吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(IDO)的色胺酮类抑制剂筛选及其体外抗肿瘤作用
杨双双杜丽莎李豪男杨 青△
(1复旦大学生命科学学院生化系 上海 200433;2金日成综合大学生命科学系 平壤)
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(IDO)的色胺酮类抑制剂筛选及其体外抗肿瘤作用
杨双双1杜丽莎1李豪男2杨 青1△
(1复旦大学生命科学学院生化系 上海 200433;2金日成综合大学生命科学系 平壤)
目的评价色胺酮衍生物吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶 (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,IDO)的抑制活性,并研究其作为IDO抑制剂的抗肿瘤作用。方法采用基因工程手段表达、纯化重组人IDO(rhIDO),建立IDO活性检测体系;以色胺酮衍生物作为对象,进行IDO抑制活性初筛,对抑制类型、半数抑制浓度以及抑制常数进行测定;构建高表达人IDO的pcDNA3.1(+)-hIDO转染HEK 293细胞,评价色胺酮衍生物在细胞水平上的IDO抑制活性;采用MTT比色法考察色胺酮衍生物3对人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞的生长抑制作用。结果6个被测色胺酮衍生物均具有IDO抑制活性,且细胞水平上的抑制效力高于酶活水平,抑制效力均优于目前通用的IDO抑制剂1-甲基色氨酸(1-methyl-tryptophan,1-MT)。色胺酮衍生物3作为最强的IDO抑制剂,其Ki值为0.161μmol/L。MTT实验结果显示,色胺酮衍生物3显著抑制 A549细胞生长,IC50为8.77μmol/L。结论色胺酮衍生物是一类新型高效的IDO抑制剂,在体外对A549细胞具有较强的抗肿瘤活性。
活性检测; 色胺酮衍生物; 吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶 (IDO); 抗肿瘤作用
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,IDO)是肝脏以外唯一催化色氨酸沿犬尿氨酸途径(kynurenine pathway,KP)代谢的限速酶[1],已被证实与肿瘤、阿尔茨海默病、抑郁症和老年性白内障等多种人类重大疾病密切相关。而IDO的表达或活性的异常增高,是导致上述疾病的一个重要因素[2],所以筛选高效的IDO抑制剂可以为这些疾病提供有效治疗药物。
自1967年IDO被发现以来,至今未被商品化,这给IDO活性检测系统的建立带来了困难,所以国内少有开展IDO抑制剂的化学合成与天然提取的相关工作。本研究采用基因工程手段获得纯化的rhIDO,以此建立了稳定的IDO生物活性检测系统,利用该系统进行IDO抑制剂的筛选工作。尽管IDO抑制剂的研究在国外已经开展数十年,但是目前还没有IDO抑制剂药物问世。现有的IDO抑制剂普遍存在抑制效率低下、无法透过细胞膜以及产生吲哚环结构代谢物质等问题[3]。20世纪90年代发现的1-甲基色氨酸(1-methyl-tryptophan,1-MT)是目前体内外实验中普遍使用的IDO抑制剂,其抑制常数(Ki)为34μmol/L[4]。
近年来,抑制IDO在肿瘤治疗中的作用引起了众多学者的关注[5-6]。研究证实IDO在多种实体肿瘤如肺癌、肝癌、乳腺癌、结肠癌等肿瘤组织中的表达明显增强,且与预后密切相关[7]。Friberg等[8]研究发现1-MT体外能增强肿瘤细胞对T细胞免疫刺激的敏感性,体内在Lewis肺癌小鼠模型中能够延缓肿瘤的生长。Muller等[9]发现在自发性乳腺癌 MMTVNeu小鼠模型中,1-MT与化疗药紫杉醇、顺铂、环磷酰胺和阿霉素合用,能引起肿瘤的消除。
因此,使用IDO抑制剂可能成为一种治疗肿瘤的有效方法。本研究建立稳定的IDO活性检测体系,筛选新型高效的IDO抑制剂,并进行IDO抑制剂抗肿瘤作用的初步研究。
材料和方法
药品与试剂1-MT、L-犬尿氨酸、IPTG、MTT、DMSO (美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);L-色氨酸、亚甲基蓝、过氧化氢酶、对二甲氨基苯甲醛(日本Wako公司);HEK 293 细胞(ATCC CRL-1573)、DMEM 培养基、opti-MEM 培养液、胎牛血清、Lipofectamin 2000、Hank's平衡盐溶液(美国Gibco公司);大肠埃希菌BL21、Top10(博大泰克公司);Endofree Plasmid Kit(上海天根公司)。
仪器和设备电热恒温水浴锅(上海精宏实验设备有限公司),隔水式电热恒温培养箱(江苏太仓实验设备厂),SCS-24恒温摇床(江苏太仓实验设备厂),722分光光度计(上海分析仪器总厂),倒置显微镜(CKX-41-32,日本 OLYMPUS公司),Forma series CO2培养箱、Multiskan MK3酶标仪(美国Thermo scientific公司),SW-CJ-1FD洁净工作台(苏州安泰空气技术有限公司)。
重组人IDO表达及纯化经测序验证的p ET28a-hIDO表达质粒转化BL21感受态细胞,从转化平板上随机挑取单菌落于含50μg/m L卡那霉素的培养基中,37℃ 过夜培养;按1∶50将过夜培养物接种于含50μg/m L卡那霉素的LB中,当D600=0.6时加入血红素生物合成中间体α-氨基乙酰丙酸(ALA)同时将温度降至30℃,最后加IPTG至终浓度为0.5 mmol/L,30℃诱导表达6 h。3968×g离心10 min收集菌体;用适量PBS(含1 mmol/L PMSF)重悬菌体,超声破碎;4℃下3968×g离心10 min,取上清。将上清注入预先用含10 mmol/L咪唑的磷酸盐缓冲液(20 mmol/L,p H 7.4)平衡的Ni柱上,用含40 mmol/L咪唑的PBS洗去杂蛋白后,用含250 mmol/L咪唑的PBS洗脱下rhIDO,Sephadex G25柱脱盐,得到纯化的rhIDO蛋白质。
体外IDO活性检测体系的建立IDO活性检测体系在Littlejohn等[10]研究的基础上进行优化。在500μL反应体系中,先将50 mmol/L磷酸钾缓冲液(p H 6.5)、40 mmol/L抗坏血酸、200μg/m L过氧化氢酶、20μmol/L亚甲基蓝、底物L-色氨酸和待测样品混合,混合液37℃ 预热5 min,再向上述混合液内加入0.05μmol/L rhIDO酶,37℃反应30 min,酶促反应后加入30%(W/V)三氯乙酸200 μL使终止反应,反应液在65℃加热15 min,使之完成从N-甲酰犬尿氨酸到犬尿氨酸的转化。然后13523×g离心10 min,取上清与等体积2% (W/V)对-二甲氨基苯甲醛的乙酸溶液混合,使用酶标仪在492 nm观测犬尿氨酸与之反应产生的黄颜色。以1-MT作为阳性对照,验证本实验建立的IDO活性检测体系是否有效。
抑制类型及Ki、IC50值测定利用上述反应体系,加入50μmol/L抑制剂和不同浓度的IDO酶,其他处理方法同上,最后以反应速度对酶浓度作图,根据所得曲线的关系判断抑制剂类型。抑制常数Ki及IC50值的测定同样利用上述反应体系,加入不同浓度底物L-色氨酸,在一个底物浓度下,加入不同浓度的抑制剂,其他处理方法同上,最后以Dixon作图法得到Ki值[11],利用改良寇氏法计算出IC50值。
细胞水平IDO抑制活性测定将 HEK 293细胞以2.5×104/孔的密度接种于96孔板中,DMEM培养基培养(含10% 胎牛血清、50 U/mL青霉素,50 mg/mL链霉素),置于37℃、湿度95%、5%CO2的培养箱中培养。24 h后使用脂质体Lipofectamin 2000介导pcDNA3.1(+)-hIDO质粒转染。转染24 h后加入待测药物,孵育5 h后,取140μL上清到另一96孔板中,加入10μL 30%(W/V)三氯乙酸,65℃加热15 min,13523×g离心10 min,取等体积2%(W/V)对-二甲氨基苯甲醛的乙酸溶液混合显色,最后采用酶标仪在492 nm检测吸光度(D)值。
MTT法测定色胺酮衍生物3对A549细胞的生长抑制作用取对数生长期的A549细胞接种于96孔培养板(细胞数为5×104/孔,100μL/孔),加入不同浓度的色胺酮衍生物3,使其终浓度分别为0、5、10、20、40、80μmol/L,最后用 DMEM 全培养基补充至每孔200μL,置于37℃、湿度95%、5%CO2的培养箱中培养。24 h后每孔加人20μL MTT溶液(5 g/L),继续培养4 h后,吸去培养基,每孔加入150μL DMSO,37℃ 水平摇床振荡10 min,使蓝紫色结晶物充分溶解,酶标仪570 nm波长处测定吸光度(D)值。生长抑制率=(1-D实验孔/D对照孔)×100%,并求IC50值,实验重复3次。
结 果
体外IDO活性检测体系的建立实验检测了纯化rhIDO的活性,制作了酶反应进程曲线(图1A)。通过绘制L-犬尿氨酸标准曲线(图1B),得到吸光度与浓度关系曲线。从进程曲线中可以看出纯化所得rhIDO具有色氨酸催化活性。利用该体系,测得1-MT的IC50为328μmol/L,与文献报道的380μmol/L相近[4],并且可以重复。因此我们认为IDO抑制剂的体外酶活筛选体系已经成功建立,可用于IDO抑制剂的筛选。
IDO抑制剂的筛选利用上述体外IDO活性检测体系对一系列色胺酮衍生物进行筛选,发现6个化合物均具有很强的IDO抑制活性,其中色胺酮衍生物3和4的IDO抑制效果比色胺酮显著(图2),6个化合物都是优于1-MT的IDO抑制剂。
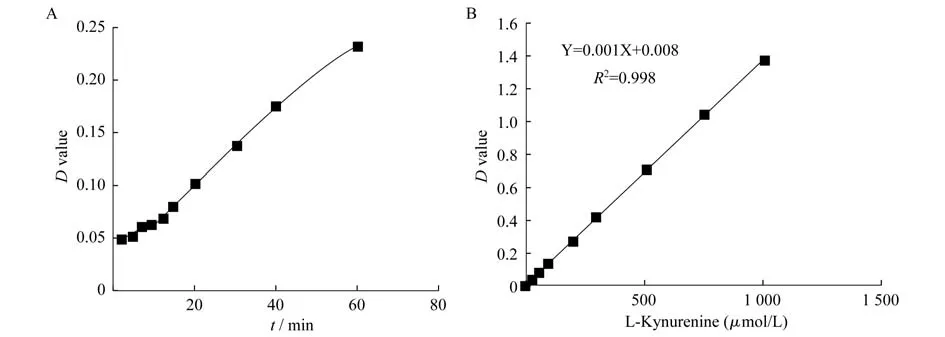
图1 rhIDO酶反应进程曲线和L-犬尿氨酸标准曲线Fig 1 The curve of rhIDO enzyme reaction and the standard curve of L-kynurenineA:Curve of rhIDO enzyme reaction;B:Standard curve of L-kynurenine.

图2 色胺酮衍生物的IDO抑制活性Fig 2 IDO inhihitory activity of tryptanthrin derivativesControl:No inhibitor.The concentrations of tryptanthrin derivatives and 1-MT were 100μmol/L.Results are expressed as±sfrom 3 independent experiments.
抑制类型判定及Ki、IC50的测定在固定抑制剂浓度的条件下,用一系列不同浓度的酶与抑制剂反应并测定反应速度。以反应速度对酶浓度作图[12],根据曲线的特征可以判定6个色胺酮衍生物均为可逆抑制剂(图3)。同时利用IDO活性检测体系,测定抑制常数Ki及半数抑制浓度IC50(图3,表1),结果发现6个化合物中3、4的Ki和IC50值已达到了纳摩尔级别。
细胞水平IDO抑制活性利用质粒pcDNA 3.1(+)-IDO转染 HEK 293细胞,使其高表达IDO,然后测定5个色胺酮衍生物在细胞水平的IDO抑制活性。结果显示色胺酮衍生物对细胞内的IDO同样具有抑制作用,并且抑制效果优于体外酶活效果 (图4)。
色胺酮衍生物3对A549细胞的生长抑制作用体外酶活水平和细胞水平的IDO抑制结果表明,色胺酮衍生物3是一个具有很大潜力的IDO抑制剂(图5)。MTT法进一步研究其对A549细胞生长的抑制作用,结果发现,随着色胺酮衍生物3的浓度增加,其对A549细胞的生长抑制作用增强,半数抑制浓度IC50为8.77μmol/L,而1-MT即使在最高浓度80 μmol/L时也几乎不能抑制A549细胞的生长。

表1 色胺酮衍生物的抑制常数Ki和IC50值Tah 1 The kinetic parameters and IC50values of tryptanthrin derivatives
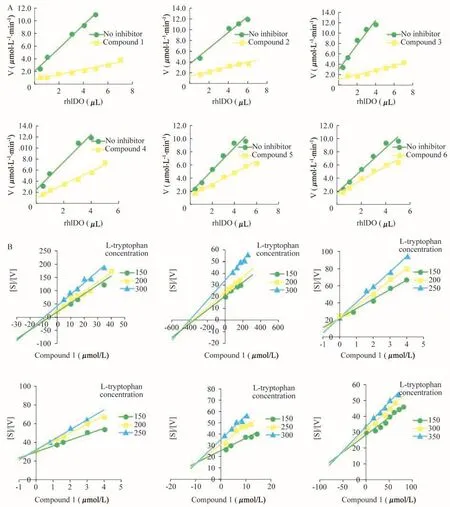
图3 色胺酮衍生物的抑制类型和Ki值的测定Fig 3 Determination of the inhihition types and kinetic parameters of tryptanthrin derivativesA:Plot of reaction rate[V]against enzyme amount[E].The concentrations of L-tryptophan and the inhibitor were 300μmol/L and 50 μmol/L,respectively.B:Determination of the kinetic parameters.Plot of[S]/[V]against the concentration of the inhibitor([I]).L-tryptophan concentration varied from 150μmol/L to 350μmol/L.The intersection point in the plot stands for measuring the apparent inhibition constant Ki.

图4 色胺酮衍生物细胞水平的IDO抑制活性Fig 4 Cell-hased assay of IDO inhihition of tryptanthrin derivativesPercent inhibition against log[I]was plotted and IC50value was determined.

图5 色胺酮衍生物3对A549细胞生长抑制作用Fig 5 Inhihitory effect of compound 3 on A549 cells
讨 论
基于IDO在肿瘤免疫耐受的形成和维持中所发挥的重要作用,IDO已被证实是一个抑制恶性肿瘤形成和提高肿瘤免疫治疗效果的新靶点[13]。IDO抑制剂作为相关治疗的潜在药物,具有非常广阔的应用前景。
目前已有的IDO抑制剂主要分为以下几个类别:竞争性抑制剂,如色氨酸衍生物1-MT[4];非竞争性抑制剂,如苯基咪唑[14];反竞争性抑制剂,如生物碱exiguamine A[15];通过其他作用机制的抑制剂。1-MT作为与底物色氨酸结构最接近的抑制剂,已经成为体内外实验中普遍使用的IDO抑制剂。遗憾的是,虽然经过多年的努力,目前只有2个IDO抑制剂进入临床研究[16-17],世界上还没有IDO抑制剂类药物上市。
本实验通过建立稳定的IDO活性检测体系,筛选得到6个具有IDO抑制活性的色胺酮衍生物,其中色胺酮衍生物3的抑制效果最强,其抑制常数Ki值为0.161μmol/L,IC50值为0.534μmol/L,抑制活性远远高于1-MT(Ki值34μmol/L,IC50值380 μmol/L)[4],其他5个化合物的抑制效果也在很大程度上优于1-MT。进一步实验表明,色胺酮衍生物对细胞水平IDO同样具有抑制作用,且抑制效果远远优于体外酶活水平,表明色胺酮衍生物能够很好地穿过细胞膜,在细胞水平发挥IDO抑制作用。MTT实验发现色胺酮衍生物3能够对人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞具有明显的抑制作用,且呈剂量依赖性,其半数抑制浓度为8.77μmol/L。
色胺酮作为一种喹唑啉酮生物碱,其具有抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤等多种药理活性,但作为IDO抑制剂还是第一次被发现。近年来,色胺酮的抗肿瘤作用受到了越来越广泛的关注,研究者对多种人类肿瘤细胞进行了体外实验[18],但体内抗肿瘤实验寥寥无几,对人非小细胞肺癌A549的抗肿瘤作用研究尚未见报道。
本实验通过抑制类型的判定、Ki和IC50值的测定,发现色胺酮衍生物是一类新型高效的IDO抑制剂,在体外对人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞具有较强的抗肿瘤作用。体内动物实验有待进一步探索,通过使用色胺酮衍生物来控制IDO的活性,逆转由IDO介导的肿瘤细胞免疫耐受,从而控制肿瘤细胞的生长,可能成为防治恶性肿瘤的有效方法,也可能成为色胺酮的一种新的抗肿瘤机制。
[1] Takikawa O,Yoshida R,Kido R,et al.Tryptophan degradation in mice initiated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].J Biol Chem,1986,261(8):3648-3653.
[2] Takikawa O.Clinical aspects of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-initiated tryptophan metabolism:IDO is a target of drug discovery for various diseases[J].Int Cong Seri,2007,1304:290-297.
[3] Vottero E,Balgi A,Woods K,et al.Inhibitors of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase identified with a target-based screen in yeast[J].Biotechnol J,2006,1(3):282-288.
[4] Cady SG,Sono M.1-Methyl-DL-tryptophan,beta-(3-benzofuranyl)-DL-alanine (the oxygen analog of tryptophan),and beta-[3-benzo(b)thienyl]-DL-alanine(the sulfur analog of tryptophan)are competitive inhibitors for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].Arch Biochem Biophys,1991,291(2):326-333.
[5] Prendergast GC.Immune escape as a fundamental trait of cancer:focus on IDO[J].Oncogene,2008,27(28):3889-3900.
[6] Soliman H,Mediavilla-Varela M,Antonia S.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase:is it an immune suppressor? [J].Cancer J,2010,16(4):354-359.
[7] Uyttenhove C,Pilotte L,Theate I,et al.Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].Nat Med,2003,9(10):1269-1274.
[8] Friberg M,Jennings R,Alsarraj M,et al.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to tumor cell evasion of T cellmediated rejection[J].Int J Cancer,2002,101(2):151-155.
[9] Muller AJ,Duhadaway JB,Donover PS,et al.Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1,potentiates cancer chemotherapy[J].Nat Med,2005,11(3):312-319.
[10] Littlejohn TK,Takikawa O,Skylas D,et al.Expression and purification of recombinant human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].Protein Expr Purif,2000,19(1):22-29.
[11] Cortes A,Cascante M,Cardenas ML,et al.Relationships between inhibition constants,inhibitor concentrations for 50%inhibition and types of inhibition:new ways of analysing data[J].Biochem J,2001,357(Pt 1):263-268.
[12] 王镜岩,朱圣庚,徐长法.生物化学(上)[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2002:369-370.
[13] Liu X,Newton RC,Friedman SM,et al.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,an emerging target for anti-cancer therapy[J].Curr Cancer Drug Targets,2009,9(8):938-952.
[14] Sono M,Cady SG.Enzyme kinetic and spectroscopic studies of inhibitor and effector interactions with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.1.Norharman and 4-phenylimidazole binding to the enzyme as inhibitors and heme ligands[J].Biochemistry,1989,28(13):5392-5399.
[15] Brastianos HC,Vottero E,Patrick BO,et al.Exiguamine A,an indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)inhibitor isolated from the marine sponge Neopetrosia exigua[J].J Am Chem Soc,2006,128(50):16046-16047.
[16] Hou DY,Muller AJ,Sharma MD,et al.Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells by stereoisomers of 1-methyl-tryptophan correlates with antitumor responses[J].Cancer Res,2007,67(2):792-801.
[17] Liu X,Shin N,Koblish HK,et al.Selective inhibition of IDO1 effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity[J].Blood,2010,115(17):3520-3530.
[18] Sharma VM,Prasanna P,Seshu KV,et al.Novel indolo[2,1-b]quinazoline analogues as cytostatic agents:synthesis,biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2002,12(17):2303-2307.
Screening of tryptanthrin derivatives of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO)inhihitor and their antitumor activityin vitro
YANG Shuang-shuang1,DU Li-sha1,RI Ho-nam2,YANG Qing1△
(1Department of Biochemistry,School of Life Science,Fudan University,Shanghai200433,China;2Department of Biochemistry,Faculty of Life Science,KimⅡSung University,Pyongyang,D.P.R.Korea)
activity assay; tryptanthrin derivatives; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO);antitumor activity
Q 331
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2014.02.002
2013-03-13;编辑:王蔚)
国家自然科学基金(30873153)
△Corresponding author E-mail:yangqing68@fudan.edu.cn
【Ahstract】 OhJectiveTo evaluate the inhibitory activity of tryptanthrin derivatives of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO),and to explore the effects on human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell growth.MethodsIDO activity assay system was established with recombinant human IDO (rhIDO),which was expressed and purified by the technology of genetic engineering.Based on the system,we detected the IDO inhibitory activity of tryptanthrin derivatives,and determined the inhibition type,kinetic parameters and IC50values.We also evaluated the IDO inhibitory effects of tryptanthrin derivatives on HEK 293 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1(+)-hIDO.Inhibitory activity of tryptanthrin derivatives on A549 cell growth inhibition was analysed by MTT assay.ResultsSix tryptanthrin derivatives displayed higher IDOinhibitory activity than 1-methyl tryptophan (1-MT),which is the commonly used IDO inhibitor.IC50values of tryptanthrin derivatives,obtained from the HEK 293 cell-based assay,were much lower than that from the enzyme assay.Compound 3 was the best inhibitor and had Ki value of 0.161μmol/L.Treating A549 cells with 3 remarkably inhibited the cell growth,and its IC50value was 8.77μmol/L.ConclusionsTryptanthrin derivatives are novel and potent IDOinhibitors,and can significantly inhibit human non-small cell lung cancerA549 cell growthin vitro.
*This work was supported hy the National Natural Science Foundation of China(30873153).

