Vapor-liquid equilibrium modeling for binary system of R152a/R1234ze(E)
Chuang Pan,Yuande Dai,Yiwu Yi,Yu Liao
School of Advanced Manufacturing, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
Keywords:Binary mixture Binary interaction coefficient PR+HV model SRK+HV model Vapor-liquid equilibrium
ABSTRACT At present,the environment impact of refrigerants has been given attention.The binary mixture R152a/R1234ze(E) is an environmentally friendly refrigerant,which solves problems of poor cooling performance of the R1234ze(E)cycle and flammability of R152a.In order to obtain its basic thermal and physical parameters,it is necessary to carry out vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) research,and the cubic equation of states (EOS) is often used in the calculation of the thermodynamic properties of mixtures.In this paper,the VLE predicted models for R152a/R1234ze(E) in the temperature range of 298.15–328.15 K were constructed using Soave-Redlich-Kwong (SRK),Peng-Robinson (PR) equations of state(EOS)combined with van der Waals(vdW),Huron-Vidal(HV)mixing rules,respectively.The equilibrium pressures and vapor-phase mole fractions of the models were obtained by calculation,and all four models presented an extreme correlation with the experimental data.And it can be concluded that the calculated results of the PR+HV model are closer to the experimental data than those of the other three models,with the average absolute deviation of 0.0027 for vapor-phase mole fraction(AAD(ycal))and the average absolute relative deviation of 0.243% for equilibrium pressure (AARD(pcal)),which provides a basis for accurately calculating the thermophysical properties of the mixture R152a/R1234ze (E).
1.Introduction
With global warming and the increasingly serious air pollution problem,the environmental issues of refrigerants have attracted widespread attention from society in the field of refrigeration and air conditioning.The elimination speed of the secondgeneration refrigerants,hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs),has been accelerated due to their relatively high ozone depletion potentials (ODP) and global warming potentials (GWP) [1,2].As the third-generation refrigerants,hydrofluorocarbons’ (HFCs)ODP are 0,but they have a relatively high GWP [3,4].According to the Montreal Protocol and its amendments,refrigerants with high GWP and ODP that are not equal to zero must be phased out [5,6].Therefore,HFCs will be eventually replaced as transitional refrigerants [7].
With the continuous advancement of refrigerant replacement,hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) with good cycle performance and environmental characteristics have been found.R1234ze(E) (ODP=0,GWP=4)is a non-toxic and chemically stable HFO with a relatively short atmospheric lifetime,indicating that R1234ze(E) is an environmentally friendly refrigerant with poor thermodynamic properties and a low heat transfer coefficient [8,9].R152a(ODP=0,GWP=124)possesses excellent cooling and heat transfer performance but has some flammability[10,11].Therefore,it is not difficult to imagine mixing R152a and R1234ze(E)to obtain a new mixture with complementary advantages and good comprehensive performance [12,13].
Vapor-liquid equilibrium(VLE)reflects the correlation between the temperature or pressure of the system and the composition or density of the vapor and liquid phase when the mixed system reaches a phase equilibrium state,and it is the basis for researching the thermophysical properties of mixtures.The cubic equation of states (CEOS) are often used in the calculation of the thermodynamic properties of mixtures [14,15].Soave-Redlich-Kwong (SRK)EOS and Peng-Robinson (PR) EOS are developed on the basis of Redlich-Kwong (RK) EOS,which have higher calculation accuracy than RK EOS and are widely used in the prediction model for the study of binary VLE [16–18].However,when the equations are used to calculate the thermodynamic properties of mixtures,appropriate mixing rules should be added [19].The mixing rule includes the conventional vdW mixing rule and the new mixing rule combining the equation of state with the activity coefficient.This new mixing rule is called the‘‘excess free energy mixing rule”,mainly including the HV mixing rule,WS mixing rule,MHV1 mixing rule,MHV2 mixing rule,LCVM mixing rule,and CHV mixing rule,etc.In recent years,some scholars have used the cubic equation combined with different mixing rules to study the VLE of binary mixtures composed of HFO and HFCs,as shown in Table 1[20–24].The relevant research in Table 1 shows that the vdW mixing rule and the HV mixing rule can be well combined with the PR equation of state and the SRK equation of state,respectively,and are widely used.At present,there are few studies on the VLE of R152a/R1234ze(E).Yanget al.[25] measured the VLE data of R152a/R1234ze(E) from 258 to 288 K by using the static method,then correlated the data with the Huron-Vidal (HV) mixing rule through the PR EOS,and finally found that the R152a/R1234ze(E)system exhibited an azeotropic phenomenon.Fenget al.[26]used the data obtained from the experiments of Yanget al.to construct a VLE calculation model of R152a/R1234ze(E) using PR EOS combined with the van der Waals (vdW) mixing rule.The accuracy of the VLE calculation data affects the subsequent derivation of its thermophysical properties,so it is important to use the appropriate EOS and mixing rule when studying the VLE calculation model.Therefore,it is necessary to use different EOS combined with different mixing rules to filter out the VLE calculation model suitable for the R152a/R1234ze(E) system.

Table1 Summary of VLE calculation models for binary mixtures composed of HFOs and HFCs
The above research results show that the temperature range of the phase equilibrium experiment of the R152a+R1234ze(E)blend is 258.15–313.15K.R152a,R1234ze(E),and their mixtures are used as alternative refrigerants respectively to R134a in automobile air conditioning system.Under standard air-conditioning conditions,condensing temperature of refrigerant in the system is about 323.15 K.In order to fully study thermodynamic properties of R152a/R1234ze(E) in automobile air conditioning system,we expand the temperature range from 298.15 K to 328.15 K.And,the VLE predicted models for R152a/R1234ze(E) were constructed using SRK,PR EOS combined with vdW,HV mixing rules,respectively,to obtain a proper calculation model for the R152a/R1234ze(E)system.This provides a basis for accurately calculating the thermophysical properties of the R152a/R1234ze(E) mixture and a reference for selecting the VLE calculation model of the binary mixture composed of HFO and HFCs.
2.Experimental
2.1.Materials
The experimental chemical R1234ze(E)was supplied by Honeywell Trading Co.,Ltd.R152a was supplied by Zhejiang Yonghe Refrigeration Co.,Ltd.Detailed information about the two samples is listed in Table 2.All chemicals were found to be within acceptable purity specifications by gas chromatography (GC) analysis(>0.999) and were used without further purification.
2.2.Apparatus
As shown in Fig.1,the vapor–liquid equilibrium experiment was completed with the liquid phase recirculation analytical apparatus.The apparatus mainly consists of the VLE cell,the recirculation section,the sampling and analysis section,the thermostatic bath section,and the measurement section.To provide the stable temperature circumstance,a thermostatic water bath of approximately 28 L was served.The nominal volume of equilibrium cell is about 200 ml.The pump was used for circulating the liquid phase,which was sucked from the cell bottom to the top.The liquid phase and the vapor phase were sampled by a four-port valve with a 2 μl internal sample loop and a six-port valve with a 0.5 ml external sample loop,respectively.
A platinum resistance thermometer with an accuracy of 10 mK(model:PT100,Xi’an Xiatech Electronics Co.,Ltd)was used to measure the temperature of the system.The pressure was measured by a high-precision silicon resonance pressure transducer (Model TERPS 8000,Baker Hughes) with a range of 0–7 MPa.Gas chromatography(model:GC2014C,SHIMADZU)with a flame ionization detector (FID) was applied to examine the compositions of the vapor and liquid mixtures.The sample was configured by using a digital balance (Model ZCS,Ruian Haozhan Weighing Instrument Co.,Ltd)with resolution of 0.1 g.Three analyses at least were made for the vapor and liquid mixtures to make sure that the fluctuation of mole fractions was less than 0.003,and all apparatuses had been calibrated before the experiment.
2.3.Experimental procedure
The specific procedure of the VLE experiment of binary mixed refrigerant is as follows:(1)Before the experiment,the equilibrium cell was washed using a small amount of R1234ze(E) or R152a to remove the air.Then after a few minutes,the system was evacuated by a vacuum pump,and the pressure should meet under 5 Pa standards.Repeat this step 3–4 times.(2) An amount of R1234ze(E) and R152a was introduced into the sample cylinder in proportion before being mixed.Then the sample was poured into the equilibrium cell after vacuuming the system.(3) When the water bath temperature fluctuated not more than ±0.05 K/30 min,the run can start.(4) The liquid phase circulating pump canbe turned off in the case of the established equilibrium at the desired temperature.And the vapor sample was taken into the gas chromatograph to measure its mole fraction before the measurement of the liquid sample was taken into the gas chromatograph through the six-port valve.To improve the accuracy of the results,take the average of the three measurements as the final result of the mole fractions of each phase.(5) Resetting the temperature and repeating steps (3) and (4).(6) The proportion of the sample was adjusted after vacuuming the system.Then repeat steps (2)–(5) to obtain the VLE experimental data of different sample proportions under four temperatures (298.15 K,308.15 K.318.15 K,328.15 K),respectively.

Table2 Sample information for R152a and R1234ze(E)

Fig.1. The diagrammatic sketch of the VLE experimental set-up(1—isothermal liquid bath;2—vacuum vessel;3—equilibrium cell;4—vapor phase six-port valve;5—liquid phase four-port valve;6—sample needle value;7—liquid phase circulating pump;8—differential pressure transmitter;9—stirrer;10—circulation bath;11—thermometer;12—digital acquisition;13—computer;14—pressure transducer;15—platinum resistance;6—sample cylinder;17—vacuum pump;18—gas chromatography).
3.Establishment of Models
3.1.Equation of state
The CEOS are widely used to calculate the VLE characteristics and derive the thermophysical properties of mixtures due to their simple form and high accuracy [28].Both the PR equation and the SRK equation belong to CEOS,and they can be applied to calculate the VLE of mixtures because they consider the vapor pressure of hydrocarbons at different temperatures and improve the ability to express the VLE of pure substances.
The PR EOS is expressed in the following form [29]:
wherep,T,and v are pressure,temperature,and molar volume,respectively,andRis the universal gas constant with the value of 8.3145 J∙mol-1∙K-1.a(T) andbare the energy parameter and covolume parameter,respectively,which are related to the critical pressure (pc),critical temperature (Tc),and acentric factor (ω).a(T) is the product of the two factors expressed by Eq.(2),whereacis the constant at the critical temperature,showing thata(Tc),α(Tr,ω) are functions of temperature and ω.
The expression of the SRK EOS is as follows [30]:
wherea(T) used an expression similar to Eq.(2),with:
3.2.Mixing rules
The expressions for vdW mixing rules are shown as below[31]:

Table3 Basic physical properties of the R152a and R1234ze (E) [27].
wherexiandxjare the molar fractions of componentsiandjis the binary interaction coefficient,andkij=kji,kii=kj j=HV mixing rule is derived from the following equations [32]:
The NRTL activity factor model is used to calculate the excess free energy [33]:
where αii=αjj=0,τii=τjj=0,and τijare the adjustable parameters.In this paper,αij=0.3.
Table 3 listed the pure refrigerants’ physical properties used in the calculations.The critical properties and acentric factors(ω)for R152a and R1234ze(E) were taken from REFPROP 9.0 [27].
4.Results of the Computational Models
4.1.Experimental data and reliability verification
As presented in Table 4,a total of 44 experimental VLE points of the R152a+R1234ze(E)mixture were measured at four isothermsT=(298.15,308.15,318.15,328.15) K,and the query data of REFPROP 9.0 under the same conditions.
The expressions of δprefand AARD(pref) are shown as below:
From Table 4,it can be seen that the maximum absolute relative deviation of the equilibrium pressures between the REFPROP9.0 data and the VLE experimental data is 2.501%,and the minimum absolute relative deviation is only 0.016%.The AARD(pref) from 298.15 to 328.15 K are 1.467%,1.268%,1.058%,and 0.899%,respectively,which verified the accuracy of the vapor–liquid phase equilibrium model built.And,the bubble point and dew point pressure curves for R152a/R1234ze(E) are presented in Fig.2.

Table4 Experimental VLE data for R152a/R1234ze(E) system and correlated results of REFPROP9.0 [34]
It can be seen that no matter how the mole fraction of R152a changes at constant temperature,the bubble point pressure and the dew point pressure in the experiment of R152a/R1234ze(E)and the REFPROP9.0 database are all extremely close.Even at high temperatures,the difference between the bubble point pressure and the dew point pressure is still very small,indicating that R152a/R1234ze(E) is a binary azeotropic mixed refrigerant.

Fig.2. Pressure-composition relationship between experimental results and REFPROP9.0 database for the R152a/R1234ze(E) system.
4.2.Calculation results and error analysis
Based on the SRK and PR EOS combined with vdW and HV mixing rules,respectively,the VLE prediction model of R152a/R1234ze(E) mixture was constructed by correlating the VLE experimental data of R152a/R1234ze(E).The binary interaction coefficientskijand adjustable parameters τijand τjiare the optimized parameters to ensure the accuracy of the model calculation,as shown in Table 5.
The absolute deviations of vapor phase mole fractions for the four calculation models are shown in Fig.3,where the maximum absolute deviations are–0.0134,–0.0134,–0.0151,and–0.147,respectively.As shown in Fig.4,it is the relationship between the equilibrium pressure and the vapor-phase mole fraction of R152a at different temperatures calculated from the four models,wherepexpis the experimental equilibrium pressure,thepcal(PR+vdW),pcal(SRK+vdW),pcal(PR+HV)andpcal(SRK+HV)belong to the four calculation models,respectively.The relative deviations of the equilibrium pressures are shown in Fig.5.It can be seen thatthe maximum relative deviation of equilibrium pressure is 0.752%for the PR+vdW model,1.886% for the SRK+vdW model,0.685%for the PR+HV model,and 1.888% for the SRK+HV model,all of which are smaller than 2.501% in the above REFPROP9.0 data.The above results show that all four models presented an extremely content correlation with the experimental data.

Table5 Optimized parameters for R152a/R1234ze(E)

Fig.3. Deviations of the calculated and experimental values of R152a/R1234ze(E) about mole fraction of vapor phase.

Fig.4. Equilibrium pressure curves of R152a/R1234ze (E) by calculation models: (a) T=298.15 K.(b) T=308.15 K.(c) T=318.15 K.(d) T=328.15 K.
In order to compare the correlation effects of the calculation models,the average absolute deviations for vapor-phase mole fractions(AAD(ycal))and average absolute relative deviations for equilibrium pressures (AARD(pcal)) of the four models are listed in Table 6,where AARD(pcal) is consistent with Eq.(19).
The equation for AAD(ycal) is shown as below:
It can be seen that the AAD(ycal)maxand AAD(ycal)avgfor the PR+vdW calculation model are 0.0031 and 0.0027,respectively,the AARD(pcal)maxand AARD(pcal)avgare 0.414%and 0.361%,respectively,and the AAD(ycal)maxand AAD(ycal)avgfor the SRK+vdW calculation model are 0.0042 and 0.0032,respectively,the AARD(pcal)maxand AARD(pcal)avgare 0.750% and 0.678%,respectively,and the AAD(ycal)maxand AAD(ycal)avgfor the PR+HV calculation model are 0.0034 and 0.0027,respectively,the AARD(pcal)maxand AARD(pcal)avgare 0.307% and 0.243%,respectively,and the AAD(ycal)maxand AAD(ycal)avgfor the SRK+HV calculation model are 0.0044 and 0.0032,respectively,the AARD(pcal)maxand AARD(pcal)avgare 0.697% and 0.610%,respectively.The above results prove that the PR+HV calculation model has a better correlation with the experimental data of R152a/R1234ze(E) than the other three models.Both the PR and the SRK EOS are obtained by improving the RK EOS,and the expression of the RK EOS is as follows:
Comparing Eqs.(1) and (6) with Eq.(21),it can be seen that both the PR EOS and the SRK EOS take into account other temperature (a(T)) besidesTc.In addition,the PR EOS increases the constant ‘‘b(v–b)” in the gravitational term,and the power ofbincreases,which improves the derivation accuracy ofa(T)and critical compressibility factor (Zc) [26,28].It explains why PR EOS has higher accuracy than SRK EOS.Besides,the HV mixing rule combines the equation of state and activity coefficient through an excessive thermodynamic property,which can enhance the prediction ability of the activity coefficient method for polar systems and compensate for its discontinuity in the critical region [35],so the calculation accuracy of PR+HV model is better than the other three models.
5.Conclusions
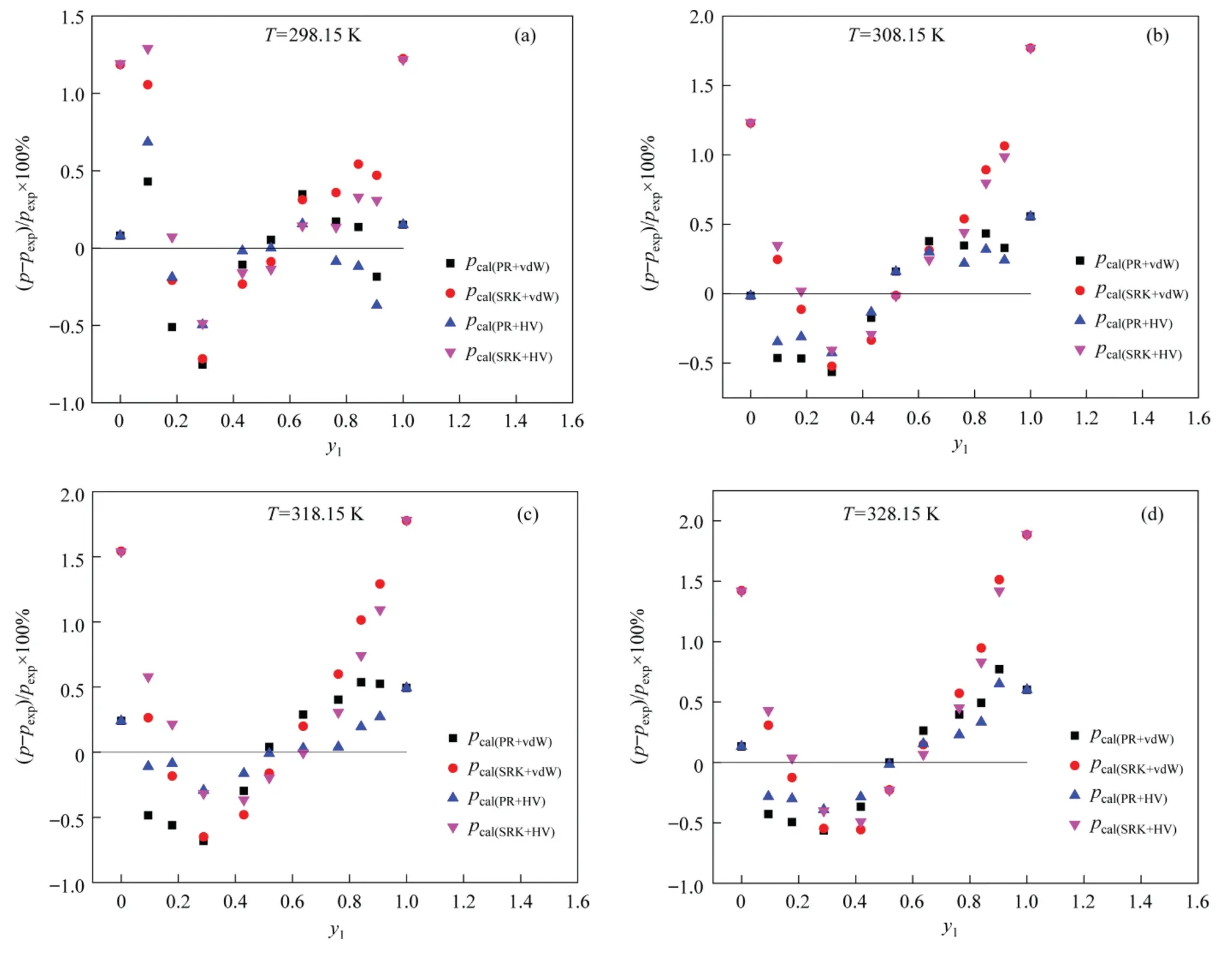
Fig.5. Deviations of the calculated and experimental values of R152a/R1234ze(E) about Saturation-pressure.

Table6 Deviations of the calculation models for each temperature
The VLE model for the binary system R152a/R1234ze(E) in the temperature range 298.15–328.15 K was developed using the PR and SRK EOS with the vdW and HV mixing rules,respectively.Then,the experimental data were used to optimize the binary interaction coefficientsk12in the vdW mixing rule and τ12in the NRTL activity coefficient model.The equilibrium pressures and vapor-phase molar fractions were obtained by the calculation models,and it was found that all four models showed a high correlation with the experimental data.The calculated results show that the AAD(ycal) for all four models are within 0.005,and the AARD(pcal) are within 0.8%,which are much smaller than the AARD(pref)avgof 1.173% for the REFPROP9.0.Among them,the calculated results of the PR+HV model are closest to the experimental data,with the AAD(ycal)avgof 0.0027 and the AARD(pcal)avgof 0.243%.In addition,based on the fact that the PR EOS introduces more constants in the gravitational term based on the SRK EOS,and the PR EOS has a better match with the HV mixing rule than the SRK EOS,it shows that the PR+HV model has a higher calculation accuracy compared with the other three models.
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: ‘Yuande Dai reports financial support was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.22068024).’.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22068024).
Nomenclature
aenergy parameter,J∙m3∙mol-2
bvolume parameter,m3∙mol-1
ffree energy,kJ∙kg-1
kijbinary interaction parameter
Mmole molecule mass,g∙mol-1
ppressure,MPa
Runiversal gas constant,J∙mol-1∙K-1
Ttemperature,K
vmolar volume,cm3∙mol-1
xmolar fraction of liquid phase
ymolar fraction of vapor phase
Zcompressibility factor
aijNRTL model parameter
τijbinary interaction parameter of NRTL model
ω acentric factor
Subscripts
avg average
c critical
cal calculated
exp experimental
i,jcomponent index
lliquid
m mixture
max maximum
r contrast state
ref the data are taken from REFPROP 9.0
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2023年10期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2023年10期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- High catalytic performance of CuCe/Ti for CO oxidation and the role of TiO2
- Experimental and numerical studies of Ca(OH)2/CaO dehydration process in a fixed-bed reactor for thermochemical energy storage
- Volumetric and ultrasonic properties of thiamine hydrochloride drug in aqueous solutions of choline-based deep eutectic solvents at different temperatures
- Synthesis of zeolite A and zeolite X from electrolytic manganese residue,its characterization and performance for the removal of Cd2+ from wastewater
- Metal-organic framework-derived Co-C catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde to cinnamic alcohol
- A pseudo transient nonequilibrium method for rigorous simulation of multicomponent separation columns
