Status of research on non-conventionaltechnology assisted single-point diamond turning
Zhuang Chen, Guangjun Chen,,a) Zhiwei Yu, Jiashuai Huang, and Hong Wei
AFFILIATIONS 1 Tianjin Key Laboratory of High Speed Cutting and Precision Processing,Tianjin 300222,China
2School of Mechanical Engineering,Tianjin University of Technology and Education,Tianjin 300222,China
ABSTRACT With the increasing use of difficult-to-machin materials in aerospace applications,machining requirements are becoming ever more rigorous.However,traditional single-point diamond turning(SPDT)can cause surface damage and tool wear.Thus,it is difficul for SPDT to meet the processing requirements,and it has significan limitations.Research indicates that supplementing SPDT with unconventional techniques can,importantly,solve problems due to the high cutting forces and poor surface quality for difficult-to-machin materials.This paper firs introduces SPDT and reviews research into unconventional techniques for use with SPDT.The machining mechanism is discussed,and the main advantages and disadvantages of various methods are investigated.Second,hybrid SPDT is briefl described,which encompasses ultrasonic-vibration magnetic-fiel SPDT,ultrasonic-vibration laser SPDT,and ultrasonic-vibration cold-plasma SPDT.Compared with the traditional SPDT method,hybrid SPDT produces a better optical surface quality.The current status of research into unconventional techniques to supplement SPDT is then summarized.Finally,future development trends and the application prospects of unconventional assisted SPDT are discussed.
KEYWORDS Single-point diamond turning,Machined surface quality,Tool wear,Unconventional auxiliary technique
I.INTRODUCTION
With the continual development of materials such as tungsten carbide,many high-strength,high-melting point,and hightoughness materials have been widely applied in aerospace and other fields Therefore,single-point diamond turning (SPDT) has become an important method in material processing.Although traditional SPDT can reduce the machined surface roughness of difficult-to-machin materials,it has several problems,such as high cutting force,high cutting temperature,and serious tool wear.1–3The diamond tools used,workpiece materials,cutting parameters,and lubrication conditions all affect the surface roughness of SPDT,which in turn affects the surface quality after machining.4–9
In recent years,many scholars have proposed various unconventional techniques to assist SPDT and,thus,improve performance.According to research,such combined methods have had unexpected results in terms of improving surface finis and extending tool life.10Unconventional auxiliary techniques can have a significan impact on factors such as machining accuracy,machining quality,and tool wear.Therefore,the further development of such methods may be important for SPDT.When investigating the use of SPDT for different materials,Zhanget al.11identifie the mechanism of elliptical-vibration SPDT,which significantl enhanced SPDT.Not only was the turning capacity higher but also the turning ability of hard and brittle materials was enhanced.Researchers have determined how unconventional techniques can assist SPDT in machining different materials.For example,Xuet al.12adopted unconventional techniques to assist SPDT with difficult-to-machin materials.These techniques greatly improved the surface quality of the machined workpiece,increased machining efficiency reduced the cutting forces,and extended tool life.The machined workpiece also met the actual machining requirements.As a result,unconventional assisted SPDT has gradually become an important method of turning difficult-to-machin materials.13–16Compared with using a single unconventional technique to assist SPDT,using a hybrid combination of unconventional methods can obviously reduce the cutting force and improve machined surface quality and tool wear.Hybrid SPDT mainly combines two unconventional techniques to assist SPDT,such as ultrasonic-vibration laser SPDT,ultrasonicvibration magnetic-fiel SPDT,and ultrasonic-vibration plasma SPDT.However,there have been relatively few studies on hybrid SPDT,so that further research is necessary.

FIG.1.Combinations of techniques considered in this paper.
First,this paper introduces SPDT and discusses the principal factors affecting the surface quality realized by SPDT.Then it introduces the most recent research on unconventional techniques for assisting SPDT,namely laser SPDT,ultrasonic-vibration SPDT,magnetic-fiel SPDT,cold-plasma SPDT,and ion-beam SPDT.Next,it proposes novel processing methods,hybrid forms of SPDT,which use two unconventional methods to assist SPDT.The combinations of techniques considered in this paper are illustrated in Fig.1.Finally,the paper concludes by discussing the future prospects of unconventional assisted SPDT.
II.SINGLE-POINT DIAMOND TURNING
SPDT is the most advanced processing technology for ultraprecision machining.It was firs proposed by American scholars in the 1960s.This technology gradually became popular.In the 1990s,the tools used were mainly natural diamond.For example,computer-controlled diamond tools are used to turn aspherical optical parts.SPDT is an effective method for processing high-precision and complex structural optical surfaces.17–19The optical parts processed by SPDT can have a shape accuracy of 0.1 μm and a surface roughness of 0.025 μm.20–23At present,SPDT can be used in the nanofabrication of a wide range of materials,24–26mainly resins and plastics (methacrylate resins),27infrared crystals,28some nonferrous and ferrous metal materials,29and optical components.30SPDT has the advantages of high machining efficiency high machining accuracy,and great repeatability.Therefore,it can also be used to machine sulfur-based materials,31–33aspheric optical elements,34micro-structures,35,36such as micro-lens arrays,37,38compound eye lenses,39and sinusoidal grids,40,41as shown in Fig.2.However,when processing difficult-to-machin materials,such as hightemperature superalloys,it is difficul for traditional turning methods to satisfy the required processing requirements.At high temperatures and pressures,in particular,it can have excessive cutting forces,surface machining damage,tool wear,and even workpiece fractures.
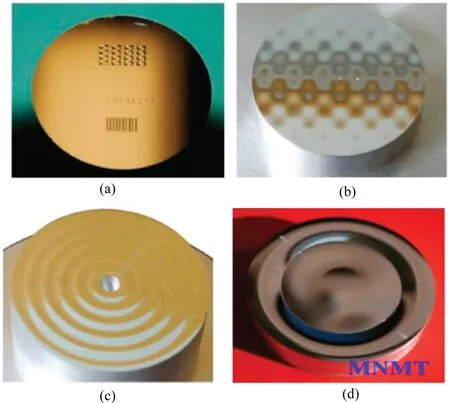
FIG.2.A variety of complex surfaces can be machined by ultra-precision diamond turning: (a) Machined mold insert for a micro-Alvarez lens array.(b) Sine grid surface.(c)Sine wave surface.(d)Freeform surface.Reproduced from Huang et al.24
Various factors affect the surface quality of SPDT,such as the tool,machining process,and machine tool.42–45In addition,it is also influence by environmental factors in the workplace(indoor air quality,humidity,temperature,and vibration)and cutting parameters (cutting depth,cutting speed,and feeds).46,47The roughness of the machined surface is an important aspect of surface quality.48–51Tool wear,spindle error,material defects,manufacturing accuracy,and lubrication conditions can directly affect the surface roughness of SPDT.52–54Wear resistance,corrosion resistance,fatigue strength,and fi of the part can also affect the machined surface quality of the workpiece.55,56Shuping57studied the surface roughness of ZnSe after SPDT,findin that when the tool edge radius was used for compensation,a high-precision surface quality could be realized.However,if the cutting depth was increased,the cutting forces also increased so that the surface quality of the machined ZnSe crystalline parts became worse.The surface quality of the workpiece was better when the spindle speed and rake angle were increased while the cutting force was decreased.Consequently,predicting and controlling the surface roughness of machined parts is not simple,as several factors affect the smoothness of the machined surface.58–60In practice,several experimental studies have identifie some of these factors,such as the cutting parameters,that need to be controlled to realize a high-precision machined surface quality.For example,it is essential to use a large rake angle and a high spindle speed during machining to minimize the cutting depth and the cutting speed.
In terms of tool life,viable materials,and machined surface quality,SPDT has significan limitations.Machining difficult-to machine materials,such as high-temperature alloys,can cause tiny discontinuous defects on the cutting edge.Parts of the tool may fracture,leading to severe tool wear and shortening tool life.When machining high-temperature alloys,titanium alloys,stainless steels,high-strength steels,and hard and brittle materials,meeting the machining requirements directly is challenging.Hard and brittle materials have excellent optical and chemical properties.In SPDT,material is primarily removed through brittle fractures,which can lead to surface damage and defects,such as cracks and pits in the surface.This damage can reduce the material properties.Some materials are expensive to process and comparatively challenging to work with.Meanwhile,slip dislocations are produced on the machined surface with other challenging materials,such as monocrystalline silicon.These dislocations cause microcracks in and surface damage to the machined surface,wearing out the diamond tool and reducing tool life.
In conclusion,SPDT has a wide range of applications.It is commonly used to machine difficult-to-machin materials,such as tungsten carbide.Its advantages include high machining effi ciency and accuracy,better repeatability,low surface roughness,and lower machining costs.Many factors affect the quality of the machined surface: rake angle,spindle speed,cutting parameters,etc.When processing optical materials,SPDT is more suitable for medium-sized and small optical parts produced in medium-sized batches.
According to research,the introduction of unconventional techniques to assist SPDT has resulted in the wear on the cutting edge of the tool being more uniform.There are no visible defects on the tool,tool wear is significantl reduced,and tool life is extended.Unconventional assisted SPDT has better processing conditions and is viable for more materials,such as semi-ductile materials.It can also process some non-ferrous and ferrous metals,and the range of processes has progressively been extended.In addition,the machining methods can be optimized to increase the ductility of the workpiece material and reduce its brittleness.To improve the optical surface quality,it is important not to cause defects,such as microcracks and pits,on the machined surface.A variety of processing methods are used to complement SPDT,giving rise to laser SPDT,ultrasonic-vibration SPDT,magnetic-fiel SPDT,cold-plasma SPDT,and ion-beam SPDT.
III.LASER SPDT
In the 1980s,two academics at the University of Southern California in the USA used lasers to cut metal.Lasers were then widely used in precision and ultra-precision machining.It is also one of the primary heat-treatment techniques.60–62In laser machining,the laser energy is mainly concentrated on the surface of the workpiece.This partially heats and softens the material,increasing its plasticity and weakening it.Thus,it improves processing efficienc and prevents cracks and fractures on the processing surface.63–67Laser turning mainly reduces the hardness and elastic properties of the workpiece material by increasing its thermal softening capacity,increasing its plasticity,and reducing its fragility and brittleness.It also increases the critical depth of cutting and improves the way the material cuts.As a result,the cutting pressure and surface roughness are decreased and tool life is prolonged.68–71After laser turning,the dislocation density of the workpiece increases,the yield strength decreases significantly and the plastic deformation increases significantly.Laser turning also causes a rise in the residual stresses on the product surface,which aids in suppressing surface flaw like microcracks and pits.
Linet al.72used laser SPDT for fused silica.Their experimental results showed that the machined surface quality and the machining efficienc were significantl improved.As shown in Fig.3,without laser processing,the machined surface had areas with fragmentation.With the introduction of the laser,the machined surface improved dramatically and became smooth.When using the optimal cutting parameters,the roughness of the machined surface was fell by 84.3%.In laser machining,the rake angle,feed rate,depth of cut and machining,and laser power all affect the machined surface roughness.73When turning monocrystalline silicon (111),Mohammadiet al.74used a combination of micro-laser technology and SPDT.Their experimental results showed that the surface roughness of monocrystalline silicon fell from 80 to 16 nm.The machined surface quality was significantl improved in comparison with conventional SPDT.It has also been investigated experimentally whether the laser power,tool front tilt angle,and crystal orientation affect the surface roughness.To avoid affecting the machined surface quality,it was concluded that the optimal laser power was 20 W and the optimal tool front tilt angle was-25°.Based on this,Shahinianet al.75also used laser SPDT to process monocrystalline silicon.During processing,brittle fractures had significantl reduced and diamond tool life was increased by 150%compared to conventional SPDT.
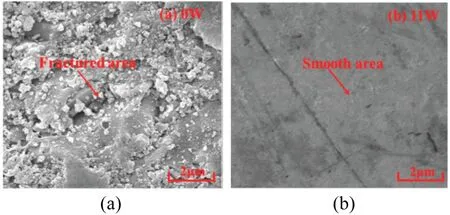
FIG.3.Scanning electron micrography (SEM) images of machined surfaces obtained by SPDT with a laser power of (a) 0 W or (b) 11 W.Reproduced from Lin et al.72
You and Fang76adopted laser SPDT to machine binderless tungsten carbide (WC).Their experimental studies found that the chip rejection rate was significantl improved when the laser power was low,which helps prevent the diamond tool from being graphitized.Furthermore,the residual stresses on the machined workpiece were reduced because the local heating of the workpiece was higher than over the rest of the workpiece.Langanet al.77used laser SPDT to machine brittle materials.Within a specifi range,they significantl reduced the residual stresses on the processed surface.The quality of the machined surface finis was also significantl improved.Ravindraet al.78proposed a combination of laser ablation and SPDT.Their experimental results demonstrated that the machined surface quality was significantl better.Tool wear was reduced to a minimum value.The material removal rate was significantl increased.Based on these advantages,Navareet al.79combined SPDT with laser technology for turning and machining ZnS.They found that the crystal orientation of the diamond tool affects the degree of tool wear and the surface roughness of the machined surface.It was initially determined that the best machining results,the least amount of tool wear,and the smoothest machined surface were achieved with the {100} cutting plane and 〈110〉 cutting direction.
Laser SPDT has been applied more widely than conventional SPDT as it is highly efficient Youet al.80investigated the removal mechanism of a polycrystalline material.They combined a laser with SPDT for binderless tungsten carbide and conducted real-time monitoring of the turning process.Their results showed that there was a significan improvement in machining stability and cutting forces,as well as improved machining efficienc and surface quality.They also found that annealing occurred during machining,which makes the machined surface smoother and effectively inhibits the graphitization of diamond tools.Hongdaet al.81analyzed the machining performance of laser SPDT for single-crystal germanium.Compared with conventional SPDT,the experimental results revealed that the quality of the machined surface was significantl improved.In addition,by comparing the dislocation density with the residual stress,it was found that the surface defects of the workpiece machined byin situlaser SPDT were significantl reduced.The dislocation density decreased by 26.6%.They also found that preheating was not required for laser SPDT.It can also be used for more efficien turning.Those authors also found that the best cutting parameters were a laser power of 20 W and a negative rake angle of -25°,which achieved the smallest surface roughness Ra.Youet al.82found that for laser SPDT of tungsten carbide,the best cutting parameters were a tool rake angle of-25°,a feed rate of 1 μm/rev,a cutting depth of 6 μm,and a laser power of 10 W.This set of parameters produced the smallest surface roughness.
In conclusion,compared with conventional SPDT,laser SPDT can extend the life of diamond tools and avoid the graphitization of the tools.Laser SPDT can improve the surface quality and smoothness of the machined surface.It also reduces stiffness while inhibiting amorphous layers that have been damaged.Moreover,laser SPDT has lower production costs and higher machining efficiency However,the laser machining increases the cutting temperature,so that the tool experiences sticky wear,occasional thermal expansion,and other problems.Further research is needed to solve these problems for laser SPDT.
IV.ULTRASONIC-VIBRATION SPDT
Ultrasonic-vibration machining can be used for onedimensional,two-dimensional,or three-dimensional processing.The process was invented in 1927.Junichiro Kuma in Japan firs put forth the idea for ultrasonic-vibration cutting in the middle of the 20th century.The theoretical and practical basis for ultrasonics has been established.Ultrasonic-vibration technology is widely applied in various processing fields including ultrasonic-vibration turning,ultrasonic-vibration drilling,ultrasonic-vibration grinding,and ultrasonic-vibration cutting.Ultrasonic-vibration turning is a composite machining technique.It has important applications for difficult-to-machin materials such as engine shafts and housings.83–85The main components of an ultrasonic-vibration system are an ultrasonic generator,an ultrasonic transducer,an ultrasonic horn,and a tool system.Ultrasonic-vibration turning is primarily a combination of tool vibration and machining.The tool system is made to vibrate,which changes the form of the contact between the tool,the workpiece,and the chip.86This results in a cyclical separation between the tool and the workpiece,thus achieving intermittent cutting.This method of machining signifi cantly improves the machinability of the workpiece by reducing the bond between the workpiece material and the tool.It also avoids phenomena such as chip tumors and reduces the cutting forces and chip thickness.87Moreover,the application of ultrasonic vibrations enhances the stability of the system.During ultrasonic vibratory turning,the cutting direction of the tool constantly changes during each cycle as the turning process is reciprocal,with chips being cut off by the vibrating tool.This process minimizes the size of surface pits,lessens surface harm to the workpiece,and enhances the quality and surface profil of the machined surface.It also lowers the degree of material deformation.Ultrasonic vibratory turning produces uniform and flatte chips with regular vibratory marks on the machined surface.It reduces the shock forces and prevents microcracks,wear,and breakage of the tool,thus extending tool life.88–90Because of these processing advantages,ultrasonic-vibration processing is,therefore,frequently used to assist SPDT for difficult-to-machin materials,such as high-temperature superalloys.91–94
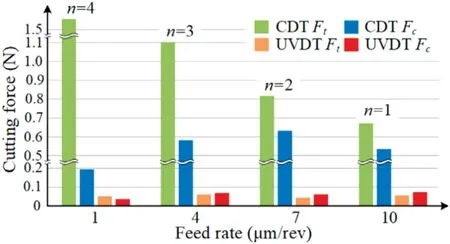
FIG.4.Cutting forces for conventional diamond turning (CDT) and ultrasonicvibration diamond turning(UVDT)at different feed rates.Reproduced from Zhang et al.95

FIG.5.Experimental setup for ultrasonic-vibration SPDT:(a)cutting and(b)real-time monitoring of tool settings.Reproduced from Li et al.101
To turn the high-entropy alloy FeCrCoMnNi,Zhanget al.95used high-frequency ultrasonic-vibration machining combined with SPDT.This processing technology reduces the chip thickness and the cutting force to within a certain range and reduces tool wear.It also improves the integrity of the machined surface and eliminates any scratches remaining on the machined surface (Fig.4).Ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration turning mainly involves applying a high-frequency,low-amplitude vibration to the tool tip parallel to and perpendicular to the cutting direction.The tool tip,thus,moves along an elliptical trajectory and cuts intermittently.As the vibration amplitude was increased,the cutting force was significantl decreased,and the machined surface roughness Ra was signifi cantly reduced.Simultaneously,when the feed rate was lower,the turning machining effect was better.96Zhanget al.97found that,compared to SPDT,ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration turning produces better machining results with significantl lower cutting forces.In addition,Weiet al.98adopted ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration turning for machining the superalloy GH4169.Their experimental results show that the cutting parameters have a clear effect on the cutting force.Turning has been simulated with the finit element program ABAQUS,which showed that the cutting force decreased significantly extending tool life.Furthermore,Duet al.99summarized the status of research into ultrasonic-vibration SPDT,findin that this technique is significantl superior to conventional SPDT.Thus,ultrasonic-vibration SPDT has been widely applied to turning and machining difficult-to-machin materials,such as tungsten carbide.Based on the above experiments,Yanet al.100found that the surface morphology of ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration turning was significantl better than that of conventional turning.Moreover,the cutting force and cutting temperature were significantl reduced.The chip elimination efficienc was significantl improved,the machining accuracy and surface roughness were better,and tool life was significantl extended.
Liet al.101used a combination of ultrasonic-vibration technology and SPDT to improve the machining efficienc of tungsten carbide.The experimental setup is illustrated in Fig.5.Their experimental results show that the surface roughness (Ra) of the machined surface was proportional to the degree of tool wear.The surface roughness of tungsten carbide reached a minimum when the tip radius was lower.They also found that machining efficienc and quality were significantl enhanced with an inclined negative front angle in ultrasonic-vibration SPDT.Zouet al.102explored ultrasonic-vibration SPDT for 3Cr2NiMo mold steel,findin that graphitization of the tool was significantl decreased and that diamond diffusion wear was reduced by 58%.Additionally,the tool life was significantl extended.That work has laid a solid theoretical foundation for subsequent studies of tool life.
In conclusion,ultrasonic-vibration machining can efficientl solve the problems of traditional SPDT.It decreases the friction between the tool and the surface being machined.It also decreases the cutting forces and the roughness (Ra) of the surface.It produces a smooth machined surface with a significantl higher chip removal rate.However,ultrasonic-vibration SPDT is not suitable for all materials.Tremors often occur during machining,affecting the accuracy and producing surface damage and burrs.
V.MAGNETIC-FIELD SPDT
Magnetic-fiel machining was firs developed in the 1950s.A magnetic fiel is applied during SPDT to cut materials quickly and efficiently It improves dislocation mobility and avoids cracking.Moreover,it improves tool life and reduces the residual stresses on the machined surface.It enhances the thermal conductivity and cutting stability of nickel-based high-temperature alloys.103How to change the isotropy and anisotropy of materials during magneticfiel machining has been a matter of academic interest.Experiments have found that some of the workpiece materials were strained,and the grains of different materials were oriented and ordered.This demonstrates that metal alloys are sensitive to magnetic fields which also influenc diffusive phase changes.104–107The magneticfiel density is closely related to the material-cutting process.As the magnetic-fiel density is increased,the shear angle increases significantl and the friction coefficien decreases.Deformation of the workpiece material is reduced,and the friction angle gradually decreases.Magnetic-fiel turning has a damping effect due to eddy currents,which prevent the machining system from vibrating,thus reducing the surface roughness of the workpiece.It is beneficia for reducing dislocation slips,increasing the plasticity of the material,improving cutting,preventing any deformation of the material,and forming continuous chips.Applying a magnetic fiel results in a significan reduction in the wear on the flan and rake faces of the tool,extending tool life.To investigate the effect of magnetic flu density on the surface integrity of nickel-based alloy 718 and its low-cycle life,Talebizadehsardariet al.108applied a magnetic fiel during SPDT.This method successfully reduced the tensile residual stresses on the machined surface.Furthermore,it improved the machined surface quality,reduced the crack extension rate on the machined surface,and enhanced the low-cycle life.Wuet al.109also applied a magnetic fiel in SPDT to machine nonferrous materials.They found that the cutting force ratio and friction coefficien were reduced by 16%.The cutting performance of the metal was improved,and the roughness Ra of the machined surface was successfully reduced from 16.2 to 15 nm.
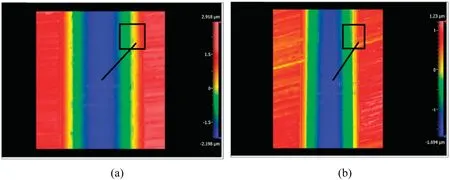
FIG.6.(a)The plane views of surface roughness with magnetic field,and(b)the plane views of surface roughness without magnetic field.Reproduced from Yip and To.110

FIG.7.Experimental setup for magnetic-field SPDT.Reproduced from Khalil et al.111
In experiments exploring magnetic-fiel SPDT of a titanium alloy,Yip and To110compared the surface roughness with or without a magnetic field as illustrated in Fig.6.Their experimental results show that applying a magnetic fiel reduced the machined surface roughness and increased the shape accuracy.In addition,the experiments revealed that the material recovery problem could be solved if the magnetic-fiel strength was 0.02 T.Moreover,Khalilet al.111developed and designed a machining system for SPDT with a magnetic field Figure 7 shows how the experiment was set up.The process improved the machinability of Ti6Al4V.For single-crystal copper,it contributed to the formation of smooth chips,reduced the machined surface roughness Ra,reduced the wear rate of the tool and workpiece(Fig.8),extended the tool life,and improved the quality of the machined surface.Keet al.112found that applying a magnetic fiel in machining successfully increased the clipping angle and reduced the degree of plastic transformation.The machined surface quality was greatly enhanced,the occurrence of material deformation was reduced,and the machinability of the material was improved.
In summary,compared with conventional SPDT,magneticfiel SPDT reduces the surface roughness,improves surface quality,and avoids material deformation.It also avoids the deformation of the material,reduces the swelling effect on the machined surface,and facilitates the turning of the workpiece.Furthermore,it reduces tool wear,reduces tool–workpiece interactions,and improves part machinability.However,there have not been any in-depth studies into the intrinsic mechanism of magnetic-fiel SPDT.
VI.COLD-PLASMA SPDT
In cold-plasma machining,a cold plasma is applied to the cutting area of the workpiece,effectively cooling it down.It increases the heat transmission efficienc and lubrication capacity of the cutting surface.There is a reduction in chemical affinit between the tool and the machined surface,thus reducing the wear of the diamond tool and extending tool life.113–116A cold-plasma atmosphere can efficientl prevent the friction interface from contacting oxygen,thus protecting the machined surface from oxidative wear.Jianget al.117proposed using ion processing of brittle materials to increase processing efficiency Their experimental results show that the elasticity of single-crystal silicon was significantl enhanced and the cutting force had declined considerably.Daiet al.118utilized molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the effect of ionic injections on the properties of silicon carbide machined by SPDT.That study showed that such injections suppressed the increase in temperature,decreased the cutting force,improved the machined surface roughness,and increased the machinability of the plastic region.Those researchers also found that the higher the ionic energy,the higher the internal damage and the lower the cutting force.In addition,to alleviate the susceptibility of machined surfaces to brittle fracture,Wanget al.119recommend adopting a combination of SPDT and cold-plasma machining based on the above research.They successfully fabricated microstructures on the surface of brittle materials,and their experimental results show that there was a significan increase in the brittle–ductile transition depth of silicon and a considerable reduction in tool wear.Liet al.120combined SPDT with spark plastination,successfully obtaining ultra-smooth surfaces and suppressing surface grain coarsening.Consequently,ion-beam techniques have been widely used for machining ultra-high-precision optical components as well.121Liuet al.122used cold-plasma SPDT to machine Ti6Al4V,and the experimental results showed that there were significan improvements in lubrication and cooling of the cutting area.Furthermore,the cutting force and tool wear were reduced(Fig.9),improving tool life and obtaining good surface integrity.
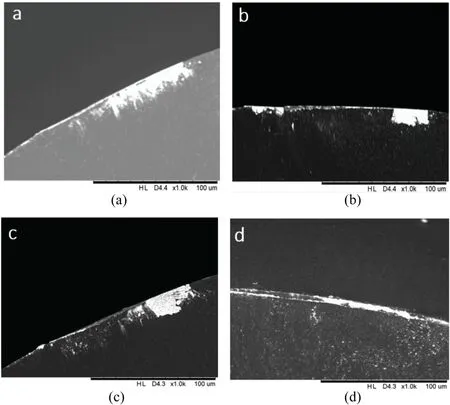
FIG.8.(a)Tool front face without a magnetic field.(b)Tool front face in machining with a magnetic field.(c)Rear face of tool without a magnetic field.(d)Tool rear face.SEM image of the tool.Reproduced from Khalil et al.111
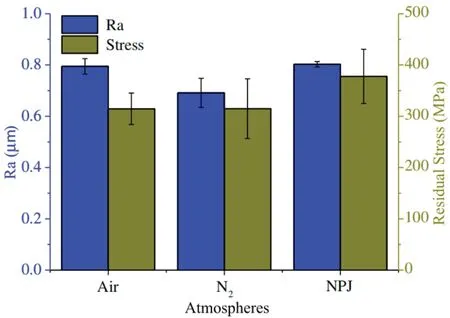
FIG.9.Surface quality and residual stress when cutting Ti6Al4V under different atmospheres.Reproduced from Liu et al.122
In conclusion,compared with conventional SPDT,cold-plasma SPDT significantl reduces the cutting forces and diamond tool wear and extends tool life.On the one hand,it improves the lubrication and cooling of the cutting zone.On the other hand,it avoids residual marks on the machined surface while enhancing its quality.The disadvantage of plasma SPDT is that it is a relatively complex process and is useful only for a limited range of materials.Furthermore,several of the parameters in ion injection affect the mechanism of ion SPDT,which still needs to be explored.
VII.ION-BEAM SPDT
In ion-beam processing,an ion beam is produced by passing an inert gas through an ion source.When atomic energy builds up on the machined surface,material is removed due to sputtering.Ion-beam SPDT makes the surfaces of a micro-fabricated structure smoother and less likely to stick together,significantl improving surface quality.Regarding tool wear,it reduces the bonding on the flan and rake faces of the tool.It improves cutting performance and makes the tool surface more lubricating and wear-resistant.After further treatment,an ion beam is projected onto the machined surface to assist in precision and ultra-precision machining.123Huanget al.124proposed using an ion beam to increase the performance of SPDT.They successfully decreased the machined surface roughness.Within a specifi range,the process eliminated the turning marks on the machined surface (Fig.10) and improved machining accuracy.Based on these findings when exploring the effect of an ion beam on the machining performance of SPDT,Liet al.125discovered that the roughness of the machined surface was significantl reduced by spraying and ion flattening
Compared with other machining methods,ion-beam SPDT is faster and more accurate.However,the processing machines and equipment are relatively costly.
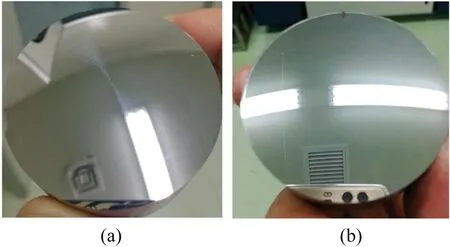
FIG.10.Images of Al surface machined by SPDT before (a) and after (b) ionbeam figuring,showing that the color pattern caused by the turning marks had been removed.Reproduced from Huang et al.124
VIII.HYBRID SPDT
In recent years,many scholars have discovered that when machining difficult-to-machin materials,such as tungsten carbide,the unconventional techniques described above can be combined with SPDT to achieve excellent results in improving one aspect of the process.However,an auxiliary technique can occasionally cause chatter and adhesive wear on the tool during machining.To alleviate such problems,many scholars have proposed hybrid SPDT,such as ultrasonic-vibration magnetic-fiel SPDT,ultrasonic-vibration laser SPDT,and ultrasonic-vibration cold-plasma SPDT,which are described below.
A.Ultrasonic-vibration magnetic-field SPDT
Wanget al.126proposed a novel hybrid processing technique.They applied a magnetic fiel in ultrasonic-vibration machining to enhance the processing of thick parts.The magnetic field and ultrasonic-vibrations are often used to assist in processing by lowspeed electric cutting machines.The experimental results revealed that the discharge was more uniform,the machining efficienc was higher,and the machined surface quality was higher.Thus,scholars have proposed using this novel hybrid method to assist SPDT.Experiments have found that doing so enhances processing.During ultrasonic-vibration SPDT,chattering can occur in the tool and machine tool,which affects machining accuracy and is not conducive to machining stability.Chattering can be avoided and tool wear reduced by applying a magnetic fiel during ultrasonicvibration SPDT.Yipet al.127adopted ultrasonic-vibration technology combined with magnetic-fiel technology to assist SPDT of titanium alloys to reduce surface damage and burrs.The experimental setup is shown in Fig.11.Applying a magnetic fiel is a secondary form of assistance.By comparing the surface morphology with and without a magnetic field those researchers found that applying a magnetic fiel reduced the surface scars left by ultrasonic-vibration SPDT.It also prevented chattering during machining,improved the quality of the machined surface,and suppressed the degree of material swelling.
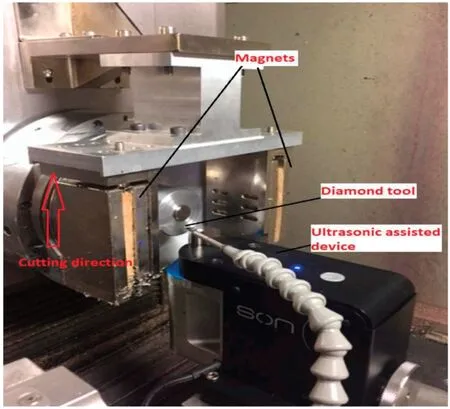
FIG.11.Experimental setup for ultrasonic-vibration SPDT with a magnetic field.Reproduced from Yip et al.127
In conclusion,ultrasonic-vibration magnetic-fiel SPDT,compared with single SPDT,significantl reduces surface scars and markedly improves machining efficiency It also prevents chattering and reduces tool wear.However,there has been relatively little experimental research into ultrasonic-vibration magnetic-fiel SPDT of difficult-to-machin materials,and the fiel is still in the primary research stage.
B.Ultrasonic-vibration laser SPDT
The combination of ultrasonic-vibration technology and laser technology has been widely used for machining aspheric optical molds and carbide.The depth of cutting is significantl greater than that of single auxiliary cutting.The cutting speed is increased,the surface roughness of the machined surface is significantl lower than that of conventional cutting,and the quality of the machined surface is improved considerably(Fig.12).128–130Moreover,the cutting force and machined surface roughness decrease with an increase in laser power.131–133Compared with single SPDT,the depth of cut is increased,the surface roughness is significantl reduced,and the surface quality is improved dramatically.Graphitization of the tool is prevented,tool wear is reduced,and tool life is extended.It also significantl increases machining efficiency134These results were fully confirme in SPDT experiments by Jianfeng,135who used a hybrid of ultrasonic-vibration technology and laser technology.Their experimental results revealed that hybrid SPDT improved the machining efficienc and the surface smoothness of the workpiece.It prevented the chatter due to ultrasonic-vibration processing.Furthermore,it prevented the laser from increasing the cutting temperature and from causing phenomena such as sticky tool wear.
During ultrasonic-vibration laser SPDT,the laser parameters affect the machined surface quality,tool wear,and cutting forces.There have been few experiments on this hybrid technique.
C.Ultrasound-vibration cold-plasma SPDT
To address the issues with single unconventional assisted SPDT,many scholars have proposed combining plasma-aided machining methods with ultrasonic-vibration machining methods to assist SPDT.In the hybrid ultrasonic-vibration plasma SPDT,a high-temperature plasma arc softens the partially machined surface.Ultrasonic elliptical vibrations are used to precisely control the system characteristics,thus reducing the cutting forces and ensuring stability during turning.Whereas,cold-plasma SPDT can reduce the wear of a diamond tool,ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration SPDT can change the size and direction of the cutting force.Thus,combining these two techniques with SPDT can effectively reduce the cutting temperature and inhibit tool wear.Farahnakian and Razfar136used combined plasma and ultrasonic-vibration SPDT when quenching steel AISI 4140.This experimental study found that the cutting forces were significantl reduced.Compared to single unconventional assisted SPDT and conventional SPDT,the machined surface roughness was significantl improved.Huanget al.137used a hybrid cold-plasma ultrasonic-elliptical-vibration SPDT method for ferrous metals.Their experimental results revealed that the cutting temperature was obviously reduced.The method inhibited the graphitization of the diamond tool while reducing tool wear and extending tool life.

FIG.12.Surface profile under different cutting conditions.(a) Conventional cutting.(b) Two-dimensional ultrasonic cutting.(c) Two-dimensional ultrasonic laser cutting.Reproduced from Li.130
In conclusion,a hybrid of plasma SPDT and ultrasonicvibration SPDT can reduce the cutting forces and decrease tool wear.It can also improve the machined surface quality compared to single SPDT.However,there have been few studies on the hybrid of ultrasonic and cold-plasma machining.
IX.SUMMARY AND FUTURE PROSPECTS
This paper summarizes some unconventional techniques for supplementing SPDT and discusses the cutting forces,tool wear,surface quality,tool life,machining efficiency etc.It reviews the overall machining mechanism and discusses the main applications.Our conclusions and future perspectives can be summarized as follows:
1.Unconventional assisted SPDT is effective for processing difficult-to-machin aerospace materials,such as tungsten carbide.There are still several issues that need to be solved in the practical application of unconventional techniques with SPDT.Laser SPDT produces less surface damage and prevents the graphitization of the diamond tool.Still,it is prone to problems such as tool adhesion and wear during machining.Ultrasonic-vibration SPDT can improve the quality of the machined surface,decrease the cutting force,and reduce tool wear.However,chattering readily occurs and there can be other problems during machining,so that the stability of machining is not guaranteed.Magnetic-fiel SPDT lowers tool wear while extending tool life,avoiding material deformation,and reducing the dissolution of the machined surface.However,there is a lack of research on the intrinsic mechanism.Cold-plasma SPDT lowers the cutting forces during machining,reduces tool wear,and eliminates residual marks on the machined surface.The machining method is relatively complicated,and the effects of many parameters on machining during ion SPDT have not been determined.Ion-beam SPDT is fast and accurate,but the equipment is complicated and the costs are relatively high.Each of these unconventional techniques has different auxiliary effects,which can affect the machined surface to various degrees.Thus,for each application,it is necessary to select the appropriate unconventional technology to assist SPDT.
2.Compared with single SPDT,hybrid SPDT can avoid chattering and tool-sticking wear.An intelligent utilization of hybrid SPDT can improve the stability of turning and reduce the surface roughness due to machining.It can also improve the surface quality of machining,reduce tool wear,and prolong tool life.However,there has been little experimental research into hybrid SPDT.A theoretical analysis is also required.Various unconventional techniques can complement SPDT.The results show that a hybrid system can improve accuracy and efficiency reduce tool wear,and prolong tool life.
3.Future research into SPDT should focus on gradually increasing automation and reducing the excessive dependence on labor.Machining stability and processing efficienc both need to be improved.In addition,since it is based on electroplastic machining,energized SPDT should also be studied in future research.Studies have shown that it can improve the quality of the machined surface and inhibit chemical reactions between the tool and the machined surface.Furthermore,it can reduce tool wear and prolong tool life.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.52175431),the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin of China (Grant No.22JCZDJC00730),and the Scientifi Research Project of Tianjin Municipal Education Commission(Grant No.2022ZD021).
AUTHOR DECLARATIONS
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict to disclose.
DATA AVAILABILITY
The data that support the finding of this study are available within the article.
- 纳米技术与精密工程的其它文章
- Research trends in methods for controlling macro-micro motion platforms
- Droplet microfluidic chip for precise monitoring of dynamic solution changes
- Characteristics of the pressure profile in the accelerator on the RF negative ion source at ASIPP
- Oxidation mechanism of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al composite under laser irradiationand subsequent machining
- An optical tweezer-based microdroplet imaging technology
- Effects of laser energy on the surface quality and properties of electrodeposited zinc-nickel-molybdenum coatings

