绍兴鸭生长激素基因多态性与生长性能关联性分析
绍兴鸭生长激素基因多态性与生长性能关联性分析
李丽1,2, 徐琪1, 陈阳1, 黄学涛3, 李柳萌4, 陶仲连5, 陈国宏1*
( 1.扬州大学动物科学与技术学院,江苏 扬州225009;2.福建省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所,福州350013;
3.浙江省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所,杭州310021;4.诸暨国家级绍兴鸭保种场,浙江 绍兴311800;
5.缙云县畜牧兽医局,浙江 缙云321400)
摘要以绍兴鸭为材料,选择与生长发育密切相关的候选生长激素(growth hormone,GH)基因,通过直接测序方法扫描其单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)位点,并分析其与生长性能的关联性.结果表明:在GH基因的2 514 A>G和2 691 C>T处检测到2个SNP位点,且2个基因座均处于Hardy-Weinberg平衡状态。最小二乘法分析表明,GH基因(2 691 C>T)TT基因型个体的6周龄体质量、8周龄体质量、12周龄龙骨长、53周龄胸宽显著高于CT基因型个体(P<0.05);TT基因型53周龄胸肌质量、腹脂质量、腹脂率显著高于CT和CC基因型个体(P<0.05)。研究为在本品种选育中监测绍兴鸭公鸭的生长发育和充分利用淘汰种公鸭肉用价值提供了一定的参考材料,同时从分子水平上丰富了绍兴鸭遗传信息。
关键词绍兴鸭; 生长激素基因; 单核苷酸多态性; 生长性能
中图分类号S 834.89文献标志码A

Correlation between the polymorphism of growth hormone gene with the growth performance in Shaoxing ducks. Journal of ZhejiangUniversity(Agric. & LifeSci.), 2015,41(3):365-370
Li Li1,2, Xu Qi1, Chen Yang1, Huang Xuetao3, Li Liumeng4, Tao Zhonglian5, Chen Guohong1*(1.CollegeofAnimalScienceandTechnology,YangzhouUniversity,Yangzhou225009,Jiangsu,China; 2.InstituteofAnimalHusbandryandVeterinaryResearch,FujianAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Fuzhou350013,China; 3.InstituteofAnimalHusbandryandVeterinaryResearch,ZhejiangAcademyofAgriculturalSciences,Hangzhou310021,China; 4.ShaoxingDuckNationalConservationFieldofZhuJi,Shaoxing311800,Zhejiang,China; 5.JinyunBureauofAnimalScienceandVeterinaryMedicine,Jinyun321400,Zhejiang,China)
SummaryAs excellent germplasm resources in China, Shaoxing duck is famous for its high egg production all over the world. Laying traits, rather than the growth and development traits, are the main breeding criteria in the duck breeding at present. We usually use egg laying traits as the main breeding goal, but ignore the growth and development traits, especially in drake breeding. Defective growth and development may lead to the loss of duck breeding value and the low fertilization rate, which will finally reduce the economic benefit of drakes. Thus, drakes’ growth traits must be emphasized in breeding of laying ducks. We must pay more attention to the selection of the drakes’ growth traits.
This study analyzed the correlation between the polymorphism of growth hormone (GH) gene with the growth performance and slaughter in Shaoxing ducks, which provided some reference material for monitoring the growth and development of Shaoxing ducks breeding.
As the candidate genes,GHgene is closely related to the growth and development. The SNP loci ofGHwere scanned by direct sequencing method. The body size was measured at the age of 12 weeks, and the slaughter indexes were measured at the age of 53 weeks. All ducks were sampled randomly according to the group, and the relevance of Shaoxing duck growth performance and slaughter performance were analyzed. The genomic DNA was extracted by phenol chloroform method from blood. All data were sampled randomly according to the group. According to the publishedGHgene sequence in GenBank, the primers were designed to amplify the sequences of intron 2, exon 4 and exon 5. The SNP loci ofGHwere scanned by direct sequencing method, and the sequences were compared by using DNAStar to look for the polymorphic loci. The genotype and allele frequencies were calculated and tested by Hardy-Weinberg balance. The correlation between the genotypes and traits was calculated by using statistical software JMP 4.0 (SAS Institute, 2002) to estimate the least square means of traits.
The results showed two loci:GH2 514 A>G,GH2 691 C>T. Theχ2 test revealed that all loci were in the balance of Hardy-Weinberg (P>0.05 ). ForGH(2 514 A>G & 2 691 C>T), 6-week body mass, 8-week body mass, 12-week keel bone length, 53-week chest width of the individuals with genotype TT were higher than the genotype CT. The breast muscle mass, abdominal fat mass and abdominal fat percentage of individuals with genotype TT were significantly higher than those with genotype CT and CC (P<0.05).
It is suggested thatGHgene may be the major gene which directly control the abdominal fat and breast muscle related traits, or may be tightly linked with the major genes indirectly.
Key wordsShaoxing duck; growth hormone gene; single nucleotide polymorphism; growth trait
绍兴鸭具有产蛋多、体质量小、饲料报酬高、抗病力强等特点,是世界优秀水禽品种之一[1]。但长期以来,因绍兴鸭体型较小,对其肉用性能的研究较少,所以对绍兴鸭公鸭的遗传特征和生长性能进行深入研究,进一步了解鸭体内脂肪分布和生长发育的差异,为合理保护和利用我国地方鸭品种遗传资源,具有重要的理论和实践意义。
生长激素(growth hormone,GH)是一种具有广泛生理功能的生长调节素。GH基因对动物体的影响主要表现为显著提高生长速度,促进肌肉生长,降低脂肪含量,进而影响机体生长发育速度。GH基因由5或6个外显子和4或5个内含子组成,cDNA长度一般为800~1 200 bp,信号肽和成熟肽分别为16~27个和186~191个氨基酸[2-4]。在对畜禽的研究中发现,GH基因存在丰富的多态性[5-8]。与哺乳动物相比,禽类GH基因的研究起步较晚。本试验以绍兴鸭公鸭为材料,运用DNA直接测序技术,对GH基因进行单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)检测,对不同外显子、内含子的遗传变异进行分析,并对其多态性与生长性能进行关联分析,以期找到遗传变异位点,寻找绍兴鸭生长性能的主效基因和分子遗传标记,旨在从分子水平上分析绍兴鸭GH基因单核苷酸多态性及其与生长性能的遗传调控规律。
1材料与方法
1.1试验材料及各生长性能指标测定
绍兴鸭195只,均为公鸭,来自浙江省诸暨市国家级绍兴鸭保种场同一鸭舍、同一批次,饲料与饲养方法相同,记录其生长指标,12周龄时参照《畜禽遗传资源调查手册》[9]规定的方法测定试验鸭的体质量和体尺指标,53周龄时测定屠宰指标。所有数据资料均按群组随机取样,同一指标现场专人测定。采用酚-三氯甲烷法对全部个体血液基因组DNA进行提取,0.6%琼脂糖检测,-20 ℃保存备用。
1.2引物设计和聚合酶链反应扩增
根据GenBank公布的GH基因(登录号:AB158760.2)序列设计引物,扩增其内含子2、外显子4、外显子5序列(表1)。引物由上海翼和生物工程技术服务有限公司合成,用灭菌超纯水溶解。
聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)反应体系:缓冲液(10×,含20 mol/L Mg2+)2.0 μL,10 μmol/L脱氧核苷酸(dNTPs)2.0 μL,10 μmol/L上、下游引物各2.0 μL,模板DNA 50 ng,1 UTaqDNA聚合酶0.2 μL,加超纯水补足体积至20.0 μL。PCR反应条件:95 ℃ 2 min;随后30个循环,94 ℃ 30 s,56 ℃ 30 s,65 ℃ 1 min;最后65 ℃延伸10 min,10 ℃终止反应。PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳回收。

表1 绍兴鸭 GH基因引物信息
1.3数据统计分析
计算基因型和等位基因频率,并进行Hardy-Weinberg平衡性检验;运用DNAStar对序列进行比对,寻找其多态性位点;采用如下固定模型进行统计分析:Y=μ+G+E。其中:Y为个体的表型记录;μ为群体均值;G为该位点的基因型效应;E为随机误差。运用统计软件JMP 4.0(SAS Institute,2002)分别计算基因型与性状的相关性,估计性状的最小二乘均值。
2结果与分析
2.1GH基因多态位点筛查

(1~4):PCR产物;M:DL1500标志物。 (1-4): PCR product; M: DL1500 marker. 图1 GH基因内含子2凝胶电泳检测结果 Fig.1 Gel electrophoresis results of GH gene intron 2
经DNA提取后,分别对GH基因内含子2、外显子4、外显子5进行PCR扩增,结果见图1~3。各片段的扩增产物大小与预期的产物大小一致,且拥有较好的特异性。将PCR产物直接测序结果与GenBank中GH基因序列比对后发现,仅在GH基因内含子2发现2处突变:2 514 bp处A>G突变和2 691 bp处C>T突变(图4、图5)。

(1~4):PCR产物;M:DL600标志物。 (1-4): PCR product; M: DL600 marker. 图2 GH基因外显子4凝胶电泳检测结果 Fig.2 Gel electrophoresis results of GH gene exon 4

(1~4):PCR产物;M:DL600标志物。 (1-4): PCR product; M: DL600 marker. 图3 GH基因外显子5凝胶电泳检测结果 Fig.3 Gel electrophoresis results of GH gene exon 5

图4 GH基因2 514 bp处突变位点测序峰图 Fig.4 Partial chromatogram of GH gene mutation at 2 514 bp
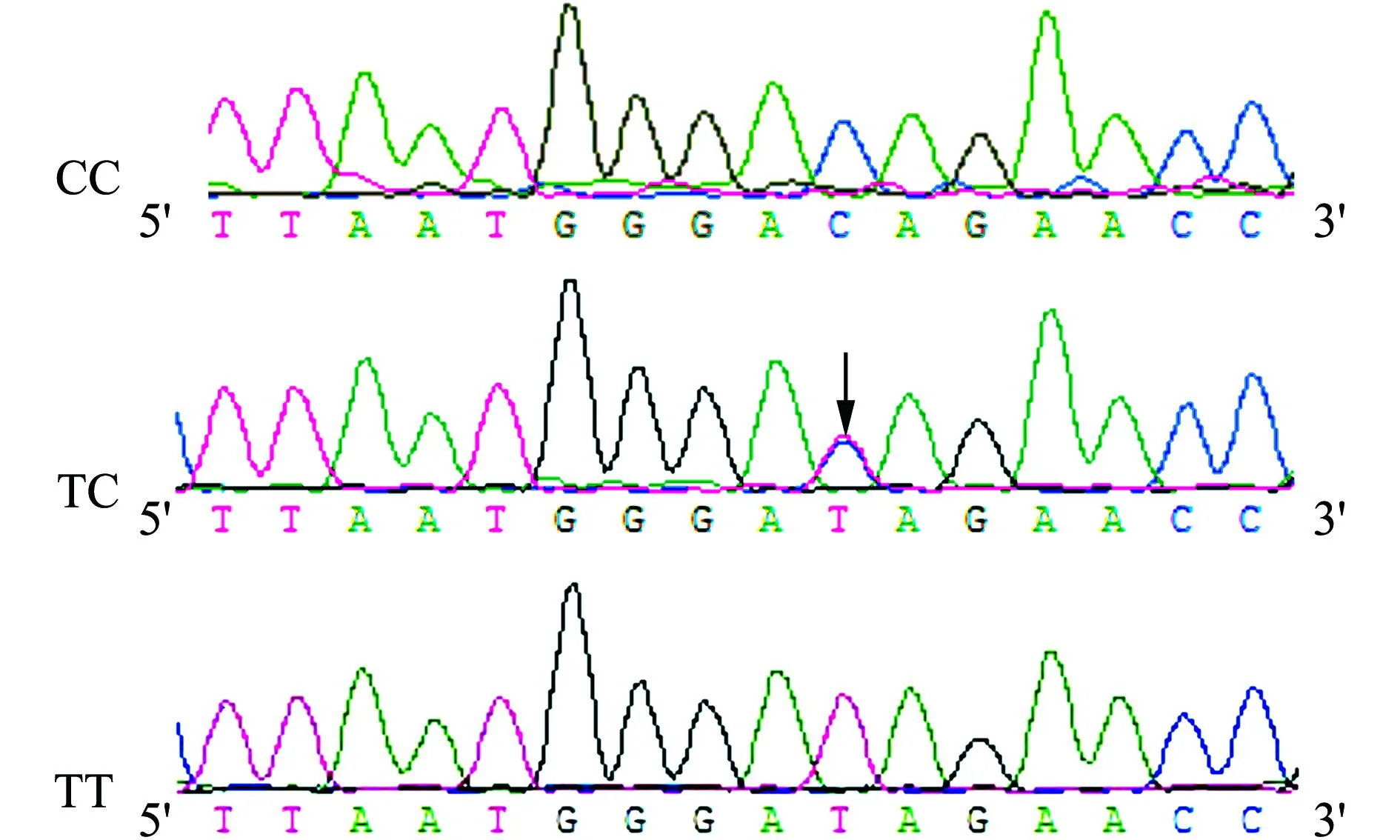
图5 GH基因2 691 bp处突变位点测序峰图 Fig.5 Partial chromatogram of GH gene mutation at 2 691 bp
2.2GH基因内含子2的群体遗传特性
对绍兴鸭群体中GH突变位点基因型分布进行统计,发现存在TT基因型、CT基因型、CC基因型以及GG基因型、GA基因型和AA基因型个体。绍兴鸭GH基因内含子2的基因型频率和等位基因频率见表2。2 514 A>G位点GG纯合子为群体中的优势基因型,等位基因G为优势等位基因,χ2检验结果表明,该基因座处于Hardy-Weinberg平衡状态;2 691 C>T位点TT纯合子为群体中的优势基因型,等位基因T为优势等位基因,χ2检验结果表明,该基因座处于Hardy-Weinberg平衡状态。
2.3GH基因内含子2多态性及其与生长发育性能和屠体性能的关联性分析
连锁不平衡分析结果表明,2 514 A>G和2 691 C>T位点之间的R2=1,处于完美连锁不平衡状态,一个位点的信息完全可以代表另外一个位点。因此,本研究只对2 691 C>T位点进行了关联性分析。采用最小二乘均值法对GH基因多态性与其生长发育性能和屠体性能进行关联性分析的结果见表3和表4。

表2 绍兴鸭 GH基因内含子2的基因型频率、等位基因频率

表3 GH基因内含子多态位点(2 691 C>T)对鸭生长发育性能的影响
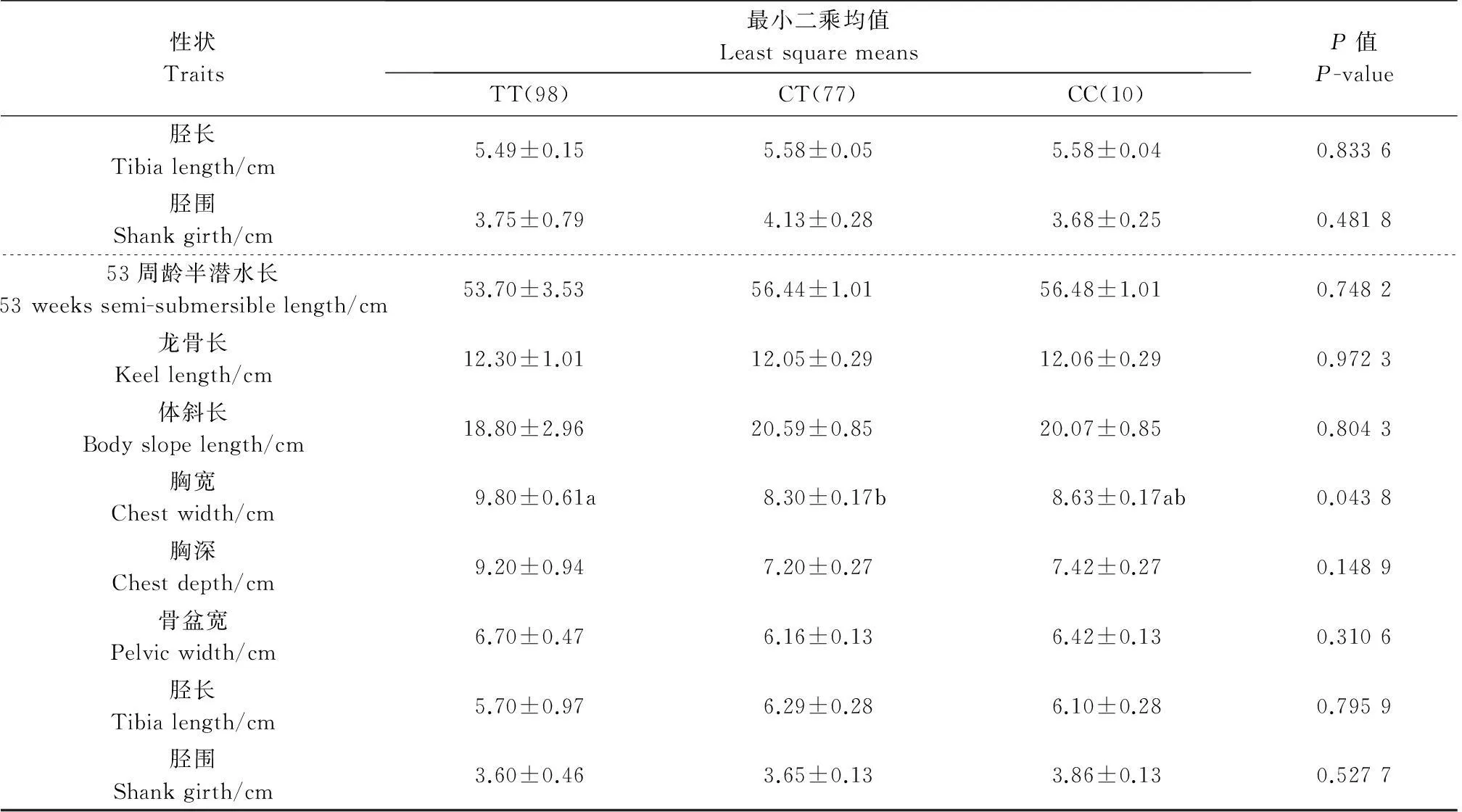
续表3 GH基因内含子多态位点(2 691 C>T)对鸭生长发育性能的影响
同行数据后的不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异有统计学意义.
Values within a row followed by different lowercase letters are significantly different at the 0.05 probability level.
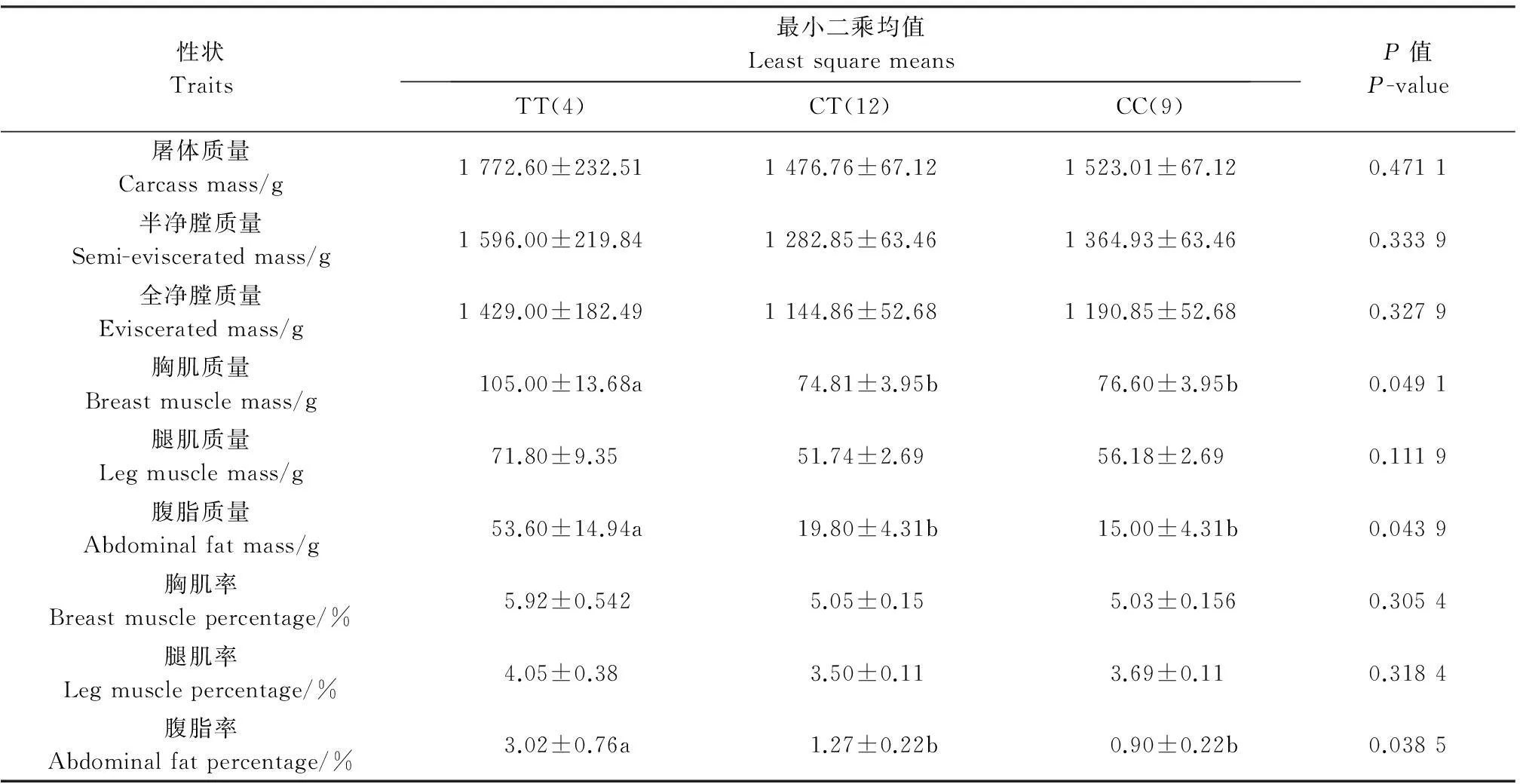
表4 GH基因内含子多态位点(2 691 C>T)对鸭屠宰性能的影响
同行数据后的不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异有统计学意义.
Values within a row followed by different lowercase letters are significantly different at the 0.05 probability level.
GH的基因型效应对生长和屠宰性能均有不同程度的影响。从生长性能(表3)可知,基因型对6周龄体质量、12周龄龙骨长和53周龄胸宽有显著影响(P<0.05);最小二乘均值分析表明,TT基因型个体6周龄体质量、8周龄体质量、12周龄龙骨长、53周龄胸宽显著高于CT基因型个体(P<0.05)。从屠宰性能(表4)可知,基因型对53周龄腹脂质量以及53周龄腹脂率有显著影响(P<0.05);最小二乘均值分析表明,TT基因型个体胸肌质量、腹脂质量、腹脂率显著高于CC和CT基因型个体(P<0.05)。本研究对2个性能进行综合分析,发现GH基因TT型在2个性状方面显著大于CC和CT基因型,可视其为绍兴鸭公鸭生长和屠宰性能的优势标记基因型。
3讨论
关于GH基因多态性与生长性能的关系已有相关研究[10-13],对山羊、秦川牛、豁眼鹅、籽鹅进行多态性检测,均发现基因型对生长性能有极显著(P<0.01)或显著(P<0.05)影响。采用DNA测序法对GH基因内含子2的遗传多样性进行分析发现,不同基因型个体的生长性能如6周龄体质量、胸宽、龙骨长以及胸肌质量、腹脂质量和腹脂率等性状间存在显著差异。说明GH可能对绍兴鸭公鸭胸肌附着的龙骨长及胸宽均有显著影响,并且对腹脂及腹脂率有一定影响。本研究对GH基因的遗传多样性进行分析发现其内含子2存在多态性。颜炳学等[10]在鸡GH基因中发现了2个多态位点,研究结果表明这些多态位点与腹脂和胸肉等屠体性状显著相关,与本研究分析结果一致,由此推测GH基因也许是直接控制腹脂和胸肌相关性状的主效基因,又或者是间接与主效基因紧密连锁的基因。
本研究结果需在其后代或家鸭品种中验证,同时还应筛查绍兴鸭GH基因编码区和其他内含子区的多态性是否对生长性能及抗病性也存在显著效应,最终获得真实可靠的分子遗传标记,以期用于绍兴鸭公鸭群体生长性能标记辅助选择的育种实践。
参考文献(References):
[1]陈国宏,王克华,王金玉,等.中国禽类遗传资源.上海:上海科学技术出版社,2004:120.
Chen G H, Wang K H, Wang J Y,etal.ChinaPoultryGeneticResources. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2004:120. (in Chinese)
[2]孙逊,朱尚权.生长激素的结构与功能.国外医学生理病理科学与临床分册,1999,19(1):6-9.
Sun X, Zhu S Q. The structure and function of growth hormone.ForeignMedicalSciencesPhysiologicalPathologyandClinicalMedicine, 1999,19(1):6-9. (in Chinese)
[3]Tyson U E. Growth hormone and bovine location.NutritionReviews,1986:4.
[4]Vasilatos-Younken R, Wang X H, Zhou Y. New insights into the mechanism and actions of growth hormone (GH) in poultry.DomesticAnimalEndocrinology, 1999,17(2/3):181-190.
[5]Chen H T, Pan F M, Chang W C. Purification of duck growth hormone and cloning of the complementary DNA.BiochimicaetBiophysicaActa(BBA):GeneStructureandExpression,1988,949(2):247-251.
[6]Ku H, Ni L, Wei G S,etal. DNA polymorphisms in the chicken growth hormone gene: Response to selection for disease resistance and association with egg production.AnimalGenetics,1997,28(2):116-123.
[7]Kansaku N, Zadworny D, Guemene D. Genomic cloning of duck growth hormone[EB/OL]. National Center for Biotechnology Information。GenBank, 2004. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AB158760.2
[8]Zhan K, Yang N. Effects of polymorphism in the coding region ofGHgene on serum GH, T3 levels and body weight of ducks//World’s Poultry Science Association.Proceedingsofthe3rdWorldWaterfowlConference. Guangzhou: World’s Poultry Science Association, 2005:242-246.
[9]陈伟生.畜禽遗传资源调查技术手册.北京:中国农业出版社,2005:56-64.
Chen W S.TechnicalManualofFarmAnimalGeneticResourcesSurvey. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. 2005:56-64. (in Chinese)
[10]颜炳学,邓学梅,费菁,等.鸡生长激素基因单核苷酸多态性与生长及屠体性状的相关性.科学通报,2003,48(12):1304-1307.
Yan B X, Deng X M, Fei J,etal. Relationship between growth hormone gene single nucleotide polymorphism with growth and carcass traits of chicken.ChineseScienceBulletin, 2003,48(12):1304-1307. (in Chines)
[11]赵文明,陈清,程金花.籽鹅GH基因内含子3多态性及其与体重和屠体性状的关联分析.畜牧兽医学报,2008,39(4):443-448.
Zhao W M, Chen Q, Cheng J H. Association analysis of gooseGHgene intron 3 polymorphism and body weight and carcass traits in Zi geese.AnimalHusbandryandVeterinaryMedicine, 2008,39(4):443-448. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12]敖金霞,李辉,王启贵,等.鹅生长激素基因内含子2单核苷酸多态性与体重性状的相关研究.中国畜牧杂志,2006,42(7):9-11.
Ao J X, Li H, Wang Q G,etal. Study of goose growth hormone gene intron 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms and weight traits.ChineseJournalofAnimalScience, 2006,42(7):9-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13]张扬,陈阳,黄正洋,等.豁眼鹅GH基因外显子2多态性与体重和体尺性状的关联分析.遗传育种,2012,48(23):1-5.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Huang Z Y,etal. Huoyan gooseGHgene exon 2 polymorphism and body weight and body size traits correlation analysis.GeneticsandBreeding, 2012,48(23):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)

