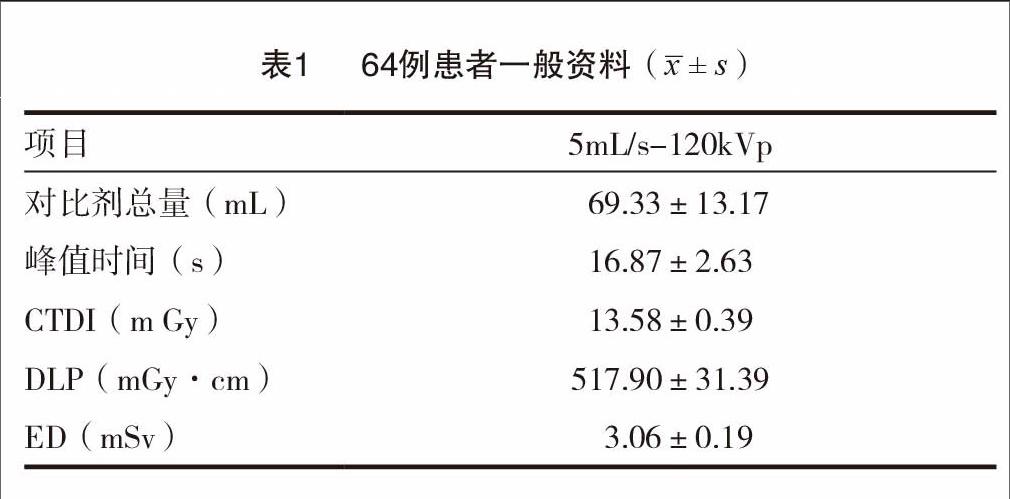
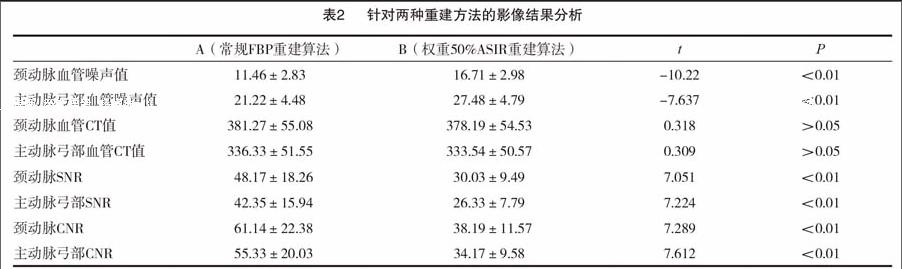
图1A~2D为同一受检者,女性,63岁,管电压120 kV,管电流480 mA。两组对应图像测量部位及测量范围采用统一标准。
3 讨论
随着医学影像学的迅猛发展,颈动脉CTA在临床诊疗中发挥着越来越重要的作用。随着人们对射线防护意识的逐步提高,颈动脉CTA所伴随的医疗各血管CT值和噪声值依次为:1a图头臂干动脉(405.14;17.06),左颈总动脉(432.51;20.6)左锁骨下动脉(414.61;19.41)。1b图右颈总动脉中段(527.41;4.57),左颈总动脉中段(530.82,;5.99),脂肪(-125.98;5.49)。1c图右侧颈内动脉中段(471.18;6.72),左侧颈内动脉中段(468.69;6.47)脂肪(-95.27;7.01)各血管CT值和噪声值依次为:2a图头臂干动脉(405.45;22.69),左颈总动脉(430.55;28.06)左锁骨下动脉(414.27;27.76)。2b图右颈总动脉中段(527.00;7.65),左颈总动脉中段(530.93,;8.53),脂肪(-125.95;7.72)。2c图右侧颈内动脉中段(473.41;9.26),左侧颈内动脉中段(469.11;10.78)脂肪(-98.20;11.04)辐射危害也越来越多大众所关注。有报道认为,头颈部CTA辐射剂量大,有较高致癌性[6]。国际辐射防护委员会提出的ALARA(as low as reasonably achievable)原则的提出,要求医疗工作者尽可能运用较少的辐射量获得较好的图像质量。我国也于2002年提出了电离辐射防护及辐射源安全基本标准GB18871-2002新基本标准,并同步提出放射诊断与核医学诊断医疗照射的最优化原则[7]。常规减少辐射剂量的方法有多种,常见的有优化光电匹配性,提高X线利用效率等。在已有的众多报道中,多是针对此类方向进行的研究,从影像学重建角度进行的研究则报道较少。
FBP是目前CT血管重建中最常用到的方法。他是以一个点来设定射线源,进而优化采集所有的数据,用于重建所需图像。他的缺点是未考虑到探测器外形与射线源的外形以及数据与量子噪声等所产生的影响。ASIR是建立在被扫描物体模型和噪声性质基础上,运用迭代重建技术对噪声加以优化,能较好处理常规FBP重建算法因为降低辐射剂量而引起的图像噪声提高[8],从而获得更为清晰的图像,在临床中具有很好的应用普及价值[9-10]。ASIR的权重范围在10%~100%。有报道显示,在ASIR重建算法中,权重大小与降低噪声效果成正比,与图像对比度成反比[11],Morgan DE[12]认为ASIR权重40%~60%具有较好影像重建效果。薛蕴菁等[13]等认为,权重50%ASIR能获得良好影像对比度,并且能有效降低背景噪声。有研究认为ASIR重建算法相对于常规FBP重建算法更能改善图像对比度及降低图像噪声[14-15]。甚至有文章认为,ASIR重建技术在能谱CT低剂量检查具有重大作用[16]。
本研究通过同组颈动脉CTA原始数据分别运用权重50% ASIR重建及常规FBP重建,通过对比两组血管噪声值、SNR、CNR及主观图像质量评分,全面分析两者影像学重建算法的优劣。由于本研究只选取了64组原始颈动脉数据,只运用两种影像学重建算法重建分析,还有较大研究空间。因此,这也是我们今后进一步研究的方向。
综上,颈动脉CTA结合权重50% ASIR重建算法较传统FBP重建算法,不仅可以很好保证影像质量,还可有效降低影像噪声,提高影像信噪比及对比噪声比。
[参考文献]
[1] Anderson GB,Ashforth R,Steinke DE,et al.CT angiography for the detection of cerebral vasospasm in patients with acute sub-arachmoid hemorrhage[J].Am J Neuroradiol,2000,21(6):1011-1015.
[2] Ayad ZA,Fuster V,Nikolaou K,et al.Computed tomograghy and magnetic resonance imaging for noninvasive coronary angiography and plaque imaging[J].Circulation,2002,106(5):2026-2027.
[3] Xia W,Wu JT,Yin XR,et al.CT angiography of the neck:value of contrast medium dose reduction with low tube voltage and high tube current in a 64-detector row CT[J].Clin Radiol,2014,69(4):183-189.
[4] Kalra MK,Maher MM,Toth TL,et al.Strategies for CT radiation dose optimization[J].Radiology,2004,230(3):619-628.
[5] Siegel MJ,Ramirez Giraldo JC,Hildebolt C,et a1. Automated loⅥ kjlovoltage selectjon in pediatrjc computed tomography an-giogmphy:phantom study evaluating effects on radiation dose and image quality[J].Invest Radiol,2013,48(8):584-589.
[6] Oh JS,Koea JB.Radiation risks associated with serial imaging in colorectal cancer patients:should we worry?[J].World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(1):100-109.
[7] Donald P,Frush MD,Lane F,et al.Computed Tomography and Radiation Risks:What Pediatric Health Care Providers Should Know[J].Pediatrics,2003,112(4):951-957.
[8] Hara AK,Paden RG,Silva AC,et a1.Herative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT:feasibility study[J].Am J Roentgen,2009,193(4):764-771.
[9] Prakash P,Kalra MK,Kambadakone AK,et a1.Reducing abdominal CT radiation dose with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique[J].Invest Radiol,2010,45(4):202-210.
[10] Oda S,UtsunomiyaD,FunamaY,et al.A knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction algorithm:can super-low-dose cardiac CT be applicable in clinical settings?[J].Acad Radiol,2014,21(1):104-110.
[11] Flicek KT,Hara AK,Ailva AC,et al.Reducing the radiation dose for CT colongraphy using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: A pilot study[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol,2010,195(1):126-131.
[12] Morgan DE.Dual-energy CT of the abdomen[J].Abdom Imaging,2014,39(1):108-134.
[13] 薛蕴菁,刘元芬,夏伟委,等.能谱CT结合低剂量碘对比剂个体化方案成像在颈动脉CT血管成像中的价值[J].中华放射学杂志,2015,49(10):774-777.
[14] Matsudal,Hanaoka S,Akahane M,et al.Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction for volume-rendered computed tomography portovenography:improvement of image quality[J].Jpnj Radiol,2010,28(9):700-706.
[15] Machida H,Fukui R,Tanaka I,et al.A method for selecting a protocol for routine body CT scan using Gemstone Spectral Imaging with or without adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction:phantom experiments[J].Jpn J Radiol,2014,32(4):217-223.
[16] Rapalino O,Kamalian S,Payabvash S,et al.Cranial CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction:improved image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2011,33(4):609-615.
(收稿日期:2016-02-23)

