MMP7蛋白在百草枯致肺纤维化大鼠肺组织中的表达及其意义
杜妍,张罡,肖莉
(中国医科大学附属盛京医院急诊科,沈阳 110004)
·论著·
MMP7蛋白在百草枯致肺纤维化大鼠肺组织中的表达及其意义
杜妍,张罡,肖莉
(中国医科大学附属盛京医院急诊科,沈阳 110004)
目的探讨基质金属蛋白酶7(MMP7)在百草枯(PQ)诱导的大鼠肺纤维化组织中的表达及意义。方法将48只雄性大鼠随机分为对照组和PQ模型组,每组各24只,PQ模型组以4 mg/mL PQ稀溶液按14 mg/kg剂量一次性腹腔注射,对照组以等量生理盐水注射。于建模后7、14、28 d每组分别处死8只大鼠,观察肺组织病理学变化,测定肺组织羟脯氨酸(HYP)含量,观察肺纤维化的严重程度,采用免疫组化染色和光密度分析观察肺组织MMP7表达情况。结果实验动物一般情况:除28 d组有1只大鼠死亡外,其余各组均全部存活至观察终点。腹腔注射PQ后,PQ模型组大鼠体质量逐渐下降,14 d左右开始回升,至28 d时仍低于盐水对照组(P<0.05)。腹腔注射PQ后,模型组大鼠肺系数逐渐增加,并于14 d时达峰值,之后开始回落。PQ模型组大鼠肺组织HYP含量在第7、14、28天时皆高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),且PQ模型组随染毒时间延长HYP含量亦明显增加,并于28 d时达峰值。HE染色显示:PQ模型组大鼠7 d时出现明显肺泡炎表现,14 d时肺泡间隔胶原纤维增生,28 d时大量肺泡结构破坏、萎陷,胶原纤维广泛增生。MMP7在对照组大鼠肺组织表达较弱,PQ模型组大鼠肺组织MMP7表达在第7、14、28天时皆高于相应对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论PQ染毒后大鼠肺组织早期以炎性反应为主,成纤维细胞增多,晚期以纤维化为主,MMP7蛋白在PQ诱导肺纤维化大鼠肺组织内的表达随着肺泡炎或纤维化程度增高而增强,于染毒后28 d时较对照组有明显变化,提示它们可能是PQ致肺纤维化的标志物。
百草枯;肺纤维化;MMP7
百草枯(1,1,-二甲基-4,4,-联吡啶二氯化物,paraquat,PQ),是目前使用最广泛的除草剂之一[1],对人体有较强毒性。PQ中毒以肺部病变最为严重,可导致明显肺纤维化[2]。PQ的中毒机制尚不完全明确,可能是因为PQ可诱导人体器官和组织内产生大量自由基所致。基质金属蛋白酶家族(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)是一类主要降解细胞外基质(extracellular cell matrix,EMC)成分的蛋白酶,本研究组的前期研究发现PQ诱导肺纤维化大鼠肺组织中MMP3和MMP8表达增强,提示二者可能是肺纤维化的标志物。本研究拟对MMP7的表达与PQ诱导肺纤维化的相关性做进一步探讨。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
8周龄雄性SD大鼠48只,体质量250~280 g,由中国医科大学附属盛京医院实验动物中心提供。PQ(99.99%,货号:856177-1G)购自西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司。MMP7抗体(货号:bs-0423R)购自北京博奥森生物技术有限公司,羟脯氨酸含量测定试剂盒(货号:A030-3)购自南京建成生物工程研究所。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 建模、分组及提取标本:将大鼠饲养1周后随机分为2组,每组动物24只。(1)PQ模型组:以4 mg/mL PQ稀释溶液按14 mg/kg给予大鼠一次性腹腔注射;(2)NS对照组:一次性腹腔注射等量0.9%生理盐水。选择固定时间测定动物体质量。分别于给药后7、14、28 d处死动物。去除左肺,-80℃冻存待行肺组织羟脯氨酸含量测定;以4%甲醛溶液对右肺组织进行内固定,以备病理组织检查及免疫组化染色。
1.2.2 肺泡炎症、肺纤维化程度判断:肺组织石蜡切片后行HE染色,在光学显微镜下观察肺组织病理学改变。按照Szapiel等[3]的方法评价肺组织病理变化严重程度。
1.2.3 肺系数的测定:根据实验设计,在建模后7、14、28 d时间点,选取大鼠并分离双肺,称质量并测定肺系数(pulmonary index),肺系数=肺质量(mg)/体质量(g)。
1.2.4 酸水解法测定肺组织羟脯胺酸含量:取-80℃冻存肺组织标本,研磨均浆后,采用酸水解法测定肺组织羟脯胺酸含量,具体步骤按试剂盒说明书操作。
1.2.5 免疫组化SABC法检验肺组织MMP7蛋白含量:肺组织石蜡切片常规脱蜡,水化,然后按免疫组化试剂盒说明书进行操作。应用NIS.Elements F230图像采集软件观察标本图片,计算平均光密度(mean optical density,MOD),应用NIS-Elements BR3.0图像分析软件,以MOD作为光密度分析的半定量参数。
1.3 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 体质量变化分析
NS对照组动物体质量持续增加;PQ模型组动物体质量先有下降,一般在14 d左右逐渐回升,但仍轻于同期对照组。见表1。
表1 2组大鼠体质量变化的比较(,g)Tab.1 Comparison of body weight changes between the two groups(,g)

表1 2组大鼠体质量变化的比较(,g)Tab.1 Comparison of body weight changes between the two groups(,g)
1)P<0.01 vs NS control group.
Group 0 d 7 d 14 d 28 d NS control 252.61±12.08 272.38±11.15 291.43±10.07 351.43±9.26 PQ model 248.33±11.07 236.32±10.431) 228.69±9.521) 242.41±7.521)
2.2 各组大鼠肺组织的病理学改变
肉眼观察:对照组大鼠肺组织表面呈粉红色,质软富有弹性,表面光滑。PQ模型组大鼠染毒第7天肺组织出现充血,表面出血点增多明显,部分呈现灶性瘀斑,肺组织肿胀,体积增大,第14天肺组织充血有所减轻,少数肺叶呈现少量瘀血,肺部肿胀减轻,第28天肺组织呈灰白色,体积减小,弹性降低,肺部表面出现凹凸及纤维化瘢痕。
光镜观察:对照组大鼠肺组织结构完整,肺泡壁结构清晰,无明显充血,水肿及炎症。PQ模型组造模第7天肺组织水肿,肺泡间隔增宽,肺泡腔内出现渗出,肺毛细管扩张充血,可见中性粒细胞及单核巨噬细胞浸润。第14天肺泡间隔进一步增宽,水肿部分消退,肺内炎性细胞聚集,胶原纤维增生。第28天肺泡结构明显增宽,部分塌陷,炎性浸润缓解减轻,胶原纤维及纤维细胞进一步明显增生。见表2,图1。
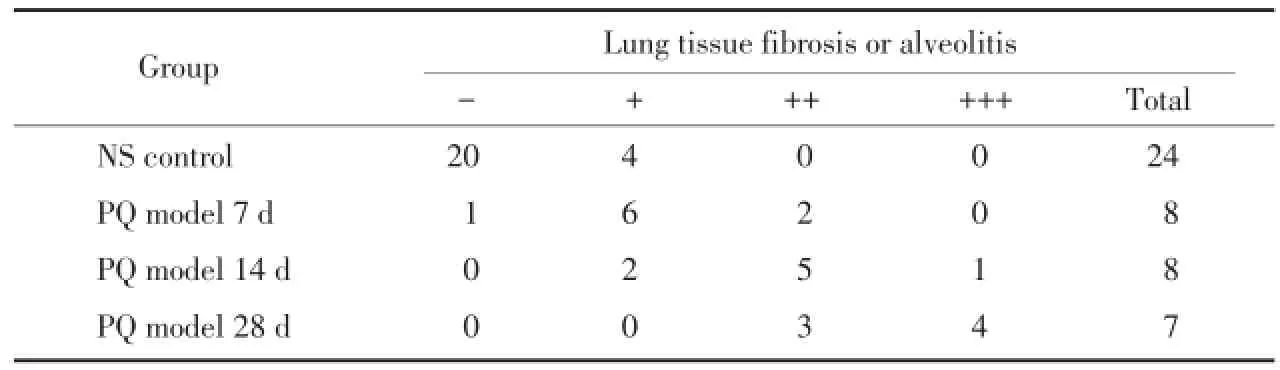
表2 肺组织纤维化或肺泡炎程度的比较(n)Tab.2 Comparison of lung tissue fibrosis or alveolitis(n)

图1 各组大鼠肺组织标本HE染色动态变化 HE×200Fig.1 HE staining dynamic changes of the rat lung tissues HE×200
2.3 各组大鼠肺系数的测定
腹腔注射PQ后,随染毒时间延长肺系数亦有差别,模型组大鼠肺系数明显增加,于14 d时达峰值,之后有所降低。见表3。
表3 各组大鼠肺系数的变化()Tab.3 Changes in lung coefficient in each group()

表3 各组大鼠肺系数的变化()Tab.3 Changes in lung coefficient in each group()
1)P<0.01 vs NS control group.
Group 7 d 14 d 28 d NS control 8.56±0.59 8.31±0.57 8.02±0.52 PQ model 11.31±1.821) 15.37±0.611) 10.15±1.671)
2.4 肺组织羟脯氨酸含量测定
造模后,模型组大鼠肺组织羟脯氨酸含量进行性增高,始终高于同期对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见表4。
2.5 免疫组化法检测MMP7在大鼠肺组织内的含量
PQ组大鼠肺组织中MMP7的表达始终高于同期NS对照组,至28 d时表达最强。见表5,图2。
表4 羟脯氨酸含量测定结果(,μg/mg)Tab.4 Hydroxyproline content in lung tissues(,μg/mg)

表4 羟脯氨酸含量测定结果(,μg/mg)Tab.4 Hydroxyproline content in lung tissues(,μg/mg)
1)P<0.05 vs NS control group:2)P<0.01 vs other time points in the same group.
Group 7 d 14 d 28 d NS control 1.394±0.043 1.402±0.057 1.395±0.064 PQ model 1.687±0.0451),2) 1.906±0.0591),2) 2.725±0.0831),2)
表5 各组标本MMP7平均光密度(MOD)值()Tab.5 The mean optical density(MOD)value of MMP7 in each group()

表5 各组标本MMP7平均光密度(MOD)值()Tab.5 The mean optical density(MOD)value of MMP7 in each group()
1)P<0.05 vs NS control group;2)P<0.01 vs other time points in the same group.
Group 7 d 14 d 28 d NS control 0.304 1±0.030 4 0.307 2±0.025 6 0.311 2±0.032 6 PQ model 0.395 1±0.040 71),2) 0.417 5±0.022 71),2) 0.473 0±0.070 81),2)

图2 各组大鼠肺组织MMP7表达的免疫组化检测结果 ×200Fig.2 MMP7 immunohistochemical observation of the rat lung tissues in each group×200
3 讨论
PQ在1962年作为除草剂上市后,由于具有遇土迅速失活,不损害植物根部,对环境无污染的特点,已在130多个国家广泛使用,而我国是最大的生产国和使用国。自1964年爱尔兰发生了第1例PQ中毒事件以来,PQ中毒日趋增多,已成为继有机磷农药中毒之后最常见的农药中毒。国内报道病死率高达85%~95%,且大多数幸存者存在肺纤维化,预后较差。PQ经多渠道吸收后,通过多胺摄取途径特异性聚集于肺脏[4],重度中毒患者可于短期内死于多器官功能衰竭,中度中毒患者于染毒后24 h迅速出现急性肺损伤症状,进行性发展为急性呼吸窘迫综合征,如1周左右患者仍存活,肺部损伤逐渐加重,可发展为不可逆的肺间质纤维化,后期多死于呼吸衰竭[5]。
羟脯氨酸为胶原纤维所特有,占胶原蛋白成分的13%。胶原纤维是肺纤维化的基础,所以通过测定羟脯氨酸含量可以间接反映胶原含量,可作为衡量胶原代谢的重要指标[6]。
MMPs是一类高度保守的锌离子依赖内肽酶,已分离鉴别出26个成员。MMPs是降解细胞外基质的最重要的酶系,其中的某些成员是迄今发现唯一能降解胶原纤维的酶[7]。MMPs直接以酶原的形式分泌到EMC中,并在正常生理条件下发挥降解作用。MMPs的这一作用可以预防或引发疾病,已在肿瘤、心脑血管疾病、风湿免疫性疾病等多方面被广泛研究[8]。MMP7是该家族中最小的成员之一。本研究组的前期研究结果提示MMP3和MMP8可能是肺纤维化的标志物。因此,本研究就MMP7的调节及其在肺纤维化中的作用进行了研究。结果提示,肺纤维化的发生与MMP7的异常表达直接相关,提示MMP7可能是PQ致肺纤维化的标志物。
综上所述,MMP7伴随肺纤维化的整体发展过程。MMP7的检测具有重要的临床意义,可提示肺纤维化的起始、进展和严重程度,从而进一步指导治疗,判断预后。然而,MMPs参与肺纤维化的分子生物学机制尚未明确,有待进一步研究探讨。
[1]Roberts DM,Wilks MF,Roberts MS,et al.Changes in the concentrations of creatinine,cystatin C and NGAL in patients with acute paraquat self-poisoning[J].Toxicol Lett,2011,202(1):69.
[2]Choi JS,Jou SS,Oh MH,et al.The dose of cyclophosphamide for treating paraquat-induced rat lung injury[J].Korean J Intern Med,2013,28(4):420-427.
[3]Tomita M,Okuyama T,Katsuyama H,et al.Mouse model of paraquatpoisonedlungs and its geneexpression profile[J].Toxicology, 2007,231(2-3):200-209.
[4]Shimada H,Hirai K,Simamura E,et al.Paraquat toxicity induced by voltage-dependent anion channel 1 acts as an NADH-dependent oxidoreductase[J].J Biol Chem,2009,284(42):28642-28649.
[5]Dinis-Oliveira RJ,Duarte JA,Sanchez-Navarro A,et al.Paraquatpoisonings:mechanisms of lung toxicity,clinical features,and treatment[J].Toxicology,2008,38(1):13-71.
[6]Bowler RP,Crapo JD.Oxidative stress in airways:Is there a role forextracellular superoxide dismutase[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2002,166(12):38-43.
[7]李苑碧,彭清华,黄学思,等.青光安对抗青光眼术后滤过道瘢痕组织中弹性纤维、MMP-7、TIMP-1的实验研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2015,15(1):20-25.
[8]Elin HO,Bodil F.Regulation of matrixmetalloproteinase activity in health and disease[J].FEBS J,201l,278(1):28-45.
(编辑王又冬)
Significance and Expression of MMP7 in Paraquat-induced Murine Pulmonary Fibrosis
DUYan,ZHANG Gang,XIAO Li
(Department of Emergency,Shengjing Hospital,China Medical University,Shenyang 110004,China)
Objective To investigate the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7(MMP7)in paraquat(PQ)-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.MethodsForty-eight SD rats were randomly divided into the control group and the pulmonary fibrosis model group(PQ model group),each group of twenty-four rats.Rats in the PQ model group received single intraperitoneal injection of 4 mg/mL PQ dilute solution and the control group were intraperitoneal injected with the same dose of saline.Eight rats of each group were sacrificed on day 7,day14 and day 28 respectively.The pathological changes of lung tissues were observed and the hydroxyproline(HYP)content in lung tissues was determined.The severity of pulmonary fibrosis was observed.The expressions of MMP7 in lungs were observed by immunohistochemistry.ResultsThe observation of general state of the experimental animals showed that except one rat died at day 28 d,all other rats survived to the end point of observation.After intraperitoneal injection with PQ,the weight of rats in the PQ model group gradually declined,and then increased around day 14,yet still much lower than that in the control group at day 28(P<0.05).After intraperitoneal injection with PQ,the pulmonary index in the model group increased gradually and then decreased after reaching the peak on day 14.The content of HYP in rat lung tissues in the PQ model group was remarkably higher than in the control group at day 7,day 14,and day 28,with statistical significance(P<0.01).In the PQ model group,the content of HYP was significantly up-regulated with the extension of infected time and reached the peak value at day 28.The results of HE staining showed significant pulmonary alveolitis at day 7,hyperplasia of abundant collagen fibers in alveolar septum at day 14,and obvious pulmonary fibrosis and collapse of alveolar structure on day 28 in the lung tissues of the PQ model group.A weak expression of MMP7 was measured in the lung tissues in the control group and the expression of MMP7 was higher in the PQ model group than in the control group at day 7,day 14,and day 28,with statistical significance(P<0.05).ConclusionParaquat poisoning was mainly manifested in inflammatory reactions of lung tissues in the early stage together with increase of fibroblasts and mainly in fibrosis in the late stage.The expression of MMP7was increased along with the severity of pulmonary alveolitis or fibrosis and showed significant changes compared to the control group at day 28 after poisoning,indicating that MMP7 may be the marker of paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
paraquat;pulmonary fibrosis;MMP7
R563.9
A
0258-4646(2015)06-0557-05
杜妍(1984-),女,医师,硕士研究生.
肖莉,E-mail:xiaoli@sj-hospital.org
2015-05-07
网络出版时间:

