Channel Correlation Based User Grouping Algorithm for Nonlinear Precoding Satellite Communication System
Ke Wang ,Baorui Feng ,Jingui Zhao ,Wenliang Lin ,Zhongliang Deng ,Dongdong Wang ,Yi Cen,Genan Wu
1 School of Information and Communication Engineering,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
2 School of Information Engineering,Minzu University of China,Beijing 100081,China
3 Institute of Spacecraft Application System Engineering,China Academy of Space Technology,Beijing 100094,China
4 Academy for Network and Communications of CETC,Science and Technology on Communication Networks Laboratory,Shijiazhuang 050081,China
Abstract: Low Earth Orbit (LEO) multibeam satellites will be widely used in the next generation of satellite communication systems,whose inter-beam interference will inevitably limit the performance of the whole system.Nonlinear precoding such as Tomlinson-Harashima precoding(THP)algorithm has been proved to be a promising technology to solve this problem,which has smaller noise amplification effect compared with linear precoding.However,the similarity of different user channels (defined as channel correlation) will degrade the performance of THP algorithm.In this paper,we qualitatively analyze the inter-beam interference in the whole process of LEO satellite over a specific coverage area,and the impact of channel correlation on Signal-to-Noise Ratio(SNR)of receivers when THP is applied.One user grouping algorithm is proposed based on the analysis of channel correlation,which could decrease the number of users with high channel correlation in each precoding group,thus improve the performance of THP.Furthermore,our algorithm is designed under the premise of co-frequency deployment and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM),which leads to more users under severe inter-beam interference compared to the existing research on geostationary orbit satellites broadcasting systems.Simulation results show that the proposed user grouping algorithm possesses higher channel capacity and better bit error rate(BER)performance in high SNR conditions relative to existing works.
Keywords: channel correlation;inter-beam interference;multibeam satellite;Tomlinson-Harashima precoding;user grouping
I.INTRODUCTION
With increasing demands for high-quality communications and broadband access,multibeam satellites will be widely used in the next generation of satellite communication systems[1],which can generate multiple adjacent beams within their on-ground coverage.On the premise of keeping the size of the ground coverage area of the whole satellite service fixed,the coverage area of each spot beam decreases with the increase of beam number,which makes more users served with similar channel conditions,so called highcorrelation channels.Meanwhile,dense beams also lead to inter-beam interference,especially when the full frequency reuse among beams is implemented,the interference of all adjacent beams will have a cumulative effect[2] and the inter-beam interference to the users will be extremely serious due to main lobes or side lobes of other beams [3].Considering the limitation of continuous stable power and large number of users on ground,multibeam satellite can not serve all users at the same time.So how to eliminate interbeam interference and select part of users to be served become tough challenges for multibeam satellite communication system.
In order to solve the problem of inter-beam interference,the existing precoding methods are mainly divided into linear precoding and nonlinear precoding.Linear precoding techniques based on channel inversion have the advantage of low complexities but have a limited performance by significantly amplifying the noise [4][5].By far,extensive studies have proved that nonlinear precoding such as THP and its improved algorithm is a promising technology to eliminate inter-beam interference[6]in satellite communication system compared with linear precoding,and now the research about THP focuses on coding structure,decoding sequence[7]and imperfect channel state information feedback[8],but does not pay attention to and solve the problem of performance degradation due to similar user channel conditions.Note that,due to the extensive use of convex optimization algorithms in terrestrial networks,some nonlinear precoding algorithms based on convex optimization[9],and also the combination of linear precoding with convex optimization also show good performance on energy efficiency[10].However to illustrate more straightforwardly the performance of nonlinear precoding in satellite grouping algorithms,THP will be used as a representative of nonlinear precoding algorithm for subsequent analysis.Furthermore,we adopt the assumption of full frequency reuse among different beams,which has been widely adopted recently in the precoding research[9].
On the other hand,multibeam satellite can’t serve all users in the whole system at a given instant due to limited power and high density data,satellites generally consider to group users first before serving users,and only serve one group of users at each time slot or frame.In existing geostationary orbit satellite communication system or 5G terrestrial cellular network,the relative position of gateways or base stations and users is basically fixed,they ususally arrange users into the same group with high similarity,which can be second-order statistical channel state information[11][12],the nomalized dynamic channel condition[13],or the locations in the Euclidean space[14]and channel vectors[15].But in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) broadband satellite communication system,number of users in each beam is large and users in overlap area will be affected by the adjacent beam interference more seriously.[16][17]scheduling users according to channel state information or geographical position,which can not guarantee fairness as users with worse channel condition are rarely served.[18]proposed a fair grouping algorithm,which filters the channel quality of each user and then puts the users with low correlation into the same grouping service.As each user needs to be considered in the screening process,the algorithm has a high complexity.[19]also proposed a geographically based grouping method to maximize the similarity of the position of each user in the group to beam reference point,however this method is only applied to the symmetric beam footprint and need extra feedback of user terminal’s geographic location.[20] added threshold judgment after user grouping,discarding part of users according to correlation threshold obtained from a large number of experiments,that is,sacrificing the service time of some users with good channel conditions to ensure that users with poor channel conditions can get services.More attention should be paid to the multiple access method used in the above works,as it will determine the number of users can be served at each time slot.Basically all of above work is done based on the assumption of the combination of space division multiple access (SDMA) and time division multiple access (TDMA).This will mean in each time slot only one user can be served in each beam based on the spatial differentiation.This method is true when the conditional satellite broadcast protocol is deployed,such as DVB.However,with the deployment of space and terrestrial integrated network,the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing access (OFDMA) has been widely discussed and considered to be an important multiple access technology for future satellite adoption.This may result in multiple users per beam being served in each time slot,and this change will also have a profound impact on the user grouping algorithm.Therefore in this paper,our algorithm is based on OFDMA satellite design.
Note that all mentioned algorithms are difficult to balance the fairness between users and the handling of exceptions,which also seldom pay attention to users’similar channel conditions,thus THP suffers a performance loss when applied within each group.In addition,the variation of inter-beam interference caused by the motion of LEO satellites should also be considered in the grouping criteria to update the group.Aiming at solving the above problems,in this paper we provide the following contributions:
(1) Modeling of inter-beam interference in the whole process of satellite motion is provided and considered as a factor for initial user grouping and subsequent group updating.
(2) Proposing the channel correlation based Minmax Correlation user Grouping algorithm(MCG) for satellite communication system using centralized THP(CTHP) that calculates various precoding filters at the gateway,which combines THP with specific user grouping algorithm that can reduce the probability of users with similar channel conditions.
(3)Comparing the simulation performance of the proposed algorithm with other schemes mentioned before and results show that the proposed algorithm improves about 7% channel capacity and possesses better BER performance in high SNR conditions relative to existing grouping algorithms.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.Section II outlines the system model so as to the model of inter-beam interference.Section III gives the detailed procedure of the proposed min-max correlation user grouping algorithm.Simulation results and analysis are provided in Section IV.Finally,Section V concludes the paper.
Notation: Vectors,matrices and sets are denoted by lowercase,uppercase boldface letters and Euler script respectively;||(.)||0represents 0-th norm of (.);(.)Tdenotes the transpose of(.)and(.)Hdenotes the Hermitian transpose of(.);(.)†denotes the pseudo inverse of (.);E[(.)] stands for the expectation operation andindicates the rounded up operation.
II.SYSTEM MODEL
As illustrated in Figure 1,we consider a scenario of LEO multibeam satellite communication system which contains a multibeam satellite equipped with phased array antenna,a on-ground gateway for control and a large number of users in each beam with full frequency reuse to provide broadband connectivity.During the movement of the satellite,the elevation angle is large and the shape of the ground beam is approximately circular.The elevation angle is small when the satellite is just connected,and the ground beam is stretched into an ellipse,and the overlap area between the beams is large at this time.Specifically,assumptions hold throughout the paper if not otherwise specified: i) the satellite payload is assumed to be transparent and equipped with S antennas,generating S on-ground beams;ii) a single gateway can obtain ideal channel vectors of all users from the uplink in order to compute the channel correlation and the precoding filters.We further assume that after users grouping,Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access(OFDMA)is implemented to serve users in one group for each time slot,and different groups are served sequentially at different time slot.The slot based scheduling is enabled in 5G NR,and each time slot contains 14 OFDM symbols whose exactly time duration is depending on the type of the numerology.
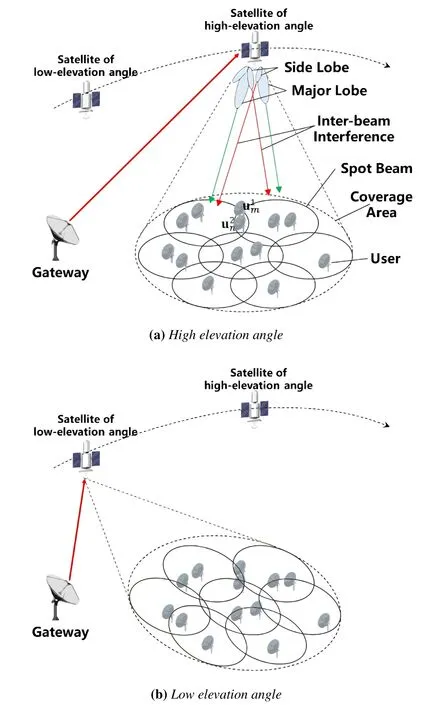
Figure 1. Multibeam satellites communication scenario.
In general,we consider the grouping algorithm with Nuusers under one transparent LEO satellite with S beams.Suppose each user has only one stream,hence there are Nustreams need to be transmitted by the gateway.The gateway firstly divide the users into I groups according to the proposed algorithm,then each group is served sequently in each time slot.For i-th group (0<i<I),there may Miusers within the group,the gateway will pick out these users’ signala=(a1,a2,···,)Tfrom Nustreams with mean signal power of.The users’ signalaare then mapped into to the OFDM resource block per beam according to the resource allocation algorithm,so there are in total S OFDM transmitted signals radiated over the multibeam coverage area.The THP is deployed in gateway within each slot,reducing the interference among the beams.Note that,the amount of users in each beam is likely more than 1 due to the usage of OFDMA.The details of mathematical models are given in the following parts.
1) Users deployment and channel model: Users’location is modeled as points in R2,which are distributed as a homogeneous Poisson point process.The users in each spot beam consists the whole user set,and the counting number of the user set before the grouping is denoted as N={N1,N2,···,NS},where Nidenotes the number of user in i-th beam,so the total number of users is NU=.Similarly,we can define the whole user set as U={U1,U2,···,Uk,···,US},where Uk=represents user set of k-th spot beam,represents m-th user in k-th spot beam whose corresponding channel vector is,
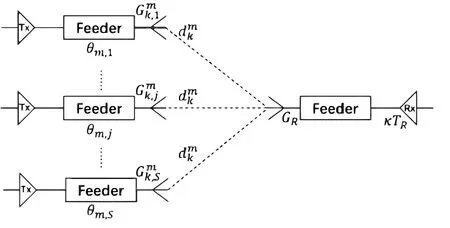
Figure 2. The channel elements for the m-th user in the kth spot beam.
In formula(2),when k=j,the elementindicates that the user covered by the k-th beam receives the channel gain from its own spot beam and when kj,the elementindicates that the user under the k-th beam receives the channel gain from other spot beams,that is,inter beam interference.Apparently,there is no interference between two far apart spot beams,thus the corresponding element in channel vectoris 0.For both,when the same satellite serves a group of users,the gain or interference depends mainly on.
For notation convenience,it is better to defineH∈as the channel matrix of the whole system,which is directly constructed by the channel measurement results of each user.Hence,based on definition of(1),we can obtain the following form:
where each column represents a user’s channel vector,and each row gives out the channel gain of each user within the same beam.Notice that,before the grouping,the upper right conner marker of each vector is initially defined by the strongest gain received by the specific user.For example,means the user lays in the 1stbeam,and the index of this user is N1.Apparently,the summation largest index of user in each beam is equal to Nu.The index of user is only used to identify the user and does not have any effect on the subsequent grouping algorithm.
After grouping operation,each user is grouped into one new user set which consists a new collection of sets as U∗=,wheredenotes i-th group,and I denotes the total number of groups.Note that,according our proposed algorithm,the users inmay be laid in different beam,and in each beam there may be more than one user.For the sake of easier the modulo operation of THP,we assume that the users in each group deploy the same modulation scheme,which is decided by the average SNR.To enhance the impact of the interference among the beams,we further assume each beam use the full bandwidth.Therefore,the users in the same beam share the full bandwidth equally.Since the transmission power of the satellite is limited,each beam is supposed to support at most Nbusers in each slot.Hence the total number of group is highly depends on the beam with the highest number of users,which is calculated by I=,the rounded up operation is needed to guarantee an integer number of groups.The authors want to point out that,although the resource allocation algorithm is straightforward,but 1)the assumption of same modulation in each time slot is consistent with widely used DVB protocol;2)the assumption full bandwidth deployment is commonly used in the existing multibeam satellite research,such as [8] [17].The number of users inis Mi=,i=1,2,···,I.For a specific user group,its channel matrixHi∈is made up of partial rows inH,that is,
our proposed grouping algorithm will not drop any user,hence the size the of the matrixHis not changed.As we explained in the latter part,the channel matrix obtained by the grouping algorithm can be considered as the column exchange of the originalH.For easier mathematical description in the latter part,we still named this matrix after permutation asH.
2) Inter-beam interference with satellite motion:Phased array antennas are highly likely to be used by the next generation of low-orbit satellites.Taking the 8×8 rectangular phased array antenna whose spacing of the array elements is half wavelength using Linearly Constrained Minimum Variance beamforming algorithm as an example,Figure 3 shows that the received power of the whole covered area increased as the color of the entire Figure 3b was more yellow than Figure 3a.With inter-beam interference,there is no significant change in the power of the beam center(see figure center),but overlapping regions at the edge of the beam can receive the signal gain of adjacent beams,resulting in a significant increase in power.On the premise that the antenna pattern is determined,the inter-beam interference of each user is affected by two factors,one is the elevation angle of the satellite,and the other is the azimuth angle formed by user-satellitebeam center.As shown in Figure 1,the elevation angle of the satellite changes during motion.The elevation angle of the satellite is the smallest when it is just connected,and then gradually increases to the top,and then becomes smaller again with the distance of the satellite.Two states of high elevation angle and small elevation angle are taken for analysis.
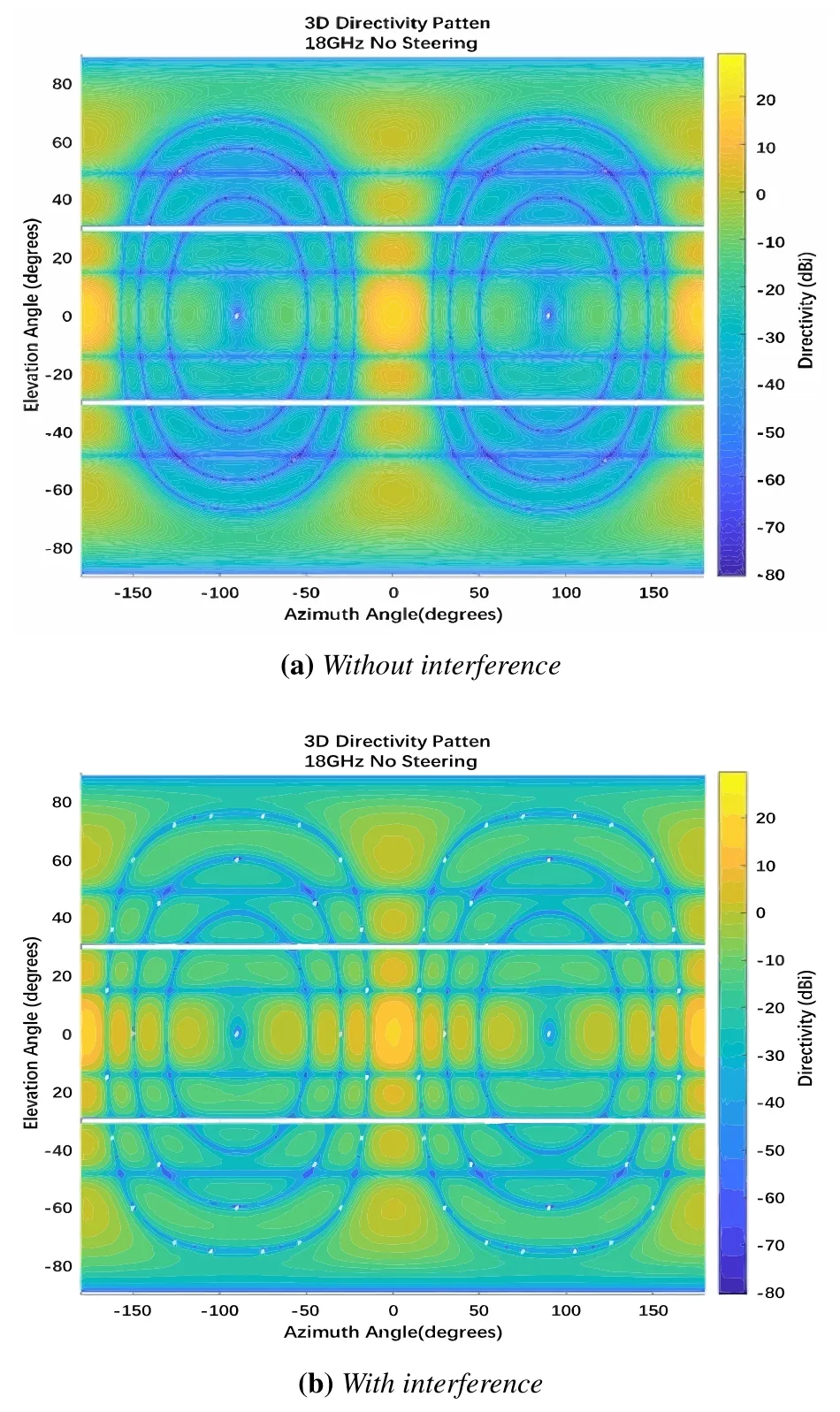
Figure 3. The power in the beam coverage area.
To facilitate comparison,the beam gain of the corresponding phased array antenna located at the target beam center on the ground is set as 0dB as the reference,and the beams of the other phased array antennas point to their respective spot beam center.In this case,the target beam center(corresponding to the azimuth angle of 0°)will still receive the gain of adjacent beams.As shown in the Figure 4,when the satellite elevation angle is high,and the gain of adjacent beams are symmetrically distributed.When the satellite elevation angle is small,and the gain of other adjacent beams are asymmetrical.can be obtained from the figure according to the azimuth angle.
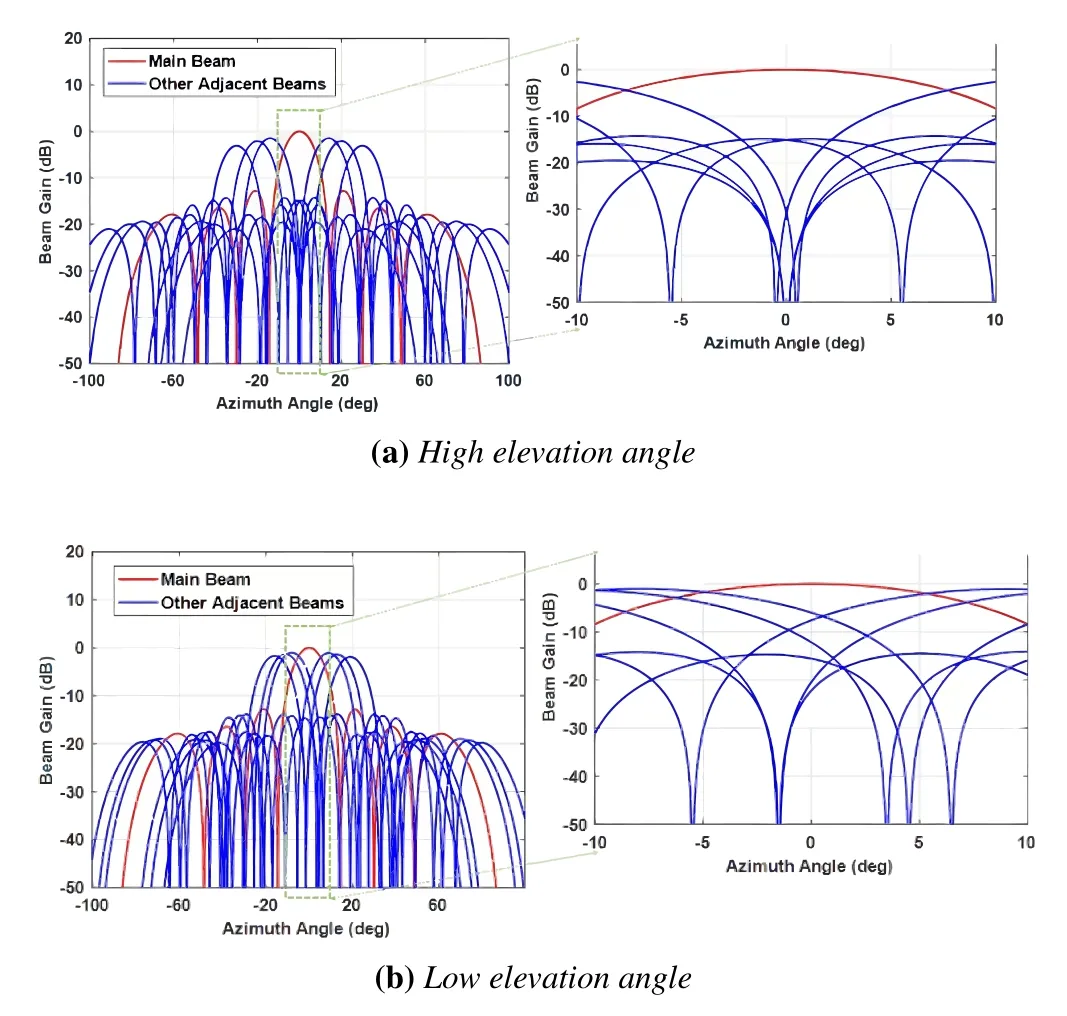
Figure 4. Beam gain at different elevation angles.
3) Multicast precoding and downlink process: In multibeam satellite systems,the signalais mapped into S beams through precoding and sent to Midifferent users during each time slot.As illustrated in Figure 5,the gateway firstly obtains the channel vector of all usersHthrough ideal uplink,then performs user grouping and calculate the various filters.For nolinear precoding,the precoded signalx∈CS×1is calculated as follow:
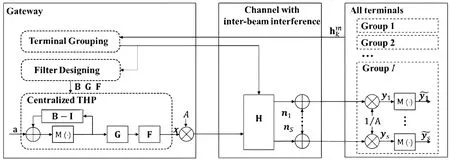
Figure 5. Multicast precoding and downlink process.
where A is the power control factor,W∈is the precoding matrix,and for nolinear precoding,a perturbation vectord∈is added to the transmitted signal.The reception vectory∈for group i can be expressed as follows:
whereHi∈is the channel matrix for the i-th group,n∈CS×1is the additive gaussian noise.More details can be seen in next Section.
III.MIN-MAX CORRELATION USER GROUPING ALGORITHM
3.1 THP Loss with Channel Correlation
In the subsequent analysis,we choose one groupto observe the performance.Assuming that users grouping is completed and the transmitted symbol vector isa=(a1,a2,···,)T.All symbols value belong to the same constellation depending on modulation method,where all constellation points are equiprobable and we can define.When we use THP to precode the transmitted symbola,the gateway caculates precoding filters such as the scaling filterG,the feedforward filterF,the feedback filterB,so called centralized THP.THP algorithm introduce the LQ decomposition toHi.
whereL∈is a lower triangular matrix with positive diagonal elements andQ∈CS×Sis a unitary matrix.Then the feedback filterB∈is calculated as follow:
whereG∈CS×Sis a diagonal matrix could be represented as follow:
where ln,n,1 ≤n ≤S is the n-th diagonal element ofL.Then,we will use matrixBto perform iterative interference cancellation for the transmitted signal:
where a is the complex input value and τ is the periodic constant of the modulo operation which is a constant as the upper limit of the amplitude of the real and imaginary parts of the modulo operation output,bounding the peak power of output signal.Different modulations possess corresponding the specific value of τ,the value could be calculated as follow:
where |c|maxis the absolute value of the constellation symbol with the maximum value,dminis the minimum Euclidean distance between constellation symbols.The modulo operation is essentially equivalent to superimposing a perturbation value ona.
After the iterative interference cancellation,the signal vector∈CS×1could be represented as follow:
wheredis a perturbation vector added to the transmmit signal which is caused by the modulo operation.
Next,the signal vector should be multiplied by the scaling matrixGand the feedforward matrixFwhich is equal to the Hermitian transpose of matrixQ.In addition,a sacling factor A should be introduced to normalize the transmit energy.The precoded signalxcould be represented as follow:
whereF=QH,The positive factor A is constant over the given instant to set the TX energy Et.
After passing through the channel,according to(6)the received signalyby users can be written as
Then for each user,a modulo operation is performed to recover the transmit signal:
the mean SNR of the detector is calculated as
which indicates that SNR in different terminals depends on ln,ncalculated byHithrough the factor multiplying Et/N0.Now let us take the first userlocated in m-th spot beam and the second userlocated in n-th spot beam in Figure 1 as an example to define what is channel correlation.Their channel vector areas we describe in (1) respectively,then the channel correlation ρ is defined as
A large ρ will cause the absolute value of the partial eigenvalue of the matrixHidecrease to nearly zero,resulting in a rank decreasing.In another word,the value of the diagonal elements of the matrixLwill be smaller,leads to a decrease ofaccording to(19),which indicates a performance loss at the receiving user.It is pointed out in[9]that when the correlation coefficient between one specific user and any other user’s channel vector is greater than a certain threshold,the introduction of the user will reduce the total capacity of the system,the threshold is calculate as follow:
where k is the user index,and ρmax,krepresents the max ρ value between channel vector of the k-th user and any other user.In our algorithm,the value α could be calculated as following:
A more detailed derivation is given in[9].However the threshold given in (21) is only applicable when there is only one pair of correlated users.It’s very common that the correlated pairs are more than one in our scenario.As far as we know,there is no close formed ρ is derived for this case.As shown in the appendix of[9]the dimension of the matrixAwhich is used to calculate value of ln,nwill rapidly increase with the increase of correlated pairs,so ln,nis hard to be expressed by the formula related to ρ.Further more,the expression of matrixLwill be complicated when the dimension of the matrix is large.So the existing research focusing on the threshold of ρ always adopt the simulation method such as [21].Therefore the threshold of ρ is obtained by simulation in this paper.Given the number of beams and users,this threshold can be uniquely determined by simulation.To figure out the quantitative influence ρ makes on system performance,we set a group of Mi=10 users to compare the system capacity C according to Shannon’s formula,
Users are placed in the center of each spot beam in the initial state,and there is no correlated channel at this time.Then the two users are gradually moved closer to each other,through which their ρ value gradually increases and the channel correlation gradually increases.To facilitate comparison,the system capacity is normalized according to the initial state.
As shown in Figure 6,we take baseline as a criterion for comparison.As |ρ| gradually increases from 0 to 0.85,the capacity of the system is not much different from the baseline.When |ρ| increases from 0.85,the system capacity decreases significantly.When|ρ|approaches 1,the system capacity decreases to 0,which means that two users with extremely related channels will make the whole system unavailable.In terms of the result of performance degradation,if more radical,the threshold value of|ρ|can be set as 0.8,which can guarantee the performance of grouping to a great extent,but will cause the processing of grouping to become complicated because there will be more judgments to be made.Considering the compromise between grouping performance and speed,we choose|ρ|=0.85 as the judgment threshold of subsequent grouping algorithms.
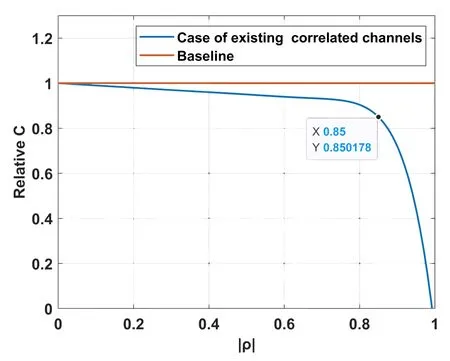
Figure 6. System capacity under different channel correlation.
As the satellite moves,its elevation changes.Taking three actual in-orbit data of LEO satellites of a certain aerospace company as an example,each curve in Figure 7 represents the elevation angle change during satellite motion on a certain date.It can be seen that the elevation angle increases first and then decreases on the whole,with the maximum value between 60°and 85°.According to the description of channel vector mentioned in Section II,the value ofis related to the elevation angle,so |ρ| is also a variable value during the satellite motion,which makes users groups need to be updated in time instead of being constant.
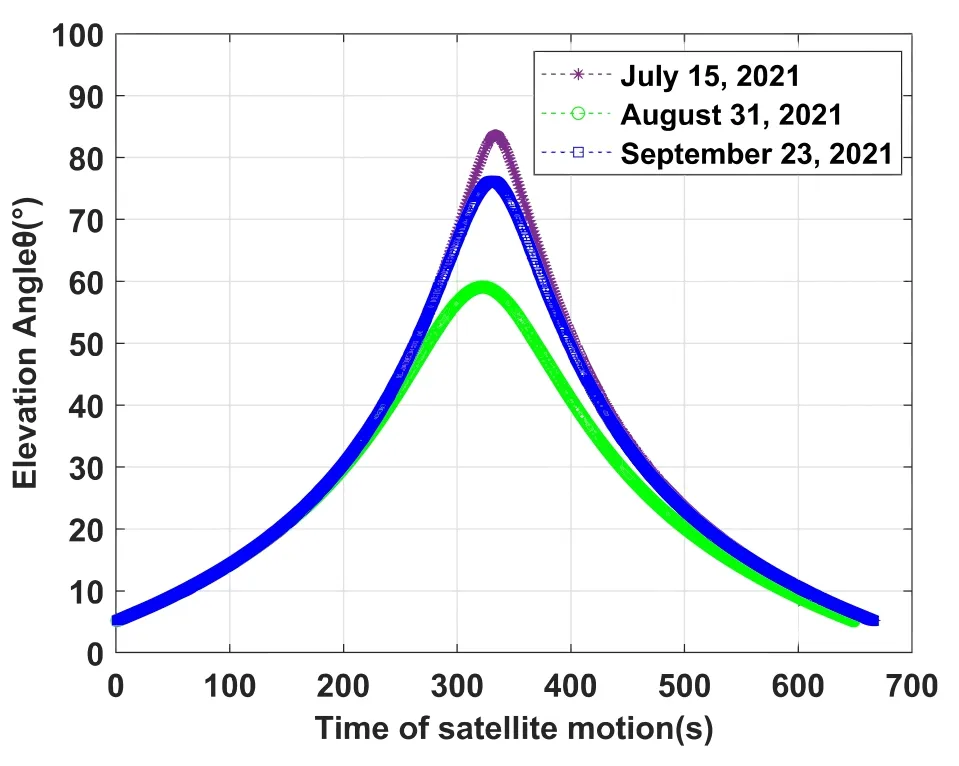
Figure 7. The elevation angle during the satellite motion on different dates.
3.2 User Grouping Algorithm
To enhance the performance of THP,we propose a min-max correlation user grouping(MCG)algorithm,which optimally groups users by make sure the correlation coefficient between users in each group is minimized.The details of the MCG is described as follows:
Firstly,all users will be initial divided into S groups according to their nearest distance to the center of each beam,hence the whole user set U and the counting number of the user set N is obtained.After that,we need to determine how many groups will be built after the grouping algorithm,which is denoted as I in this paper.As described in the Section II,the value of I is calculated by I=.So right now our task is how to group the users in U to I groups.Remember that,the collection of user set after grouping operation is denoted as U∗.In the first place,all user set in U∗is initialed as empty.In order to implement the grouping algorithm,the gateway need to collect the users’ channel vectorsand form the channel matrixH.After that,our MCG is began.
In the first iteration,I users are randomly selected out of U,and put them into each set in the U∗one by one.In the following iterations,we sequently pick out the users from U1to USand determine which set in U∗it belongs to.
As mentioned in the Section II,with the motion of the satellite,the correlation between users will change for the reason of variable beam coverage area.Therefore,the gateway need to cyclically check whether the maximum correlation of each group is lager than the predefined threshold (0.85 is used as the threshold in this work).If so,the gateway will restart the grouping algorithm again.Note that,according to the simulation results in the latter Section,the grouping result may not changed for several minutes which is comparable with the in-sight period of LEO satellite.The whole procedures above is given in Algorithm 1.
IV.SIMULATION RESULTS
In this Section,to display the performance of our proposed beam correlation based downlink transmission strategy,simulation and result analysis are conducted on random grouping(RG),user fair grouping algorithm based on threshold decision(FGA)[20],sum-rate maximization user grouping algorithm(SMUG)[22]and the proposed MCG algorithm in a single multibeam satellite communication scenario.SMUG aims to select a new user with the largest contribution to existing groups which deteriorates performance of subsequent groups.FGA equalizes the performance among all users by sacrificing the good users for the worst users to ensure fairness and low correlation within each group.The RG algorithm without constraint is used as the lower bound of performance comparison.

4.1 Simulation Conditions
We consider a LEO multibeam satellite communication senario,detailed system simulation parameters and corresponding parameter values are shown in Table 1.Unless otherwise specific,we assume a multi-beam satellite orbits in a height of 1175km equipping S=10 on board antenna feeds 10 cone spot beams on the ground with a radius of 207.2km,100 users are distributed as a homogeneous Poisson point process under the beam coverage.We also define that in each time slot the maximum number of users can be served within one beam is Nb=3 .After all users are grouped,during each time slot,the streams for each user in the serving group are QPSK modulated and CTHP precoded to eliminate inter-beam interference.After that an OFDMA based resource allocation is performed as is described in Section II.According to Shannon’s formula,the ratio of the maximum information transmission rate for the whole system to the bandwidth C can be expressed as
4.2 Performance Analysis
As shown in Figure 8,there are 100 users distributed within 10 spot beams,which are numbered 1-10 in sequence from top to bottom and left to right.According to our grouping procedures,users are divided into four groups.Let us focus more on users in the overlapping region of spot beam coverage as they may have high channel correlation.Take the three usersin the orange circle for example,=0.9244 as they received very similar gains from the sixth and ninth spot beams,so they were divided into two different groups.=0.5813 is lower than 0.85 but higher than the correlation coefficient ofwith other users in Group2,sois put into another group.
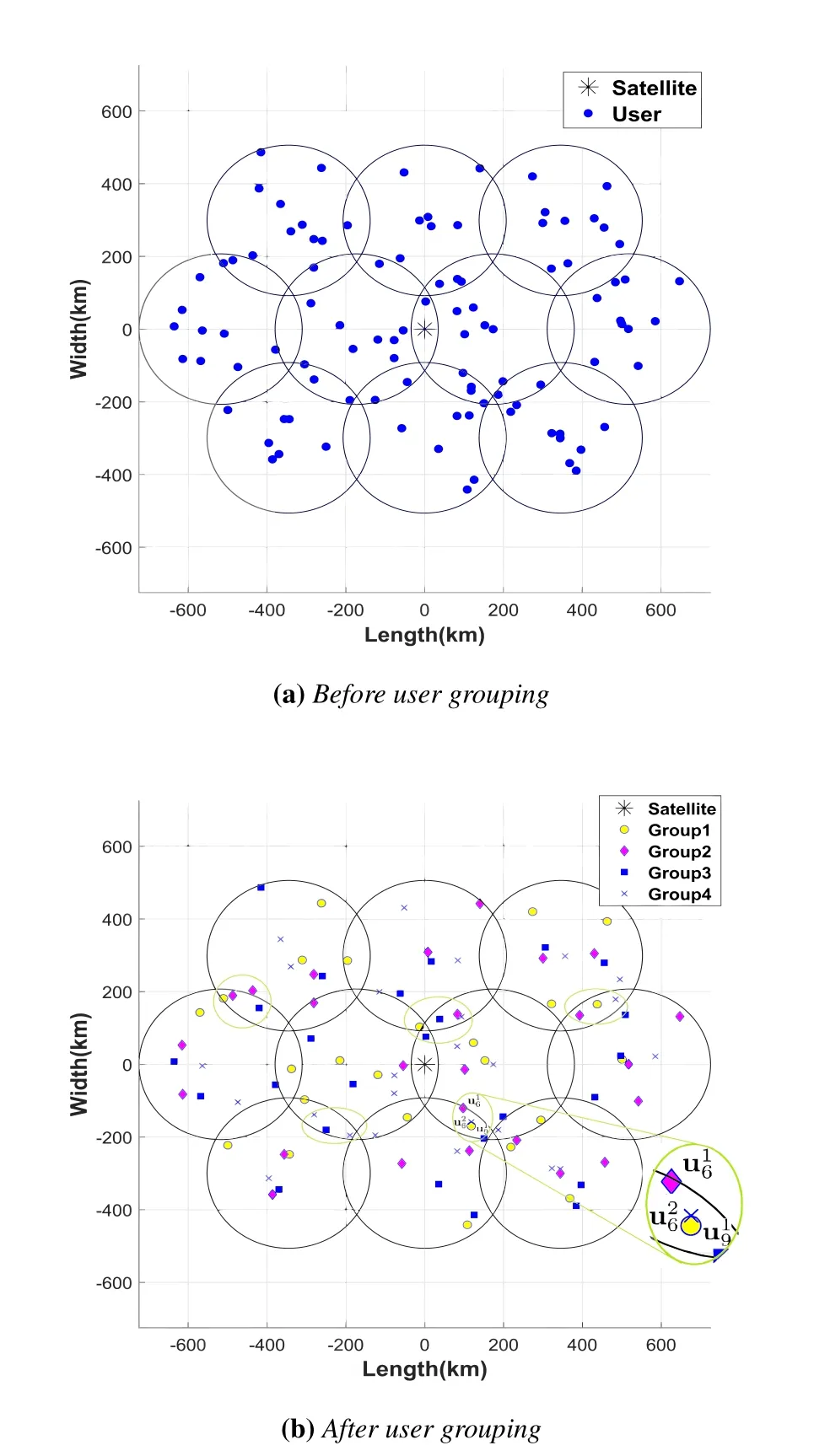
Figure 8. Example of users distribution with grouping process.
As shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10,we compare the channel capacity and BER performance of the whole multibeam satellite system and results show that under the condition of low SNR,the performance of the three algorithms is similar.In the case of high SNR(20dB or higher),the channel capacity performance of our proposed MCG algorithm is about 7%better than SMUG,12%better than FGA and 17%better than RG.There is also 3dB gain as compared to SMUG and FGA at the BER of 10−5.
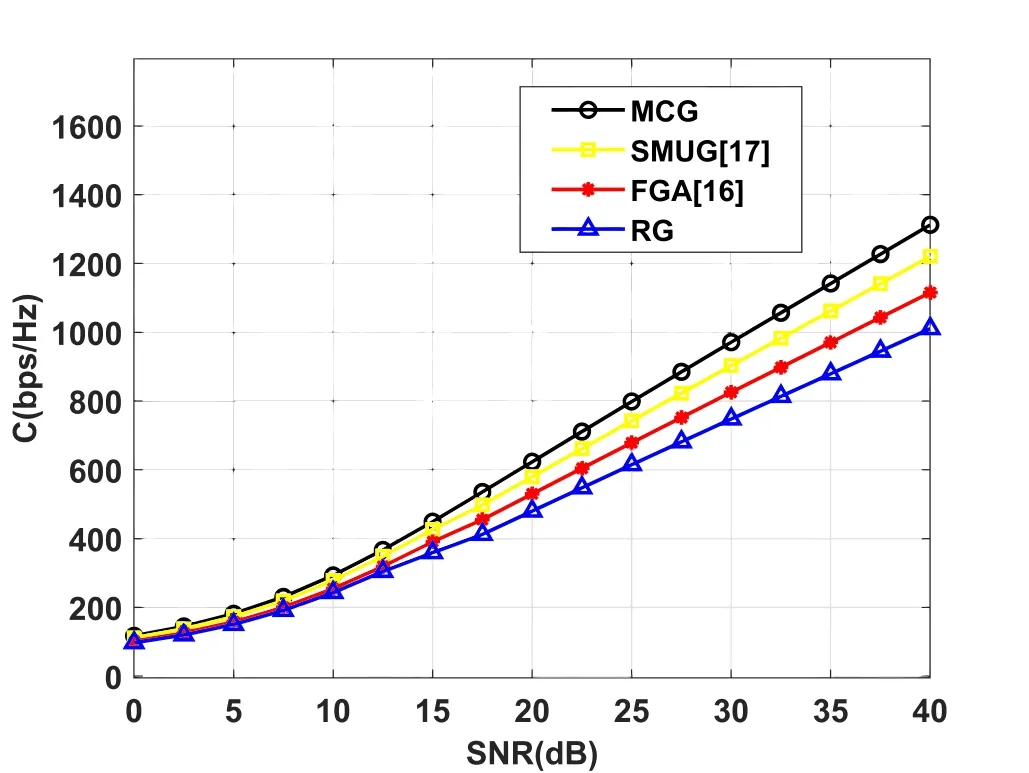
Figure 9. Channel capacity performance of different user grouping algorithms.
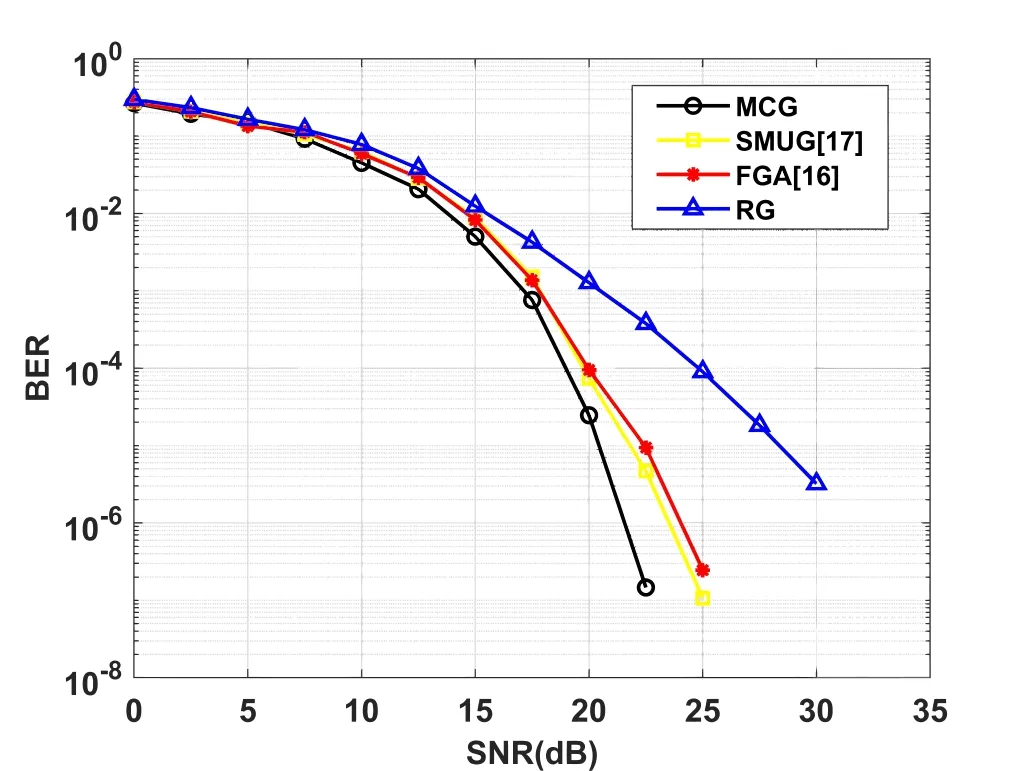
Figure 10. BER performance of different user grouping algorithms.
Through analysis,according to the process of MCG algorithm,the users with high channel correlation served by different spot beams are divided into different groups.There’s some possibility that SMUG and FGA putting high channel correlation users just likeinto the same group to serve,which leads to low ln,nin(19)when applied THP while MCG can ensure that there are no user pairs with ρ >0.85 within the same group so that improve the performance of the whole system.Part of the reasons may lies that with the low SNR,the noise power influences more on capacity while the channel correlation has more impact on capacity with high SNR.
As we mentioned at the end of the grouping Algorithm 1,user groups need to be updated periodically.Figure 11 shows that under different user group update period,satellite motion leads to changes in the normalized throughput of the system.When the update period is set to 1s,it can be regarded as the optimal performance at the cost of the computing resources of the gateway,and it can be used as the benchmark for comparison.With the increase of update period,the overall performance of the system decreases slightly,and the throughput decreases obviously without group update.In the process of maintaining the original group during the satellite movement,channel correlation between some users may gradually increase and degrade system performance.When their|ρ|value is above the set threshold 0.85,the next group update will separate these highly relevant users.
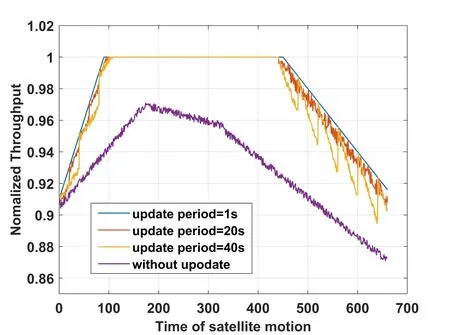
Figure 11. Nomalized throughout with different grouping update period.
4.3 Computational Complexity
In order to compare the engineering feasibility of the three algorithms,we analyze their computational complexity throughout the whole grouping process as Table 2.The computational complexity of our proposed algorithm at a time can be computed by taking into account the following single-step complexities:i) calculate the number of groups and initial groups (step 1-2 in Algorithm 1):O(S)+O(I);ii) select users randomly to join initial groups (step 7-9):O(I);iii)on average,O(I) for determine group with the fewest user(step 11),O(NS(NS−1)/2)for calculateand 2O(NS)for the min and max operation (step 12);iv)put the searched user into the group(step 13):2O(1).Notice that iii and iv are in a loop,these operations are to be repeated for S times.So the time complexity can be expressed as OMCG:
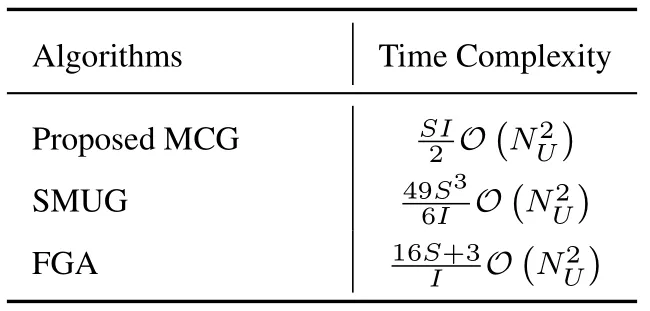
Table 2. Computational complexity.
Note that the dominant term in complexity above isis much bigger than S and I.Since S and I are small positive integers,our proposed MCG obviously achieves better performance with lower computational complexity.
V.CONCLUSION
In this paper,to eliminate inter-beam interference and improve the poor performance of nonlinear coding in high channel correlation users,we first model inter-beam interference in the whole process of satellite motion,then propose a channel correlation based uchannel correlation based Min-max Correlation user Grouping algorithm(MCG)for multibeam satellite using centralized THP.We divide users with high channel correlation into different group according to calculated channel correlation coefficient,which effectively improve the performance of subsequent cTHP operation.In particular,we consider the need for grouping updates caused by satellite motion.Compared with other transmission strategy combining user grouping and precoding,simulation results show our user grouping algorithm can reduce channel correlation and is better in channel capacity and BER performance with lower computational complexity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work is supported by the Key R&D Project of the Ministry ofScience and Technology of China(2020YFB1808005).
- China Communications的其它文章
- Design Framework of Unsourced Multiple Access for 6G Massive IoT
- 6G New Multiple Access Technology
- OFDMA-Based Unsourced Random Access in LEO Satellite Internet of Things
- Cluster-Based Massive Access for Massive MIMO Systems
- A Joint Activity and Data Detection Scheme for Asynchronous Grant-Free Rateless Multiple Access
- The Extended Hybrid Carrier-Based Multiple Access Technology for High Mobility Scenarios

