糖尿病肾病与性激素相关性研究进展
阮曙峰,丁选胜
(中国药科大学基础医学与临床药学学院,江苏 南京 210009)
◇综述◇
糖尿病肾病与性激素相关性研究进展
阮曙峰,丁选胜
(中国药科大学基础医学与临床药学学院,江苏 南京210009)
摘要:糖尿病肾病是糖尿病导致的肾脏损害,是糖尿病最常见、最严重的并发症之一,性激素在体内能量代谢中起到重要作用。该文将对糖尿病状态下性激素变化趋势进行介绍,重点综述调节性激素平衡对于糖尿病肾病发生发展作用机制研究进展,旨在为性激素替代治疗糖尿病肾病的深入研究提供参考。
关键词:糖尿病肾病;睾酮;雌二醇
糖尿病肾病(diabetic nephropathy,DN)是糖尿病导致的肾脏损害,是糖尿病最常见、最严重的并发症之一。与其他许多疾病的并发症不同,DN一旦发生将伴随糖尿病患者终生,成为糖尿病患者主要的死亡原因。由于DN患者的发病率高、治疗困难、预后差、社会负担重,在美国、加拿大等发达国家DN已成为终末期肾功能衰竭的首位病因[1],在我国DN已成为肾衰的主要原因之一。DN一旦进入终末期肾功能衰竭,将主要依靠透析和肾移植治疗,因此,如何防治DN,已成为全世界亟待解决的难题[2]。雌性动物卵巢主要分泌两种性激素-雌二醇为主的雌激素与孕激素,雄性动物睾丸主要分泌以睾酮为主的雄激素,性激素在体内调节能量代谢平衡,促进细胞增殖与分化,促进性器官发育成熟,影响神经系统发育。糖尿病状态下长期存在的高血糖以及胰岛素的不足导致一系列的组织功能病变,其中包括性器官结构和功能的改变[3-4]。基于性激素失衡对于DN发生发展的影响,平衡糖尿病患者以及动物体内性激素水平可能在一定程度上起到延缓或治疗糖尿病肾脏损伤的作用[5]。
1糖尿病状态下性激素的变化趋势
糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)是一种由遗传和环境因素相互作用所导致的内分泌疾病,由于胰岛素分泌绝对或者相对不足以及靶组织细胞对胰岛素敏感性降低,引起糖、脂、蛋白质、水和电解质等一系列代谢紊乱。糖尿病引起性激素的变化失衡,其中男性糖尿病患者表现出睾酮水平显著降低,雌二醇水平显著升高,女性患者表现出睾酮水平显著升高,雌二醇水平显著降低,1型糖尿病和2型糖尿病存在相似的变化趋势[6-9],提示糖尿病与性激素失衡有关。
性激素的合成以胆固醇为原料,通过CYP11A转化为孕烯醇酮,这一步需要转运体从线粒体膜外到线粒体膜内的跨膜转运,且是整个性激素合成的关键步骤,之后可通过孕酮,17α-羟孕酮和羟基孕烯醇酮,脱氢表雄酮两条途径生成雄烯二酮,雄烯二酮通过17HSD3酶转化成睾酮,睾酮可通过芳香化酶转化为雌二醇[10-11],见图1。
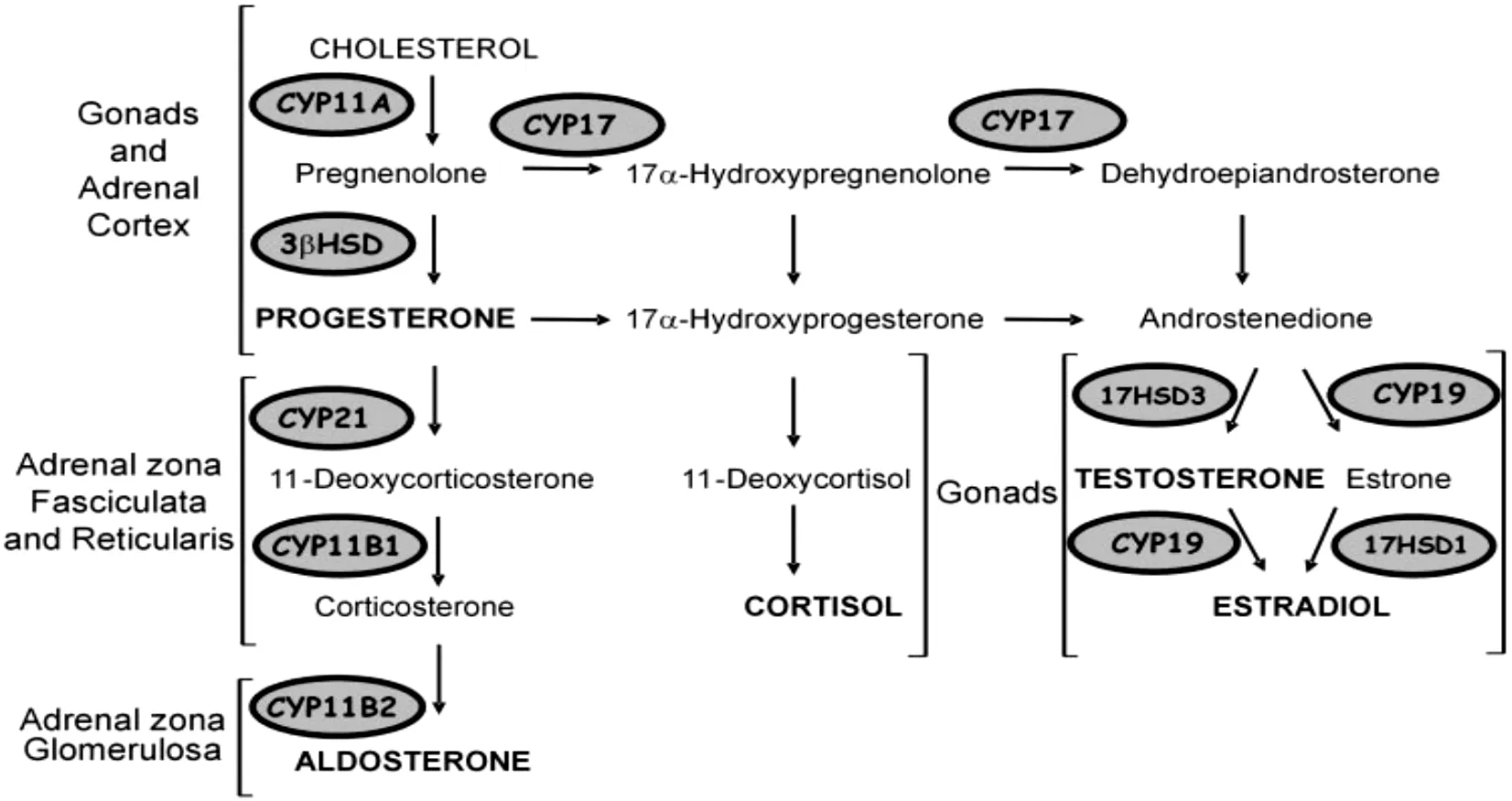
图1 性激素的合成图
研究发现,高血糖状态下,超氧化物显著增多,抑制葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶活性,导致抗氧化物减少,活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)显著增多,造成间质细胞线粒体功能障碍[12],线粒体跨膜是性激素合成的关键环节,线粒体功能障碍导致性激素合成减少,主要表现在男性糖尿病患者睾酮水平的显著降低,而女性糖尿病患者雌二醇水平的显著降低。
糖尿病的主要特点是胰腺β细胞产生的胰岛素水平降低,胰岛素在能量平衡中起着关键作用,胰岛素缺乏导致血糖升高,代谢紊乱。下丘脑-垂体-性腺功能轴(hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis,HPGA)主要由下丘脑产生促性腺激素释放激素,促进垂体产生促性腺激素,促性腺激素主要有两种,包括促黄体生成素和促卵泡生成素,促黄体生成素主要是促进性腺间质细胞产生性激素,促卵泡生成素与精子生成有关[13]。胰岛素主要通过胰岛素信号通路调节能量代谢,胰岛素与胰岛素受体结合,激活酪氨酸蛋白激酶(protein tyrosine kinase,PTK),PTK磷酸化胰岛素受体底物(insulin receptor substrate,IRS-2)使其激活,IRS-2激活PI3K,进而调控能量代谢。PI3K通过作用于大脑下丘脑,使下丘脑促性腺激素释放激素产生增加,进而刺激垂体释放促黄体生成素和促卵泡生成素,促进性腺产生性激素[14]。糖尿病状态下,胰岛素显著降低,促性腺激素释放激素释放减少,血清中促黄体生成素水平降低,性激素的产生减少[15]。瘦素是调节能量代谢的重要脂肪因子,由脂肪细胞产生,它通过下丘脑调节生殖功能[16]。体内体外实验均表明,胰岛素降低时,瘦素的产生也减少[17-18]。下丘脑中瘦素通过瘦素受体作用于IRS-2激活PI3K进而刺激下丘脑释放促性腺激素释放激素[19]。糖尿病状态下,胰岛素缺乏导致瘦素水平的降低,通过HGPA使性激素产生减少[20]。
芳香化酶是催化雄激素生成雌激素的唯一酶类,人类雌激素的生物合成受到芳香化酶的控制[21],芳香化酶主要在性腺组织中表达,但在肾脏组织中也存在芳香化酶的表达[22]。在糖尿病大鼠的研究中发现,雌性大鼠体内芳香化酶的活性显著降低,而雄性大鼠体内芳香化酶的活性显著升高,芳香化酶作为雄激素转化为雌激素的关键酶,提示高血糖状态下雌性大鼠睾酮水平显著升高,雄性大鼠雌二醇水平显著升高[23]。
2性激素变化对雄性DN的影响
男性糖尿病患者无伴随肾病血清总睾酮以及游离睾酮水平较正常男性显著降低,而伴随有微量蛋白尿或大量蛋白尿的肾病患者血清睾酮水平下降更为显著,其中1型糖尿病男性患者血清降低的睾酮水平是微量蛋白尿发展至大量蛋白尿的一个重要标志,而升高的雌二醇水平是大量蛋白尿发展至终末期肾病的重要标志[24]。有研究表明,慢性肾脏疾病男性患者相比正常人以及肾移植患者的血清睾酮水平降低[25],提示在肾病发展过程中雄性激素水平是降低的,同时在慢性肾脏疾病伴随性功能障碍的男性患者的血清睾酮水平降低,而血清促黄体生成素,促卵泡生成素水平升高,睾丸间质细胞对于促黄体生成素反应敏感性降低,提示肾脏疾病伴随性激素变化的同时存在下丘脑-垂体-性腺功能轴(hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis,HPGA)障碍[26],HPGA障碍形成的性激素失衡与慢性肾脏疾病之间相互推动,也有研究表明雄性肾脏损伤与雌二醇的升高有关。同时也有研究报道睾酮对于雄性肾脏起到保护作用[27],急性肾脏损伤研究中表明睾酮水平的恢复能够明显改善肾脏损伤[28]。
糖尿病引起性激素的变化失衡,而失衡的性激素进一步加重肾病的发展,性激素的失衡主要体现在睾酮水平降低以及雌二醇水平升高两个方面[29],在链脲佐菌素(streptozotocin,STZ)诱导的1型糖尿病研究中,小剂量补充睾酮能够明显改善肾小球及肾小管纤维化,降低转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)、Ⅰ型及Ⅳ型胶原蛋白,以及减少白介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6),肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)等炎症因子,而大剂量补充睾酮起到相反的作用,提示小剂量补充睾酮能够改善STZ诱导的1型DN[30]。同时在另一项研究中,通过抑制芳香化酶的作用,抑制睾酮转化为雌二醇,也能明显改善STZ诱导的1型DN[23],同时补充二氢睾酮和芳香化酶抑制剂能够起到相比单用睾酮补充或芳香化酶抑制剂更好的抗纤维化以及抗炎作用,对糖尿病引起的肾病起到更好的改善作用[15]。性激素对于DN作用的中心环节是对于TGF-β的调节[31],在睾酮改善心肌纤维化的研究中,睾酮通过雄激素受体(androgen receptor,AR)抑制TGF-β/PI3K/Akt以及AngⅡ/p38/Smad2两条通路抑制心肌细胞的分化,同时通过抑制TGF-β增强基质金属蛋白酶2(matrix metalloprotein-2,MMP-2)的表达,加强了基质的降解,从而抑制心肌纤维化[32]。在急性伤口恢复的研究中,雄激素通过AR作用于真皮成纤维细胞降低TGF-β的表达,其中TGF-β以及下游的Smad信号通路不仅与细胞外基质的沉积相关,同时能够激活炎症因子引起炎症反应[33],提示性激素可能通过下调TGF-β的表达起到对肾脏纤维化及肾脏炎症的改善作用。
3性激素变化对雌性DN的影响
对于雌性DN而言,雌激素的升高能够对DN起到保护作用,其中雌二醇通过激活酪氨酸激酶2(casein kinase 2,CK2)抑制TGF-β的合成,进而抑制胶原蛋白Ⅳ(CollagenⅣ)RNA的转录,降低胶原蛋白的表达,改善DN纤维化的程度,对DN起到保护作用[34]。同时,雌二醇可以通过上调CK2表达以及促进P53的磷酸化逆转TGF-β引起的系膜细胞凋亡,对DN起到保护作用[35]。雌二醇通过MAPK/AP-1信号通路抑制胶原蛋白Ⅰ(CollagenⅠ)的合成,减少胶原蛋白的来源,起到肾脏保护作用[36]。雌二醇通过激活MAPK/AP-2促进MMP-2的表达,同时刺激基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)的合成,降低纤维化水平,改善DN[37]。雌激素通过雌激素受体α(estrogen receptor α,ER-α)上调内皮一氧化氮合酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)的mRNA水平增加其蛋白水平,加速一氧化氮(nitric oxide,NO)的释放,改善NO引起的肾脏损伤[38]。雌激素通过降低血管紧张素2的水平,减少内皮素的合成,抑制肾脏血管收缩以及降低肾脏炎症反应[39]。雌激素通过抑制还原型辅酶Ⅱ(NADPH)的氧化激活,降低肾脏超氧阴离子的水平,超氧阴离子是肾脏主要的活性氧成分,降低ROS水平改善氧化应激,改善DN肾脏损伤[40]。Mankhey等[41]研究表明,STZ诱导的雌性大鼠补充17-β雌二醇可改善DN损伤。
4结语
DN发生发展中性激素起到关键的作用,动物实验已经表明以激素替代疗法为主的治疗方案对于DN的肾功能具有明显的改善作用[30]。然而,DN状态下性激素变化在性别之间差异性的原理并没有得到完全的阐释,同时一些作用于性激素的新靶点也需要再发现,为DN的治疗提供新的思路以及广阔的前景。
参考文献
[1]Collins AJ,Kasiske B,Herzog C,et al.United States Renal Data System 2011 Annual Data Report:Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States[J].American Journal of Kidney Diseases the Official Journal of the National Kidney Foundation,2012,59(1 Suppl 1):A7,e1-420.
[2]Cooper ME.Diabetes:Treating diabetic nephropathy-still an unresolved issue[J].Nature Reviews Endocrinology,2012,8(9):515-516.
[3]Ricci G,Catizone A,Esposito R,et al.Diabetic rat testes:morphological and functional alterations[J].Andrologia,2009,41(6):361-368.
[4]朱金海,方军,左泽平,等.小剂量持续服用他达拉非对糖尿病性勃起功能障碍的疗效观察[J].安徽医药,2014,18(6):1138-1140.
[5]Manigrasso MB,Sawyer RT,Marbury DC,et al.Inhibition of estradiol synthesis attenuates renal injury in male streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J].American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology,2011,301(3):F634-F640.
[6]Dhindsa S,Reddy A,Karam JS,et al.Prevalence of subnormal testosterone concentrations in men with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease[J].European Journal of Endocrinology,2015,173(3):359-366.
[7]Hackett G,Heald AH,Sinclair A,et al.Serum testosterone,testosterone replace-ment therapy and all-cause mortality in men with type 2 diabetes:retrospective consideration of the impact of PDE5 inhibitors and statins[J].International Journal of Clinical Practice,2016,70(3):244-253.
[8]Holt SK,Natalya L,James H,et al.Prevalence of low testosterone and predisposing risk factors in men with type 1 diabetes mellitus:findings from the DCCT /EDIC[J].Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2014,99(9):E1655-E1660.
[9]Torkel V,Henrik S,Inger N,et al.Low testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin levels and high estradiol levels are independent predictors of type 2 diabetes in men[J].European Journal of Endocrinology,2010,162(4):747-754.
[10] Payne AH,Hales DB.Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones[J].Endocrine Reviews,2004,25(6):947-970.
[11] Papadopoulos V,Baraldi M,Guilarte TR,et al.Translocator protein (18 kDa):new nomenclature for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor based on its structure and molecular function[J].Trends in Pharmacological Sciences,2006,27(8):402-409.
[12] Alves MG,Martins AD,Rato L,et al.Molecular mechanisms beyond glucose transport in diabetes-related male infertility[J].Biochimi Biophysi Acta,2013,1832(5):626-635.
[13] Schoeller EL,Schon S,Moley KH.The effects of type 1 diabetes on the hypothalamic,pituitary and testes axis[J].Cell & Tissue Research,2012,349(3):839-847.
[14] Boura-Halfon S,Zick Y.Phosphorylation of IRS proteins,insulin action,and insulin resistance[J].American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology & Metabolism,2009,296(4):E581-E591.
[15] Brüning JC,Gautam D,Burks DJ,et al.Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction[J].Science,2000,289(5487):2122-2125.
[16] German JP,Wisse BE,Thaler JP,et al.Leptin deficiency causes insulin resistance induced by uncontrolled diabetes[J].Diabetes,2010,59(7):1626-1634.
[17] Cammisotto PG,Bukowiecki LJ.Mechanisms of leptin secretion from white adipocytes[J].Ajp Cell Physiology,2002,283(1):C244-C250.
[18] Kolaczynski JW,Nyce MR,Considine RV,et al.Acute and chronic effects of insulin on leptin production in humans:Studies in vivo and in vitro[J].Diabetes,1996,45(5):699-701.
[19] Carvalheira JB,Torsoni MA,Ueno M,et al.Cross-Talk between the Insulin and Leptin Signaling Systems in Rat Hypothalamus[J].Obesity Research,2005,13(1):48-57.
[20] Quennell JH,Mulligan AC,Tups A,et al.Leptin indirectly regulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal function[J].Endocrinology,2009,150(150):2805-2812.
[21] Beck DT,Yarrow JF,Beggs LA,et al.Influence of Aromatase Inhibition on the Bone Protective Effects of Testosterone[J].Journal of Bone & Mineral Research the Official Journal of the American Society for Bone & Mineral Research,2014,29 (11):2405-2413.
[22] Prabhu A,Xu Q,Manigrasso MB,et al.Expression of aromatase,androgen and estrogen receptors in peripheral target tissues in diabetes[J].Steroids,2010,75(11):779-787.
[23] Manigrasso MB,Sawyer RT,Hutchens ZM,et al.Combined inhibition of aromatase activity and dihydrotestosterone supplementation attenuates renal injury in male streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats[J].American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology,2012,302(9):F1203-F1209.
[24] Christine M,Carol F,Lena T,et al.Association between testosterone,estradiol and sex hormone binding globulin levels in men with type 1 diabetes with nephropathy[J].Steroids,2010,75(11):772-778.
[25] Park MG,Koo HS,Lee B.Characteristics of testosterone deficiency syndrome in men with chronic kidney disease and male renal transplant recipients:a cross-sectional study[J].Transplantation Proceedings,2013,45(8):2970-2974.
[26] Suzuki E,Nishimatsu H,Oba S,et al.Chronic kidney disease and erectile dysfunction[J].World Journal of Nephrology,2014,3(4):220-229.
[27] Periklis D,Konstantina T,Costas F,et al.Role of testosterone in the pathogenesis,progression,prognosis and comorbidity of men with chronic kidney disease[J].Therapeutic Apheresis & Dialysis,2014,18(3):220-230.
[28] Meuwese CL,Carrero JJ.Chronic Kidney Disease and Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis Dysfunction:The Chicken or the Egg? [J].Archives of Medical Research,2013(44):591-600.
[29] Neugarten J,Golestaneh L.Gender and the prevalence and progression of renal disease[J].Adv Chronic Kidney Dis,2013,20(5):390-395.
[30] Qin X,Anjali P,Shujing X,et al.Dose-dependent effects of dihydrotestosterone in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat kidney[J].Ajp Renal Physiology,2009,297(2):F307-F315.
[31] Diamond-Stanic MK,You YH,Sharma K.Sugar,sex,and TGF-β in diabetic nephropathy[J].Seminars in Nephrology,2012,32(3):261-268.
[32] Cheng-Chih C,Rung-Chieh H,Yu-Hsun K,et al.Androgen attenuates cardiac fibroblasts activations through modulations of transforming growth factor-β and angiotensin Ⅱ signaling[J].International Journal of Cardiology,2014,176(2):386-393.
[33] Kuo TM,Yeh KT,Hsu HT,et al.ALPK1 affects testosterone mediated regulati-on of proinflammatory cytokines production[J].Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology,2015,154:150-158.
[34] Zdunek M,Silbiger S,Lei J,et al.Protein kinase CK2 mediates TGF-beta1-stimulated type IV collagen gene transcription and its reversal by estradiol[J].Kidney International,2001,60(6):2097-2108.
[35] Olivia N,Istvan B,Jun L,et al.Estradiol reverses TGF-β1-induced mesangial cell apoptosis by a casein kinase 2-dependent mechanism[J].Kidney International,2003,62(6):1989-1998.
[36] Dixon A,Maric C.17β-Estradiol attenuates diabetic kidney disease by regulating extracellular matrix and transforming growth factor-β protein expression and signaling[J].American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology,2007,293(5):F1678-F1690.
[37] Guccione M,Silbiger S,Lei J,et al.Estradiol upregulates mesangial cell MMP-2 activity via the transcription factor AP-2[J].American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology,2002,282(1):F164-F169.
[38] Silbiger S,Neugarten J.Gender and human chronic renal disease[J].Gender Medicine,2008,5(Suppl A):S3-S10.
[39] Bupp MRG.Sex,the aging immune system,and chronic disease[J].Cellular Immunology,2015,294(2):102-110.
[40] White RE,Gerrity R,Barman SA,et al.Estrogen and oxidative stress:A novel mechanism that may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease in women[J].Steroids,2010,75(11):788-793.
[41] Mankhey RW,Bhatti F,Maric C.17β-Estradiol replacement improves renal function and pathology associated with diabetic nephropathy[J].American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology,2005,288(2):F399-F405.
Advances in research on correlation between diabetic nephropathy and sex hormone
RUAN Shu-feng,DING Xuan-sheng
(SchoolofBasicMedicineandClinicalPharmacy,ChinaPharmaceuticalUniversity,Nanjing,Jiangsu210009,China)
Abstract:Diabetic nephropathy,kidney damage caused by diabetes,is the most common and serious complication of diabetes mellitus.Sex hormones play an important role in energy metabolisminvivo.This paper provides references for further study in hormone therapy in diabetic nephropathy.Here the trend of sex hormones changing in diabetes was reviewed,focusing on advances in sex hormones replacement therapy in the development of diabetic nephropathy.
Key words:Diabetic nephropathies;Testosterone;Estradiol
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(81274158)
作者简介:阮曙峰,男,硕士研究生 通信作者:丁选胜,男,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:心血管药理与临床药学,E-mail:dxs0162@sina.com
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2016.06.001
(收稿日期:2016-03-07,修回日期:2016-03-25)

