中药抗动脉粥样硬化机制研究进展
严春琳,杨 静,韩际宏,朱 彦
(1.天津中医药大学天津市现代中药国家重点实验室-省部共建国家重点实验室,天津 300193;2.天津国际生物医药联合研究院中药新药研发中心,天津 300457;3.南开大学生命科学院,天津 300193)
中药抗动脉粥样硬化机制研究进展
严春琳1,2,杨 静1,韩际宏3,朱 彦1
(1.天津中医药大学天津市现代中药国家重点实验室-省部共建国家重点实验室,天津 300193;2.天津国际生物医药联合研究院中药新药研发中心,天津 300457;3.南开大学生命科学院,天津 300193)
动脉粥样硬化的病因及发病机制极为复杂,目前关于动脉粥样硬化的病因较为一致的看法是因脂质代谢紊乱、炎症细胞浸润、氧化应激、血管内皮细胞损伤、平滑肌细胞激活等多种机制相互作用的结果,最终导致斑块的破裂,血栓形成,造成严重心脑血管疾病。中药对心血管系统疾病具有良好的临床防治效果,部分中药复方和单体抗动脉粥样硬化的多靶点协同作用机制已经得到了初步的阐明。本文从调节脂质代谢、抗炎、抗氧化、保护血管内皮细胞、抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖和迁移、改善凝血纤溶系统及稳定斑块等方面对相关中药抗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制进行综述。
动脉粥样硬化;中药药理学
众所周知,动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)是导致冠状动脉疾病发病和死亡的主要原因。AS的病因及发病机制极为复杂,它的发生发展基本上是按着脂质条纹纤维斑块粥样斑块临床合并症出现等的4个阶段进行[1]。动脉管壁内皮细胞(endothelial cells,EC)损伤及脂质沉积是目前公认的AS的始动因素[2],其基本过程为:EC在受到炎症、高血脂等刺激情况下,发生损伤及功能异常,血脂沉积在EC下并被增多的活性氧簇氧化修饰成氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,ox-LDL),血液中单核细胞与淋巴细胞浸润到EC下,释放炎症因子;血小板黏附于受损的 EC处;中膜平滑肌细胞(smooth muscle cells,SMC)迁移至内膜并大量增殖,伴胶原等细胞外基质的分泌增多;由单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞及SMC摄取ox-LDL形成泡沫细胞;坏死的泡沫细胞及组织碎片形成病变深部糜粥样部分,突出于管腔表面,再覆以较坚硬的纤维被膜。此时脂质进一步沉积,沉积的脂质进一步加重吞噬细胞的聚集、血小板的黏附和炎性因子释放,形成恶性循环。随着这一过程的进展,纤维被膜慢慢变薄,渐渐演变为不稳定斑块。不稳定斑块糜烂或破裂而形成血栓,最终导致严重心脑血管损害。
1 AS的病因与发病机制
AS的病因与发病机制极为复杂,至今为止仍然没有确定其确切的病因及发病机制,从最早被公认的危险因素到现在,文献陆续报道的已有300多个,现对近年来的一些危险因素和相关机制的研究归纳如下。
1.1 脂质代谢紊乱
流行病学资料显示,血清中胆固醇的升高与AS的发生呈正相关。随着对脂蛋白研究的深入,发现主要是LDL的水平与AS的发生呈正相关[3],其机制是LDL能通过载脂蛋白B-100(apolipoprotein B-100,ApoB-100)与细胞外基质相互作用而沉积在动脉内膜形成粥样斑块。而高密度脂蛋白(HDL)能将胆固醇逆向转运至肝,可降低机体胆固醇水平,从而起到抗AS的作用。
1.2 炎症与免疫反应
1999年,Ross等[4]提出AS的损伤反应学说,此后,越来越多的研究结果提示AS实质为血管受损后的一种慢性炎症性过程。炎症贯穿AS发生发展的整个过程:在AS起始阶段,血液中的单核细胞和淋巴细胞迁移,在炎症因子的作用下黏附至EC损伤处,穿过EC,在EC下聚集。单核细胞趋化蛋白1(monocyte chemotactic protein-1,MCP-1)可刺激单核细胞转变成巨噬细胞,后者与ox-LDL结合形成泡沫细胞。泡沫细胞破裂或凋亡,在细胞外形成脂质池导致病灶进一步恶化。大量的细胞因子参与其中,细胞因子不仅可以直接损伤周围的细胞,而且通过自分泌和旁分泌的形式作用于自身和其他细胞,生成更多的细胞因子以及炎性介质,形成恶性循环,促AS的发生发展。
1.3 氧化应激
近年来国内外大量研究表明,氧化应激参与了AS的发生与发展过程[5]。氧化应激是指机体组织或细胞内氧自由基生成增加和(或)清除能力降低,导致氧自由基及其相关代谢产物的过度积聚而引起氧化损伤的过程[6]。目前研究表明,氧化应激一方面直接对血管壁细胞造成损伤,另一方面通过影响血管壁细胞转录因子的水平,调节基因的表达,参与AS的发生发展[7-8]。
1.4 血管内皮细胞损伤
研究表明,EC并不单纯是血管的屏障,也是一个功能强大的内分泌器官,能合成和分泌多种生物活性物质,参与机体复杂的功能调节。正常血管EC能调节血管收缩及血管结构,能分泌抗凝和抗血小板物质,防止血液中的细胞向血管壁的黏附与聚集[9]。EC功能障碍与AS的发生发展密切相关,受损的EC可促进白细胞的黏附和聚集、EC下脂质的沉积、SMC的增殖和迁移、粥样斑块脆性的增加与破裂。
1.5 SMC的增殖和迁移
SMC在泡沫细胞分泌的细胞因子的趋化下由中膜迁移至内膜并大量增殖,摄取脂质成为肌源性泡沫细胞,内膜增厚而形成粥样病灶或纤维脂质斑块,血管SMC的增殖与迁移是AS形成的关键因素[10]。
1.6 AS发病机制研究新进展
在2013年的戈登学术会议上提出巨噬细胞亚群表型的改变、表观遗传学以及循环系统的中微RNA(microRNA,miRNA)在AS的发生发展中也扮演了重要的角色。
1.6.1 巨噬细胞亚群表型的改变与AS
巨噬细胞参与机体的先天性免疫和获得性免疫。巨噬细胞存在一系列连续的功能状态,M1型和M2型是巨噬细胞连续状态的两个极端类型。M1型巨噬细胞通过分泌促炎性细胞因子和趋化因子,并专职提呈抗原,参与机体正向免疫应答,发挥免疫监视的功能;M2型巨噬细胞仅有较弱的抗原提呈能力,通过分泌抑制性细胞因子白细胞介素10 (interleukin-10,IL-10)和(或)转化生长因子-β等下调免疫应答,参与组织修复与重建[11]。有研究表明,干扰素γ与脂多糖的联合作用是将巨噬细胞向M1方向诱导的经典刺激方法,而IL-4单独作用则是将巨噬细胞向M2方向诱导的经典刺激方法[12]。通过对巨噬细胞亚群表型转变的研究,对AS的防治将起到重要的作用。
1.6.2 表观遗传学与AS
研究表明,表观遗传学与AS的发生发展密切相关,表观遗传学是在不改变基因序列的前提下,通过DNA和组蛋白化学修饰、RNA干扰、染色质重塑等多种机制影响和调节基因的功能与特性。表观遗传修饰,可影响基因表达而不改变当前基因的遗传变化,是生物复杂性的主要驱动力,并可以在多种疾病的发生中发挥一定作用。对AS表观遗传学的深入研究,是未来研发AS防治药物的潜在靶标。表观遗传修饰与DNA的转录活性密切相关,DNA甲基化和组蛋白H3赖氨酸9(H3K9)甲基化可抑制基因转录,DNA去甲基化和组蛋白乙酰化则促进基因转录,而非编码RNA通过募集甲基化的DNA以及修饰特异性的组蛋白残基而使染色体重塑[13]。目前对组蛋白修饰的研究主要集中于组蛋白的乙酰化修饰,催化组蛋白乙酰化的酶是组蛋白乙酰转移酶,去乙酰化则由组蛋白去乙酰化酶催化。如Findeisen等[14]研究表明,干扰素β通过组蛋白去乙酰化酶作用于基质金属蛋白酶9(matrix metalloproteinases9,MMP-9)启动子,抑制MMP-9启动子组蛋白H3的乙酰化,从而抑制激活蛋白1的结合,最终抑制MMP-9的转录,调节SMC的增殖迁移,稳定AS斑块。
1.6.3 循环系统的中miRNA与AS
miRNA是一类长度为 19~25个核苷酸的RNA,miRNA存在于基因组非编码区,在基因转录及转录后加工、细胞增殖、细胞分化、细胞凋亡、个体发育、遗传和表观遗传等生命活动中都发挥着重要作用[15-16]。近年来发现,miRNA参与调控AS发生发展各个环节的炎性细胞,包括血管内皮细胞和单核细胞的发育、分化及其功能的执行。对miRNA参与调控这些细胞的机制进行深入研究,将有可能阐明miRNA在AS发病过程中的意义与作用。如在人脐静脉内皮细胞中miRNA-21随着血管所受振荡剪切应力增加而表达增加,miRNA-21通过增加黏附分子表达提高巨噬细胞在内皮细胞表面的黏附,相应的黏附分子包括血管细胞黏附分子1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule1,VCAM-1)和MCP-1,miRNA也可以作用于过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(peroxisomeproliferatoractivatedreceptor alpha,PPARα),使 PPARα表达减少,AP-1的活性增高,形成正反馈的调节,促进AS的发生发展[17]。
近年来发现,内皮祖细胞(endothelial progenitor cell,EPC)的数量减少及功能受损与AS的发生发展密切相关,并可作为心血管疾病的独立危险因子。EPC是存在于骨髓、脐血和外周血的一种具有高增殖潜能的前体细胞,在一定条件下可诱导分化为成熟的血管内皮细胞。EPC在生理和病理条件下的血管重构过程中发挥着重要作用[18]。EPC在AS血管内皮损伤和修复过程中发挥极其重要的作用,其数量减少及功能受损与AS的发生发展密切相关。几乎所有AS的危险因素均伴有EPC数量的减少和迁移能力的下降[19],EPC可能成为AS的重要预测因子[20]和新的治疗靶点。如高脂血症是AS的主要危险因素,研究表明高脂血症通过增加氧化应激水平,极大地降低EPC迁移活性和黏附能力[21]。
由于以上相关因素的相互作用,导致AS斑块的形成,最终AS斑块由稳定状态进入不稳定状态,斑块破裂,血小板黏附聚集,血栓形成是急性心脑血管疾病共同的病理基础。AS与众多因子相关,表1系统总结了AS相关的因子及其调控。
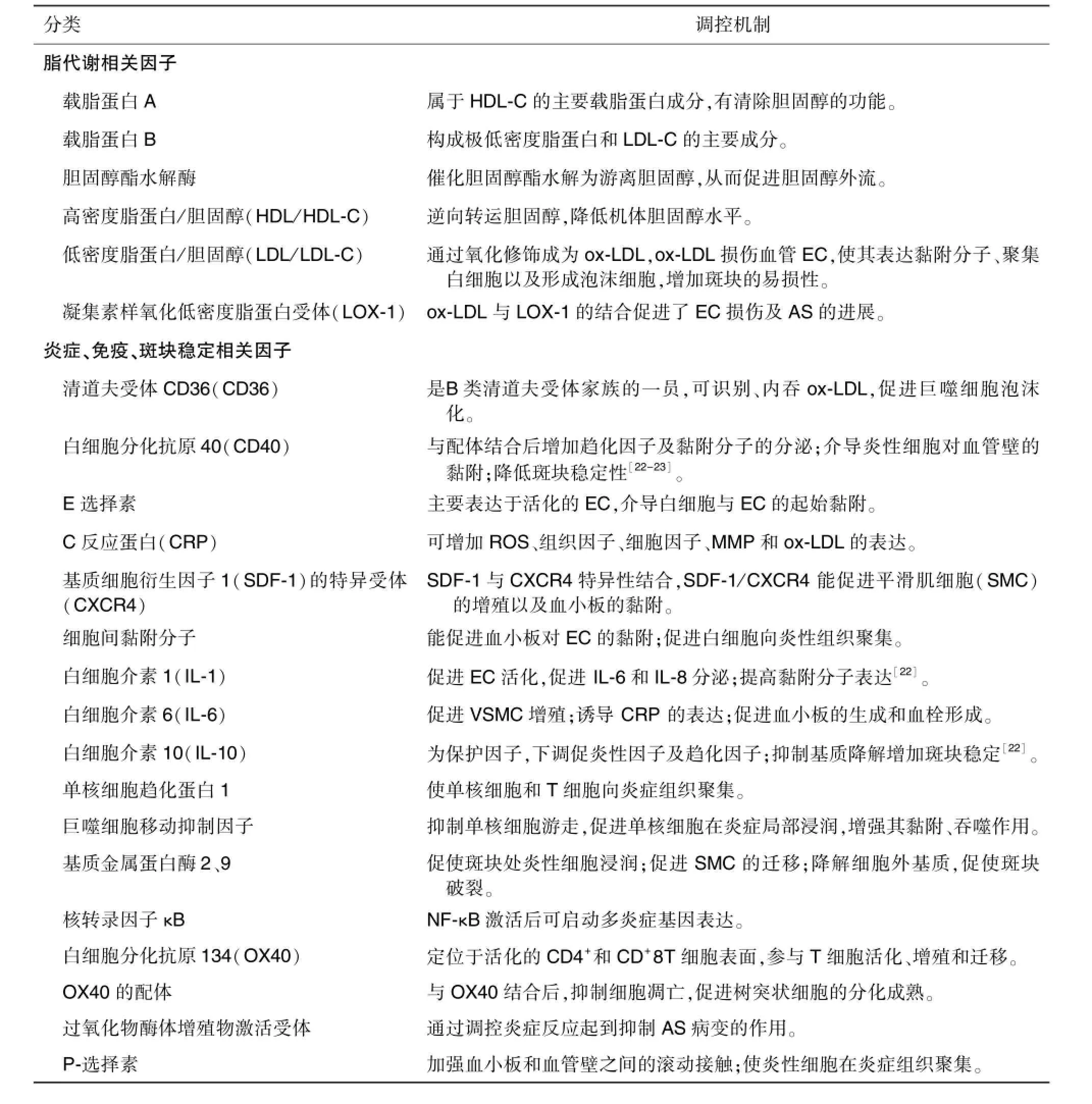
表1 与动脉粥样硬化相关的因子分类及其调控机制

续表1
2 中医药理论对AS的认识及中医药的防治作用
中医并无AS这一病名,但根据其临床表现可涉及中医学眩晕、头痛、健忘、痴呆、中风和胸痹等疾病。中医从整体观入手,辨证论治,大多数学者均认为该病为本虚标实之证,本虚即五脏(主要是肝、脾、肾三脏)气血阴阳的亏虚,标实即瘀、痰、热、毒等。随着众多医家和学者对AS病因病机的进一步探讨,对AS病因病机取得了许多新的认识。如“伏邪”、“脉浊”的概念。① 伏邪与AS:人体感受邪气,未能及时清除,或邪气潜伏于正虚之所不易祛除,则致邪气留滞,潜伏于人体,待时而发,待机而作,即谓之“伏邪”。根据中医理论,身体中的物质,适中则为正常,缺少则为虚为亏,多余则为实为邪为浊。血中之脂质为水谷食物中厚浊富有营养之部分所化,适当则为身体所必需,过多则为邪为害。其留滞多余者,犹如水液聚为痰浊,笔者认为如若将此命名为“伏邪”高血脂为“脂浊,如此,创新中医传统的病因学概念,使之既与现代医学的认识互通,又符合传统中医理论,从而更好地利用中医方法解决临床问题[25]。②脉浊与AS:中医的脉作为奇恒之腑与西医学的血管系统具有高度相关性。医家对浊邪的认识不同,但在中医学中浊是一个很复杂的东西,它具有特定的致病特点、临床表现及治疗方法对于多种现代难治病证具有重要的临床指导意义。脉为奇恒之腑,浊留于脉则致脉浊。脉浊的概念充分强调了脉作为奇恒之腑的独立性和整体性,使临床实践中的辨证与辨病能够更好地结合起来,增强了中医对动脉粥样硬化干预的目的性和准确性[26]。
中西医对AS的发病机制及防治均作了大量研究。西药在治疗AS中机制明确,取得了显著的作用,但作用往往效果单一,且副作用较大。中药以中医理论为指导从宏观着手,整体施治,对于AS这类复杂疾病具有独特的优势。近年来中药治疗AS取得了较大的进展,很大程度上弥补了现代医学之不足。中药抗AS主要从调节脂质代谢,抗炎、免疫调节,抗氧化、保护EC,抑制SMC的增殖与迁移、稳定斑块、改善凝血纤溶系统上取得了显著的效果。
2.1 中药复方
中医药治疗疾病立足于整体,辨证论治,中药在抗AS方面疗效肯定。研究表明,大量中药复方能从不同角度调控AS的发生与发展,在AS的研究领域具有潜在的特色和优势。大部分学者认为AS的病机为“本虚标实”,本虚涉及肝、脾、肾诸脏,标实多为瘀、痰、热、毒等。所以在治疗上,大都采用祛瘀化痰,清热解毒、益气固本等治疗方法。表2中复方中药,分别具有不同程度的活血(桃仁、红花等),祛痰(瓜蒌、薤白等),清热解毒(金银花、玄参等),益气固本(黄芪、党参等)功效,契合了AS本虚标实,瘀、痰、热、毒互结之病因病机。
2.2 中药有效成分
随着对中药有效成分抗AS研究的不断深入,其机制的研究也日趋广泛,已深入到细胞及分子水平,其可通过多种机制防治AS及其并发症。AS发病机制复杂,中药对于复杂疾病,能从多途径、多环节、多靶点干预AS病理过程,具有多靶点协同作用的优势和潜力。如丹参酮ⅡA为唇形科植物丹参(Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge.)的干燥根及根茎中的有效成分。研究表明,丹参酮ⅡA可以降低TC,TG,LDL-C及升高HDL-C,通过调节血脂水平来调控AS[73];通过抑制相关的炎症因子如:NF-κB,VCAM-1等抑制炎性反应,抑制 AS的发生发展[73-74];调节ET水平,降低氧化应激对血管壁的损伤[75];下调TXA2水平,上调 PGI2水平,抑制血小板的聚集,改善血流变相关指标[75],改善凝血纤溶系统,抑制血栓的形成,能从多途径、多环节、多靶点起到防治AS及其并发症的作用(表3)。
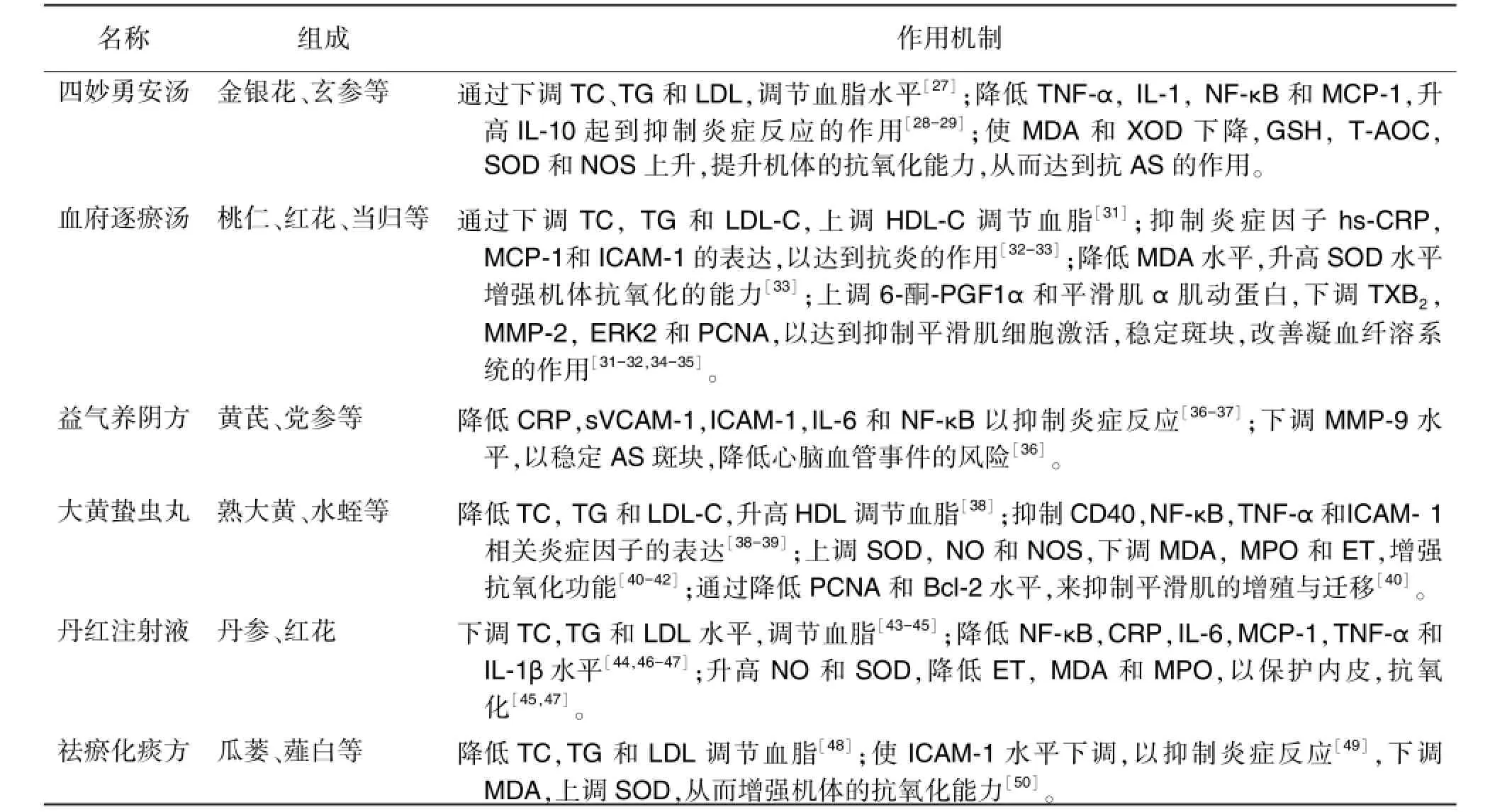
表2 中药复方抗动脉粥样硬化作用机制

表3 中药有效成分抗AS作用机制
3 展望
目前认为AS是一种慢性炎症性疾病,其发病机制十分复杂,涉及脂质代谢紊乱,氧化应激,内皮细胞的损伤,SMC的增殖和迁移等多个方面,最终以斑块的破裂造成急性心脑血管疾病,严重威胁人们的健康。中医药以整体观为指导,辨证论治,能系统治疗,多靶点整合起效,且毒副作用小,对于复杂疾病的治疗有其独特的优势。但是中药治疗AS具体的起效成分及作用机制在细胞和分子生物学上的研究还不够广泛和深入。因此,将新的科学技术及治疗理念引入到中药的研究领域,对于深入探究中药防治AS的作用机制必将取得更大的成就。如高内涵技术的应用、脂代谢组学深入研究、表观遗传修饰等。高内涵分析技术是一种应用高分辨率的荧光数码影像系统,在细胞水平上实现检测标的多元化和功能化的筛选技术,旨在获得被筛样品对细胞产生的多维立体和实时快速的生物效应信息。高内涵分析技术非常适用于中药的复杂成分和多靶点作用机制的研究,对揭示中药复方的科学性和合理性,促进中药现代化的发展有重要意义。而脂质代谢组学作为重要的代谢组学分支,从系统水平上研究生物体内的脂质代谢,揭示其相互作用及与其他生物分子的作用,是一门研究脂质代谢调控在各种生命现象中作用机制的新学科,随着对脂代谢组学研究的日益广泛和深入,将有助于人们更深入地理解脂代谢在AS发生发展的作用,为中药抗AS的提供新的研究方向。表观遗传修饰可能是链接环境因素与遗传因素的桥梁,深入了解表观遗传修饰如 DNA甲基化、组蛋白修饰以及miRNA对AS形成和发展的影响及其作用机制,将进一步阐明AS的发病机制。并且由于表观遗传修饰可逆性,这可能为AS的治疗提供新的策略和靶点。经过进一步的研究与探析,中药防治AS将取得更大的成就。
[1] Li YL.Pathology(病理学)[M].6th ed.Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing Press.2004.
[2] Williams JK,Sukhova GK,Herrington DM,Libby P. Pravastatin has cholesterol-lowering independent effects on the artery wall of atherosclerotic monkeys [J].J Am Coll Cardiol,1998,31(3):684-691.
[3] Skålén K,Gustafsson M,Rydberg EK,Hultén LM,Wiklund O,Innerarity TL,et al.Subendothelial retention of atherogenic lipoproteins in early atherosclerosis[J].Nature,2002,417(6890):750-754.
[4] Ross R.Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory disease [J].N Engl J Med,1999,340(2):115-126.
[5] Papaharalambus CA,Griendling KK.Basic mechanisms of oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular injury[J].Trends Cardiovasc Med,2007,17(2):48-54.
[6] Zhao K,Yang WS.Oxidative stress and endothelial damage caused by hypertension[J].Tianjin Med J (天津医药),2006,34(12):907-909.
[7] Higashi Y,Noma K,Yoshizumi M,Kihara Y.Endothelial function and oxidative stress in cardiovas-cular diseases[J].Circ J,2009,73(3):411-418.
[8] Antoniades C,Shirodaria C,Leeson P,Antonopoulos A,Warrick N,Van-Assche T,et al.Association of plasma asymmetrical dimethylarginine(ADMA)with elevated vascular superoxide production and endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling:implications for endothelial function in human atherosclerosis[J]. Eur Heart J,2009,30(9):1142-1150.
[9] Hu ZY,Wang QJ,Ding XS.Review on endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis and drug therapy [J].Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther(中国临床药理学与治疗学),2006,11(5):481-484.
[10] Qin C, Liu Z.In atherogenesis,the apoptosis of endothelial cell itself could directly induce overproliferation of smooth muscle cells[J].Med Hypotheses,2007,68(2):275-277.
[11] Yang Y,Xu XY.Research progress on the role of macrophages in endometriosis[J].Chongqing Med(重庆医学),2011,40(15):1532-1534.
[12] Chen T, Liang X, Yuan ZY.Introduction and identification of M1/M2 phenotype of RAW264.7 cells[J].Mol Cardiol China(中国分子心脏病学杂志),2011,12(2):117-120.
[13] Bonasio R,Tu S,Reinberg D.Molecular signals of epigenetic states[J].Science,2010,330(6004): 612-616.
[14] Findeisen HM,Gizard F,Zhao Y,Qing H,Heywood EB,Jones KL,et al.Epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima formation by histone deacetylase inhibition[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2011,31(4):851-860.
[15] Bahadori M.New advances in RNAs[J].Arch Iran Med,2008,11(4):435-443.
[16] Sonkoly E,Pivarcsi A.Advances in microRNAs: implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases[J].J Cell Mol Med,2009,13(1):24-38.
[17] Zhou J,Wang KC,Wu W,Subramaniam S,Shyy JY,Chiu JJ,et al.MicroRNA-21 targets peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-alpha in an autoregulatory loop to modulate flow-induced endothelial inflammation[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2011,108(25):10355-10360.
[18] Grisar JC, Haddad F, Gomari FA, Wu JC. Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular disease and chronic inflammation:from biomarker to therapeutic agent[J].Biomark Med,2011,5(6): 731-744.
[19] Liu Y, Wei J, Hu S, Hu L.Beneficial effects of statins on endothelial progenitor cells[J].Am J Med Sci,2012,344(3):220-226.
[20] Bakogiannis C,Tousoulis D,Androulakis E,Briasoulis A,Papageorgiou N,Vogiatzi G,et al.Circulating endothelial progenitor cells as biomarkers for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes[J].Curr Med Chem,2012,19(16):2597-2604.
[21] Haddad P, Dussault S, Groleau J, Turgeon J,Maingrette F,Rivard A.Nox2-derived reactive oxygen species contribute to hypercholesterolemiainduced inhibition of neovascularization:effects on endothelial progenitor cells and mature endothelial cells[J].Atherosclerosis,2011,217(2):340-349.
[22] Tedgui A,Mallat Z.Cytokines in atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways[J].Physiol Rev,2006,86(2):515-581.
[23] Henn V,Slupsky JR,Gräfe M,Anagnostopoulos I,Förster R,Müller-Berghaus G,et al.CD40 ligand on activated platelets triggers an inflammatory reaction of endothelial cells[J].Nature,1998,391(6667):591-594.
[24] Miniati DN, Hoyt EG, Feeley BT, Poston RS,Robbins RC.Ex vivo antisense oligonucleotides to proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Cdc2 kinase inhibit graft coronary artery disease[J].Circulation,2000,102(19 Suppl 3):Ⅲ237-Ⅲ242.
[25] Liang H.To investigate the etiology and pathogenesis of atherosclerosis from Fuxie theory[J].J Changchun Univ TCM(长春中医药大学学报),2009,25(5):802-803.
[26] Chen WQ,Wang YL.Based on the″pulse cloud″theoryon the pathogenesisofatherosclerosis further understanding[J].J TCM(中医杂志),2013,54(17):1450-1452.
[27] Xu B,Nie B,Xu Y,Wu SX,Guo P,Chen LX. Study on regularity ofcompatibility based on ApoE-/-mice atherosclerosis modelofSimiao Yong′an decoction active sites[J].Liaoning J TCM (辽宁中医杂志),2013,40(6):1250-1252.
[28] Zhu HB,Hao JJ,Zhu X.Effect of Simiao soup on the SOCS1 and SOCS3 in atherosclerotic rat[J]. Chin Hosp Pharm J(中国医院药学杂志),2013,33(14):1122-1125.
[29] Zhang JP,Xu YZ,Li M,Li LJ,Peng L,Zhang GY,et al.Effect of Simiao Yong′an Decoction on oxidative stress and inflammation on atherosclerosis model rabbits[J].J TCM(中医杂志),2010,51 (1):72-74.
[30] Zhu HB,Hao JJ,Zhang G,Zhu X.Protective effect of Simiao soup on atherosclerosis oxidative damage in rats[J].J China-Jpn Friendship Hosp(中日友好医院学报),2013,27(3):168-171.
[31] Huang W, Dong C, Liu H, Yang YB,Ren JJ. Xuefu Zhuyu soup influence on atherosclerosis prostacyclin and thromboxane A2in rats[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res(时珍国医国药),2012,23(5):1130-1132.
[32] Dong C,Huang W,Yang Y,Ji PX,Liu HR,Yao Q.The effect and mechanism of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction on the rats with atherosclerosis[J].Her Med(医药导报),2013,32(5):579-582.
[33] Dong C,Huang W, Geng ZH,Gao S.Effects of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction on intercellular adhesion molecule and lipid peroxidation of experimental atherosclerosis rats[J].J Hebei Univ(Nat Sci Ed)〔河北大学学报(自然科学版)〕,2012,32(6):650-654.
[34] Xie H,Luo NYY,Long ZJ,Zhou XQ,Yang FA,Lei YP.The effect of Xuefuzhuyu Decoction and its seperating prescription on expression of ERK2 mRNA in atherosclerotic vascular smooth muscle cells[J].Chin J Integr Med Cardio-/Cerebrovas Dis(中西医结合心脑血管病杂志),2008,6(12): 1422-1423.
[35] Luo YY, Xie H, Xie HB, Zhou XQ,Liu XH. Effects of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction on neointimal formation of atherosclerosis in rabbits[J].J TCM Univ Hunan(湖南中医药大学学报),2008,28 (5):33-35.
[36] Xie X,Wu J,Shao XH,Zhu CL,Ding YQ.Experimental study of Yiqiyangyin Fang on atherosclerosis immune and inflammatory factors IL-6,MMP-9 and NF-κB in rats[J].J Sichuan TCM(四川中医),2013,31(6):58-60.
[37] Xie X,Wu J,Zhu CL,Shao XH,Ding YQ.Experimental study of Yiqiyangyin Fang on atherosclerosis immune and inflammatory factors hs-CRP,sVCAM-1 and sICAM-1 in rats.[J].Jiangsu J TCM(江苏中医药),2013,45(3):73-74.
[38] Jia YQ,Hou GY,Si QJ,Liu ZX,Zhao H.Experimental study of Dahuang Zhechong pill on the formation of atherosclerotic plaque and expression of CD40[J].Hebei J TCM(河北中医),2010,32 (3):426-427,463.
[39] Si QJ,Zhang YH,Wang XG,Jiang YJ,Wang GJ. Effects of Dahuang Zhechong pillon the expression of NF-κB pathway and inflammatory factors in atherosclerosis rats[J].Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form(中国实验方剂学杂志),2013,19 (7):254-258.
[40] Han CJ,Liu JT,Zhang Y,Li M,Pang XM,Mao JJ.Mechanism of Dahuang Zhechong pill against atherosclerosis induced by balloon angioplasty in rabbits[J].J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2011,34 (12):1919-1922.
[41] Zhang L, Li DY.Dahuang Zhechong pill on rat model of atherosclerosis and the expression of ET-1 NO randomized controlled study of effect[J]. J Pract Tradit Chin Intern Med(实用中医内科杂志),2012,26(4):27-28.
[42] Zhang L,Li DY.Effect of Dahuang Zhechong pill on the expression of NO and NOS in atherosclerosis rats[J].Jilin J TCM(吉林中医药),2012,32 (3):280-281.
[43] Xu XM,Wang JY.Effects of Danhong injection on blood lipid and hemorheology of rabbits with atherosclerosis[J].Chin J Lab Diagn(中国实验诊断学),2009,13(6):820-821.
[44] Guan GF,Hua XP,Wang L,Du L,Kong XH.The effects of Danhong injection on vascular inflammation in rabbit model with atherosclerosis[J].Chin J Integr Med Cardio-/Cerebrovasc Dis(中西医结合心脑血管病杂志),2006,4(10):884-886.
[45] Guan GF,Hua XP,Wang LD,Kong L,Kong XH. Effects of Danhong injection on lipid metabolism and vascular endothelial function in rabbit model with experimental atherosclerosis[J].J Clin Cardiol (临床心血管病杂志),2007,23(4):304-306.
[46] Gao LN,Cui YL,Wang QS,Wang SX.Amelioration of Danhong injection on the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated systemic acute inflammatory reaction via multi-target strategy[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2013,149(3):772-782.
[47] Wan LM,Tan L,Wang ZR,Liu SX,Wang YL,Liang SY,et al.Preventive and therapeutic effects of Danhong injection on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2013,149(1):352-359.
[48] Yang XW,Zhao HS,Shang S,Guo JJ,Liu FQ,Mu Y,et al.Effect of Quyuhuatan Decoction on blood lipid level of rats with atherosclerosis[J]. Beijing J TCM(北京中医药),2012,31(12):927-929.
[49] Yu J,Gong YP,Chen M,Chen Y.Research on Quyuhuatan decoction and kidney tonifying dampness Decoction on hyperlipidemia rats vascular cell adhesion factor-1 expression[J].Zhejiang J TCM (浙江中医杂志),2010,45(3):176-177.
[50] Shang S,Xu LP,Yang XW,Mu Y,Zhao HS,Guo JJ,et al.Protective effect of Quyuhuatan decoction on cardiovascular damage with atherosclerosis in rats[J].Beijing J TCM,2012,3(2):143-147.
[51] Wang M, Liu XQ, Chen HQ, Yu X,Gu QQ,Wang QZ.Effects of baicalin on serum adiponectin,high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor α in ApoE deficiency mice[J].Chin J Gerontol (中国老年学杂志),2013,33(1):101-103.
[52] Guo ZY.Protective effect of baicalin on lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage of endothelial cells [J].J Chin Med Mater(中药材),2012,35(2): 288-291.
[53] Li X, Yan RH, Peng J.Baicalin suppressed inflammatory reaction by decreasing nuclear factorκB and soluble monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in hyperlipdemia rat[J].Chin J Arterioscler(中国动脉硬化杂志),2010,18(8):611-613.
[54] Hu HJ,Han M,Sun RH,Liu B,Wen JK.Baicalin inhibits VSMC proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia in rats[J].Basic Med Clin(基础医学与临床),2010,30(12):1252-1256.
[55] Jiang F,Qian J,Chen S,Zhang W,Liu C.Ligustrazine improves atherosclerosis in rat via attenuation of oxidative stress[J].Pharm Biol,2011,49 (8):856-863.
[56] Wang GF,Shi CG,Sun MZ,Wang L,Wu SX,Wang HF,et al.Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates atherosclerosis development and protects endothelial cells from ox-LDL[J].Cardiovasc Drugs Ther,2013,27(3):199-210.
[57] Jiang X.Investigation on efficacy of ligustrazine′s antagonism to free radicals in SD rats with atherosclerosis[J].J Hubei Univ TCM(湖北中医药大学学报),2011,13(3):14-15.
[58] Wang GF,Zhao X,Li N,Cui HM.The effects of ligustrazine on expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax in ox-LDL-induced atherosclerotic model through improving endothelial functions[J].Chin J Clin(Electron Ed)〔中华临床医师杂志(电子版)〕,2011,5(23): 6898-6901.
[59] Yang WH,Gong GQ,Zhou Y,Zhang ZX,Li J. Effect and mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine on antithrombotic[J].Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther(中国临床药理学与治疗学),2012,17(3):241-245.
[60] Yang Q,Wang S,Xie Y,Wang J,Li H,Zhou X,et al.Effect of salvianolic Acid B and paeonol on blood lipid metabolism and hemorrheology in myocardial ischemia rabbits induced by pituitrin[J].Int J Mol Sci,2010,11(10):3696-3704.
[61] Chen XL,Zhang YY,Gu RY.Salvianolic acid B on immune pathways of OX40/and OX40L in rats with atherosclerosis[J].Shaanxi J TCM(陕西中医),2012,33(6):758-761.
[62] Bao Y,Wang L,Xu Y,Yang Y,Wang L,Si S,et al.Salvianolic acid B inhibits macrophage uptake of modified low density lipoprotein(mLDL)in a scavenger receptor CD36-dependent manner[J]. Atherosclerosis,2012,223(1):152-159.
[63] Pan CH,Chen CW,Sheu MJ,Wu CH.Salvianolic acid B inhibits SDF-1α-stimulated cell proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing CXCR4 receptor[J].Vasc Pharmacol,2012,56(1-2):98-105.
[64] Xie LX,Durairajan SS,Lu JH,Liu CL,Kum WF,Wang Y,et al.The effect of salvianolic acid B combined with laminar shear stress on TNF-alphastimulated adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells[J].Clin Hemorheol Microcirc,2010,44(4):245-258.
[65] Hur KY,Kim SH,Choi MA,Williams DR,Lee YH,Kang SW,et al.Protective effects of magnesium lithospermate B against diabetic atherosclerosis via Nrf2-ARE-NQO1 transcriptional pathway[J].Atherosclerosis,2010,211(1):69-76.
[66] Zhang FX,Guan N,Sun DP,Li CG,Guo WS. The mechanism of resveratrol from increases of the expression of cholesterol ester hydrolase to inhibit atherosclerosis[J].Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch(解放军医学院学报),2013,34(2):164-166.
[67] Qu Q,Jiao JJ,Wang CH,Wang QQ,Du YX. Influence of resveratrol on expression of nuclear factor-κB in aorta of rat with atherosclerosis[J].J Anhui Agri Sci(安徽农业科学).2010,38(4): 1671-1672,1694.
[68] Bai YX.Study of the effect and the mechanism of resveratrol on platelet aggregation in hyperlipidemia rats[J].Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther(中国临床药理学与治疗学),2013,18(7):769-773.
[69] Deng ZY,Kuang R,Zhu SM,Wang D,Kang H,Zhao J.Effects of resveratrol on multiple anti-oxidant systems in hyperlipidemia rats[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull(中国药理学通报),2013,29(1):147-148.
[70] Ruan JM,Zhu PL,Jiang N,Shang XL,Lin F. Effects of resveratrol on expression of PPARγ and related inflammatory factors in rabbits with atherosclerosis[J].Chin J Arterioscler(中国动脉硬化杂志),2013,21(3):203-208.
[71] Wakabayashi I, Takeda Y.Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on MCP-1,IL-6,and IL-8 production in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2013,386(9):835-839.
[72] Gao P,Si LY,Xu Q,Wang XM.Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by angiotensinⅡand its underlying mechanism[J].Med J Chin PLA(解放军医学杂志),2013,38(4):269-273.
[73] Wang JX,Shen XJ.Experimental study of tanshinoneⅡA in regulation of NF-κB pathway and antiatherosclerosis[J].Henan TCM(河南中医),2013,33(5):681-683.
[74] Li HZ,Lu YH,Chen Q,Huang GS.Effects of tanshinoneⅡA on expression of VCAM-1 in atherosclerotic mice[J].Chin J Gerontol(中国老年学杂志),2011,31(19):3736-3737.
[75] Li ZL,Shi QL,Zhu PX.Intervention effect of tanshinoneⅡA on vascular endothelial cell function in patients with atherosclerosis[J].J Nanchang Univ (Med Sci)〔南昌大学学报(医学版)〕,2012,52 (7):44-45,48.
Advances in anti-atheroscIerosis mechanisms of traditionaI Chinese medicine
YAN Chun-lin1,2,YANG Jing1,HAN Ji-hong3,ZHU Yan1
(1.Tianjin State Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300193,China;2.Research and Development Center of Chinese Medicine,Tianjin International Joint Academy of Biotechnology and Medicine,Tianjin 300457,China;3.College of Life Sciences,Nankai University,Tianjin 300193,China)
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases,including coronary heart disease,peripheral vascular disease and atherosclerosis,are the first cause of death worldwide.The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is a complex process that involves a number of cellular processes and molecular mechanisms,such as disorder of lipid metabolism,inflammatory cell infiltration,oxidative stress,vascular endothelial cells injury and activation of smooth muscle cells.Their interaction eventually leads to plaque rupture and thrombus formation,causing serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.Chinese medicine has displayed rich anti-AS activities and clinical applications.This review summarizes the antiatherosclerosis effects and possible mechanisms of Chinese medicine in regulating lipid metabolism,anti-inflammation and antioxidation,protecting endothelial cells,inhibiting the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells,improving coagulation and fibrinolysis systems and stabilizing the plaque.
atherosclerosis;pharmacology(TCD)
ZHU Yan,E-mail:yanzhu.harvard@gmail.com
R285,R966
:A
:1000-3002(2014)06-0904-10
10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2014.06.014
Foundation item:The project supported by National Science and Technology Major Project(2013ZX 09201020);and Tianjin Key Program of Applied Infrastructure and Cutting-edge Technology Research(12JCZDJC26500)
2013-11-18 接受日期:2014-02-10)
(本文编辑:乔 虹)
国家科技重大专项(2013ZX 09201020);天津市应用基础与前沿技术研究计划重点项目(12JCZDJC26500)
严春琳(1989-),女,硕士研究生,主要从事心血管药理的研究,E-mail:yanchunlin08@163.com
朱 彦,E-mail:yanzhu.harvard@gmail.com

