埃克替尼治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效及预后观察
贺小停,刘超英,陆培华,杭志强
·专题研究·
埃克替尼治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效及预后观察
贺小停,刘超英,陆培华,杭志强
目的 探讨埃克替尼治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的疗效及预后。方法 选取2011—2013年无锡市人民医院收治并经病理证实的晚期NSCLC患者46例,口服埃克替尼125 mg/次,3次/d,直至肿瘤进展或出现不能耐受的毒副作用,评估无进展生存期(PFS)、疾病控制率(DCR)及毒副作用。结果 46例患者中位PFS为6个月。Cox回归分析结果显示,吸烟、病理类型、埃克替尼治疗、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)与中位PFS有回归关系(P<0.05);性别、东部肿瘤协作组(ECOG)评分与中位PFS无回归关系(P>0.05)。EGFR阳性NSCLC患者中,埃克替尼一线治疗者较二线治疗者PFS延长(χ2=10.99,P<0.001)。46例患者未观察到完全缓解(CR)患者,部分缓解(PR)19例,稳定(SD)17例,疾病进展(PD)10例,DCR为78.3%(36/46)。不同性别、吸烟、ECOG评分、病理类型、埃克替尼治疗、EGFR的NSCLC患者DCR比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。主要的毒副作用是Ⅰ~Ⅱ级皮疹、腹泻、转氨酶升高,总治疗相关毒副作用发生率为26.1%(12/46)。结论 埃克替尼是不吸烟、EGFR阳性的晚期腺癌NSCLC患者安全有效的治疗选择。且对于EGFR阳性的NSCLC患者,埃克替尼应作为一线治疗药物。
癌,非小细胞肺;埃克替尼;治疗结果
贺小停,刘超英,陆培华,等.埃克替尼治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效及预后观察[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(9):998-1001.[www.chinagp.net]
He XT,Liu CY,Lu PH,et al.Efficacy of icotinib in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer and prognosis evaluation[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(9):998-1001.
肺癌是肿瘤死亡的第一位原因,其中,80%为非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC),长久以来,晚期NSCLC的主要治疗方式为化疗,中位生存期只有8~11个月[1-3]。表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)-酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKI)极大提高了EGFR突变的晚期NSCLC患者的临床疗效。Sebastian等[4]综合分析了针对有EGFR突变的NSCLC的一线治疗的Ⅲ期临床试验,认为吉非替尼、厄洛替尼及阿法替尼等EGFR-TKI是标准治疗,且应该作为一线治疗。埃克替尼作为我国首个自主研发的小分子EGFR-TKI,Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期临床试验显示,埃克替尼有较好的临床疗效及安全性[5-6]。Ⅲ期临床试验提示,埃克替尼二、三线治疗NSCLC的疗效与吉非替尼相当,亚组分析提示,埃克替尼治疗非腺癌NSCLC患者的无进展生存期(PFS)甚至优于吉非替尼,而安全性方面,埃克替尼治疗相关毒副作用和腹泻的发生率更低[7]。本研究回顾性评估埃克替尼治疗晚期NSCLC的疗效及预后。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 选取2011—2013年无锡市人民医院收治并经病理证实的晚期NSCLC患者46例为研究对象,其中男22例,女24例;年龄24~82岁,中位年龄65岁;腺癌30例,非腺癌16例;EGFR阳性33例,阴性13例。入组标准:均为经病理证实的晚期NSCLC,进行EGFR检测,至少有一个可进行实体瘤疗效评价标准(RECIST)[8]评估的病灶,按东部肿瘤协作组(ECOG)[9]评价功能状态为0~2分,预计生存期大于3个月,至少口服盐酸埃克替尼片(凯美纳)4周。患者均知情同意。
1.2 治疗方法及临床评估 口服埃克替尼125 mg/次,3次/d,直至肿瘤进展或出现不能耐受的毒副作用。给药4周后进行首次评估,以后每6周评估1次,按RECIST[8]评价近期疗效,包括完全缓解(CR)、部分缓解(PR)、稳定(SD)和疾病进展(PD)。主要指标为PFS及疾病控制率〔DCR=(CR+PR+SD)/总例数〕。毒副作用分级按照加拿大国立癌症研究所扩大通用毒性标准(NCIC CTG)[10]。
1.3 统计学方法 采用Stata 12.0软件进行统计分析,应用Cox回归分析评估临床病理因素对PFS的影响;χ2检验评估临床病理因素对DCR的影响;亚组间生存分析应用Kaplan-Meier分析和Log-rank检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 NSCLC患者中位PFS影响因素Cox回归分析 46例患者中位PFS为6个月。以中位PFS为因变量,性别、吸烟、ECOG评分、病理类型、埃克替尼治疗、EGFR为自变量(见表1),进行Cox回归分析,结果显示,吸烟、病理类型、埃克替尼治疗、EGFR与中位PFS有回归关系(P<0.05);性别、ECOG评分与中位PFS无回归关系(P>0.05,见表2)。EGFR阳性NSCLC患者埃克替尼一线治疗较二线治疗PFS延长,差异有统计学意义(χ2=10.99,P<0.001,见图1)。
2.2 DCR 46例患者中CR 0例,PR 19例,SD 17例,PD 10例,DCR为78.3%(36/46)。不同性别、吸烟情况、ECOG评分、病理类型、埃克替尼治疗、EGFR的NSCLC患者DCR比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表3)。
表1 NSCLC患者中位PFS影响因素赋值
Table 1 Assignment of influencing factors for median PFS of patients with NSCLC
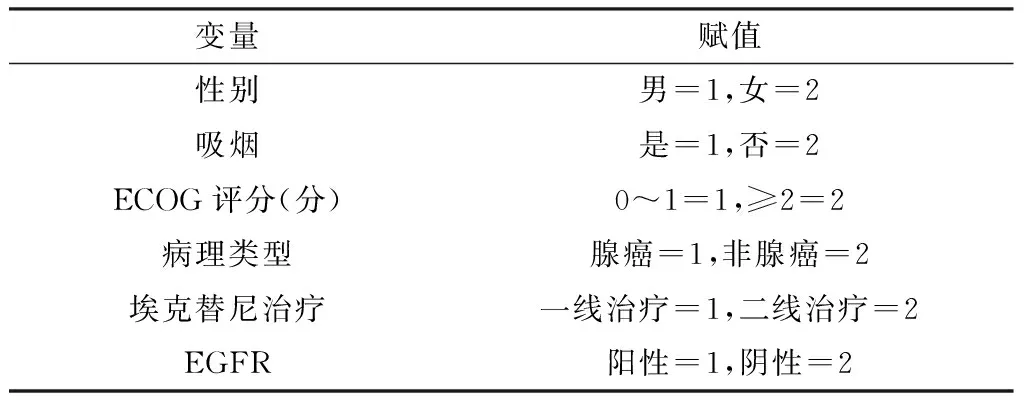
变量赋值性别男=1,女=2吸烟是=1,否=2ECOG评分(分)0~1=1,≥2=2病理类型腺癌=1,非腺癌=2埃克替尼治疗一线治疗=1,二线治疗=2EGFR阳性=1,阴性=2
注:ECOG=东部肿瘤协作组,EGFR=表皮生长因子受体
表2 NSCLC患者中位PFS影响因素Cox回归分析
Table 2 Multivariate Cox regression analysis on influencing factors for median PFS of patients with NSCLC
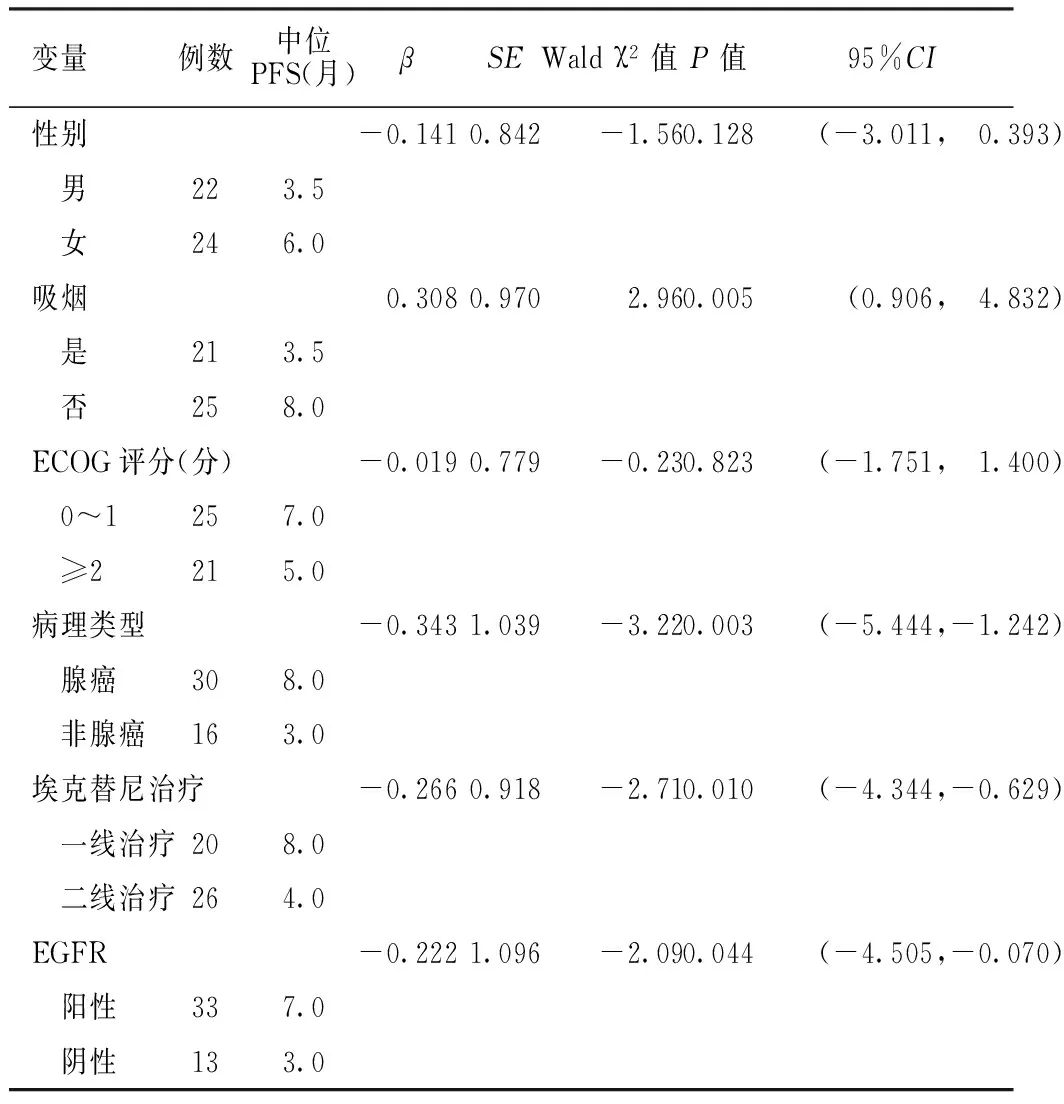
变量例数中位PFS(月)βSEWaldχ2值P值95%CI性别-0.1410.842-1.560.128(-3.011, 0.393) 男223.5 女246.0吸烟0.3080.9702.960.005(0.906, 4.832) 是213.5 否258.0ECOG评分(分)-0.0190.779-0.230.823(-1.751, 1.400) 0~1257.0 ≥2215.0病理类型-0.3431.039-3.220.003(-5.444,-1.242) 腺癌308.0 非腺癌163.0埃克替尼治疗-0.2660.918-2.710.010(-4.344,-0.629) 一线治疗208.0 二线治疗264.0EGFR-0.2221.096-2.090.044(-4.505,-0.070) 阳性337.0 阴性133.0
注:PFS=无进展生存期
表3 不同临床病理特征NSCLC患者DCR比较
Table 3 Comparison of DCR among NSCLC patients with different clinical pathological characteristics
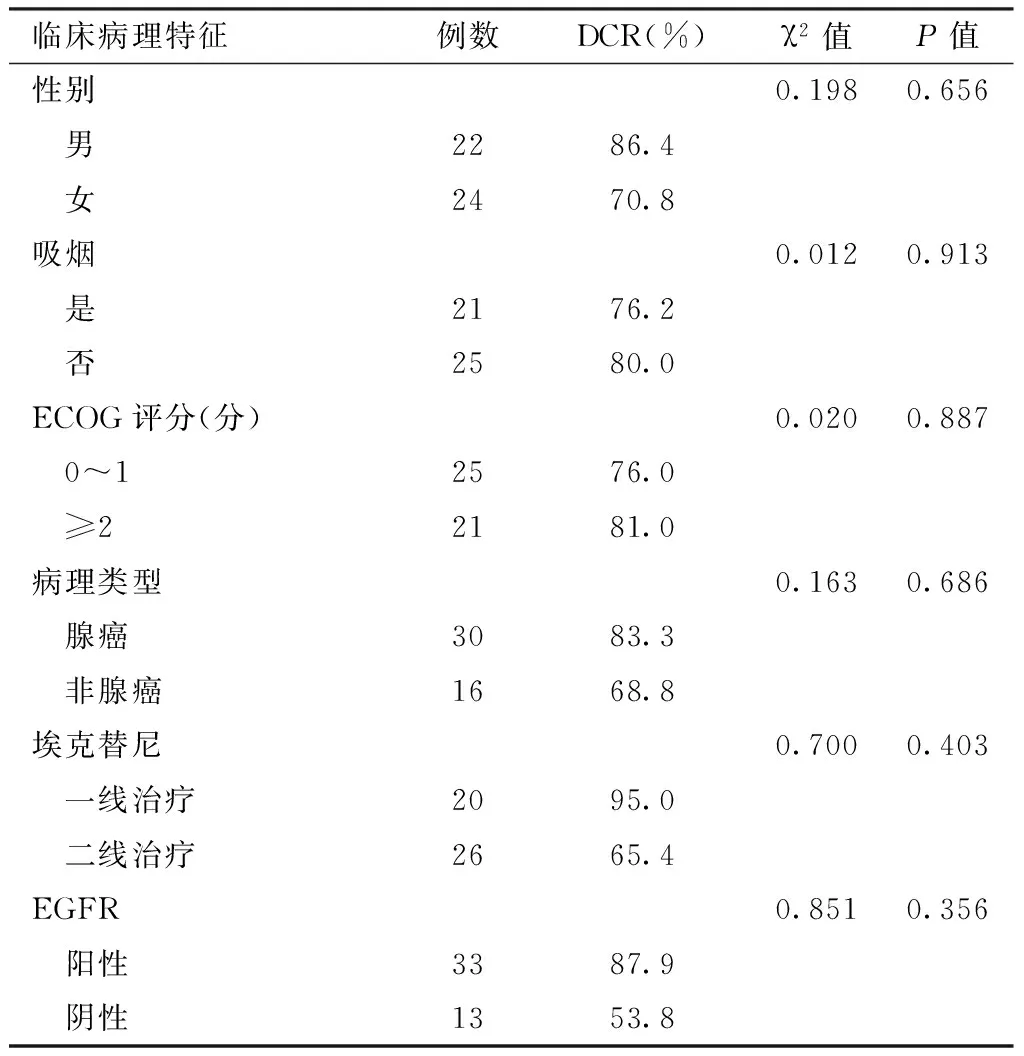
临床病理特征例数DCR(%)χ2值P值性别0.1980.656 男2286.4 女2470.8吸烟0.0120.913 是2176.2 否2580.0ECOG评分(分)0.0200.887 0~12576.0 ≥22181.0病理类型0.1630.686 腺癌3083.3 非腺癌1668.8埃克替尼0.7000.403 一线治疗2095.0 二线治疗2665.4EGFR0.8510.356 阳性3387.9 阴性1353.8
注:DCR=疾病控制率
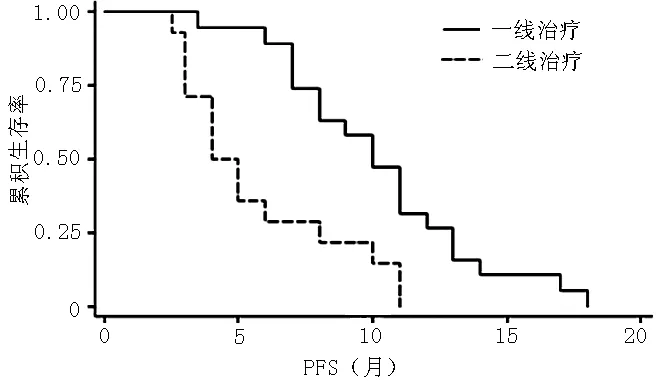
注:PFS=无进展生存期
图1 EGFR阳性NSCLC患者埃克替尼一线治疗与二线治疗PFS比较
Figure 1 Comparison of PFS between EGFR positive NSCLC patients using icotinib as first-line therapy and using icotinib as second-line therapy
2.3 毒副作用 46例患者主要的毒副作用是Ⅰ~Ⅱ级皮疹、腹泻和轻度转氨酶升高,皮疹和腹泻多在用药1周~1个月内出现,其中单纯皮疹3例(6.5%),单纯腹泻4例(8.7%),腹泻合并皮疹2例(4.3%),腹泻总发生率为13.0%(6/46),皮疹总发生率为10.9%(5/46),轻度转氨酶升高3例(6.5%),总治疗相关毒副作用发生率为26.1%(12/46)。未出现Ⅲ级以上的毒副作用,未观察到血液系统毒性及间质性肺炎表现。
3 讨论
超过50%的亚洲人群存在EGFR突变[11],包括外显子19和外显子21(L858R),两者的突变导致酪氨酸酶的活化,进而对小分子的TKI治疗敏感,如厄洛替尼、吉非替尼和阿法替尼[12]。回顾性研究证实,有EGFR突变的肺腺癌患者,EGFR-TKI单药治疗的客观缓解率为80%,中位PFS为13个月[13]。
埃克替尼作为我国首个自主研发的小分子EGFR-TKI,在临床应用中显示了较好的疗效。本研究结果显示,不吸烟、腺癌、EGFR阳性的患者接受埃克替尼治疗可获得更长的PFS,这与既往EGFR-TKI的研究一致[14]。本研究共随访36个月,4例未达到PFS的研究终点,中位PFS为6个月。Shao等[15]研究提示,埃克替尼二、三线治疗NSCLC的中位PFS为5.03个月,一项大宗的头对头Ⅲ期临床试验显示,埃克替尼二、三线治疗晚期NSCLC的中位PFS为4.6个月[7],与吉非替尼相当,结果要略低于本研究,除了考虑本研究中EGFR阳性患者的比例较高,还可能因为本研究中包括埃克替尼一线治疗所致。
本研究中有5例EGFR阴性患者因高龄或体能状态较差,不愿进行全身化疗而一线应用埃克替尼,二线治疗中有6例EGFR阴性患者应用埃克替尼,部分为回顾性检测,这与当时的共识有关,即二线治疗中不需要检测EGFR状态有关。本研究提示,EGFR阳性NSCLC患者埃克替尼一线治疗PFS长于二线治疗,可能与化疗会影响EGFR的突变状态。研究显示,是否经历过全身治疗(化疗或TKI治疗)会影响EGFR的突变状态,在NSCLC的发展过程中,进行过全身治疗的患者中EGFR状态改变发生率为13.6%,未经过全身治疗的为9.3%,而进行过TKI治疗的则高达26.3%[16]。以上提示,对于EGFR阳性的NSCLC患者,埃克替尼应作为一线治疗,同时也在一定程度上解释了TKI耐药的原因。除了治疗的影响外,原发病灶的不同部位[17]、原发灶与转移灶之间[18]、肿瘤发展的不同时期[16]、检测方法[19]均会影响EGFR的结果。因此,为了提高TKI治疗NSCLC的疗效,需要进一步研究来确定更好的检测部位、更灵敏的检测方法,并且要在病情变化后重新检测EGFR的状态。但本研究的样本量相对较小,且未进行总生存期(OS)分析,无法判断对于EGFR阳性的NSCLC患者是先靶向治疗序贯化疗较好还是化疗序贯靶向治疗较好,因此尚需进一步研究证实。
Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期临床试验显示,埃克替尼最常见的毒副作用为皮疹和腹泻[5-6]。Ⅲ期临床研究显示,埃克替尼治疗相关毒副作用的发生率为61%,低于吉非替尼[7]。埃克替尼较高的安全性考虑与其对EGFR的高度选择性有关[20],埃克替尼可以通过CYP2E1、CYP2C19等多种酶代谢降低药物蓄积产生的毒副作用[21]。Ⅲ期临床研究显示,埃克替尼治疗NSCLC的DCR为69.7%[16]。本研究中,DCR为78.3%,未观察到CR患者,PR 19例、SD 17例,与既往研究相当[5-7,15]。
综上所述,埃克替尼是EGFR阳性的晚期NSCLC有效、安全的治疗方法,对于不吸烟、腺癌患者效果更好;且与吉非替尼、厄洛替尼相比,埃克替尼的化学结构、作用机制和临床疗效与其相仿,但因其价格低、毒副作用少[22],故更适合中国的国情。
[1]Siegel R,Naishadham D,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2013[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2013,63(1):11-30.
[2]Méndez M,Custodio A,Provencio M.New molecular targeted therapies for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J].J Thorac Dis,2011,3(1):30-56.
[3]Ramalingam S,Belani C.Systemic chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer:recent advances and future directions[J].Oncologist,2008,13(Suppl 1):5-13.
[4]Sebastian M,Schmittel A,Reck M.First-line treatment of EGFR-mutated nonsmall cell lung cancer:critical review on study methodology[J].Eur Respir Rev,2014,23(131):92-105.
[5]Wang HP,Zhang L,Wang YX,et al.Phase Ⅰ trial of icotinib,a novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J].Chin Med J(Engl),2011,124(13):1933.
[6]Zhao Q,Shentu J,Xu N,et al.Phase Ⅰ study of icotinib hydrochloride (BPI-2009H),an oral EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor,in patients with advanced NSCLC and other solid tumors[J].Lung Cancer,2011,73(2):195-202.
[7]Shi Y,Zhang L,Liu X,et al.Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ICOGEN):a randomised,double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J].Lancet Oncol,2013,14(10):953-961.
[8]Eisenhauer EA,Therasse P,Bogaerts J,et al.New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1)[J].Eur J Cancer,2009,45(2):228-247.
[9]Buccheri G,Ferrigno D,Tamburini M.Karnofsky and ECOG performance status scoring in lung cancer:a prospective,longitudinal study of 536 patients from a single institution[J].Eur J Cancer,1996,32A(7):1135-1141.
[10]Shimizu T,Saijo N.Common toxicity criteria:version 2.0,an improved reference for grading the adverse reaction of cancer treatment[J].Nihon Rinsho,2003,61(6):937-942.
[11]Hirsch FR,Bunn PA Jr.EGFR testing in lung cancer is ready for prime time[J].Lancet Oncol,2009,10(5):432-433.
[12]Langer CJ.Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer:is afatinib better or simply newer? [J].J Clin Oncol,2013,31(27):3303-3306.
[13]Miller VA,Riely GJ,Zakowski MF,et al.Molecular characteristics of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and adenocarcinoma,bronchioloalveolar carcinoma subtype,predict response to erlotinib[J].J Clin Oncol,2008,26(9):1472-1478.
[14]Kris MG,Natale RB,Herbst RS,et al.Efficacy of gefitinib,an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase,in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer:a randomized trial[J].JAMA,2003,290(16):2149-2158.
[15]Shao L,Zhang B,He C,et al.Efficacy and safety of icotinib in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer after failure of chemotherapy[J].Chin Med J (Engl),2014,127(2):266-271.
[16]Chen ZY,Zhong WZ,Zhang XC,et al.EGFR mutation heterogeneity and the mixed response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors of lung adenocarcinomas[J].Oncologist,2012,17(7):978-985.
[17]Sakurada A,Lara-Guerra H,Liu N,et al.Tissue heterogeneity of EGFR mutation in lung adenocarcinoma[J].J Thorac Oncol,2008,3(5):527-529.
[18]Park S,Holmes-Tisch AJ,Cho EY,et al.Discordance of molecular biomarkers associated with epidermal growth factor receptor pathway between primary tumors and lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer[J].J Thorac Oncol,2009,4(7):809-815.
[19]Bai H,Wang Z,Wang Y,et al.Detection and clinical significance of intratumoral EGFR mutational heterogeneity in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J].PLoS One,2013,8(2):e54170.
[20]Tan F,Shen X,Wang D,et al.Icotinib (BPI-2009H),a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor,displays potent efficacy in preclinical studies[J].Lung Cancer,2012,76(2):177-182.
[21]Liu D,Jiang J,Zhang L,et al.Metabolite characterization of a novel anti-cancer agent,icotinib,in humans through liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry[J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2011,25(15):2131-2140.
[22]Guan YS,He Q,Li M.Icotinib:activity and clinical application in Chinese patients with lung cancer[J].Expert Opin Pharmacother,2014,15(5):717-728.
(本文编辑:陈素芳)
Efficacy of Icotinib in Treatment of Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Prognosis Evaluation
HEXiao-ting,LIUChao-ying,LUPei-hua,etal.
DepartmentofOncology,WuxiPeople′sHospital,Wuxi214043,China
Objective To investigate the efficacy of icotinib in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and prognosis.Methods 46 patients with pathologically proven advanced NSCLC who were admitted to Wuxi People′s Hospital from 2011 to 2013,were selected as study subjects,all cases take icotinib orally (125 mg per time,3 times a day),when tumor development or intolerant toxic and side effects were observed,the icotinib treatment was terminated.The progression-free survival (PFS),disease control rate (DCR) and toxic and side effects were evaluated.Results The median PFS of 46 cases was 6 months.According to Cox regression analysis results,smoking,pathological type,icotinib treatment and EGFR were significantly associated with median PFS (P<0.05),while gender and ECOG score were not significantly associated with median PFS (P>0.05).Among EGFR positive NSCLC patients,PFS of patients using icotinib as first-line therapy was significantly longer than that of patients using icotinib as second-line therapy (χ2=10.99,P<0.001).Among 46 cases,CR was not found,19 cases reached PR,17 cases reached SD,10 cases reached PD,the disease control rate (DCR) was 78.3%(36/46).The DCR of NSCLC patients did not vary significantly by gender,smoking,ECOG score,pathological type,icotinib treatment type and EGFR property (P>0.05).No complete response occurred.The main toxic and side effects were grade 1 or 2 rash,diarrhea and elevation of transaminase,the incidence of therapy-related toxic and side effects was 26.1% (12/46).Conclusion Icotinib is effective and safe for nonsmoking patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC.And for patients with EGFR mutation,icotinib should be used as the first-line treatment.
Carcinoma,non-small cell lung;Icotinib;Treatment outcome
214043江苏省无锡市人民医院肿瘤科
杭志强,214043江苏省无锡市人民医院肿瘤科;E-mail:87876806@qq.com
R 734.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.09.005
2014-06-18;
2015-01-21)

