Slope Protection with Vegetation of Baoji(Shaanxi)-Hanzhong(Shaanxi)Expressway
Xuanbin XU
State Key Laboratory of Soil Erosion and Dryland Farming on Loess Plateau, Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, China
With construction of infrastructure in full swing, environment protection has drawn more and more attention in China.For instance, the construction of expressway has considerably advanced national economy,but the accompanying environmental problems can never be ignored, slope protection and treatment has become a difficult issue to be resolved[1-2]. Although engineering protection of expressway proves efficiency, the construction cost is high,and landscape effect performs poor.Currently, in order to reduce destruction of expressway on original ecosystem[3], slope protection technique with vegetation has been extensively applied,which wins popularity,because it plays an important role in restoring the destroyed eco-environment by project construction, replacing mortar rubble and concrete. Still, the research on slope protection with vegetation of expressway maintains in an exploration phase,which has been conducted from the perspectives of civil engineering, water and soil conservation,and landscape architecture. This research explored slope protection of Baoji (Shaanxi)-Hanzhong(Shaanxi)Expressway in order to guarantee the technology would protect slopes and prevent scouring, as well as integrate well with nearby eco-landscapes,promoting development of slope conservation of expressway.
The Project Region
As shown in Fig.1, Baoji (Shaanxi)-Hanzhong (Shaanxi) Expressway,one passage of Dingbian (Shaanxi)-Hanzhong (Shaanxi) Expressway, begins from Shaanxi-Gansu boundary to the starting point of Baoji Expressway,the intersection with Lianyungang Khorgas,and ends at entrance of Micang Mountain Tunnel. Furthermore,the roads from Hanzhong to Sichuan-Shaanxi boundary starts from the intersection of Laodaosi Town and Shiyan-Tianshui Expressway, and ends at Xiaoba,a boundary of Shaanxi and Sichuan, and the control points covering Jinzhai Village, a starting point, Changlin, Liangshan, Yangchun, Nanzhengxi, Xieshui, Qingshu,Hongmiao, Xishenba, and Xiaoba, a boundary of Shaanxi and Sichuan,going through Changlin Town,LiangshanTown, Yangchun Town, Nanzheng County,Xieshui Town,Qingshu Town,Hongmiao Village, Xishenba Village,and Xiaoba Village. The distance from Baoji (Shaanxi)-Hanzhong (Shaanxi)Expressway to Shaanxi -Sichuan boundary is 53.768 km, without consideration of Micang Mountain Tunnel of 13.803 km, and 6 interchanges are arranged, including two pivot overpasses, namely, Shimen and Liangshan and 4 common overpasses,namely,Hanzhongxi,Nanzheng,Nanhu,and Xishenba. Additionally, two connecting lines are set, including Hanzhongxi connecting line of 7.8 km and Nanzheng connecting line of 4.96 km. In general, 52 major bridges are set, totaling 20 885 m, 12 tunnels, totaling 17 700 m,a service area,4 ramp toll-stations, a toll-station of Shaanxi-Sichuan boundary, a management center, two maintenance and management stations, and a tunnel management station. Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway is one of"2637"expressway network, planned and constructed by Shaanxi Province, and it starts from Daqiao Village,Baoji City,and ends at Micang Mountain,in Shaanxi-Sichuan boundary. It is planned the expressway runs about 400 km in Shaanxi Province, which connects Lianyungang-Khorgas, Shiyan-Tianshui and Beijing-Kunming Expressways,as well as Qingyang, western Guanzhong,southern Shaanxi, and eastern Sichuan, so that regional transportation pressure from south to north is relieved and economic relationship between Guanzhong and southern Shaanxi can be intensified.
Water and Soil Erosion
Water and soil erosion is a process of soil erosion, movement and sedimentation by water flows.In natural condition, , the eroded process of surface soils proceeds quite slowly resulting from pure natural factors, and keeps balance with soil formation, so slopes could maintain complete[4-5].It is called natural erosion or geologic erosion[6-7].Nevertheless,human activities have increased the erosion occurring rate , especially after slope vegetation was seriously destroyed by human[8-9].The amount of moved soils caused by exogenic processes is called soil erosion amount. The project region is located along Han River in Pingchuan,hills and moderate mountains of Ta-pa Mountains. In accordance with Soil Erosion Classification Standard and Soil and Water Conservation Division of Shaanxi Province, soil erosion modulus is from the range of 162 to 2 591 t/(km2·a) in the project region where erosion intensity includes slight and moderate erosion, dominated by light erosion. Basis onthe survey along the project region,national or local soil and water conservation key projects are not available.With consideration of the project, most expressway sections in Han River in Pingchuan and the landform are quite flat. Soil erosion modulus in the project region averages 150-800 t/(km2·a)and 300-3 000 t/(km2·a)in hills of Ta-pa Mountains(Table 1).

Table 1 Distribution of water and soil erosion and soil erosion intensity along expressways
Soil and water erosion in the project region is mainly caused by natural and human factors. Specifically, natural factors include rainfall, soil and vegetation, of which rainfall is a dominant one[10], and human factors mainly refer to frequent production or construction, resulting in destruction of vegetation and surface structure[11].Recently, as regional economy develops, construction of infrastructure is highlighted,and human activities,covering dredging, soil collection, rock blasting,and brick firing,become more and more frequent,leading to destruction on landform and vegetation, as well as occasional collapse. It is obvious that human activity-caused water and soil erosion has become a major factor preventing regional agriculture and eco-construction development[12].This project is a construction project,and belongs to national key prevention and protection region,as well as a key treatment region of Shaanxi Province,according to Announcement on Clas-sification of Key Prevention Region of National Water and Soil Erosion. In accordance with Soil Erosion Classification and Grading Standards(SL190-2007), admissible value of soil erosion in the project region is 500 t/(km2·a).
Risks of Water and Soil Erosion in the Project Region
This region from Baoji-Hanzhong Road to Shaanxi-Sichuan boundary are situated in the areas of Han River of the Yangtze River,the starting point is the intersection of Laodaosi Town and Shiyan-Tianshui Expressway,going through southwestern Chengguan Town, Nanzheng County, western Xishui Town, Sanguanmiao, Qingshu,Hongmiao,Xishenba and Xiaoba.This project region is in upstream of Han River, and Qinba mountains, consisting of Qinling and Ba Mountain. It is a complete fold mountain since the end of Mesozoic.The project passes along Han River in Pingchuan, hills and moderate mountains of Ta-pa Mountains, keeping generally high in south and low in north,with altitudes of 500-1 000 m. Within the region, mountains rise and gullies are widely distributed,with a concentration at 2.1 kg/km2.During construction of the project,original landform has been destroyed, soil and water erosion has been deteriorated, and it is urgent to take measures for water and soil conservation.
Destruction and influences on land resources
The area from Hanzhong to Shaanxi-Sichuan boundary of Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway is about 582.7 hm2, covering subgrade and management service region, totaling 554.92 hm2, as well as construction road and other temporary grounds. Therefore,original landform, soil structure and surface vegetation would be changed or injured in varying degrees,and soils of plough layers and vegetation layers are dug,removed or buried,leading to rapid reduction, soil fertility loss and water conservation, as well as degradation of nearby land productivity. If they are piled along slopes,riverbanks or benchlands, the abandoned soils and dregs dug from subgrades of hills are prone to be rushed away,resulting in new soil and water erosion.
Effects on regional eco-environment
The project region is located along Han River in Pingchuan, hills and moderate mountains of Ta-pa Mountains. In accordance with Soil Erosion Classification Standard and Soil and Water Conservation Division of Shaanxi Province, soil erosion modulus range is from 162 to 2 591 t/(km2·a)in the project region where erosion intensity includes slight and moderate erosion, dominated by light erosion.Basis on survey along the project region, national or local soil and water conservation key projects are not available. With consideration of this project,most expressway sections are in Han River in Pingchuan and the landform is quite flat. I Soil erosion modulus in the project region averages 150-800 t/(km2·a) and 300-3 000 t/(km2·a) in hills of Ta-pa Mountains.According to Water and Soil Conservation Technology Standard of Development or Construction Projects(GB50433-2008),the duty of preventing water and soil erosion involves project construction and direct influential region.The design of body project and on-site inspection indicated that the prevention region from Baoji -Hanzhong Expressway to Shaanxi -Sichuan boundary totals 754.40 hm2,of which construction region of projects reaches 582.72 hm2, and direct influential region reaches 171.68 hm2(Table 2). The destroyed water and soil conservation facilities and the facilities with the function is as high as 527.62 hm2, resulting from the project construction. Unfortunately, soil structure and vegetation, in or nearby, are damaged,reducing water and soil conservation function, deteriorating erosion. In addition, since distributed in belts,reconstruction of vegetation becomes more difficult. Although natural or artificial vegetation would inevitably suffer destruction in the process of road construction, the coverage rate of original forests or grasses in the project region, as well as crops, reduces to zero, and local eco-environment is degrading and environment capacity is declining, deteriorated by natural disasters[13].
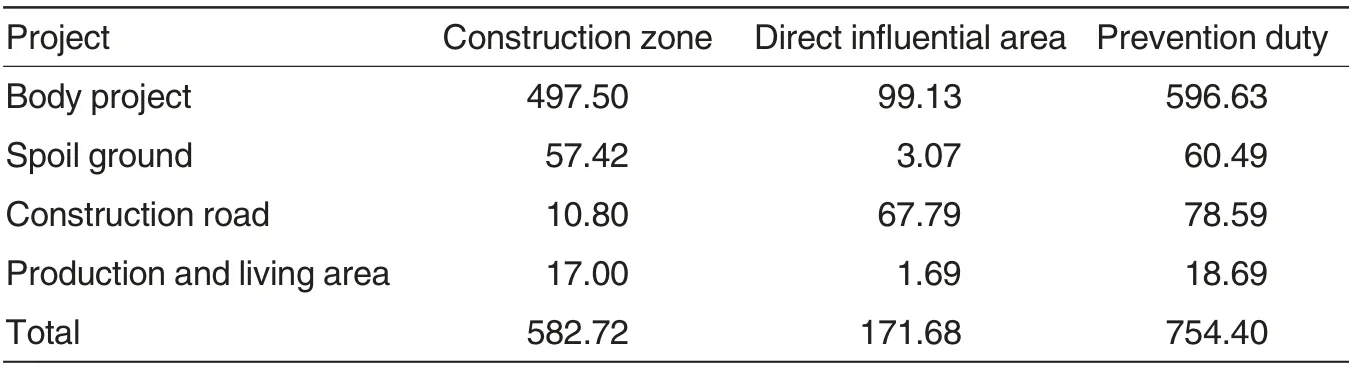
Table 2 Ranges of water and soil erosion prevention in the project region
Effects on flood carrying capacity
Since reform and opening-up, regional economy develops fast along roads. Meanwhile, water conservation projects are increasing based on watercourses, which cover large discharge areas. In flood period, water table of a watercourse grows, preventing water, and changing water flows in watercourse, so some waterflow energies have transformed into turbulent kinetic energy,scouring constructions or buildings and affecting stability of constructions, evolution of riverbed and stability of riverbanks.Therefore, if buildings are not designed in a proper location, flood carrying capacity, bank security, and water transportation would be all affected.When roads pass slopes and valleys or pass through watercourses, collapse or landslide probably occur due to the destruction of slope by subgrade digging[14]. Furthermore, the abandoned dregs(5.549 9 million m3)located in 17 sites should be well treated timely, or the dregs possibly cause high-intensity erosion or debris flow at rainstorm or deteriorate floods, increasing sand transportation by rivers,affecting human safety,downstream.
Effects on road safety
At planning of road construction,eco-environment along roads possibly destroyed of the design departments have an improper choice on road routes or not well recognized local environment. For example, most watercourse-crossing designs are cut-bend projects and economical span of bridge is computed as per flood frequency, which reduces project costs,but ignores the effects on regional ecoenvironment,which is adverse for road safety and natural eco-environment.Furthermore, attention should be paid on newly-dug unstable steep slopes or newly-filled bare slopes at sides of subgrades, which would cause slope erosion or even collapse, destroying roads or facilities at rainstorm or successive rainy days, if none countermeasures was taken[15]. Additionally,spoil grounds built in upstream regions possibly result in debris flow at rainstorm, , and lead to destruction on road facilities and affecting road transportation and safety without effective measures. After the construction,however, original natural structure is prone to be affected also without environment protection.Still,the extension of expressway in belts would destroy natural landscapes and cause environmental culture loss.
Countermeasures of Protecting Slope Ecology
The construction engineer of road is close to natural environment, the scale is large, projects are more and concerning range is wide. Lots of bare earths and rocks of slopes, produced by filling or digging, destroy native vegetation, and affect local eco-environment. Previously, engineering protection is always a priority, such as mortar rubble and ejector anchor,which will lead to destruction of vegetation, water and soil erosion, landslide, and unstability of slopes. With social developments, our country gives highlights to eco-construction and environment protection in engineer construction. For instance, the State Council issued file[2000]No. 31 of Announcement on Further Advancing Construction of Green Channel,and eco-construction and environment protection in engineer construction has been proposed, which is of significance for the implementation of sustainable development strategy.Specifically, slope protection with vegetation refers to fox slopes and improve scouring-resistance of slopes, depending on plant roots, stems and soil adhesion[26]. It is a technology developed with construction of expressway worldwide. Compared with traditional technologies, slope protection with vegetation integrates protection from projects and plants, making full use of deep fixation by projects and surface fixation with vegetation, which plays a role in conserving water resources,reducing water and soil erosion, purifying airs, andbenefiting economic,social and ecological.
Concepts of slope protection technology with vegetation
Ecology refers to interactions among organisms and their environment and the science of ecology is produced based on research of individual organism. Currently, science of ecology has beenwider and wider applied in different areas. For example,the word of ecology is quite popular when someone wants to define something of beauty, involving healthy,beautiful and harmony aspects.
Slope protection projects are the projects constructed on slopes for fixation to prevent collapse,which reduces costs and saves labor, with a high speed. In general, the project constructed using mortar rubble, concrete block, latticed-shaped framework, and whitewashing.
Eco-protection of slopes refers to grow plants on dug slopes and to protect and fix slope surface based on interplay between plants and rocks or soils, in order to keep slope surface stable and restore destructed natural eco-environment,simultaneously[17].
The technology of slope protection with vegetation use vegetation’s function of fixing soils and conserve water to stabilize slopes and beautify environment, concerning geotechnical engineering, soil and water conservation, environmental protection, ecology,botany, landscape architecture,and soil fertilizer science[18],which improves eco-environment from different aspects and achieves integration of human and environment, playing an active role in sustainable development.
Vegetation is assemblages of plant species and the ground cover,and it is a word from botany, ecology,agronomy,or geoscience.It is obvious that vegetation can be divided as per growing environment, such as alpine vegetation and steppe vegetation.
In addition,slope protection technology with vegetation refers to making use of plants, civil engineering or non-living materials,individually or collectively, to reduce instability and erosion of slopes.It is thus a new technology for stabilizing slopes and beautifying environment on basis of plants’functions of conserving water and fixing soils, involving edaphology, engineering science,and botany[20-21].Nevertheless, slope protection with vegetation develops into a science recently,and an appropriate term is not given yet,with some names abroad,such as biotechnique, soil bioengineering,vegetation or revegetation. The first international meeting themed by slope protection with vegetation was held in September 1994 in Oxford, when the explored technology is not the socalled landscaping planting technology.Instead, it is a new technology to stabilize rock or soil based slopes in accordance with the principle of vegetation in conserving water and fixing soils, concerning geotechnical engineering, soil and water conservation,and environmental protection.
With construction of infrastructural projects, different types of slopes are formed,posing threats to eco-environment,and even causing disasters[19].At present,slope protection with plants or plants and non-living materials is popular at home and abroad, replacing pure engineering protection. Protecting slopes with vegetation would prevent rainfall dropping, reduce runoffs and sands, and decrease runoff flow speed, increase infiltration, and improve soil resistance. With earth or rock based slopes stable,the technology would beautify environment and protect ecology. It is a technology involving geotechnical engineering, soil and water conservation,environmental protection,ecology,botany,landscape architecture, and soil fertilizer science.Hence, it is urgent and necessary to select slope protection model with vegetation in order to stabilize slope and guarantee vegetation coverage in accordance with specific site conditions.
Protection role by vegetation
Fine roots of plants grow and intwine together on surface slopes, and root system can be considered as three-dimensional reinforcement materials with prestress. Fine root system of vegetation and soils contribute to a root-soil complex, changing me-chanical property of earth and improving resistance of earth[22-23], because root systems are able to pass through loose soil layers of slopes.Soils play fixing role with depths of 0.75-1.5 m[24-25], and anchor role of block, cracked or scatted rocks. At present, more and more attention is paid to environment protection and human living quality,protection with vegetation has become a major trend for road protection[26], meantime, geosynthetic fiber mattress, hydraulic seeding, bunch planting, trench sowing,lawn nursery strip, green net and stepped vegetation are available for slope protection. After all, the dug slopes along expressways destroy original ecosystems, so natural disasters, such as debris flow, possibly occur.It is urgent to find an effective way to restore the destroyed slopes and prevent the disasters.Slope protection with vegetation is just optimal choice for resolving the issue,for full exploitation of natural forces,supplemented by human practices should be a fundamental way for restoring and afforestation of roads. Respecting nature and conducting afforestation within natural admission may be the best way.
Specifically, vegetation plays a role of reducing kinetic energy of rainfall, slowing down surface runoff, improving soil property and reinforcing soils in terms of canopy,dried soil layer,surface,and root system[27-28].From canopy and dried layer,rainfall actually experiences redistribution by interception,decreasing rainfalls might causing erosion and reducing kinetic energy of rainfall as well[7].On ground surface,stems of plants and fallen materials increase slope resistance coefficient and roughness, slow down rate of surface runoff and lowering sand-carrying capacity. It is researched that within a rational range, as ground diameter grows and row spacing reduces, energy loss of surface flow would enhance[29].The research of Zha indicated that under influence of decomposition of fallen materials and root growth,the content of soil waterstable aggregate grows significantly, soil bulk density declines and porosity increases, improving soil resistance to erosion and infiltration. The distribution, intwining and fixation of roots increase soil resistance to scouring[30], especially for herbaceous plants(Fig.2).
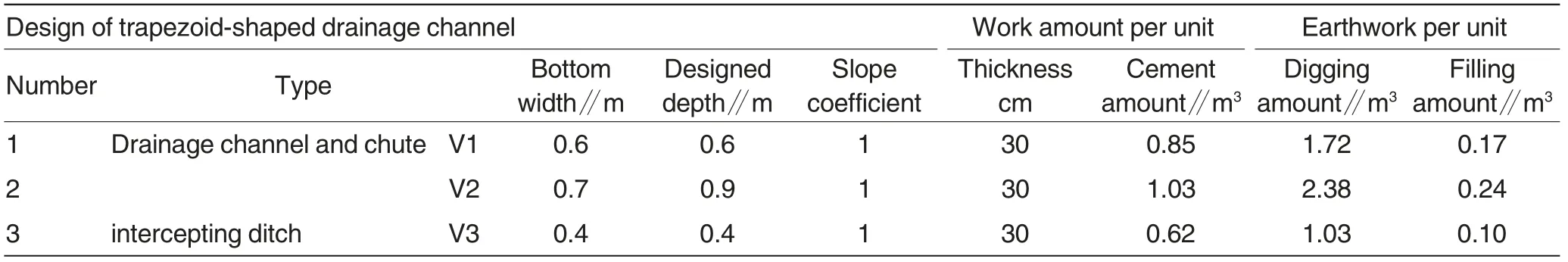
Table 3 Cross-section of drainage ditch,chute and intercepting ditch of platform and work volume per unit area
The adoption of slope protection with vegetation
Protection with vegetation of embankment roads A subgrade lays foundation for a road, undertaking transportation loads, together with road surfaces, constructing as per road routes with specific technology. It is clear that quality of subgrade directly affects the stability of a road track. As for embankment roads, soil texture,moisture content, compaction and other natural or human factors all matter. Specifically, the floor space of major road-body involves major subgrade, interchange and service zones,and management and facilities and of road routes takes 5 m of up-slope and 30 m of down-slope in hills, 2 and 2 m of two sides of routes in valley zones,and 2 m in interchange, service and management zones,and 30 m extending to upstream regions and 150 m to downstream regions, with a bridge as a center for computing affected areas by bridges. Road construction from Baiji-Hanzhong Express to Shaanxi-Sichuan boundary totally destroyed 582.72 hm2of original landform, lands and vegeation; the area of constructing the destroyed water and soil conservation facilities,and similar facilities is 567.62 hm2in total. In conclusion,water and soil erosion reached as high as 96 170 t, of which the erosion amount during construction process was 85 314 t,and in restoration phase was 10 856 t, with extremely strong erosion as maximal erosion modulus.
The critical height of eco-protection is an important index for the choice of engineering protection or eco-protection, which tends to be volatile upon site conditions. Analysis was conducted on storm precipitations in different areas, accumulated water on roads with different widths,drainage ways and protection capacities of varying plants, and critical heights of different eco-protections of expressway slopes were determined.For Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway,multiple eco-protection ways were used upon slopes(Table 3).
(1) Slopes with embankment height below 3.5 m. Water on roads flooded to slopes, and grass seeds were directly scattered on slopes and some shrubs were grown.
(2) Slopes with embankment height of 3.5-5 m. A catchwater was dug on road shoulder and a chute was arranged on slopes for drainage, reducing scouring on slopes. Furthermore, grass seeds were directly scattered on slopes and some shrubs were grown.
(3) Slopes with embankment height over 5 m. Single-layer or double-layer cement concretes-based precast block can be arranged according to specific conditions and grass seeds were directly scattered and some shrubs were grown in the circled region.
(4) Slopes with embankment height over 7 m. Slopes were treated step by step and drainage ditch was arranged on steps. The whole slopes were divided into 2-3 sub-slopes with height below 3.5 m and grass seeds were directly scattered on slopes and some shrubs were grown.
(5)Roads with appropriate nearby conditions. The original designed slope rate was reduced to 1:2 in order to improve critical height of eco-protection and reduce the proportion of engineering protection.
Protection with vegetation of rockbased embankment Baoji -Han-zhong Expressway is situated in hills,and some measures can be taken to reduce the destruction of gravels on environment, collected earth amount and engineering costs.
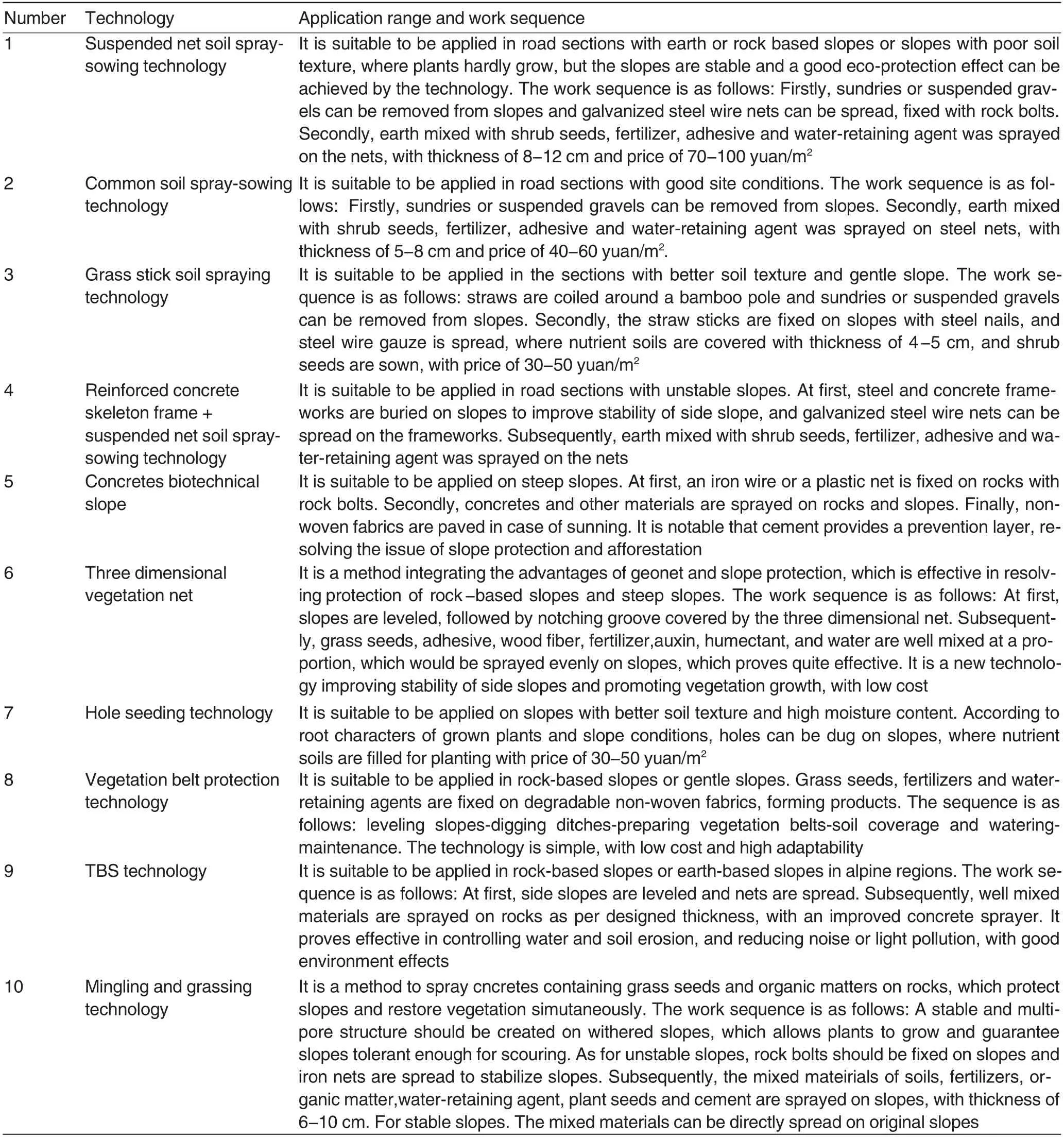
Table 4 Slope protection technology with vegetation applied in Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway
(1) Dry stone pitching. Before filling upon layers, dry stones were pitched with a specific height and the thickness over 2 m.
(2)Unloading.At constructing,the transportation routes of aggregated rock should be well designed and materials were unloaded as per the principle of horizontal stratification, lowerfirst and high later, and sides first and center following. It is notable that thickness of uncompacted layer should be below 50 cm,and the maximal grain size of rocks should be lower than 2/3 of compacted thickness.
(3) Levelling. The extensive surface of rocks should face down and rocks were piled closely, with cracks filled with gravels or aggregate chips.Because filling thickness of every layer is large, the leveling work should be conducted with large bulldozers, supplemented by human work. If rock grades are poor and size is large,gravels, the large cracks among rocks can be filled with aggregate chips or coarse sands.
(4) Rolling compaction. After being pushed and loosened with a bulldozer, the rocks were densely compacted with a heavy road roller, when cracks can be filled with gravels or aggregate chips until compacted surface is stable, leveled, and tight. The compaction times should be determined by local test and approved by supervising engineers.
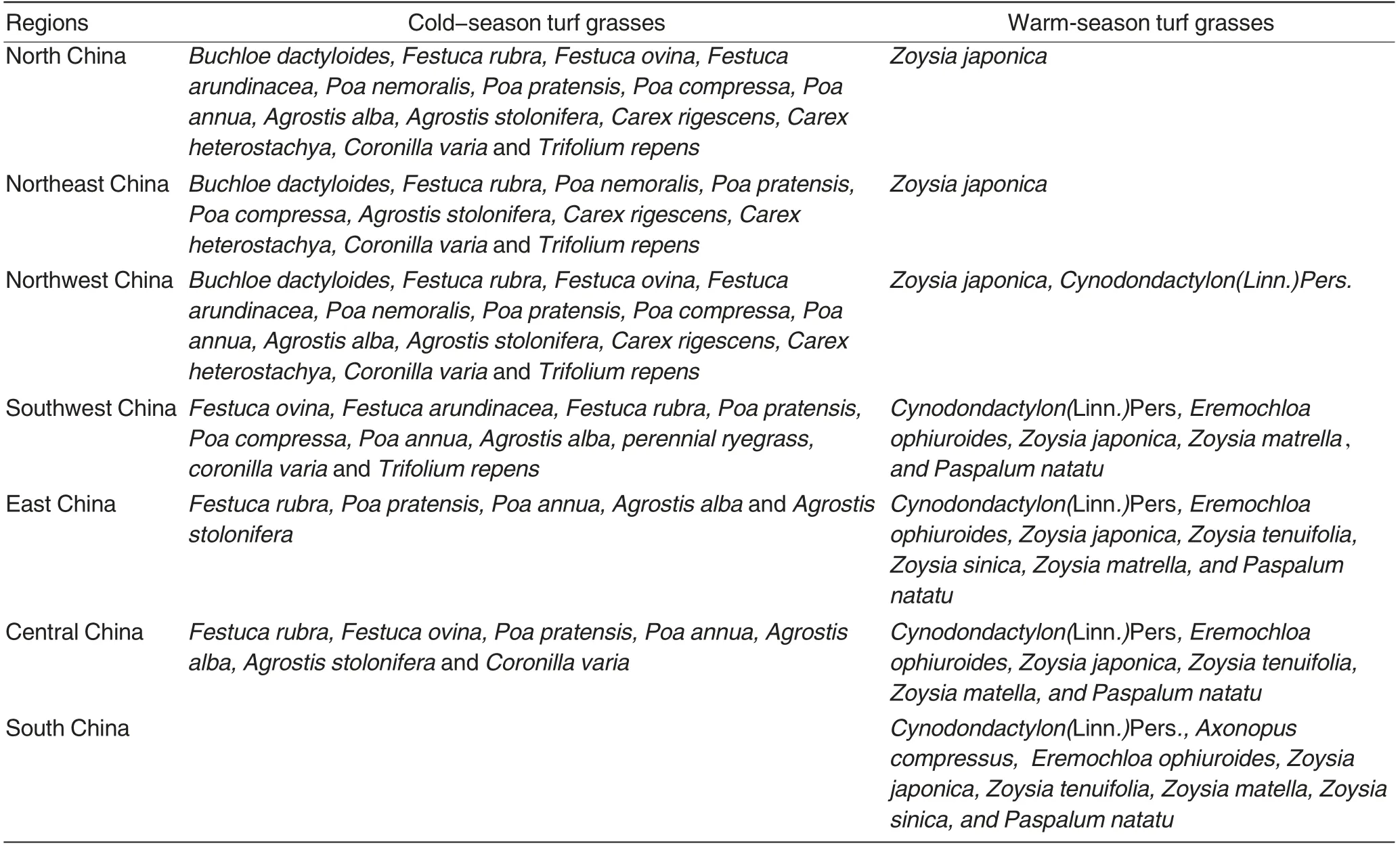
Table 5 Vegetation for slope protection in different regions[23]

Table 6 Shrubs available for slope protection in most areas in China
In addition, the dug stones would be used for filling subgrade and the filled slopes should be treated as follows:
Stone-based subgrades shouldbe filled with sticky soils at 1 m and at sides, providing conditions for following afforestation. After filling of subgrades, similar slopes can be treated with the same method.
Large-size rocks should be pitched at sides of subgrades step by step and the cracks can be filled with soils for vegetation growth.
As for subgrades filled with gravels, plant seeds and shrub seeds can be sprayed on slopes for protection.
Eco-protection of excavation section Slope protection technology with vegetation along expressway is newly developed in the decade, functioning well in protecting slopes and improving environment, which forms sloe protection system, together with traditional engineering protection. According to different soil textures of slopes, many specific technologies have been developed, including artificial grassing, turf paving, hydraulic seeding, geomat grassing, and soil spraying. The aim of slope protection with vegetation is to fix soils and protect slopes, prevent scouring and beautify environment. In construction,expressways would go through some hills, and excavation would be a priority,taking place of constructing tunnels,shaping most slopes and bare rocks,and posing threats on road servicelife,transportation, eco-environment and social effect. In contrast, countermeasures are provided above responding to specific demands,considering slope property and soil texture, which would guarantee eco-protection effects(Table 4).
Eco-protection of interchange and service station Eco-protection of interchange and service station could make full use of interchange functions and improved services. With the principle of "necklace" design, natural landscape units along Baoji -Hanzhong Expressway are connected, integrating the whole design, and the road goes well with nearby environment, creasing attracting natural scenery, improving natural environment and weakening artificial trace[31].The service station, Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway, besides providing necessary services, will become a displaying and releasing center of tourism-resources and information,oriented by traveling, sightseeing and relaxing. The whole "necklace" route has omitted boring landscapes,and invisibly introduced attracting landscapes for drivers or passengers,shading and introducing methods, so that the drivers and passengers are allowed to drive while enjoying countryside landscape, wetlands, forests and mountains. It can be concluded that the design and construction of Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway firstly introduced the concept of "necklace",characterized by ecology,environment protection,traveling and landscape.As for eco-protection, grass seeds and shrub seeds can be directly sprayed on slopes and the within ranges should be well arranged,adding radiance and beauty to each other among forestsdensely planted trees in mountains,countryside-water flowing beneath a little bridge in planes, and water landscape-aquatic plant in networks of water,nearby landforms and terrain.
Selection of plants for eco-protection According to characters of expressway and the objective of slope planting, vegetation for slope protection should meet following demands[23].
The plants should be adapted to local climate with high tolerance to drought; the plants should be developed roots and tolerant to soil poverty and extensive management; seeds should perform excellently in germination and upgrade fast; with a long greening period, the plant should be perennial; the plant should be easily for cultivation with a high fecundity;the plant should have a long sowing and planting period.In general,most plants for slope protection belong to families of Gramineae and Leguminosae, for gramineous plants usually grow fast,with largely developed roots, but require more fertilizers. As shown in Table 5, on basis of survey on local plants,the chosen plants was coincided with the principle of adapting to local conditions and was suitable to be planted. Hence, most local wild and healthy plants with high adaptability and ornamental value are applied,such as Bermuda grass, ryegrass,Orychophragmus violaceus, wild chrysanthemum flower,Jasminum mesnyi,winter jasmine, Euonymus fortunei,ivy, Lespedeza, Casin bicapsularis,Pyracantha fortuneana,Photinia serrulata, and Pleioblastus yixingensis,which beneficial for plants growth and avoid damages of eternal plants on original eco-environment.
Therefore, different plants area was available according to specific slopes. For example, the combination of grass, grass flower, bamboo, shrub and ivy would well protect eco-environment from short, moderate or long terms consideration, and present an attracting landscape as well. On the other hand, shrubs are less used in China, including Amorpha fruticosa,Caragana microphylla, sea-buckthorn,Lespedeza, rose willow and aalii(Table 6). Currently, the protection from body construction along roadside slopes meets the demands of water and soil conservation,but afforestation of service station and interchanges is not well considered. The research just provided supplementation in terms of common afforestation and landscapestyle demands, respectively, of which the former is suitable for central dividing strip area and side road, and the latter is suitable for service station and interchange.Additionally,forests along the project regions are generally economic forests, consisting of arbor and shrub,which would be transplanted by property owners,individuals or departments, after compensated from construction units. Therefore, the case is not being taken into consideration.
Conclusions
Slope protection should integrate engineering projects and vegetation,from the perspective of ecology to maximize slope protection technology with vegetation,fix slopes and prevent scouring and adapt to nearby ecolandscapes in a coordinated way[32].As environment protection consciousness improves, traditional way for slope protection can not meet social development. In contrast, slope protection technology with vegetation increasing stability of subgrade slopes and restores the destroyed eco-environment,simultaneously.For example,the construction of Baoji-Hanzhong Expressway is of benefits in terms of environment, economy and society, advancing local development. Although original landform is damaged to certain ex-tent, and the abandoned soils and dregs pose threats to erosion, the slope protection technology with vegetation proves to be effective in controlling water and soil erosion.
In conclusion,construction work is complicated and much more for the project region,and it is inevitable to destroy local water and soil conservation facilities because of human activities,such as ground leveling, digging,transportation and filling. The technology of slope protection with vegetation has been widely applied on slopes,but still lag behind of present research and engineering.It has become a research theme of slope protection of subgrade to integrate the technology with engineering protection to improve environment with a premise of slope stability, according to divided erosion duties and prevention ranges, as well as natural and human factors causing erosion. In constructing a project,slope protection technology with vegetation should be well made to prevent water and soil erosion, supplemented by other technologies, in order to maintain eco-environment in the project zone and avoid the destruction of water and soil.
[1]CUI SX(崔淑祥).The application of protection technology with vegetation in subgrade slopes (植被防护技术在路基边坡中的应用)[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering(西部探矿工程),2008(2):160-163.
[2]CUI YQ (崔玉强).Discussions on slope stability and eco-protection(浅议边坡稳定与生态防护)[J].Railway Engineering(铁道建筑),2005(5):68-69.
[3]DUAN XM(段晓明).Ecological application of ecological slope protection and vegetation community selection for slope protection(生态护坡应用及护坡植物群落的选择)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (安徽农业科学).2009(31):45-47.
[4]Highway committee (高速公路丛书编委会).Highway Planning and Design(高速公路规划与设计)[M]. Beijing: Chian Communications Press(北京:人民交通出版社),2003.
[5]GAO ZL(高照良),PENG KS(彭珂珊).Ecological restoration and returning farmlands to forests and grasses in western China(西部地区生态修复与退耕还林还草研究)[M].Beijing:China Culture(北京:中国文史出版社),2005
[6]GAO ZL(高照良).Theory and practice of water and soil conservation compensation in Xinjiang (新疆水土保持生态补偿理论与实践研究)[M].Chengdu:Sichuan S&T Press (成都: 四川科技出版社),2013.
[7]HU ZH(胡中华).Lawn and ground cover plant(草坪与地被植物)[M].Beijing:China Forestry Press(北京:中国林业出版社),1995.
[8]CCCC second highway consultants (交通部第二公路堪察设计研究院). The Handbook of HighwayDesign -Subgrade (公路设计手册一路基)[M].2nd edition. Beijing: China Communications Press(北京:人 民交通出版社),1997.
[9]LI X(李西),LUO CD(罗成德),CHEN QB(陈其兵). Selection of rock-based slopes with vegetation(岩石边坡植被护坡选择初探)[J].Chinese Landscape Architecture(中国园林),2004(9):52-53.
[10]LI XH (李小华). Slope afforestation methods of expressway(高速公路边坡绿化方式的研究)[J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry Science and Technology (内蒙古林业科技),2003(1):47-50.
[11]LI XG(李旭光),WANG WB(王文碧),XU FY (徐福有). Slope afforestation and protection of highway in Japan(日本的公路边坡绿化与防护)[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (公路交通科技),1995(2):59-64.
[12]LI YH (李永红), GAO ZL (高照良),PENG KS (彭珂珊).Farmland protection and sustainable use in China(中国耕地资源保护与可持续利用研究)[M].Beijing:China Yanshi Press(北京:中国言实出版社),2011.
[13]LIU HB (刘洪波).Application of spraying and seeding technology in slope protection of expressways(喷混植草在高速路岩质边坡防护工程中的应用)[J].Shanxi Architecture (山西建筑), 2011(1):47-50..
[14]Shaanxi government(陕西省人民政府).Planning of Beautiful Mountains and Rivers in Shaanxi Province (陕西省山川秀美工程规划)[M].Xi’an:Shaanxi people’s Publishing House(西安:陕西省人民出版社),1999.
[15]Shaanxi provincial department of water resources (陕西省水利厅. 陕西省志)·Water Resources Records (水利志)[M].Beijing:WaterPower Press (北京:水利电力出版社),1997.
[16]Shaanxi water and soil conservation department(陕西省水土保持局.Water and Soil Conservation Division of Cities of Shaanxi Province(陕西省地市水土保持区划)[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi people’s Publishing House(西安:陕西省人民出版社),1988.
[17]WANG Q (汪 群), XU ZC (徐忠诚),ZHOU JW (周建文). Application of spraying and seeding technology in rock-based slope protection and afforestation (喷混植生技术在岩石边坡护坡绿化中的应用)[J].Highway(公路),2007(1):7-8.
[18]WANG DW(王大为),HAN JG(韩继国).Eco-protection of slopes in excavation road sections (高等级公路挖方路段边坡生态防护浅析)[J].Jilin S&T of Communications (吉林交通科技),2007,23(3):3-4.
[19]WANG LX(王礼先).Forestry ecoengineering sciences(林业生态工程学)[M].Beijing:China Forestry Press( 北京:中国林业出版社),1998.
[20]WANG ZG(王志刚),LUO P(罗萍).Exploration of countermeasures of water and soil erosion of expressways in Guangdong Province(广东省高速公路水土流失防治措施探讨)[J]. Guangdong Building Materials (广东建材),2011,21(8):114-116.
[21]XIN J (辛娟).Research of eco-protection of slopes of expressways(高速公路边坡生态防护技术研究)[D].Chang’an University(长安大学),2006.
[22]ZHANG HT(张海涛).Characteristics of water and soil erosion of highways in western China(我国西部公路施工中水土流失特点浅析) [J]. Hunan Hydro&Power (湖南水利水电),2011,21(3):61-63.
[23]ZHANG HJ(张华君),WU SG(吴曙光).Ecologicl protection ways for slope and election of plants(边坡生态防护方法和植物的选择)[J].Technology of Highway and Transport (公路交通技术),2004.23(2).84-86.
[24]ZHANG JY (张俊云),ZHOU DP (周德培),LI SC(李绍才).Brief introduction of study on slope eco -engineering for rock slope protection(岩石边坡生态护坡研究简介)[J].?Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation (水土保持通报),2000(8):44-49.
[25]CHONG XL(种秀灵).高速公路生态绿化植物的选择研究[D].武汉理工大学,2007 年.
[26]ZHOU LE (周利恩),SHANG Y (尚 彦),YU JX (余建新).The summaize of protection technology of project side slope ecological(工程边坡生态防护技术)[J].Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University(云南农业大学学报),2006(8):70-72.
[27]ZHOU QT(周庆桐).Slope afforestation methods(坡面绿化施工法)[M].Beijing:China Communications Press(北京:人民交通出版社),1988.
[28]ZHOU Y(周跃).Vegetation and erosion control: exploration on basic principle of slope engineering(植被与侵蚀控制:坡面生态工程基本原理探索)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报),2000(2):297-300.
[29]XU XB(徐宣斌),ZHAO J(赵军),LI SQ(李世清).Restricted factors in ecological recovery in western area and the selection of evaluation index(西部地区生态修复限制因子及评价指标筛选)[J].Research of Soil adn Water Conservation(水土保持研究),2005(6):42-45.
[30]XU XB (徐宣斌). Exploration of ecoconstruction of water and soil conservation in loess plateau(中国黄土高原地区水土保持生态建设的探讨)[J]. Ecological Economy (生态经济),2012(1):389-393.
[31]XU XB (徐宣斌). Analysis on western development and eco-environment reconstruction at present (现阶段西部大开发与生态环境重建之分析)[J].Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University(Social Science Edition)(青岛农业大学学报(社会科学版)),2002(4):13-165.
[32]LI JQ (李鉴清),ZHANG QG (张庆国).Effects of climate changes on major crops in China and countermeasures(气候变化对我国主要农作物的影响以及适应对策)[A]. Development of Lowcarbon Agriculture to Respond to Climate Change-Low-carbon Agriculture Proceedings (发展低碳农业应对气候变化——低碳农业研讨会论文集)[C].2010 年.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Optimization Model of the Effects of Transplanting Density,Nitrogen and Potassium Fertilization on Yield and Quality of an Aromatic Hybrid Rice "Luyoumingzhan"
- Effects of Anti-wind Erosion with Peanut Stubbles in Sandy Lands during Fallow Period
- Analysis on Resistance of Rice Cultivar Lianjing 7 to Rice Black-streaked Dwarf Disease
- Reduction of Cd,Cu,Ni and Pb Mobility by Active Si
- Seed Morphology and Seedling Variation of Four Ornamental Lupin Pedigrees
- Effects of Planting Density on Yield and Mechanical Harvesting Loss Rate of Brassica napus L.
