钙蛋白酶活化在小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用
钙蛋白酶活化在小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用
张双1,2,徐磊2,岳荣川2,张辉1,王欢2,陈海燕2,谭春燕2,张荣驿2,倪海燕1
(1.什邡市人民医院心内科,四川什邡618400; 2.川北医学院附属医院心内科,四川南充637000)
【摘要】目的:探讨钙蛋白酶在小鼠心肌缺血/再灌注(Ischemia/Reperfusion,I/R)损伤中的作用。方法:采用结扎/松解左冠状动脉前降支的方法建立小鼠心肌I/R模型。将实验动物随机分为假手术组、I/R组(冠状动脉结扎45 min,再灌注3 h)及PD + I/R组(I/R前30 min静脉注射钙蛋白酶抑制剂-PD150606 1 mg/kg)。再灌注结束后,测定各组心肌梗死面积、细胞色素C含量、caspase-3活性。结果:与I/R组相比,PD150606预处理组心肌梗死区域面积明显减小,且PD150606能明显抑制由I/R引起的细胞色素C含量及caspase-3活性增加。结论:钙蛋白酶活化介导的心肌细胞凋亡在小鼠心肌I/R损伤中发挥了重要的作用。
【关键词】钙蛋白酶;缺血/再灌注;凋亡
钙蛋白酶是一类钙依赖的非溶酶体半胱氨酸蛋白酶,普遍存在于哺乳动物的细胞内[1-2]。大量研究[3-5]表明,钙蛋白酶参与心肌缺血/再灌注(Ischemia/Reperfusion,I/R)损伤,抑制钙蛋白酶活性可减轻心肌I/R损伤。然而,钙蛋白酶引起心肌I/R损伤的具体机制仍不清楚。因此,本研究应用钙蛋白酶特异性抑制剂PD150606预处理小鼠I/R模型,观察其对心肌I/R损伤的作用,并进一步探讨其可能的作用机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验动物分组
C57BL/6小鼠随机分成3组:①假手术组:麻醉开胸后只穿线,不结扎血管;②缺血/再灌注(I/R)组:穿线结扎血管缺血45 min,再灌注3 h;③PD150606预处理(PD + I/R)组:缺血前30 min给予PD150606 1 mg/kg,然后进行I/R处理。
1.2小鼠心肌I/R模型建立
本实验根据之前实验方法采用结扎/松解左冠状动脉前降支(LAD)的方式建立小鼠心肌I/R损伤模型[6]。具体方法描述如下:实验动物术前6 h禁食,自由进水。腹腔注射4%戊巴比妥钠(40 mg/kg)麻醉C57BL/6小鼠,去除胸前毛发,将其仰卧固定于鼠台,行气管插管,小动物呼吸机维持通气。在小鼠胸部左侧3~4肋间剪开皮肤,钝性分离肌层,弯镊子撑开胸腔,暴露心脏,撕开心包膜。在显微镜下,用8-0丝线阻断LAD血流造成心肌缺血并关闭胸腔;假手术组只穿线不结扎。缺血45 min后重新打开胸腔,松解结扎线实现缺血后再灌注,按上述方法关闭胸腔并逐层缝合切口。再灌注3 h后取材并进行各项指标的检测。
1.3心肌梗死面积计算
小鼠心肌缺血45 min,再管灌注3 h后,采用的Evens Blue和2、3、5-氯化三苯基四氮唑(Triphenyl Tetrazolium Chloride,TTC)双染色法确定梗死和缺血区域[7-8]。
1.4ELISA测定心肌细胞中细胞色素C含量
根据我们之前实验中的方法,采用双抗体夹心法测定标本中细胞色素C的水平。
1.5测caspase-3的活性
根据文献[9-10]中的方法,用caspase-3荧光检测试剂盒来检测细胞caspase-3活性。
1.6统计学分析
所有数据均以均数±标准误表示,采用Graph-Pad Prism 5.0软件统计分析并作图,多组总体采用one way ANOVA分析,两组间差异比较用Newman-Keuls分析,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1钙蛋白酶活性对I/R后心肌梗死面积的影响
结扎小鼠冠状动脉45 min,再灌注3 h。如图1、图2所示,PD + I/R组与I/R组相比,梗死区域面积明显减小(P<0.05),说明抑制钙蛋白酶活性能减轻I/R损伤。
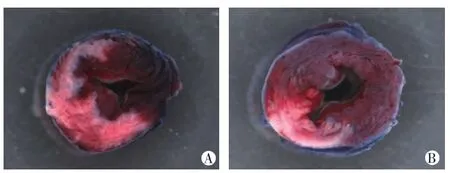
图1 心肌缺血再灌注后小鼠心脏横切面
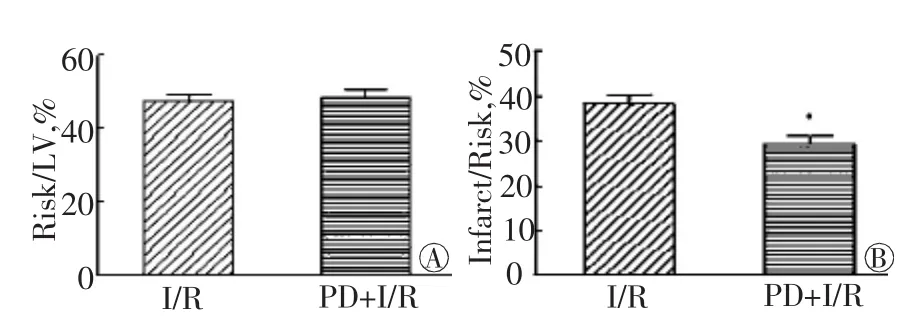
图2 小鼠心脏I/R后心肌梗死面积分析
2.2抑制钙蛋白酶活性能减少I/R引起心肌细胞凋亡
为明确抑制钙蛋白酶活性减轻心肌I/R损伤是否与阻断心肌细胞凋亡有关,我们检测了细胞caspase-3的活性及细胞色素C的释放情况。与对照组比较,I/R组小鼠心脏梗死周围区域细胞胞浆细胞色素C水平显著增加(P<0.01),经PD150606预处理后细胞胞浆细胞色素C水平与I/R组相比明显降低(P<0.05,图3); I/R组caspase-3活性明显增加(P<0.01); PD + I/R组与I/R组相比,caspase-3活性明显降低(P<0.05,图4),说明抑制钙蛋白酶活性能阻断心肌细胞凋亡。

图3 各组心肌组织Cyt C释放

图4 各组心肌组织内caspase-3活性
3 讨论
心肌I/R损伤指缺血心肌在恢复血流灌注后引起心肌超微结构、心功能和电生理等方面出现的进一步损伤[11],其分子机制可能与氧化应激、Ca2 +超载、内皮功能障碍、代谢性酸中毒、ATP合成障碍、炎症反应及免疫激活等有关[12-13]。近年来,钙蛋白酶的作用日益受到关注,研究表明钙蛋白酶的异常激活与多种心脏疾病有关,包括I/R损伤、心肌梗死、梗死后心室重构及心衰等[14-16]。钙蛋白酶主要是以无活性的酶形式定位于胞浆中,并与其内源性抑制剂钙蛋白酶抑制蛋白(Calpastatin)结合;一旦被激活,钙蛋白酶将水解细胞膜上或胞浆中的底物蛋白[2],活化的钙蛋白酶可以介导细胞凋亡[17]。
心肌细胞凋亡是心肌I/R损伤的最主要的病理形式。为明确钙蛋白酶在I/R损伤中的作用及其可能的分子机制,本研究选用C57BL/6小鼠,通过结扎/松解冠状动脉前降支的方法建立小鼠I/R模型,观察钙蛋白酶抑制剂PD150606对I/R后心肌梗死面积及心肌细胞凋亡的影响。结果发现钙蛋白酶抑制剂PD150606使I/R后的心肌梗死面积明显减小,而且PD150606能有效的阻断I/R引起的细胞色素C的释放和caspase-3的活化。这些结果表明钙蛋白酶活化在心肌I/R损伤中发挥了重要的作用,其引起小鼠心肌I/R损伤的机制可能与其介导的心肌细胞凋亡有关。但钙蛋白酶通过何种方式介导心肌细胞凋亡还需要进一步的研究。
参考文献
[1]Storr SJ,Pu X,Davis J,et al.Expression of the calpain system is associated with poor clinical outcome in gastrooesophageal adenocarcinomas[J].Journal of gastroenterology,2013,48(11):1213-1221.
[2]Goll DE,Thompson VF,Li H,et al.The calpain system[J].Physiological reviews,2003,83(3):731-801.
[3]Hernando V,Inserte J,Sartorio C,et al.Calpain translocation and activation as pharmacological targets during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion[J].Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology,2010,49(2):271-279.
[4]Zhang CM,Gao L,Zheng YJ,et al.Berbamine protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury by maintaining cytosolic Ca(2 + )homeostasis and preventing calpain activation[J].Circulation journal,2012,76(8):1993-2002.
[5]Zheng D,Wang G,Li S,et al.Calpain-1 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis following hypoxia/reoxygenation[J].Biochim biophys acta,2015,1852(5):882-892.
[6]Yue R,Xia X,Jiang J,et al.Mitochondrial DNA Oxidative Damage Contributes to Cardiomyocyte Ischemia/Reperfusion-Injury in Rats: Cardioprotective Role of Lycopene[J].Journal of cellular physiology,2015,doi:10.1002/jcp.24941.
[7]Hu H,Xenocostas A,Chin-Yee N,et al.Transfusion of fresh but not old stored blood reduces infarct size and improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in anemic rats[J].Critical care medicine,2012,40(3):740-746.
[8]Hu H,Xenocostas A,Chin-Yee I,et al.Effects of anemia and blood transfusion in acute myocardial infarction in rats[J].Transfusion,2010,50(1):243-251.
[9]Yue R,Hu H,Yiu KH,et al.Lycopene protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction in primary neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes[J].PloS one,2012,7(11): e50778.
[10]岳荣川,胡厚祥,罗涛,等.Calpain活化在H2O2诱导的成年小鼠心肌细胞损伤中的作用[J].西部医学,2012,24(3):426-429.
[11]Goldhaber JI,Weiss JN.Oxygen free radicals and cardiac reperfusion abnormalities[J].Hypertension,1992,20(1):118-127.
[12]Rassaf T,Weber C,Bernhagen J.Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury[J].Cardiovascular research,2014,doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu071.
[13]Turer AT,Hill JA.Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy[J].The American journal of cardiology,2010,106(3):360-368.
[14]Galvez AS,Diwan A,Odley AM,et al.Cardiomyocyte degeneration with calpain deficiency reveals a critical role in protein homeostasis [J].Circulation research,2007,100(7):1071-1078.
[15]Inserte J,Barba I,Hernando V,et al.Delayed recovery of intracellular acidosis during reperfusion prevents calpain activation and determines protection in postconditioned myocardium[J].Cardiovascular research,2009,81(1):116-122.
[16]Li X,Li Y,Shan L,et al.Over-expression of calpastatin inhibits calpain activation and attenuates myocardial dysfunction during endotoxaemia[J].Cardiovascular research,2009,83(1):72-79.
[17]Hu H,Li X,Li Y,et al.Calpain-1 induces apoptosis in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells under septic conditions[J].Microvascular research,2009,78(1):33-39.
Effects of calpain activation in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury of mouse
ZHANG Shuang1,2,XU Lei2,YUE Rong-chuan2,ZHANG Hui1,WANG Huan2,CHEN Hai-yan2,TAN Chun-yan2,ZHANG Rong-yi2,NI Hai-yan1
(1.Department of Cardiology,People’s Hospital of Shifang,Shifang 618400; 2.Department of Cardiology,Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College,Nanchong 637000,Sichuan,China)
【Abstract】Objective: To determine whether and how calpain involved in ischemia/reperfusion(I/R)-injury.Methods: Ligation and release of the left coronary artery was performed to establish mouse myocardial I/R-injury models.Mice were randomly divided into Control group,I/R group and PD + I/R group.Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC)stain was employed to observe the myocardial infarction area in different groups.The level of Cytochrome C and the activity of caspase-3 were also detected.Results: Calpain inhibitor PD150606 significantly reduced the myocardial infarction area caused by I/R.Moreover,we found the level of Cytochrome C and the activity of caspase-3 were significantly increased in I/R group compared with Control group.However,these changes were blunted by PD150606; the increase of Cytochrome C level and caspase-3 activity was inhibited in PD + I/R group.Conclusion: Calpain mediated cardiac myocytes apotosis plays an important role in myocardial I/R-injury of mouse.
【Key words】Calpain; Ischemia/reperfusion; Apotosis
作者简介:张双(1987-),女,四川彭州人,硕士,住院医师,主要从事心血管疾病方面的研究。E-mail: gcyyzs.136@163.com
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(81070101)
收稿日期:2015-02-08
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2015.02.03
【文章编号】1005-3697(2015)02-0144-03
【中图分类号】R542.2
【文献标志码】A
网络出版时间: 2015-5-1 01∶33网络出版地址: http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20150501.1333.033.html

