Research trends in methods for controlling macro-micro motion platforms
Lufan Zhang, Pengqi Zhang,Boshi Jiang,and Heng Yan
AFFILIATIONS College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou 450001,China
ABSTRACT With ongoing economic,scientific and technological developments,the electronic devices used in daily lives are developing toward precision and miniaturization,and so the demand for high-precision manufacturing machinery is expanding.The most important piece of equipment in modern high-precision manufacturing is the macro-micro motion platform(M3P),which offers high speed,precision,and efficienc and has macro-micro motion coupling characteristics due to its mechanical design and composition of its driving components.Therefore,the design of the control system is crucial for the overall precision of the platform;conventional proportional–integral–derivative control cannot meet the system requirements,and so M3Ps are the subject of a growing range of modern control strategies.This paper begins by describing the development history of M3Ps,followed by their platform structure and motion control system components,and then in-depth assessments of the macro,micro,and macro-micro control systems.In addition to examining the advantages and disadvantages of current macro-micro motion control,recent technological breakthroughs are noted.Finally,based on existing problems,future directions for M3P control systems are given,and the present conclusions offer guidelines for future work on M3Ps.
KEYWORDS Macro-micro motion platform,Precision positioning,Control method,Piezoelectric driver,Voice coil motor
I.INTRODUCTION
Combining a high-speed motion positioning module and a high-precision motion module,macro-micro motion platforms(M3Ps) are long-range and precise motion systems.Compared to standard single-stage motion positioning modules,M3Ps have high precision and rapid acceleration while still benefittin from the rapid response,high torque,small volume,and low noise of singlestage motion modules.Because of these advantages,several sectors have adopted M3Ps,including precision integrated circuit fabrication,vibration control,optical fibe calibration,and micro-nano detection.1–8M3Ps are vital components in systems that require enormous strokes and high levels of precision,with location precision being the most important performance metric.9–11However,an M3P is a multilevel drive system comprising two interconnected motion modules,and therefore there is substantial motion coupling involving interaction of the two motion modules,12–14with such coupling reducing drastically the overall positioning precision of motion.Currently,the key strategy used to address such coupling issues is decoupling the control system design,15–17and so that design is crucial for ensuring the accuracy of M3Ps.
To date,there have been numerous studies involving the creation of M3P control systems.18,19Ganet al.addressed the modeling and control of the piezoelectric drive in a micro-drive platform,20while Yanget al.addressed applications of high-precision positioning platforms and M3Ps.21However,those studies were mostly concerned with investigating a single macro-motion platform or micro drive positioning platform,and there have been few review articles to date devoted to the design of M3P control systems.
Therefore,this review focuses on M3P control systems,outlines the overall control strategy and the composite control strategies for the two-stage drive module,compares various control techniques,and identifie future research hotspots and new opportunities for M3Ps.The remainder of this paper is structured as follows.Section II describes an M3P,Sec.III describes its control strategies,Sec.IVdescribes the existing challenges and potential development trends,and Sec.V provides a summary and conclusions.
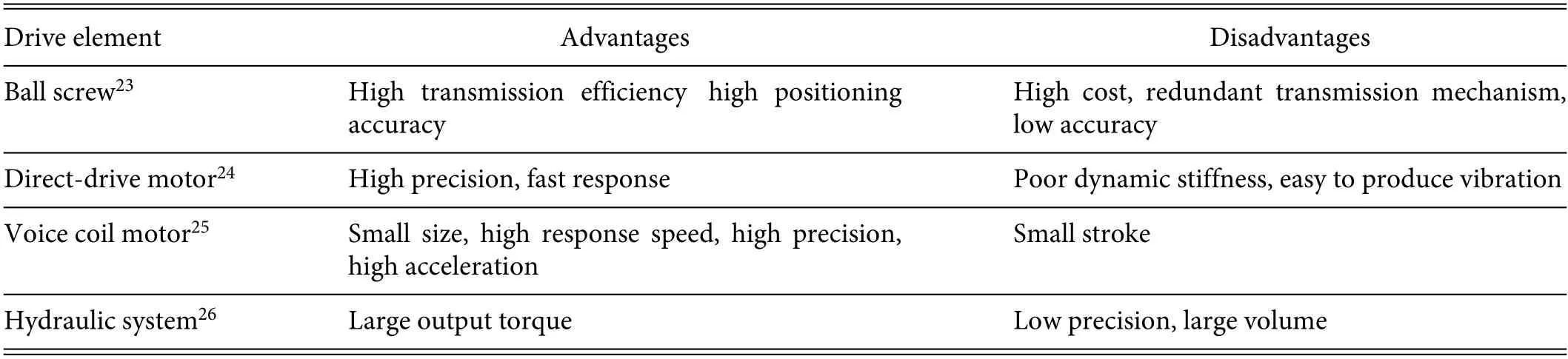
TABLE I.Comparison of macro drive elements.
II.OVERVIEW OF MACRO-MICRO MOTION PLATFORM
Based on the macro-micro two-stage drive concept due to Sharon and Hardt,22an M3P is a novel type of platform used to achieve large stroke and high positioning accuracy,and it involves both macroscopic and microscopic motion.The macromotion component is responsible for the workbench’s large stroke,high-speed action,and initial positioning,and typically the macromotion mode is powered by a linear voice coil motor (VCM),a ball screw,a static pressure screw,or a hydraulic rod.Table I outlines the advantages and disadvantages of the various driving components.Compared to a regular linear motor,a VCM has the advantages of small size and straightforward design.Also,there is no redundant transmission mechanism,which allows for greater precision,whereas the hydraulic technique produces greater precision but requires additional supporting systems.Therefore,because of these considerations,a VCM is chosen as the macro drive for the most popular macro drive components,and herein VCMs are investigated in detail.23–26Meanwhile,the micro-motion component is responsible for the table’s fina location,and involved in micro-motion are phase-change-material drivers,thermaldeformation drivers,shape memory alloy (SMA) drivers,electromagnetic drivers,electrostatic drivers,magnetostrictive drivers,electrorheological drivers,electrostrictive drivers,and piezoelectric drivers.
Figure 1 shows the various drive elements used for the macroand micro-motions.The precision is strongly associated with the micro drive component,and Table II analyzes the pertinent characteristics of various micro drive components.
Piezoelectric ceramics have fast response,low power consumption,and are ideal for micro-motion drivers,which is why they are currently the main choice.The micro-motion positioning structure involves mainly a piezoelectric ceramic either cooperating with flex ible mechanisms or driving the motion directly,being responsible for the fina positioning of the work table.33–36To date,numerous research groups have investigated M3Ps.Pahket al.integrated a micro-motion platform powered by piezoelectric ceramics with a macro-motion platform driven by electric motors and used a high-resolution laser interferometer as the position feedback to build a closed loop in order to achieve high positioning precision;however,because to its size and expense,the system can only be used as an experimental platform and cannot be implemented on a broad scale.37Choiet al.conducted kinematic analysis on the VCM and piezoelectric ceramic used to drive various modules designed by them.38Matsubaraet al.also incorporated a macro-motion system and a micro-motion system to achieve a steady precision of 19 nm.39As shown in Fig.2,Jieet al.at the Harbin Institute of Technology created a two-dimensional,high-precision positioning platform that uses the XY-direction driving structure of a VCM piezoelectric ceramic;the driving structure of the VCM piezoelectric ceramic was modeled and decoupled dynamically,and a positioning accuracy of 21 nm under 5gacceleration was attained.40As shown in Fig.3,using a combination of double closed-loop feedback and active disturbance rejection control,Heet al.at Guangdong University of Technology reduced the response time by 60.93%with a positioning precision of 1 nm.41
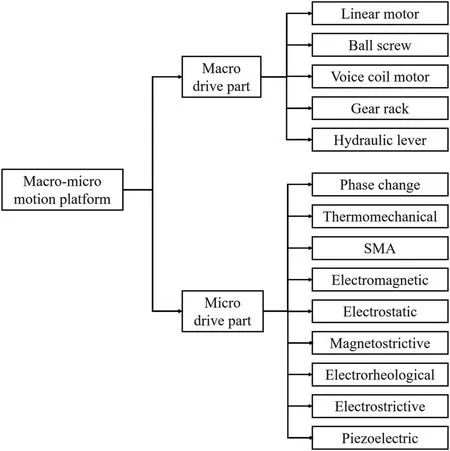
FIG.1.Classification of driving elements for macro-micro motion platforms(M3Ps).

FIG.2.Two-dimensional workbench.40
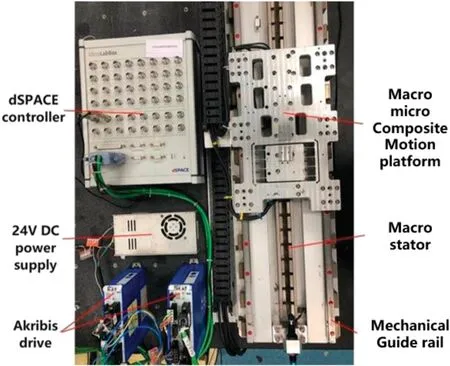
FIG.3.M3P driven by linear motor.41
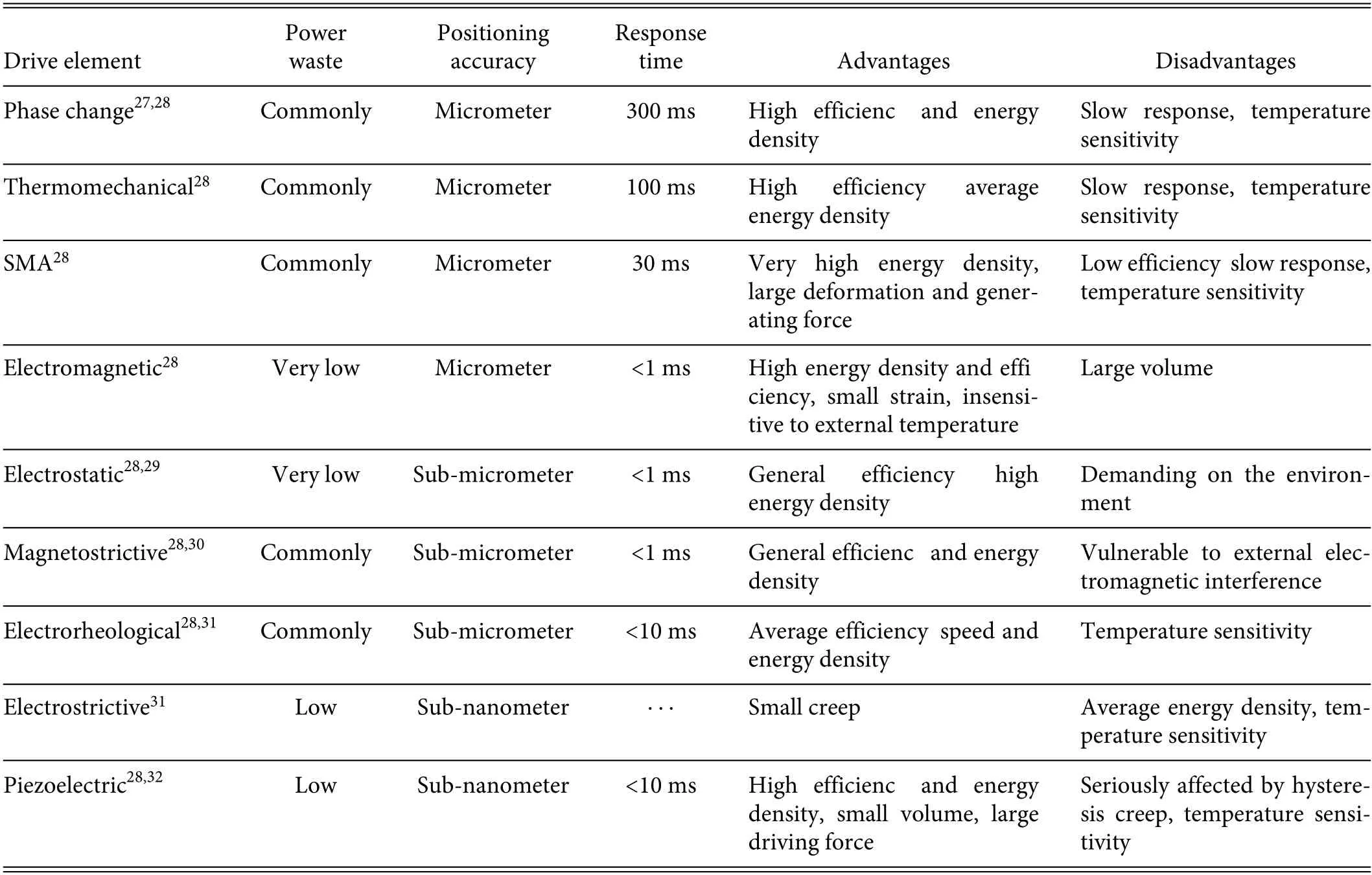
TABLE II.Comparison of characteristics of micro drivers.
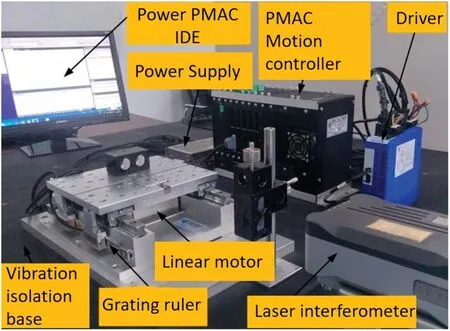
FIG.4.Experimental M3P.42

FIG.5.M3P with damping platform.43
As shown in Fig.4,Wanget al.at Guangdong University of Technology used a micro-motion incremental proportional–integral–derivative (PID) control method to achieve a positioning accuracy of 68 nm and an overall stability time of 62.3 ms.42As shown in Fig.5,Chen and Dwang at the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology used piezoelectric actuators for incremental positioning and examined the control approach;by optimizing the control method,they obtained a positioning precision of 10 nm for the entire platform.43As shown in Fig.6,Shinnoet al.at Tokyo University of Technology developed a large-travel macro-micro positioning system with sub-nanometer resolution,using a servo motor and ball screw to achieve large travel motion,a VCM and air-floate guide rail drive to achieve micro-movement precision positioning,and a laser interferometer as the platform’s position sensor;the positioning system achieved a positioning precision of 0.3 nm across a travel range of 150 mm,but its pace was modest.44Maoet al.also created a nanoscale positioning system;its location precision and travel distance were 400 mm and 2 nm,respectively,but its speed and acceleration increases were perpetually problematic.45As shown in Fig.7,Donget al.at the University of Connecticut developed a one-dimensional,high-precision positioning platform in which a micro-motion platform was linked to a VCM,with flexibl hinges connecting piezoelectric ceramics to the micro-motion platform and capacitive sensors providing position feedback;air flotatio eliminated all platform friction,and the platform’s precision reached 20 nm,but the suspension increased the cost and required more equipment,and it was difficul to manage the vibration.46
Jieet al.implemented macro-motion with a VCM,using the combination of piezoelectric ceramics and flexibl hinges for micromotion and double-grating cross-scale displacement measurement for closed-loop position feedback;they achieved a motion range of 20 mm × 20 mm and nanometer positioning accuracy.47Gaoet al.at Guangdong University of Technology proposed a new M3P comprising a VCM and piezoelectric ceramics;the combination of a preload spring and nut ensured rigidity of the piezoelectric ceramics,and the preload could be adjusted via the preload nut.48Xuet al.at Hefei University of Technology adopted a new grating fast subdivision algorithm and grating signal acquisition and processing method based on complementary functions,which met the requirements of fast response and precise measurement;they used the wavelet differential driving mode to overcome the problem of minimum speed limit,and the minimum displacement fluctuatio was reduced from 100 nm to 10 nm.49

FIG.7.One-dimensional motion platform.46

FIG.8.X65P83K M3P.50

FIG.9.NFL5DP20S M3P.51
Many commercial companies already offer developed M3P products.Figure 8 shows the single-axis X-direction piezoelectric M3P (X65P83K) from Harbin Core Tomorrow Science &Technology Co.,Ltd.;exact positioning is performed by a piezoelectric actuator with a stroke of 25 μm,coarse positioning is performed manually using a micrometer with a positioning stroke of 13 mm and an accuracy of 10 μm,the maximum load is 20 N,and the theoretical precision is 0.5 nm when operating in closed-loop mode.50Figure 9 shows the NFL5DP20S M3P from Thorlabs,Inc.,which also uses a micrometer for coarse positioning;it has a positioning stroke of 5 mm with an accuracy of 50 μm,a micro positioning stroke of 20 μm with an accuracy of 0.6 nm,and a maximum load 10 N.51Figure 10 shows the F-131 M3P from Power Integrations,Inc.,in which three M-111 single-axis linear platforms are combined to create a three-axis positioning platform that is then used in conjunction with a P611.3 three-axis piezoelectric actuator system to create a three-axis M3P;the accuracy is 50 nm with a 15-mm stroke length for the three axes of coarse positioning,the theoretical accuracy of the three-axis precise positioning system is 0.2 nm,and the stroke is 100 μm and the maximum load is 6 N.52Figure 11 shows the F-712.MA1 optical-fibe M3P from Power Integrations,Inc.;the three-axis coarse positioning stoke is 25 mm,the three-axis precise positioning stoke is 100 μm,and the precision is 0.3 nm in theory.53
It is evident from the aforementioned products that standardization and modularization are current trends for high-precision positioning platform products.By interlinking several motion platforms,a composite positioning system with high accuracy and extensive travel can be created,but all of its control systems use the strategy of micro-motion after macro-motion.Positioning failure occurs when the macro-motion positioning error is too great and the micro-motion platform is unable to correct it.Via experiments,Hirakuet al.showed that the positioning method combining macro positioning and micro positioning can achieve accurate positioning of the workbench,and they noted that combined control systems are the trend of future control-system development.54For a highprecision M3P,the control system must be designed according to requirements,so the design of the control system is a key part of ensuring positioning accuracy.
III.MACRO-MICRO MOTION SYSTEM CONTROL

FIG.10.F-131 M3P.52

FIG.11.F-712.MA1 M3P.53
The positioning accuracy of an M3P is an important standard for evaluating its quality,and many aspects affect that accuracy,including control strategy,structural optimization,and platform vibration.The control strategy plays an obvious role in improving accuracy and response speed,and since the conceptualization of M3Ps,researchers have continuously optimized the control strategy.55Macro-micro motion control—also known as coarse–fin coupling control—usually involves macro-motion and micro-motion actuators.During the movement of the M3P,the micro-motion is driven by piezoelectric ceramics,which are seriously affected by hysteresis creep and other characteristics.Because of the high requirements for positioning accuracy in the process of moving the M3P,the design of the control system for its motion system is essential.56,57The concept of macro-micro control was firs proposed in the 1980s in the robot manufacturing industry.In 1983,Kanniet al.proposed a new control strategy to improve the working performance of a two-dimensional work table,58and later that year,Sharonet al.analyzed the feasibility of macro-micro control through the inherent characteristics of system dynamic response.22Later,after the work by Sharonet al.,the idea of macro-micro control became widely used in various field of industrial production,the firs being numerical-control machining and hard disk drives;indeed,this technology is still the key technology for hard disk drives.
M3Ps are prone to external factors during operation,such as voltage instability,nonlinear friction coefficient and other factors that seriously affect the positioning accuracy.58–60M3Ps are usually driven by VCMs and piezoelectric ceramics;an M3P can be seen as a dual-input single-output(DISO)system,and usually in the design of the control system,we divide the motion control into the macro-motion system and the micro-motion system as two singleinput single-output (SISO) systems.42The macro-motion control system is used mainly to control the driving motor to make the working part carry out large-stroke movement on the work table,and the micro-motion part controls the movement of the piezoelectric ceramics to ensure the positioning accuracy of the work table.In the control system,control strategies such as master–slave control,feedback double closed-loop control,and master–slave feedforward control are usually used.61–63To date,the macro-micro control strategy has been used widely in hard disk drives.When designing of an M3P,designing its control strategy is also very important.
A.Nonlinear control strategy for macro-micro motion platform
When designing the macro control strategy of a micro platform,the focus is mainly on designing the motion control strategy,and control strategies for micro-motion platforms have also become key for determining the control strategy of an M3P.A piezoelectric actuator is usually used as the driver of a micro-motion platform because of its advantages listed previously herein.As typical representatives of nonlinear hysteresis characteristics,piezoelectric actuators are ideal for researching hysteresis nonlinearity,but the inherent hysteresis characteristics of piezoelectric materials greatly affect their positioning accuracy.Therefore,how to suppress effectively the hysteresis phenomenon caused by piezoelectric materials has become an important topic for experts and scholars in recent years.
For dealing with the nonlinear characteristics of a piezoelectric actuator,the most common control method in the fiel of automatic control is voltage control.Commonly used control methods include digital PID control,adaptive control,neural network control,sliding mode variable structure control and fuzzy control,64as shown in Fig.12 and introduced briefl below.
1. PID control
PID control is a very common control method that is used widely in engineering,and generally it offers good control.PID is proportional–integral–differential control,and by adjusting these three parameters,we can reduce overshoot,eliminate static error,and increase system stability.65Because of its simple principle and characteristics,PID is also used widely in M3Ps.Sunet al.at Harbin Engineering University used PID control to realize displacement negative feedback to achieve closed-loop control of piezoelectric ceramics.66
2. Adaptive control
Adaptive control is a control method that involves on-line parameter identification including model reference adaptive control,self-correction control,and parameter adaptive control.The firs involves constructing a reference model,then designing a controller with fixe mode structure,and finall designing the self-adaptation rate to achieve the adaptive effect.The second involves achieving self-correction by adding an on-line parameter estimator and controller.67The third involves designing an adaptive rate to construct an adaptive system by adding an observer to the controller.By the early 1970s,Lyapunov stability theory and the rank convergence theorem had achieved great success in many applications through adaptive control algorithms.Later,a complete theoretical system and method of adaptive control were formed.68,69When analyzing the errors of M3Ps,Fanet al.introduced a linear state observer to compensate for the error caused by disturbance.70Wuet al.added an auto disturbance rejection controller in the control of a giant magneto piezoelectric hybrid drive mechanism to meet the preset error requirements.71
3. Neural network control
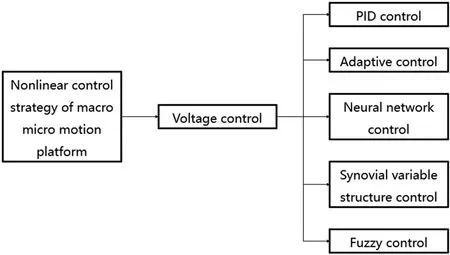
FIG.12.Nonlinear control modes for M3Ps.64
In 1943,McCulloch and Pitts proposed the concept of a neural network,which can approximate complex systems well and is better at adapting to some dynamic characteristics of nonlinear systems.Because of having a large number of neurons that are widely connected with each other,even if some neurons are destroyed,the main function of the system is unaffected,thus showing strong robustness.72These characteristics of a neural network give it great potential in the fiel of nonlinear control.A neural network has strong learning ability and its weighting is updated to reduce errors,making it very effective in controlling nonlinear systems.73Weiet al.used the neural network method to optimize a control algorithm,which reduced significantl the average and maximum errors.74,75
4. Sliding-mode variable structure control
Sliding-mode variable structure control is a nonlinear control method proposed by former Soviet scholars Emelyanovet al.in 1960.This control has switching characteristics in the continuous time domain,which can force the state of the system to move on a fluid-shape line or plane,often called the “sliding mode.”This mode can be designed by developers and has nothing to do with the external interference environment.However,sliding-mode variable structure control has a very serious disadvantage,i.e.,chattering;this phenomenon can easily have an adverse impact on the system and ultimately affect its control performance,and it causes relatively large interference in practical applications.76,77In the control of piezoelectric ceramics based on the Bouc–Wen hysteresis model,Fanget al.combined PID,a fuzzy algorithm,and a slidingmode variable structure control algorithm,and they verifie the effectiveness of the control algorithm by experiments.78
5. Fuzzy control
Fuzzy control is a computer-based control technology;applied initially to boilers and steam engines,after a period of development it is now used widely in various control fields Fuzzy control is a regular control method that does not need an accurate mathematical model to be establish,so it is convenient for use in practical applications.Fuzzy control is actually a method of simulating human experience;the system can be said to be capable of automatic adjustment,and the robustness of fuzzy control is relatively strong.It has strong anti-interference ability for external unknown factors,and has good adaptability for nonlinear,time-varying and pure lag systems.However,fuzzy control also has obvious disadvantages,such as low precision,being unsuitable for cases with high precision requirements,limited adaptive ability,and easily produced oscillations.79,80Jieet al.designed a control algorithm combining fuzzy control and PID control in the positioning system of a piezoelectric ceramic and flexur hinge.47
B.Macro-motion control method
Macro-motion control mainly controls the driving part to carry out large stroke motion,and usually the motion of a single degree of freedom is completed under the drive of a VCM.The latter is a permanent-magnet synchronous motor that directly outputs linear motion,and its principle is the force received by a conductor in a magnetic field Compared with other types of driving motors,there is a certain distance between the energized coil and the permanent magnet in a VCM,without contact;therefore,when working,there is no friction between the permanent magnet and the energized coil,and there is no cogging effect.81Because of the structure of piezoelectric ceramics,the stroke of the micro-motion work table is very short,so the macro stage usually requires large stroke,high speed,and high positioning accuracy.Therefore,a VCM is used as the macro driving element,and its characteristics make up for the shortcomings of the micro-motion table.Its fast response and high-precision characteristics are also necessary for the performance requirements of macro-micro control,with the fina positioning completed by micro-motion.At the same time,the displacement is measured with a grating ruler,and the displacement signal is connected with the control system to form a closed-loop feedback control system.Therefore,this requires not only the macro-motion control system to have the ability of fast response,but also a certain anti-interference ability.Equations (1)–(4) constitute the mathematical model of a VCM:82
whereRais the armature resistance of the VCM,Ftis the motor thrust,Fwis the interference force(including friction),eis the motor back-EMF (electromotive force),Ktis the motor thrust constant,andKeis the back-EMF constant.
The classical control theory headed by PID is used widely in macro-motion control and has the characteristics of simple structure,clear principle,and good robustness.However,because of the characteristics of PID control,its gain coefficient have a great impact on the fina control results,so the selection of PID gain coefficient is very critical.83–85Consequently,in a high-speed and high-precision motion system,it is difficul to meet the usage requirements with single PID control,and so to compensate for the shortcomings of PID,scholars in China and elsewhere are constantly improving the PID control method.Chenget al.used a self-adjusting PID controller in an ultrasonically driven piezoelectric-ceramic nano-positioning system,adding a parameter self-adjusting module to the PID link to automatically adjust the PID gain coefficients86Fanet al.introduced an extended state observer(ESO)to compensate for the error in the PID control link,and they compensated for disturbances via calculation to reduce the impact of environmental disturbances on the dynamic performance of the control system;they showed the effectiveness of their approach by experiments.70For disturbances in the macro-motion process,Heet al.used auto disturbance rejection control in the macro-motion control part and designed a linear auto disturbance rejection controller(LADRC)based on PID control to actively reduce the error;experiments showed that the response time was shortened by 20.58%with the introduction of LADRC,and the fluctuatio amplitude was smaller,allowing the steady state to be entered faster.41Wanget al.introduced the Luenberger observer into PID control to reduce the interference of high-frequency noise,reduce the impact of environmental disturbance,and make the VCM run more smoothly.87Chenet al.used approximate time-optimal time control (PTOC)in the macro process,and they used an ESO to compensate for unknown disturbances,thereby overcoming the limitations of conventional PID.57Weiet al.used neural network self-tuning PID and a genetic algorithm to optimize their model and reduce the error.74,75Dinget al.used an adaptive robust synovial control algorithm to compensate for the nonlinear friction in the motion process of the moving platform.88Huanget al.used a particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimize the parameter selection of PID to meet the required response time and positioning accuracy of driving motor.89Wanget al.used a gain-scheduling PID compound control method based on the combination of a disturbance observer and velocity–acceleration feedforward,which improved the positioning accuracy and response time of the moving platform.42Huet al.used a robust control algorithm to control a linear motor,and experiments showed that the macro-motion system controlled by a robust control algorithm had better dynamic and steady-state characteristics.90Yanget al.used a backpropagation neural network to optimize the PID parameters,and they established a neural-network PID feedforward control model.91
C.Micro-motion control method
Micro-motion is mainly responsible for M3P positioning.The micro-motion table is often located above the macro-motion table,and the displacement of the former is measured mainly by a laser interferometer or a grating sensor;a laser interferometer has the advantages of high measurement resolution and large measurement range,while a grating sensor has the advantages of easy installation,small volume,and simple principle.49Because an M3P requires high positioning accuracy,the micro-motion requires high resolution,and the common driving element is a piezoelectric ceramic,which has the advantages of high efficiency high energy density,small volume,and large driving force and is considered to be an ideal micro-motion driving element.60However,piezoelectric ceramics are affected seriously by hysteresis and creep,and their unique nonlinear characteristics pose great challenges to the control of micro-motion.47Research teams in China and elsewhere have conducted extensive research into the nonlinear hysteresis control of piezoelectric ceramics,and the commonly used hysteresis models of piezoelectric ceramics include the Preisach hysteresis model,92the Prandtl–Ishlinskii model,93the Krasnosel’skii–Pokrovskii model,94and the Bouc–Wen model.95Currently,there are two common control methods:one is feedforward compensation control based on the nonlinear hysteresis model of piezoelectric ceramics;in the other method,usually by establishing a more accurate nonlinear hysteresis model of piezoelectric ceramics,the hysteresis inverse model is used for feedforward compensation control to achieve accurate control.
Zhaoet al.obtained a displacement output feedforward control function for the micro-motion table based on orthogonal experiments and regression analysis,and the compensation effi ciency reached 83%in experiments.96Zhaoet al.approximated the response curve from the fittin curve of driving voltage and output displacement,based on which they constructed a feedforward compensation control algorithm.32Chenet al.used composite nonlinear feedback in the piezoelectric actuator and introduced an ESO to compensate for unknown disturbances.58
Weiet al.used a genetic algorithm to optimize the nonlinear hysteresis model of piezoelectric ceramics,and they used artifi cial neural network self-tuning PID as the control strategy.74,75Liet al.used hysteresis feedforward compensation combined with a multi-mode generalized predictive PID control algorithm.97On the other hand,the displacement relationship of piezoelectric ceramics involves a very complex nonlinear relationship,hence the established nonlinear hysteresis model must differ from the actual situation,leaving a gap in the quest for accurate control.Another control method is hysteresis control with closed-loop feedback.27Heet al.used the synovial variable structure control method by analyzing the mechanical characteristics of the positioning work table.60Jieet al.designed a fuzzy self-tuning PID control for the micromotion part.47Heet al.used the double closed-loop servo control system based on PID to control the micro-motion platform.41Saltonet al.proposed a constrained optimal trajectory for preview control of double-stage actuators;redundant preview control,which depends on the actuator,allows the primary stage to move before the transition time and compensates for its movement using the secondary stage.98Kwonet al.used a new type of robust control for piezoelectric ceramic actuators,achieving better control accuracy.99Minoruet al.proposed a position control method for a two-stage actuator based on double feedback and self-detection,which was driven by a DC servo motor and a piezoelectric ceramic:PID control was adopted for the DC servo motor,and PI plus feedforward control was adopted for the piezoelectric ceramic;experimental results showed the effectiveness of the proposed control system,and the performance of the two-stage actuator servo system was better than that of a single-stage actuator.100Fanget al.used a driving mechanism that combined a piezoelectric driver and a flexur hinge,and the parameters based on the Bouc–Wen hysteresis model were optimized by particle swarm optimization: through analysis,the hysteresis of piezoelectric ceramics was regarded as bounded interference,and for the model,a control mode combining fuzzy control,synovial variable structure control,and PID control was constructed,with a Lyapunov function constructed for the proposed control method to verify its stability;finally experiments showed that this control strategy is effective for improving the hysteresis of piezoelectric drivers.78
Regarding the master–slave feedforward control system,its control diagram (Fig.13) shows that the micro-motion platform compensates dynamically for the errors caused by macro-motion in the motion process,thereby improving the positioning accuracy of the platform.However,because of the limited stroke of micro-motion,if macro-motion produces a large positioning error,then the output of the micro-motion platform will be saturated.For double-feedback closed-loop control,the whole control system can be regarded as two SISO systems,thereby reducing the complexity of control system design.Because of the fina output signal of micro-motion tracking,the micro-motion platform is affected by the environmental disturbance caused by the macro-motion platform,which reduces the positioning accuracy of the whole platform.41

FIG.13.Schematic of master-slave feedforward control.41
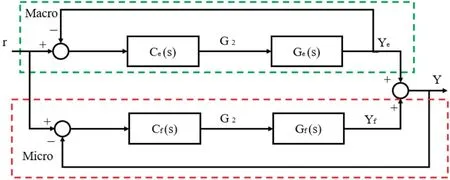
FIG.14.Schematic of double-feedback closed-loop control.41
D.Macro-micro motion control method
Macro-micro motion is a DISO system,with macro-motion and micro-motion undertaking different tasks in the operation process of the system.Macro-motion is responsible mainly for largescale motion and preliminary positioning at the macroscopic level in the motion of the positioning device,while micro-motion is responsible mainly for the fina positioning of the device.Therefore,for macro-motion control,large stroke and high running speed are important,while the characteristic of micro-motion is high positioning accuracy.101The control strategies of the master–slave structure can be divided into the following two types: (i) micro-motion followed by macro-motion (i.e.,micro-motion dominates) and (ii)macro-motion followed by micro-motion(i.e.,macro-motion dominates),and the two control strategies are analyzed as follows(Fig.14).
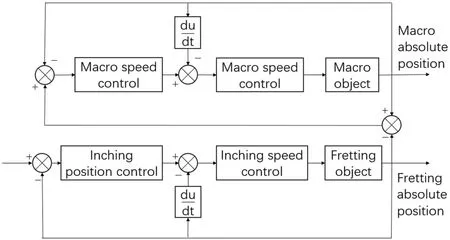
FIG.15.Block diagram of macro-micro control system.70
In the control system dominated by micro-motion,the micromotion control system is dominant in the whole control system,while the macro-motion control system is in the passenger seat.Regarding the system operation process and input and output,the macro-motion control system follows the micro-motion control system,and the system control block diagram of macro-motion following micro-motion is shown in Fig.15.The position signal and speed signal are used as feedback,and the micro-motion system mainly follows the system displacement signal.Meanwhile,the macro-motion system takes the relative displacement of the macromotion and micro-motion tables as the input to adjust the macromotion link,i.e.,the output displacement of the micro-motion table is the displacement of the system.70In the macro-micro control system dominated by micro-motion,the displacement of the macromotion table is controlled by the macro-motion system,and the displacement of the micro-motion table is controlled by the micromotion control system.102From the perspective of model coupling,the balance mass is negligible,and the single-degree-of-freedom macro-micro mechanical model is shown in Fig.16,wheremlis the mass of the macro stage,mvis the mass of the fretting table,Flis the driving force of the macro motion table,Fvis the driving force of the micro stage,ylis the absolute position of the macro stage,yvis the relative position of the micro-motion and macro-motion tables,andyis the absolute position of the micro-motion table.The following mechanical relationships can be established,and Eqs.(5)and(6)can be expressed as the transfer function matrix from motor thrust to displacement:70
When micro-motion is followed by macro-motion,the position output of the micro-motion system is that of the macro-micro system,which is very beneficia to the position control of the macro-micro system(Fig.17).
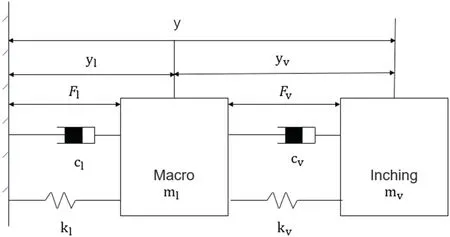
FIG.16.Mechanical model of single-degree-of-freedom M3P.
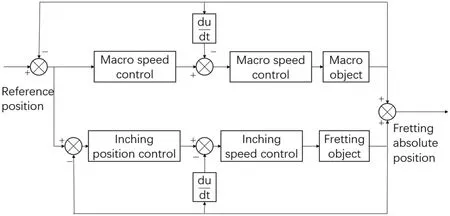
FIG.17.Block diagram of micro-following-macro control system.70
Next,we analyze the master–slave control strategy of macromotion followed by micro-motion.Similar to the above analysis method,in this control strategy macro-control is the active controller,micro-control is the slave controller,and micro-control adjusts the position after macro-control is completed.103From the perspective of system input and output,in the structure where macro-motion is followed by micro-motion and macromotion control is dominant,the macro-motion platform is usually used to approach the position signal,and the micro-motion control system mainly tracks the deviation between the micromotion and macro-motion tables.After the macro-motion table is tracked,the micro-motion table compensates for the displacement error of the macro-motion and micro-motion tables,and so the total output of the system is the sum of the displacements of the macro-motion and micro-motion tables.Therefore,in the control strategy in which macro-motion is followed by micromotion,the macro-motion table is responsible mainly for tracking the position of the reference signal,while the micro-motion table is responsible for outputting the displacement to compensate for the deviation between the macro-motion and micro-motion tables.104
It can be seen from Fig.13 that because (i) the micro-motion in the system follows the driver for adjustment and(ii)the macromotion part is responsible for tracking the input reference position of the system,the micro-motion system performs error compensation in the macro-motion.The macro-motion system does not set high positioning accuracy in the macro-motion part in order to minimize costs in the design requirements,so there are large design positioning errors in the macro-motion part.These cannot be eliminated in the design of the control system,and because the micro-motion system is responsible for compensating for the deviation from the macro-motion part,the displacement deviation of the macro-motion part is transferred to the micro-motion part during the deviation compensation of the micro-motion part,and the stroke of the micro-motion part is limited and cannot compensate for all the positioning errors,so the errors generated in the macromotion part are transmitted to the micro-motion part,Thus,the positioning accuracy of the whole system is affected.105From the perspective of system output,its position comprises the sum of the position outputs of the macro and micro parts,so the errors of the macro and micro parts are transmitted to the output error of the system.106
The above analysis shows that in the system of macro-motion followed by micro-motion,the macro-motion and micro-motion systems respectively control the displacement of the macro-motion table and the displacement of the micro-motion table relative to the macro-motion table.107,108Therefore,the following mechanical relationships can be established:
According to the model shown in Fig.16,in the control object of macro-motion followed by micro-motion,there is mutual coupling between the macro-motion and micro-motion systems,109and if the coupling effect is strong,then it will also affect the control performance of the macro system.110
Large stroke,high speed,and high positioning accuracy are contradictory characteristics,therefore the key issue in macro-micro motion control is better coordination of macro-motion control and micro-motion control to meet the requirements of the system,111and this is currently a research hotspot in China and elsewhere.Fanet al.analyzed and compared two master–slave macro-micro control strategies,established relevant models,and finall selected the strategy whereby the micro controller tracks the reference signal and the macro system follows the relative displacement between the micro and macro stages;an extended state amplifie was introduced,and through experimental analysis,the steady-state error was controlled at 5.5 nm and the maximum tracking error was controlled at 0.35 μm.70Shinnoet al.realized a full closed-loop control system with laser-interferometer feedback by using PID and an acceleration feedforward compensator,with the control system relying on the accurate feedback of the laser interferometer to ensure the accuracy of the overall system.112Donget al.used the double-feedback PID control strategy as shown in Fig.18.113Mitrovicet al.proposed a control algorithm based on distancecontrol driving force,and based on this design,a controller using a PID compensation algorithm achieved high motion accuracy in a two-stage drive system with only total output as feedback.114Shotaet al.designed a micro-brake high-bandwidth controller based on the characteristics of the micro-actuator in a two-stage system for compensating for low-frequency vibration: they reduced the required stroke of the micro-actuator by increasing the feedback gain of the VCM and compensated for the instability of the VCM driver at high frequencies through the micro driver,thereby ensuring the stability of the overall system;compared with traditional control methods,their control system improved the positioning accuracy and reduced the required micro-actuator stroke.115Zhanget al.used the inertial vibration of micro-motion for macromotion to achieve damping,reduce the switching and positioning time between macro-motion and micro-motion,and achieve rapid positioning.116
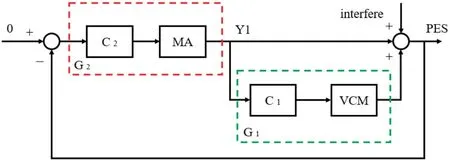
FIG.18.Schematic of master-slave control.41
IV.PROBLEMS AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS OF MACRO-MICRO MOTION PLATFORMS
A.Problems with macro-micro motion control methods
In recent years,there has been much research into M3P control.Because of the unique hysteretic creep characteristics of piezoelectric materials,traditional control theory cannot achieve very accurate control of piezoelectric ceramics,which are nonlinear materials.27However,with the continuous development of modern control theory,more and more modern control strategies are being constantly applied to M3Ps,and traditional control methods are also constantly being optimized.117At the same time,there are more and more ways to build mathematical models of piezoelectric-ceramic displacement hysteresis,and the application of neural networks and population optimization algorithms in macro-micro control is also improving.31,85
M3Ps are the basis of precision machining and a key technology for microelectronic manufacturing equipment.However,there are currently still many problems in M3P motion control,as discussed below.
(1) The aims of an M3P are high acceleration and high positioning accuracy.However,it is sensitive to interference,coupling,and various disturbances during operation,which prevent the control strategy from reaching a particularly ideal state.
(2) Piezoelectric actuators have nonlinear hysteresis characteristics,and their motion curves change depending on the material.Unfortunately,the controller’s design is not fully compatible with drivers exhibiting varying hysteresis characteristics,and so the control strategy is heavily dependent on the control model and cannot fully compensate for the error produced by the hysteresis effect.
(3) Currently,the commonly used closed-loop control strategy inevitably increases the complexity of the whole system because of its feedback,and more space is required for the various associated equipment in experiments.Also,in actual production,some types of production equipment do not have enough space for feedback facilities such as laser interferometers to be installed on the positioning platform,so the open-loop control strategy must be selected instead,and its accuracy is difficul to control.Therefore,it is also very important to improve the accuracy of open-loop control strategies and reduce the complexity of the double closed-loop control strategy.
(4) Currently,important features such as flexibl hinges and connecting rods are included in the micro-motion platform in the design of some M3Ps,but adding these components results in varying degrees of movement interference.Also worth discussing is how to attain high-precision location in the presence of interference.
B.Development trends in macro-micro motion control methods
The above discussion shows that M3P control is constantly developing from traditional control theory to modern control theory,and intelligent control methods are being used increasingly in the control process.The combination of modern control theory and intelligent control has gradually become an important tool for modeling and controlling nonlinear piezoelectric materials,and future research trends may be as follows.
(1) In the motion process of macro and micro motion platforms,there are both high-precision and high-acceleration characteristics.Due to their contradictions,a single control algorithm is difficul to achieve precise control.The design of the controller must be combined with the M3P dynamic model.At the same time,the control strategy should combine modern control theories,such as variable structure control,adaptive control,active disturbance rejection control,sliding fil and Sliding mode control,to achieve accurate control.
(2) The controller algorithm should be further optimized to reduce the dependence of the controller on the control object,thereby improving the adaptability of the controller to different driving components,and thus reducing the production cost of macro and micro motion platforms.
(3) The open-loop control strategy has the advantage of small device size,but its accuracy is low.The closed-loop control strategy has the advantage of high accuracy,but its large volume cannot be applied in industrial environments.Therefore,improving the accuracy of open-loop control strategies or reducing the volume of closed-loop control systems,combining the advantages of both,is the future development direction of M3P.
(4) With continuous theoretical and technological developments,research on control methods for macro-micro motion will involve many fields Therefore,one way to promote the development of macro-micro motion control is to develop a controller with strong robustness and strong anti-interference capability designed by combining different advanced theories from different disciplines.
V.CONCLUSIONS
Because of the rapid scientifi and technological developments in the 21st century,mechanical equipment is becoming increasingly miniaturized and precise.M3Ps play a crucial role in precision instrument processing,and high-precision positioning equipment is evolving toward downsizing and modularization.Herein,we reviewed a wide range of M3P literature,analyzed (i) the control strategies therein for macro-micro motion and(ii)current developments in macro-,micro-,and macro-micro motion control methods and other related topics,and assessed existing issues and development trends in M3P motion control by comparing pertinent research results.In short,the future of M3P motion control lies in combining current control methods and intelligent control,and using modern technologies from other industries to optimize macro-micro motion control merits further investigation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported financiall by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation,the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51705132),the Young Backbone Teacher Training Program in Henan University of Technology,the Education Department of Henan Province Natural Science Project (Grant No.21A460006),and the Natural Science Project of Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology(Grant No.222102220088).
AUTHOR DECLARATIONS
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict to disclose.
DATA AVAILABILITY
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
- 纳米技术与精密工程的其它文章
- Status of research on non-conventionaltechnology assisted single-point diamond turning
- Droplet microfluidic chip for precise monitoring of dynamic solution changes
- Characteristics of the pressure profile in the accelerator on the RF negative ion source at ASIPP
- Oxidation mechanism of high-volume fraction SiCp/Al composite under laser irradiationand subsequent machining
- An optical tweezer-based microdroplet imaging technology
- Effects of laser energy on the surface quality and properties of electrodeposited zinc-nickel-molybdenum coatings

