miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6与前列腺癌病理特征的关系及对手术预后的影响
【摘 要】目的:探讨微小RNA-296-5p、S期激酶相关蛋白2(S-phase kinase-associated protein 2,Skp2)、核糖体蛋白L6(ribo? somal protein L6,RPL6)与前列腺癌病理特征的关系及对手术预后的影响。方法:选取2018年1月至2023年1月120例前列腺患者,均行腹腔镜前列腺癌术治疗,对比不同病理特征患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平,分析各指标与病理特征的关系。根据术后1年是否生化复发分为复发组(n=21)与未复发组(n=97),比较2组临床资料、miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平,分析miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6对手术预后的影响及预测价值。结果:不同病理分期、Gleason评分、术前血清前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)水平、淋巴结转移患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平比较,差异有统计学意义(F=12.927、22.416、10.088、34.239、20.180、12.208,t=4.649、-5.770、-5.713、4.716、-5.647、-6.884,均P=0.000);miR-296-5p与Gleason评分、病理分期、术前血清前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)水平、淋巴结转移呈负相关(r=-0.578、-0.539、-0.517、-0.556,均P<0.001),Skp2、RPL6 mRNA与Gleason评分、病理分期、术前血清PSA水平、淋巴结转移呈正相关(r=0.531、0.507、0.476、0.493、0.494、0.473、0.420、0.505,均P<0.001);复发组淋巴结转移、病理分期、切缘阳性率、Glea? son评分、高于未复发组,术后辅助治疗率低于未复发组(P<0.05);复发组miR-296-5p表达水平低于未复发组,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平高于未复发组(P<0.05);校正前,logistic回归分析,病理分期、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移、切缘阳性、术后辅助治疗、miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA是前列腺癌患者术后生化复发的影响因素(P<0.05),校正后,miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA仍是前列腺癌患者术后生化复发的影响因素(P<0.05);miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6联合预测前列腺术后生化复发的AUC为0.902(95%CI=0.833~0.949),大于各指标单独预测(P<0.05)。结论:前列腺癌患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6表达水平与病理特征、术后复发密切相关,三者联合预测前列腺术后生化复发具有较高的参考价值。
【关键词】微小RNA-296-5p;S期激酶相关蛋白2;核糖体蛋白L6;前列腺癌;病理特征;手术;预后
【中图分类号】R114【文献标志码】A【收稿日期】2024-06-30
基金项目:2023年度河南省医学科技攻关计划资助项目(编号:LHGJ20230885)。
Association of miR-296-5p,S-phase kinase-associated protein 2,and ribosomal protein L6 with the pathological features of prostate cancer and their influence on surgical prognosis
Zhang Canfeng1,Liu Jiaxin2,Yang Wenbo1
(1. Urology 2nd Ward;2.Critical Care Medicine 1st Ward,Xinxiang Central Hospital,The Fourth Clinical College of Xinxiang Medical College)
【Abstract】Objective:To explore the relationship between microRNA-296-5p(miR-296-5p),S-phase kinase-associated protein 2(Skp2),ribosomal protein L6 (RPL6) and pathological characteristics of prostate cancer,as well as their impact on surgical prognosis. Methods:A total of 120 patients with prostate cancer who were treated from January 2018 to January 2023 were enrolled,and all pa? tients underwent laparoscopic therapy for prostate cancer. The mRNA expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 were com? pared between the patients with different pathological features,and the association between each indicator and pathological features was analyzed. According to the presence or absence of recurrence at 1 year after surgery,the patients were divided into recurrence group with 21 patients and non-recurrence group with 97 patients. The two groups were compared in terms of clinical data and the mRNA expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6,and the influ? ence of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 on surgical prognosis and their predictive value were analyzed. Results:There were statisti?cally significant differences in the expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 mRNA among patients with different pathologi? cal stages,Gleason scores,preoperative serum prostate specific antigen(PSA) levels,and lymph node metastasis(F=12.927,22.416,10.088,34.239,20.180,12.208;t=4.649,-5.770,-5.713,4.716,-5.647,-6.884;P=0.000 for all). miR-296-5p was negatively corre? lated with Gleason score,pathological stage,preoperative serum PSA level,and lymph node metastasis(r=-0.578,-0.539,-0.517,-0.556;P<0.001 for all),while Skp2 and RPL6 mRNA were positively correlated with Gleason score,pathological stage,preoperative serum PSA level,and lymph node metastasis(r=0.531,0.507,0.476,0.493,0.494,0.473,0.420,0.505;P<0.001 for all). Compared with the non-recurrence group,the recurrence group had significantly higher lymph node metastasis,pathological stage,rate of positive margin,and Gleason score and a significantly lower rate of postoperative adjuvant therapy(P<0.05). Compared with the nonrecurrence group,the recurrence group had a significantly higher expression level of miR-296-5p and significantly lower mRNA ex? pression levels of Skp2 and RPL6(P<0.05). Before correction,the logistic regression analysis showed that pathological stage,Gleason score,lymph node metastasis,positive surgical margin,postoperative adjuvant therapy,and the mRNA expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 mRNA were influencing factors for postoperative biochemical recurrence in patients with prostate cancer(P< 0.05),and after correction,the mRNA expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 were still influencing factors for postopera? tive biochemical recurrence in patients with prostate cancer (P<0.05). The ROC curve analysis showed that the combination of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 had an area under the ROC curve of 0.902(95%CI=0.833~0.949) in predicting biochemical recurrence af? ter prostate cancer surgery,with a significantly larger AUC than each indicator alone(P<0.05). Conclusion:The expression levels of miR-296-5p,Skp2,and RPL6 are closely associated with pathological features and postoperative recurrence in patients with prostate cancer,and the combination of the three indicators has a high reference value in predicting biochemical recurrence after prostate can? cer surgery.
【Key words】microRNA-296-5p;S-phase kinase-associated protein 2;ribosomal protein L6;prostate cancer;pathological features;surgery;prognosis
国际癌症数据显示,2020年全球前列腺癌新发病例为141.4万,占全部男性癌症14.10%,是全球男性第二位恶性肿瘤,其死亡率在男性癌症中位居第五位[1]。腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术是治疗前列腺癌有效途径之一,能延长患者生存期,但由于恶性肿瘤生物学特性、细胞残留及远处微转移等原因,术后生化复发较为严重,影响预后[2]。微小RNA(mi? croRNA,miRNA)属于非编码RNA,在肿瘤发生发展过程发挥抑癌或原癌基因作用,有证据显示,miRNA与前列腺癌进展有关[3]。如Lee KH等[4]研究发现,miR-296-5p在前列腺组织和细胞中低表达,过表达miR-296-5p能明显抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖和克隆形成能力。S期激酶相关蛋白2(S-phase kinase-associated protein 2,Skp2)是F盒蛋白家族成员,在细胞周期、转移及侵袭中扮演着重要角色,段松等[5]研究发现,Skp2在前列腺癌组织高表达,与术后复发及临床病理特征有关。核糖体蛋白L6(ribo? somal protein L6,RPL6)是核糖体大亚基因之一,在多种实体瘤中异常表达,如RPL6在前列腺癌中高表达,与细胞损伤、细胞增殖及侵袭等有关[6]。但临床关于miR-296-5p、RPL6、Skp2联合在前列腺癌中的研究鲜见。基于此,本研究主要探究miR-296- 5p、Skp2、RPL6与前列腺癌病理特征的关系,并分析三者联合对患者术后的预测价值,以期为临床个性化治疗提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2018年1月至2023年1月新乡市中心医院泌尿外科诊治的120例前列腺患者,其中年龄54~79岁,平均(69.58±7.64)岁;病理分期:19例T1期,79例T2期,22例T3期;术前血清前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)水平:13例<10 ng/mL,35例10~20 ng/mL,72例>20 ng/mL;Gleason评分:51例<7分,69例≥7分;84例无淋巴结转移,36例有淋巴结转移。本研究患者知情同意,并签订知情同意书。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:前列腺癌诊断标准符合2021年版《前列腺癌筛查中国专家共识》[7];经病理检查确诊为前列腺癌;均行腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术治疗,无手术禁忌证;自愿参与研究且签署协议书;均为T1、T2、T3期。
排除标准:传染性或感染性疾病;其他泌尿系统疾病,如尿路结石等;严重肾脏疾病;其他恶性肿瘤;内分泌疾病;凝血功能异常或出血性疾病;精神疾病或认知功能障碍;自身免疫系统疾病;入组前接受放射、化疗等药物治疗;术后血清PSA≥0.2 ng/mL;术前发生远处转移;既往前列腺手术史;预计生存期≥6年;长期使用免疫抑制剂。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 病理特征和基线资料 收集所有受试者年龄、术前血清PSA水平、病理分期、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移、切缘阳性、术后辅助治疗(调强放疗、放射性粒子植入及内分泌治疗)。Gleason评分[8]:1~4分为高分化、低级别癌,5~6为中分化癌,7~10分为低分化或未分化、高级别癌,评分越高提示病情恶化较为严重。采集患者空腹肘静脉血4 mL,室温静置30 min后,经3 000 r/min离心10 min收集血清,放射免疫法测定血清PSA水平。
1.3.2 miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6检测 采集所有患者空腹肘静脉血,室温静置30 min后,用Trizol试剂提取血清总RNA,检测RNA浓度和纯度后参照逆转录试剂盒(miR-296-5p采用miRNA试剂盒进行转录、Skp2、RPL6使用Scien? tific RevertAid RT试剂盒转录)合成cDNA,以cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增。扩增体系:SYBR Green Master 5 μL,上、下游引物各0.2 μL,cDNA模板1 μL,无酶水补足至10 μL。miR-296-5p上游5’-GTCACAGCTCGGAT-3’,下游5’-GAG AGGCTAGGCGAAGG-3’;U6上游5’-ACGAATTTGCGTGTC ATCCTTGCG-3’,下游5’-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACT A-3’;RPL6上游5’-ATGGCGGGTGAAAAAGTTG-3’,下游5’-TCCTCACAAATTGGTGTTCTAAAT-3’;SKP2上游:5’-A TGCCCCAATCTTGTCCATCT-3’,下游:5’-CACCGACTGAG TGATAGGTGT-3’;GAPDH引物序列:上游5’-GGATTTGGT CGTATTGGG-3’,下游5’-GGAAGATGGTGATGGGATT-3’。2-ΔΔCt法计算miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平,miR-296-5p以U6作为内参,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA以GAPDH作为内参。
1.3.3 预后评估 所有患者术后随访1年,失访2例,118例患者完成随访。以术后当天作为起始日期,随访终点为2024年1月31日,经核素骨、电子计算机断层扫描、磁共振成像等影像学检查前列腺形态变化,连续测得2次PSA升高≥0.2 ng/mL可判定为生化复发,反之为未复发[9]。
1.4 观察指标
①分析不同病理特征患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平。②miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA与病理特征的关系。③比较复发组与未复发组临床资料、miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平。④分析miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6对手术预后的影响及对手术预后的预测价值。
1.5 统计学方法
采用软件SPSS 26.0分析数据,计量资料行K-S正态性检验、Levene方差齐性检验,呈正态分布、方差齐性时以均数±标准差(-x±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,事后比较采用LSD-t检验,组内比较采用配对样本t检验;计数资料用例数(百分比)表示、采用χ2检验,相关性分析采用Spearman,采用logistic进行多因素分析,AUC及ROC评估预后价值。检验水准α=0.05。
2 结 果
2.1 不同病理特征患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平
不同年龄患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平差异无统计学意义(t=-0.368、-0.233、-0.359,P=0.714、0.816、0.720);miR-296-5p随着病理分期、术前血清PSA水平、Gleason评分增加呈不断下降趋势,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平随着病理分期、术前血清PSA水平、Gleason评分增加呈不断升高趋势(F=12.927、22.416、10.088、34.239、20.180、12.208,P=0.000、0.000、0.000、0.000、0.000、0.000);Gleason评分≥7分患者miR-296-5p mRNA表达水平低于Gleason评分<7分患者,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平高于Gleason评分<7分患者(t=4.649、-5.770、-5.713,P=0.000、0.000、0.000);淋巴结转移患者miR-296-5p mRNA表达水平低于无淋巴结转移患者,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平高于无淋巴结转移患者(t=4.716、-5.647、-6.884,P=0.000、0.000、0.000),见表1。
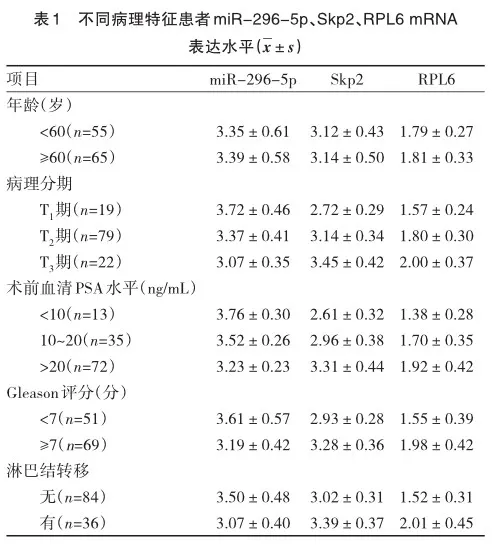
2.2 miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6与病理特征的关系
Spearman相关性分析,miR-296-5p与病理分期、术前血清PSA水平、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移呈负相关,Skp2、RPL6与病理分期、术前血清PSA水平、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移呈正相关(P<0.05),见表2。
2.3 复发组与未复发组临床资料
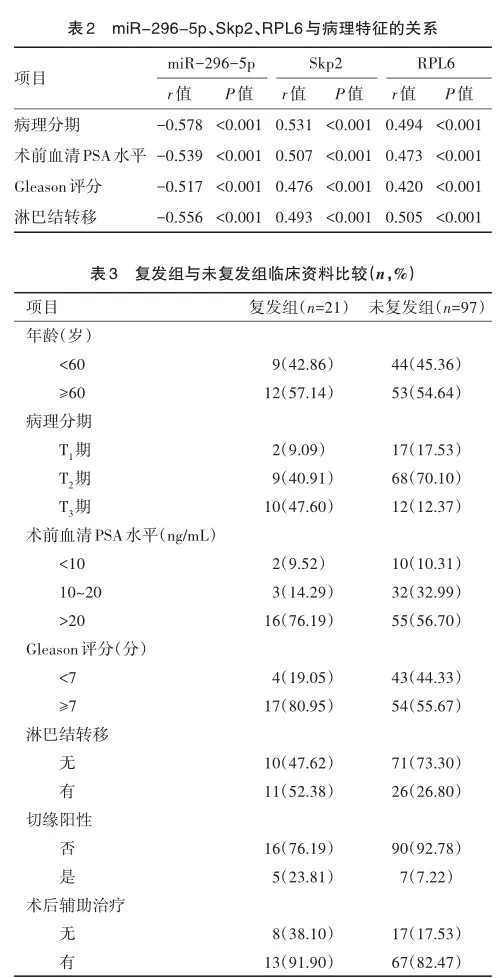
随访1年,失访2例,118例患者完成随访。2 组年龄、术前血清PSA水平差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.044、1.282,P= 0.834、0.199);复发组病理分期、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移、切缘阳性率高于未复发组,术后辅助治疗率低于未复发组(χ2=2.597、4.604、5.247、5.203、4.374,P=0.010、0.032、0.022、0.023、0.036),见表3。
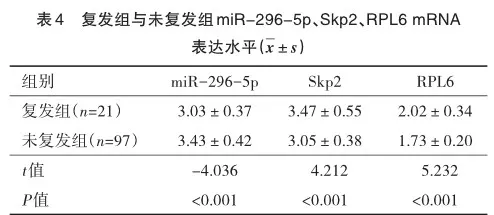
2.4 复发组与未复发组miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平
复发组miR-296-5p表达水平低于未复发组,Skp2、RPL6 mRNA表达水平高于未复发组(P<0.05),见表4。
2.5 miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6对手术预后的影响
以术后1年是否生化复发作为自变量(否=0,是=1),Gleason评分、病理分期、Skp2、淋巴结转移、miR-296-5p、切缘阳性、RPL6、术后辅助治疗作为自变量,logistic回归分析,病理分期、切缘阳性、淋巴结转移、Gleason评分、术后辅助治疗、miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6是前列腺癌患者术后生化复发的独立影响因素(P<0.05);将病理分期、淋巴结转移、切缘阳性、Gleason评分、术后辅助治疗等其他因素校正后,miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6仍是前列腺癌患者术后生化复发的独立影响因素(P<0.05),见表5。
2.6 miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6对手术预后的预测价值
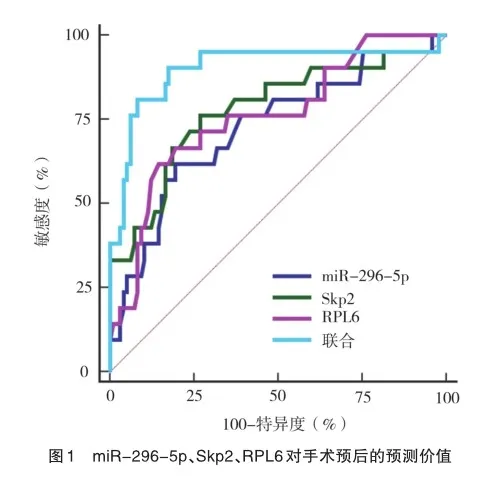
ROC曲线分析,miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6预测前列腺术后生化复发的AUC分别为0.725(95%CI=0.635~0.803)、0.779(95%CI=0.694~0.850)、0.759(95%CI=0.672~0.833),敏感度分别为61.90%、76.19%、61.90%,特异度分别为80.41%、73.20%、85.57%;将三者进行logistic二元回归拟合,Logit(P)作为独立检验变量,获取联合预测前列腺术后生化复发的AUC为0.902(95%CI=0.833~0.949),大于各指标单独预测,敏感度为90.48%,特异度为82.47%,见图1。

3 讨 论
前列腺癌发病原因尚未阐述清楚,可能与年龄、雄性激素、高脂肪饮食及遗传等因素有关,上述因素均可影响前列腺癌发生发展[10]。腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术是治疗前列腺癌的主要途径,能延长患者生存期,但术后27%~53%患者可能会出现生化复发[11]。本研究中,术后1年内生化复发率为17.50%明显低于魏英等[12]的报道,可能与术后随访时间、纳入样本量不同有关。相关研究报道显示,前列腺癌不良预后与临床病理特征有直接关联性,可见早期诊断前列腺癌对改善患者预后、延长生存期具有重要作用。
miRNA是内源性非编码RNA转录本,通过调节靶基因转录后水平参与肿瘤细胞生物学进展[13]。miR-296是miRNA家族成员,涉及miR-296-5p、miR-296-3p,miRase在线数据库显示,miR-296是miR-296-5p之前名字,主要位于20q13.32区域,最近癌症数据显示,miR-296-5p在多种恶性肿瘤中异常表达,表现出明显异质性,通过作用不同靶基因,呈现不同抑癌或促癌作用[14]。但关于miR-296-5p在前列腺癌血清及与临床病理特征的研究未见报道。本研究结果显示,不同病理分期、术前PSA水平、Gleason评分、淋巴结转移患者miR-296-5p存在明显差异,复发组miR-296-5p表达水平低于未复发组,提示miR-296-5p与临床病理特征、术后复发密切相关。PSA是早期诊断和监测前列腺癌常用指标,正常情况下PSA几乎不表达,若前列腺发生癌变后引起血-上皮细胞屏障破坏,导致PSA进入血液中,血清PSA浓度与恶性肿瘤呈相关[15]。Glea? son评分≥7分提示前列腺癌处于低分化或未分化,为高级别癌,患者术后复发或转移风险较高[16]。miR-296-5p不仅参与肿瘤血管生成、细胞迁移和侵袭、细胞增殖,还能调节肿瘤干细胞表现、诱导细胞凋亡等[14]。于峰等[17]研究发现,miR-296-5p在前列腺癌细胞中低表达,沉默Circ-0033074可能通过上调miR-296-5p抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,并诱导细胞凋亡,提示miR-296-5p有望成为前列腺癌作用靶点,但具体作用机制尚不清楚,有待下一步考究。
Skp2是一种与细胞周期有关的蛋白,与DNA复制有关,主要位于5p13区域,首次在1995年呈现细胞S期中发现,可与细胞周期蛋白CyclinA相互作用,从而参与细胞增殖分化、周期进展[18]。既往研究显示,Skp2在胃癌、前列腺癌等组织中高表达,沉默Skp2能明显抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和细胞进展,并诱导晚期细胞凋亡[19-20]。本研究结果显示,Skp2与病理分期、Gleason评分、术前血清PSA水平、淋巴结转移呈正相关,复发患者Skp2高于未复发组,这与段松等[5]的研究结果相同,提示Skp2与前列腺癌病理特征和术后复发有关。Skp2水平升高能阻滞细胞周期进展,导致G1/S期比例升高,加剧肿瘤细胞增殖分化,加快前列腺癌发展[21]。Skp2丝氨酸和巯基结构也能促进肿瘤细胞持续复制,加快肿瘤细胞增殖分化[22]。相关研究认为,Skp2表达越高,主要是因为PSA水平越高,肿瘤恶性程度严重,肿瘤细胞增殖速度较快,Skp2合成和释放越明显[23]。
RPL6是核糖体蛋白主要成分,近年证据显示,核糖体蛋白除了参与核糖体组成外,还能参与细胞增殖分化、DNA复制和转录、凋亡及迁移等过程[24]。RPL6主要位于12q24.1区域,有研究表明,RPL6在前列腺癌组织中高表达,与病理分期、术后生化复发密切相关[6]。本研究结果显示,RPL6与病理分期、Gleason评分、术前血清PSA水平、淋巴结转移呈正相关,复发组RPL6 mRNA表达水平高于未复发组,这与上述研究观点一致,提示RPL6与前列腺癌发生发展密切相关。Zhang J等[25]研究发现,下调RPL6能抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和转移,并诱导细胞凋亡。本研究进一步分析发现,miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6联合预测前列腺术后生化复发的AUC大于各指标单独预测,提示三者联合预测患者术后生化复发具有良好参考价值。
综上所述,前列腺癌患者miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6表达水平与病理特征、术后复发存在一定关系,miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6可用于前列腺术后生化复发预测,三者联合预测价值更高,可用作前列腺癌术后复发评估的指标,为前列腺癌术后评估提供参考依据,有助于临床医师早期制定合理干预措施。但本研究存在不足,本研究仅随访1年,下一步动态监测血清指标表达,延长随访期限,观察其对术后复发患者的预测价值。
参 考 文 献
[1] Sung H,Ferlay J,Siegel RL,et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 can? cers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249.
[2] Azal WN,Capibaribe DM,Dal Col LSB,et al. Incontinence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy:a reverse systematic review[J]. Int Braz J Urol,2022,48(3):389-396.
[3] Ziogou A,Giannakodimos A,Giannakodimos I. The role of urinary miRNAs in the diagnosis,management and follow- up of prostatic can? cer[J]. Microrna,2023,12(2):83-86.
[4] Lee KH,Lin FC,Hsu TI,et al. MicroRNA-296-5p (miR-296-5p) functions as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by directly target? ing Pin1[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,2014,1843(9):2055-2066.
[5] 段松. 前列腺癌组织中Skp2的表达及其与前列腺癌术后复发的关系[J]. 东南国防医药,2016,18(1):47-50. Duan S. The expression of Skp2 in prostate cancer and its relationship with postoperative recurrence[J]. Mil Med J Southeast Chin,2016,18(1):47-50.
[6] 孙铭强,张建勇,袁 瑛,等. 前列腺癌患者组织中RPL6的表达及临床意义[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2018,18(4):745-749. Sun MQ,Zhang JY,Yuan Y,et al. Prostate cancer:expression and clini? cal significance of ribosomal protein L6[J]. Prog Mod Biomed,2018,18(4):745-749.
[7] 中国抗癌协会泌尿男生殖系统肿瘤专业委员会前列腺癌学组.前列腺癌筛查中国专家共识(2021年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志,2021,31(5):435-440. Prostate Cancer Group,Urogenital Cancer Committee,Chinese AntiCancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on prostate cancer screening(2021 edition)[J]. Chin Oncol,2021,31(5):435-440.
[8] Epstein JI,Zelefsky MJ,Sjoberg DD,et al. A contemporary pros? tate cancer grading system:a validated alternative to the gleason score[J]. Eur Urol,2016,69(3):428-435.
[9] Mottet N,Bellmunt J,Bolla M,et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guide? lines on prostate cancer. part 1:screening,diagnosis,and local treat? ment with curative intent[J]. Eur Urol,2017,71(4):618-629.
[10] Sekhoacha M,Riet K,Motloung P,et al. Prostate cancer review:genetics,diagnosis,treatment options,and alternative approaches[J]. Molecules,2022,27(17):5730.
[11] Cornford P,van den Bergh RCN,Briers E,et al. EAU-EANMESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. part II-2020 up? date:treatment of relapsing and metastatic prostate cancer[J]. Eur Urol,2021,79(2):263-282.
[12] 魏英,蔡维敏,王飞,等. 血清睾酮联合红细胞分布宽度、白蛋白碱性磷酸酶比值对腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术后生化复发的预测价值[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2023,23(4):755-760. Wei Y,Cai WM,Wang F,et al. Predictive Value of serum testosterone combined with red blood cell distribution width and albumin alkaline phosphatase ratio for biochemical recurrence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Pro in Mod Bio,2023,23(4):755-760
[13] Giannakodimos I. Urinary miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for prostatic cancer:current dilemmas and novel potential role for a digital rectal examination[J]. Curr Med Chem,2022,29(25):4311-4313.
[14] 刘小四,丁凯阳. miR-296-5p在恶性肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 徐州医科大学学报,2017,37(9):627-630. Liu XS,Ding KY. Research progress of microRNA-296-5p in tumors[J]. J Xuzhou Med Univ,2017,37(9):627-630.
[15] Kachuri L,Hoffmann TJ,Jiang Y,et al. Genetically adjusted PSA levels for prostate cancer screening[J]. Nat Med,2023,29(6):1412-1423.
[16] Mokoatle M,Mapiye D,Marivate V,et al. Discriminatory Gleason grade group signatures of prostate cancer:an application of machine learning methods[J]. PLoS One,2022,17(6):e0267714.
[17] 于峰,刘先艮,杨帆,等. Circ-0033074靶向miR-296-5p对前列腺癌细胞增殖、侵袭、迁移及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2023,43(7):1740-1745. Yu F,Liu XG,Yang F,et al. Effects of Circ-0033074 targeting miR-296-5p on proliferation,invasion,migration and apoptosis of prostate cancer cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2023,43(7):1740-1745
[18] Rezaeian AH,Phan LM,Zhou XB,et al. Pharmacological inhibi? tion of the SKP2/p300 signaling axis restricts castration-resistant pros? tate cancer[J]. Neoplasia,2023,38:100890.
[19] Asmamaw MD,Zhang LR,Liu HM,et al. Skp2 is a novel regula? tor of LSD1 expression and function in gastric cancer[J]. Genes Dis,2023,10(6):2267-2269.
[20] Celada SI,Li GL,Celada LJ,et al. Lysosome-dependent FOXA1 ubiquitination contributes to luminal lineage of advanced prostate cancer[J]. Mol Oncol,2023,17(10):2126-2146.
[21] Liang H,Zhang FM,Hong YN,et al. Synergistic silencing of Skp2 by siRNA self-assembled nanoparticles as a therapeutic strategy for advanced prostate cancer[J]. Small,2022,18(14):e2106046.
[22] Wang HC,Luo CW,Chen TY,et al. Skp2-mediated Zeb1 expres? sion facilitates cancer migration by a ubiquitination-independent path? way[J]. Life Sci,2022,311(Pt A):121135.
[23] 刘 畅,王庆伟,罗振宇,等. SKP2、kindlin-2在前列腺癌组织中的表达及其与患者临床特征的关系[J]. 癌症进展,2019,17(6):727-730. Liu C,Wang QW,Luo ZY,et al. Expression of SKP2 and kindlin-2 in prostate cancer and the relationship with clinical characteristics[J]. On? col Prog,2019,17(6):727-730.
[24] Suzuki M,Tezuka K,Handa T,et al. Upregulation of ribosome complexes at the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease patients[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2022,42(11):2134-2150.
[25] Zhang J,Ma QL,Han Y,et al. Downregulated RPL6 inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and migration and promotes cell apoptosis by regulating the AKT signaling pathway[J]. J Thorac Dis,2022,14(2):507-514.
(责任编辑:周一青)
本文引用格式:
张灿峰,刘嘉欣,杨文博. miR-296-5p、Skp2、RPL6与前列腺癌病理特征的关系及对手术预后的影响[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2025,50(2):198-203.

