The tensor algebras of Yetter-Drinfeld module
Yanhua Wang
(School of Mathematics, Shanghai University of Finance and Economics)
1 Introduction
LetHbe a Hopf algebra (bialgebra),a left-left Yetter-Drinfeld module over Hopf algebra (bialgebra)His ak-linear spaceVwhich is a leftH-module,a leftH-comodule and satisfies a certain compatibility condition.Yetter-Drinfeld modules were introduced by Yetter in [1] under the name of "crossed bimodule".Radford proved that pointed Hopf algebras can be decomposed into two tensor factors,one factor of the two factors is no longer a Hopf algebra,but a rather a Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra over the other factor[2].Subsequently,Schauenburg proved that the category of Yetter-Drinfeld module overHwas equivalent to the category of left module over Drinfeld double,and also to the category of Hopf module overH[3],and Sommerhauser studied Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra over groups of prime order[4].
Some conclusions of Hopf algebras can be applied to Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras.For example: Doi considered the Hopf module theory of Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras in [5],Scharfschwerdt proved the Nichols Zoeller theorem for Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras in [6],and Andruskiewitsch and Schneider gave the trace formula for Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras in [7].
In this paper,we generalized the antipode properties of Hopf algebras to Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras.We proved the antipode of a Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra is an anti-algebra and anti-coalgebra map,see Proposition 1 and Proposition 2.We study the tensor algebra of Yetter-Drinfeld module,and show that the tensor algebra of Yetter-Drinfeld module is a Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra under a tensor multiplication and a "twisted" comultiplication,see Theorem 4.
In the following,kwill be a field.All algebras and coalgebras are overk.All unadorned ⊗ are taken overk.
2 Preliminaries of Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras

(ab) →v=a→ (b→v), 1 →v=v.
The arrow → denotes left module action.The category of leftA-module is denoted byAM.
Let (C,△,) be a coalgebra.A leftC-comodule is ak-vector spaceVtogether with ak-linear mapρ:VC⊗V:v∑v-1⊗v0such that
∑v-2⊗v-1⊗v0=∑v-1⊗(v0)-1⊗(v0)0, ∑(v-1)v0=v.
The category of leftC-module is denoted byCM.
Let (H,m,u,△,,S) be a Hopf algebra with antipodeS.A left Yetter-Drinfeld module overHis ak-vector spaceVwhich is both a leftH-module and leftH-comodule and satisfies the compatibility condition
∑(h→v)-1⊗(h→v)0=∑h1v-1Sh3⊗h2→v0,
(1)

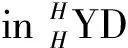
(a1)Ais a leftH-module algebra,i.e.,
h→(ab)=∑(h1→a)(h2→b),h→1A=(h)1A.
(a2)Ais a leftH-comodule algebra,i.e.,
ρ(ab)=∑(ab)-1⊗(ab)0=∑a-1b-1⊗a0b0,
ρ(1A)=1H⊗1A.
(a3)Ais a leftH-module coalgebra,i.e.,
△(h→a)=∑(h1→a1)⊗(h2→a2),(h→a)=H(h)A(a).
(a4)Ais a leftH-comodule coalgebra,i.e.,
∑a-1⊗(a0)1⊗(a0)2=∑a1-1a2-1⊗a10⊗a20,
∑a-1A(a0)=A(a)1H.
△∘m(a⊗b)=(m⊗m)(id⊗τ⊗id)(△⊗△)(a⊗b)=
∑a1(a2-1→b1)⊗a20b2,
Ais called a Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra or Hopf algebras in Yetter-Drinfeld category if it has an antipodeSthat is a convolution inverse to id,i.e.,

One easily see thatSis bothH-linear andH-colinear.In general,Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras are not ordinary Hopf algebras because the bialgebra axiom asserts that they obey (a5).However,it may happen that Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras are ordinary Hopf algebras when the pre-braiding is trivial,for details see [4].
Next,we give a basic property of Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra.It is well know that the antipode of a Hopf algebra is an anti-algebra and anti-coalgebra map,see [8-10].This is also true for Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra.The following lemma give the character.

S1)S(ab)=∑(a-1→S(b))S(a0),andS(1)=1.
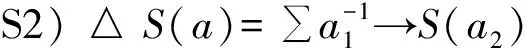
ProofIfSis an anti-algebra automorphism,then we haveSm=m(s⊗s)τands(1)=1.We take the idea of Sweedler in [10,P.74].

We have
(Sm*m)(a⊗b)=
m(Sm⊗m)△(a⊗b)=
m(Sm⊗m)(∑a1⊗a2-1→b1⊗a20⊗b2)=
S(∑a1(a2-1→b1))⊗a20b2=
∑S((ab)1)(ab)2=
u(a⊗b).
On the other hand
(m*m(S⊗S)τ)(a⊗b)=
m(m⊗m(S⊗S)τ)△(a⊗b)=
m(m⊗m(S⊗S)τ)(∑a1⊗a2-1→b1⊗a20⊗b2)=
m∑[a1(a2-1→b1)⊗m(S⊗S)τ(a20⊗b2)]=
m∑[a1(a2-2→b1)⊗m(S⊗S)(a2-1→b2⊗a20)]=
m∑[a1(a2-2→b1)⊗(a2-1→S(b2))S(a20)]=
∑a1(a2-2→b1)(a2-1→S(b2))S(a20)]=
∑a1[a2-1→(b1S(b2))]S(a20)=
∑a1(a2-1→(b))S(a20)=
∑a1(a2-1)(b)S(a20)=
∑u(b)a1S(a2)=u(b)u(a)=u(a⊗b) .
ThusSm*m=m*(m(s⊗s)τ)=u,henceSm=m(s⊗s)τ.By(1)=1 and △(1)=1⊗1,we have (S*id)(1)=S(1)1=u(1)=1.SoS(1)=1.
The proof ofSis an anti-coalgebra automorphism is similar to the proof ofSis an anti-algebra automorphism.

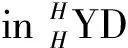
ProofBy assumption,it suffice to prove that if (id*S)(a)=u(a) and (S*id)(b)=u(b),then (id*S)(ab)=u(ab),a,b∈X.
By △(ab)=∑a1(a2-1→b1)⊗a20b2, we have
(id*S)(ab)=∑a1(a2-1→b1)S(a20b2)=
∑a1S(a2)
u(a)u(b)=
u(ab) .
This complete the proof.
3 The tensor algebra of Yetter-Drinfeld module
Assume thatVis a vector space,thenTV=V⨁V⊗V⨁… ⨁V⊗n=T0V⨁T1V⨁T2V⨁…TnVbecomes an algebra with the connected multiplication
(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vs)(w1⊗w2⊗…⊗wt)=v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vs⊗w1⊗w2⊗…⊗wt.
(2)
We have the following lemma about the tensor algebra of a Yetter-Drinfeld module.
Lemma3LetVbe a left Yetter-Drinfeld module,thenTVis also a left Yetter-Drinfeld module.
ProofDefine the module action and comodule action as follows
h→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)=∑(h1→v1)⊗(h2→v2)⊗…⊗(hn→vn)
(3)
and
ρ(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)=∑(v1-1v2-1…vn-1)⊗v10⊗v20⊗…⊗vn0,
(4)
∀h∈H,v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn∈TV.
It is easy to proveTVis a leftH-module.For anyh,g∈H,v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn∈TV.We have 1→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)=v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vnand
h→(g→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn))=
∑(h1→g1→v1)⊗(h2→g2→v2)⊗…⊗(hn→gn→vn)=
∑(h1g1→v1)⊗(h2g2→v2)⊗…⊗(hngn→vn)=
(hg)→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn).
TVis a leftH-comodule.Since
(⊗id)ρ(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)=
v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn
and
(△⊗id)ρ(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)=
(△⊗id)(∑v1-1v2-1…vn-1⊗v10⊗v20⊗…⊗vn0)=
∑(v1-2v2-2…vn-2)⊗(v1-1v2-1…vn-1)⊗(v10⊗v20⊗…⊗vn0)=
(id⊗ρ)ρ(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)
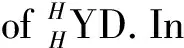
∑(h→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn))-1⊗(h→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn))0=
∑(h1→v1⊗h2→v2⊗…⊗hn→vn)-1⊗(h1→v1⊗h2→v2⊗…⊗hn→vn)0=
∑(h1→v1)-1⊗(h2→v2)-1⊗…⊗(hn→vn)-1⊗(h1→v1)0⊗(h2→v2)0⊗…⊗(hn→vn)0=
∑(h1v1-1S(h3)h4v2-1S(h6)…S(h3n+1)vn-1S(h3n+3)⊗h2→v10⊗h5→v20⊗…⊗h3n+2→vn0=
∑(h1v1-1v2-1…vn-1S(hn+2))⊗h2→v10⊗h3→v20⊗…⊗hn+1→vn0=
∑(h1v1-1v2-1…vn-1S(h3))⊗h2→(v10⊗v20⊗…⊗vn0)=
∑(h1(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)-1S(h3))⊗h2→(v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vn)0.
This complete the proof.
Theorem4IfVis a Yetter-Drinfeld module over Hopf algebraH,then the tensor algebraTVofVis a Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebra overH.
ProofFor anyx=v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vs∈TsV,y=w1⊗w2⊗… ⊗wt∈TtV,define the multiplication ofxyas the tensor multiplication
xy=v1⊗v2⊗…⊗vs⊗w1⊗w2⊗…⊗wt.
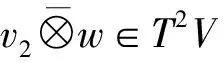
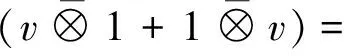



which show that △ is coassociative.
By the comultiplication ofV,forv⊗w∈T2V,we have
△(v⊗w)=(m⊗m)(id⊗τ⊗id)(△(v)⊗△(w))=
(m⊗m)(id⊗τ⊗id)((1⊗v+v⊗1)⊗(1⊗w+w⊗1)=
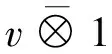
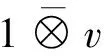
Forv⊗w⊗t∈T3V,the comultiplication ofT3Vis
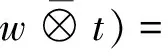


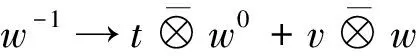
In general,we denote
⊗v2⊗…⊗vn) =
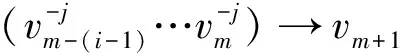
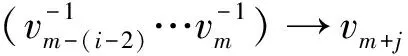
Using the above notation,the comultiplication ofTVis
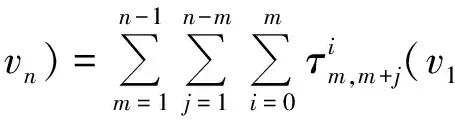
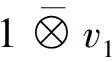

DefineS(v)=-v,v∈V,and
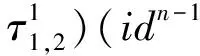
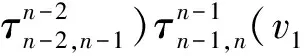
For anyv∈V,we havem(S⊗id)△(v)=s(1)v+vS(1)=0=(v) andm(id⊗S)△(v)=s(v)+vS(1)=0=(v).Therefore,the property of antipode is satisfied for generators ofTV.By Lemma 2,Sis the antipode ofTV.This completes the proof.
:
[1] D.N.Yetter.Quantum groups and representation of monoidal categories [J].Math.Proc.Cambridge Philos.Soc.,1990,108:261-290.
[2] D.Radford.The structure of Hopf algebras with a projection [J].J.Algebra,1985,92:322-347.
[3] P.Schauenburg.Hopf modules and Yetter-Drinfeld modules [J].J.Algebra,1994,169:874-890.
[4] Y.Sommerhauser.Yetter-Drinfeld Hopf algebras over groups of prime order [C]//Lecture Notes in Mathemtics,Vol.1789,Springer,2002.
[5] Y.Doi.Hopf module in Yetter-Drinfeld categories [J].Comm.Algebra,1998,26(9):3057-3070.
[6] Scharfschwerdt.The Nichols-Zoeller theorem for Hopf algebras in the category of Yetter-Drinfeld modules [J].Comm.Algebra,2001,29(6):2481-2487.
[7] Y.Doi.The trace formula for braided Hopf algebras [J].Comm.Algebra,2000,28(4):1881-1895.
[8] S.Dascalescu,C.Nastasescu,S.Raianu.Hopf algebra; An introduction [M].New York:Marcel Dekker,Inc.,2001.
[9] S.Montgomery.Hopf algebras and their actions on rings [C].CBMS Regional Conf.Series in Math.82,Amer.Math.Soc.,Providence,RI 1993.
[10] M.E.Sweedler.Hopf algebras [M].New York:Benjamin,1969.
- 上海师范大学学报·自然科学版的其它文章
- Analysis of a multi-patch dynamical model about cattle brucellosis
- The dynamics of poverty and crime
- Exact parametric representations of orbits defined by cubic Hamiltonian
- Global bifurcation of a cubic system perturbed by degree four
- Local integrable differential systems and their normal forms
- Existence of positive solutions for integral boundaryvalue problem of fractional differential equations

