陆地棉纤维优势表达基因GhRACK1的克隆与序列分析
庞伟民, 靳 茜, 王旭静, 杨江涛, 吕少溥, 唐巧玲, 王志兴
中国农业科学院生物技术研究所,北京100081
陆地棉纤维优势表达基因GhRACK1的克隆与序列分析
庞伟民, 靳 茜, 王旭静, 杨江涛, 吕少溥, 唐巧玲, 王志兴∗
中国农业科学院生物技术研究所,北京100081
纤维品质改良是我国棉花育种的主要目标之一,纤维特异或优势表达基因的挖掘是利用基因工程手段改良纤维品质的关键。根据苏棉12纤维中优势表达的GhRACK1 EST序列设计引物,通过RACE技术克隆了GhRACK1基因的全长cDNA。推导的氨基酸序列含有4个串联的WD基序,属于WD40重复家族,与已知的RACK1蛋白同源性达70%以上,PDB模拟的蛋白三维结构也与已知的RACK1蛋白结构相似。荧光定量PCR分析表明GhRACK1在纤维中的表达量比叶片中高20倍以上。研究结果为棉花纤维品质改良基因工程提供了新的基因资源。
陆地棉;纤维优势表达;GhRACK1;克隆与分析
随着时代的进步和科技的发展,人们对纤维品质的要求越来越高,我国传统育种的棉花纤维已不能满足高档纺织品的需求,根据2001-2005年农业部对我国棉花主产省主栽品种棉纤维的抽查结果表明,目前我国棉花纤维质量能够满足纺织工业纺中、低档棉纱(32~40支纱)的要求,但可纺高支纱(60~80支)的原棉纤维所占比例较少[1]。这就急需对棉花纤维品质进行改良,纤维品质改良成为我国棉花育种的主要目标之一。
由于受育种周期长、外源种质利用困难、纤维品质与产量性状间呈负相关等因素的限制,用常规育种的方法较难培育出纤维品质优良的棉花新品种。分子生物学的发展为利用基因工程技术改良棉花的纤维品质提供了新的思路。自1992年John[2]首次克隆了棉纤维特异表达基因E6以来,研究者们通过cDNA文库差示筛选技术、抑制差减杂交技术、mRNA差异显示技术等先后从棉花中克隆了数十个棉纤维优势或特异表达的基因[3~5],这为棉花纤维品质改良基因工程提供了丰富的基因资源。但目前仍缺乏有商业化应用前景的纤维发育相关基因。
蛋白激酶 C受体(receptor for activated C kinase 1,RACK1)普遍存在于动植物中,是一种高度保守的WD40重复蛋白。RACK1蛋白最早从烟草愈伤组织中被发现,目前已从拟南芥、水稻、烟草、苜蓿和藻类等多种植物中克隆到了RACK1基因[6~10]。RACK1蛋白在细胞骨架、蛋白运输、细胞信号转导及分生组织形成等生命活动中都扮演重要角色[11]。
本实验室利用差减技术克隆到了纤维伸长期中优势表达的RACK1基因的EST序列,本研究利用RACE技术克隆此EST序列的3′端和5′端序列,获得基因的全长cDNA序列,并对得到的序列进行分析,获得了新的棉纤维优势表达基因GhRACK1,以期为棉花纤维品质改良基因工程提供新的基因资源。
1 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料
取陆地棉苏棉12花后14 d(纤维伸长期)的棉铃,用灭过菌的镊子剥取纤维,液氮速冻后-70℃保存备用。
克隆载体pMD18-T购自TaKaRa公司;感受态菌株Trans10购自全式金公司;琼脂糖胶回收试剂盒购自 BioMed公司;限制性内切酶购自NEB公司和TaKaRa公司;T4 DNA连接酶购自NEB公司;其他常规试剂为分析纯。
引物合成由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司完成。本研究所用引物见表1。序列测定由上海擎科生物股份有限公司和中国农业科学院重大科学工程开放实验室测序部完成。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 全长GhRACK1 cDNA的克隆 参考3′-Full RACE Core Set(TaKaRa公司)试剂盒说明书,以3′RACE cygOuter Primer/p-F2和3′RACE cygInner Primer/p-F3为引物(表 1),通过2次PCR从棉纤维cDNA中扩增得到GhRACK1 3′末端产物,PCR反应条件为:94℃ 5 min;94℃ 45 s,55℃ 45 s,72℃ 1min,30个循环;72℃ 8 min。同理,根据TaKaRa公司的5′-Full RACE Kit试剂盒说明书,首先对纤维RNA进行脱磷、脱帽,然后以Oligo dT为引物进行反转录,最后分别以5′RACE cygOuter Primer引物和p-R2,5′RACE cyg Inner Primer引物和p-R3进行两次PCR得到5′末端产物,PCR反应条件为:94℃ 4 min;94℃ 45 s,56℃ 1 min,72℃ 1 min,30个循环;72℃ 8 min。RACE 得到的产物连接到 pMD18T-Vector (TaKaRa公司)上,筛选鉴定阳性克隆,并进行序列测定。用DNAMAN软件分析组装5′和3′序列获得GbXET全长cDNA。

表1 本研究所用引物Table 1 The primer sequences used in this study.
1.2.2 GhRACK1 cDNA基因的表达模式分析 利用热RNAprep Pure Plant Kit(天根生化科技有限公司)提取陆地棉苏棉12叶片和花后14 d纤维组织的 RNA,然后根据 RT-PCR试剂盒(Invitrogen公司)说明进行反转录获得叶片和纤维cDNA。同时根据已知的基因序列设计引物pF1和pR1。然后以pF1和pR1为引物,纤维和叶片cDNA为模板进行荧光定量PCR分析,具体操作按照7500荧光定量PCR操作手册进行。
1.2.3 GhRACK1序列分析 采用DNAMAN软件进行基因序列的拼接和同源进化树分析。利用NCBI/BLAST/BLASTp分析 GhRACK1与已知RACK1蛋白的同源性。利用PDB软件进行蛋白结构分析。用Phytozome在线软件分析其在棉花染色体上的定位。
2 结果与分析
2.1 GhRACK1基因全长cDNA的获得
根据已知的GhRACK1 EST序列设计引物,利用3′RACE和PCR扩增得到一条200 bp左右的条带,5′RACE和PCR扩增得到一条1.2 kb左右的条带(图1A、B),测序结果表明它们分别是基因的3′和5′末端序列,经DNAMAN软件分析后拼接得到了基因的全长cDNA序列。根据拼接得到的基因序列设计引物,以花后 14 d的纤维cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增,得到了GhRACK1的全长 cDNA(图 1C)。测序证明扩增得到的GhRACK1与拼接得到的序列完全一致。
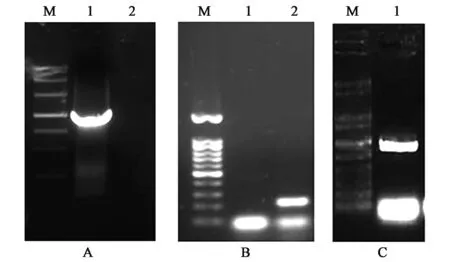
图1 GhRACK1基因扩增产物电泳图Fig.1 PCR results of GhRACK1 gene.
2.2 GhRACK1基因的序列分析
获得的 GhRACK1全长1 375 bp,其中包括67 bp的5′非翻译区,984 bp的开放阅读框(open reading frame,ORF),324 bp的3′非翻译区,ORF编码一个由327个氨基酸构成的蛋白质,分子量为32 kDa(图2)。BLASTn比对结果表明,获得的GhRACK1基因与已知的RACK1基因同源性较高,与木瓜和拟南芥中的RACK1基因的核苷酸序列同源性分别为77.13%和74.77%。Phytozome在线软件分析表明GhRACK1基因位于第6号染色体上。

图2 推导的GhRACK1蛋白的氨基酸序列Fig.2 Deduced amino acid sequence of GhRACK1 protein.
蛋白同源性分析结果表明,推导的蛋白与WD40重复蛋白家族中的RACK1蛋白具有很高的相似性,与木瓜中的RACK1蛋白(O24076)同源性最高,亲缘关系最近,相似性可达89%,其次为油菜(Q39336),相似性为88%;与其他已知的RACK1蛋白的相似性也都在80%以上,如与拟南芥(NP188441.1)和甜椒(AJE63428.1)中的RACK1相似性分别为85%和84%(图3)。而且推导的氨基酸序列中含有3个GH和5个WD二肽保守序列,形成3个串联的WD基序(图2)。PDB模拟蛋白三维结构显示,推导的氨基酸序列能形成7片螺旋桨结构,而且每个浆片包含4个反向平行的β折叠(图4,彩图见图版一)。

图3 推导的GhRACK1氨基酸序列与已知RACK1蛋白的同源进化树分析Fig.3 Homologous tree analysis of deduced GhRACK1 amino acid sequence and other known RACK1 protein.
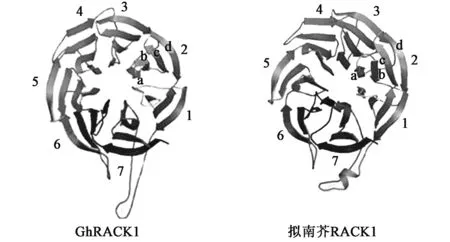
图4 模拟的GhRACK1蛋白与拟南芥RACK1三维结构之间的比较Fig.4 Comparison of dimensional structure of GhRACK1 and Arobidopsis RACK1 protein.
2.3 GhRACK1的组织表达特异性分析
以陆地棉苏棉12叶片和花后14 d纤维的cDNA为模板进行荧光定量PCR分析,结果表明GhRACK1在纤维中高表达,在叶片中只有微量表达,纤维中的表达量是叶片中表达量的20倍左右,为纤维优势表达基因(图5)。
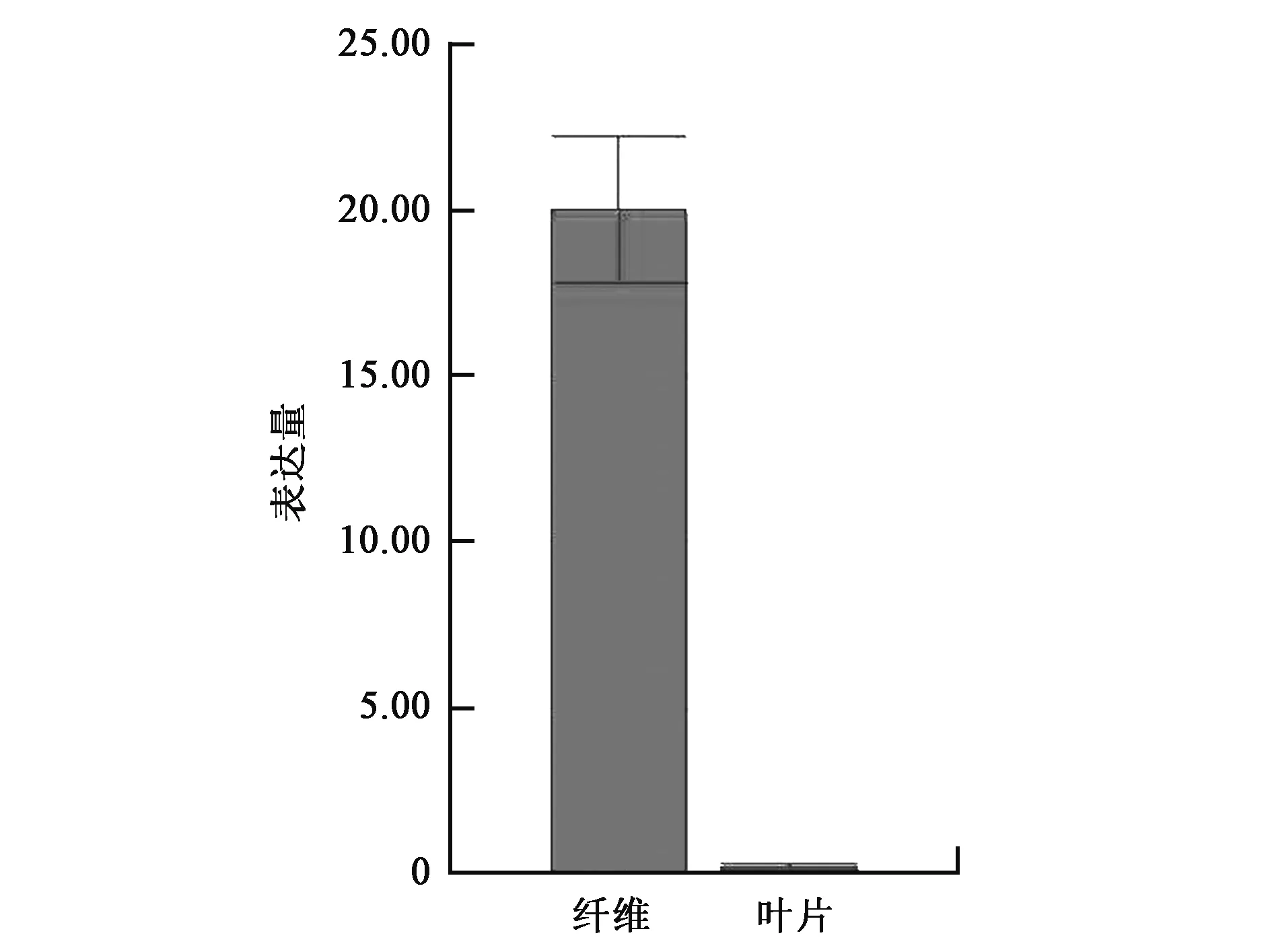
图5 qPCR分析GhRACK1基因在叶片和纤维中的表达量Fig.5 Expression analysis of GhRACK1 gene between leaf and fiber by qPCR.
3 讨论
RACK1蛋白是一种高度保守的WD40重复蛋白。WD40重复蛋白一般含有1~10个串联的WD40基序。WD40基序以甘氨酸-组氨酸(GH)开始,色氨酸-天冬氨酸(WD)保守二肽结尾[12]。Ullah等[13]研究表明拟南芥RACK1具有7片螺旋桨片,每个桨片包含4个反向平行的β折叠片。本研究克隆的基因推导的氨基酸序列与已知RACK1蛋白的同源性在80%以上,含有4个串联的WD基序,PDB预测的蛋白三维结构与已知RACK1蛋白的三维结构相似,由此推测克隆的基因为陆地棉中的RACK1基因,命名为GhRACK1。
棉花纤维的发育与激素调控、细胞壁代谢、信号传导、脂肪酸代谢、糖代谢和转录因子调控等多个方面相关[14~18]。研究表明:木葡聚糖内转糖苷酶(xyloglucan endotransglycosylases/hydrolases)是一种细胞壁松弛酶,通过改变细胞壁网络结构导致细胞壁的松弛,在细胞伸长过程中起重要作用,过量表达棉花GhXTH基因能使纤维的长度增加15%~20%[19];一些纤维素合酶基因的表达在纤维发育的次生壁沉积期明显上调[20]。ROS信号传导途径能促进纤维的伸长[21],调控细胞内H2O2含量的基因GhAPX和GhPOX在迅速伸长的棉纤维中优势表达[21~23],蛋白质组学分析表明ROS的动态平衡是调控棉纤维形态产生的主要机制[24]。乙烯作为纤维伸长信号传导过程中的顺势作用因子参与纤维发育[25,26],细胞分裂素能够抑制纤维细胞的伸长[27]。已有研究表明,植物RACK1不仅是信号传导中的主要成员,而且在激素响应中发挥重要作用。如拟南芥RACK1负调控ABA的响应[28],Chen等[29]研究表明拟南芥RACK1A发生缺失突变后,表现出对多种激素反应发生改变。本研究克隆的GhRACK1基因在纤维伸长期优势表达,但GhRACK1如何调控纤维发育仍需进一步深入研究。
[1] 杨伟华,唐淑荣.“十一五”期间我国生产领域棉花纤维品质分析[J].中国化纤,2011,8(上):18-22.
[2] John M E,Crow L J.Gene expression in cotton(Gossypium hirsutum L.)fiber:cloning of the mRNAs[J].Proc.Natl. Acad.Sci.USA,1992,89(13):5769-5773.
[3] Huang G Q,Gong SY,Li X B,et al..A fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein,GhFLA1,is involved in fiber initiation and elongation of cotton[J].Plant Physiol.,2013,161(3):1278 -1290.
[4] Pear JR,Kawagoe Y,Schreckengost W E,et al..Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase[J].Proc.Natl.Acad. Sci.USA,1996,93:12637-12642.
[5] 吕少溥,王旭静,唐巧玲,等.棉纤维特异基因及其启动子的研究进展[J].生物技术进展,2014,4(1):1-6.
[6] Ishida S,Takahashi Y,Naqata T.Isolation of cDNA of an auxin-regulated gene encoding a G protein beta subunit-like protein from tobacco BY-2 cells[J].Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA,1993,90:11152-11156.
[7] Iwasaki T,Skelton R E.The XY-centring algorithm for the dual LMI problem:a new approach to fixed-order control design [J].Int.J.Control,1995,62(6):1257-1272.
[8] McKhann GM,D'Ambrosio R,Janiqro D.Heterogeneity of astrocyte resting membrane potentials and intercellular coupling revealed by whole-cell and gramicidin-perforated patch recordings from cultured neocortical and hippocampal slice astrocytes[J].J.Neurosci.,1997,17(18):6850-6863.
[9] Kwak T J,Zedler JB.Food web analysis of southern California coastalwetlands usingmultiple stable isotopes[J].Oecologia,1997,110(2):262-277.
[10] Vahlkamp L,Palme K,AtArc A.Accession No.U77381,the Arabidopsis thaliana homolog of the tobacco ArcA gene (PGR97-145)[J].Plant Physiol.,1997,115:863.
[11] Ron D,Mochly-Rosen D.Agonists and antagonists of protein kinase C function,derived from its binding proteins[J].J.Biol.Chem.,1994,269:21395-21398.
[12] Smith T F,Gaitatzes C,Saxena K,et al..The WD repeat:a common architecture for diverse functions[J].Trends Biochem.Sci.,1999,24(5):181-185.
[13] Ullah H,Scappini E L,Moon A F,et al..Structure of a signal transduction regulator,RACK1,from Arabidopsis thaliana [J].Protein Sci.,2008,17,1771-1780.
[14] An C,Saha S,Jenkins JN,et al..Transcriptome profiling,sequence characterization,and SNP-based chromosomal assignment of the EXPANSIN genes in cotton[J].Mol.Genet.Genomics,2007,278(5):539-553.
[15] Hovav R,Udall J A,Hovav E,et al..A majority of cotton genes are expressed in single-celled fiber[J].Planta,2008,227(2):319-329.
[16] Ma J,Wei H,Song M,et al..Transcriptome profiling analysis reveals that flavonoid and ascorbate-glutathione cycle are important during another development in upland cotton[J].PLoS ONE,2012,7(11):e49244.
[17] Wang Q Q,Liu F,Chen X S,et al..Transcriptome profiling of early developing cotton fiber by deep-sequencing revealssignificantly differential expression of genes in a fuzzless/lintlessmutant[J].BMC Genomics,2010,96(6):369-376.
[18] Fang L,Tian R,Li X,et al..Cotton fiber elongation network revealed by expression profiling of longer fiber lines introgressed with different Gossypium barbadense chromosome segments[J]. BMCGenomics,2014,15(1):472-472.
[19] Lee J,Burns TH,Light G,et al..Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase genes in cotton and their role in fiber elongation[J].Planta,2010,232(5):1191-1205.
[20] Chen X Y,Gou JY,Wang L J,et al..Gene expression and metabolite profiles of cotton fiber during cell elongation and secondary cell wall synthesis[J].Cell Res.,2007,17(5):422 -434.
[21] Qin Y M,Hu C Y,Zhu Y X.The ascorbate peroxidase regulated by H2O2and ethylene is involved in cotton fiber cell elongation by modulating ROS homeostasis[J].Plant Sign. Behav.,2008,3(3):194-196.
[22] Li H,Qin Y,Pang Y,et al..A cotton ascorbate peroxidase is involved in hydrogen peroxide homeostasis during fibre cell development[J].New Phytol.,2007,175(3):462-471.
[23] MeiW,Qin Y,Song W,et al..Cotton GhPOX1 encoding plant classⅢperoxidasemay be responsible for the high level of reactive oxygen species production that is related to cotton fiber elongation[J].Acta Genet.Sin.,2009,36(3):141 -150.
[24] Padmalatha K V,Patil D P,Kumar K,et al..Functional genomics of fuzzless-lintlessmutant of Gossypium hirsutum L.cv. MCU5 reveal key genes and pathways involved in cotton fibre initiation and elongation[J].BMC Genomics,2012,13 (1):624.
[25] Qin YM,Zhu Y X.How cotton fibers elongate:A tale of linear cell-growth mode[J].Curr.Opin.Plant Biol.,2011,14(1): 106-111.
[26] Wang H,Wang M,Qin Y,et al..1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase 2 is phosphorylated by calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 during cotton fiber elongation[J].Acta Biochim.Biophys.Sin.,2011,43(8):654-661.
[27] Hinchliffe D J,Turley R B,Naoumkina M,et al..Acombined functional and structural genomics approach identified an ESTSSR markerwith complete linkage to the ligon lintless-2 genetic locus in cotton[J].BMCGenomics,2011,12:445.
[28] Guo J J,Wang JB,Xi L,Huang W D,et al..RACK1 is a negative regulator of ABA responses in Arabidopsis[J].J.Exp. Bot.,2009,60:3819-3833.
[29] Chen JG,Ullah H,Temple B,et al..RACK1mediatesmultiple hormone responsiveness and developmental processes in Arabidopsis[J].J.Exp.Bot.,2006,57:2697-2708.
Cloning and Sequence Analysis of GhRACK1 Gene Dom inant Expressed in Fiber from Gossypium hirsutum
PANG Wei-min,JIN Xi,WANG Xu-jing,YANG Jiang-tao,LV Shao-pu,TANG Qiao-ling,WANG Zhi-xing∗
Biotechnology Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Scienses,Beijing 100081,China
Fiber quality improvement is one of themain targets in cotton breeding.The discovery of specific or dominantexpressed gene in fiber is the key factor that improved fiber quality by using genetic engineering strategy.In this study,we used G.hirsutum var.Sumian12 as a starting material to clone the full-length cDNA of GhRACK1 gene by RACE techniques according known EST sequence.The deduced amino acid sequence of GhRACK1 was highly homologous to the other known RACK1 proteins and contained 4 cascade WD motifs,which belonged to WD40 family.GhRACK1 protein and known RACE1 had similar three dimensional structure by PDB simulation.qPCR results indicated that the expression level of GhRACK1 in fiber was more than 20-fold compared with leaf.This study provided new gene resource for cotton fiber improvement.
Gossypium hirsutum;fiber-superiority expression;GhRACK1;cloning and sequence analysis
10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2015.05.07
2015-06-03;接受日期:2015-07-13
国家转基因生物新品种培育重大专项(2014ZX08005-003)资助。
庞伟民,硕士研究生,研究方向为转基因生物安全。Tel:010-82109866;E-mail:543513441@qq.com。∗通信作者:王志兴,研究员,博士,主要从事植物基因工程与转基因生物安全研究。Tel:010-82106102;E-mail:wangcotton@126.com

