基于加权元学习的节点分类算法
万聪 王英


摘要: 受注意力机制和直推式学习方法的启发,提出一种基于加权元学习的节点分类算法. 首先利用欧氏距离计算元学习子任务间数据分布的差异; 然后利用子图的邻接矩阵计算捕获子任务间数据点的结构差异; 最后将二者转化为权重对元训练阶段更新元学习器过程进行加权,构建优化的元学习模型,解决了经典元学习算法在元训练阶段所有元训练子任务的损失是等权重更新元学习器参数的问题. 该算法在数据集Citeseer和Cora上的实验结果优于其他经典算法,证明了该算法在少样本节点分类任务上的有效性.
关键词: 元学习; 注意力机制; 节点分类; 直推式学习
中图分类号: TP39 文献标志码: A 文章编号: 1671-5489(2023)02-0331-07
Node Classification Algorithm Based on Weighted Meta-Learning
WAN Cong,WANG Ying
(College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China)
Abstract: Inspired by attention mechanism and transductive learning method,we proposed a node classification algorithm based on weighted m
eta-learning. Firstly,Euclidean distance was used to calculate the difference of data distribution between subtasks in meta-learning. Secondly,
adjacency matrices of subgraph was used to calculate and capture structural difference of data points between subtasks. Finally,the captured information above
between subtasks were converted into weights to weight the process of updating the meta-learner in the meta-training procedure,and an optimized m
eta-learning model was constructed to solve the problem that the loss of all meta-training subtasks in meta-training procedure of classical meta-learning alg
orithms was equal-weight to update the parameters of meta-learners. The experimental results of this algorithm on Citeseer and Cora datasets are superior to other classical algori
thms,which demonstrates the effectiveness of the algorithm on few-shot node classification task.
Keywords: meta-learning; attention mechanism; node classification; transductive learning
收稿日期: 2022-02-28.
第一作者简介: 万 聪(1997—),男,汉族,硕士研究生,从事元学习的研究,E-mail: 954011235@qq.com.
通信作者简介: 王 英(1982—),女,汉族,博士,教授,从事人工智能的研究,E-mail: wangying2010@jlu.edu.cn.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金(批准号: 61872161)、 吉林省科技发展规划项目(批准号: 2018101328JC)和吉林省发展与改革项目(批准号: 2019C053-8).
随着计算机算力和新算法的快速增加,尤其是对大数据的挖掘,使图深度学习得到了迅速发展. 但用户保护隐私意识的提升使数据变得有限,从而导致图深度学习面临两个问题: 1) 训练数据过少,模型的性能会急剧下降,并出现过拟合问题; 2) 人为标记大量数据费时费力. 通过元学习利用先验知识解决模型的过拟合问题,是解决少样本问题的有效方法,已广泛应用于图像分类[1-4]和语音识别[5-6]等领域.
目前主流的元学习方法是以MAML(model-agnostic meta-learning)[7]、 Reptile[8]、 FOMAML(first-order MAML)[9]为代表的经典算法,其中Meta-GNN(graph neural network,GNN)[10]和G-Meta(graph meta learning via local subgraphs)[11]是使用MAML完成節点分类任务的算法. 这类经典算法在面对几个少样本数据任务时,会先在大数据集的相关任务上进行预训练,然后进行微调[12-13]以适应这几个少样本数据的任务. 对应到元学习过程的描述中,在大数据集的相关任务上进行预训练的过程即是在元训练子任务上的元训练阶段,几个少样本数据任务即是元测试子任务. 上述经典算法在解决少样本数据任务的过拟合问题时取得了优异的成绩,但在上述算法的元训练阶段,多个元训练子任务的损失是等权重更新元学习器的参数,即多个元训练子任务通过元学习器传递给元测试子任务的信息是等权重的. 而在通常情况下,某个元训练子任务与元测试子任务越相关,则它传递给元测试子任务的信息越重要,因此上述经典算法仍有提升空间.
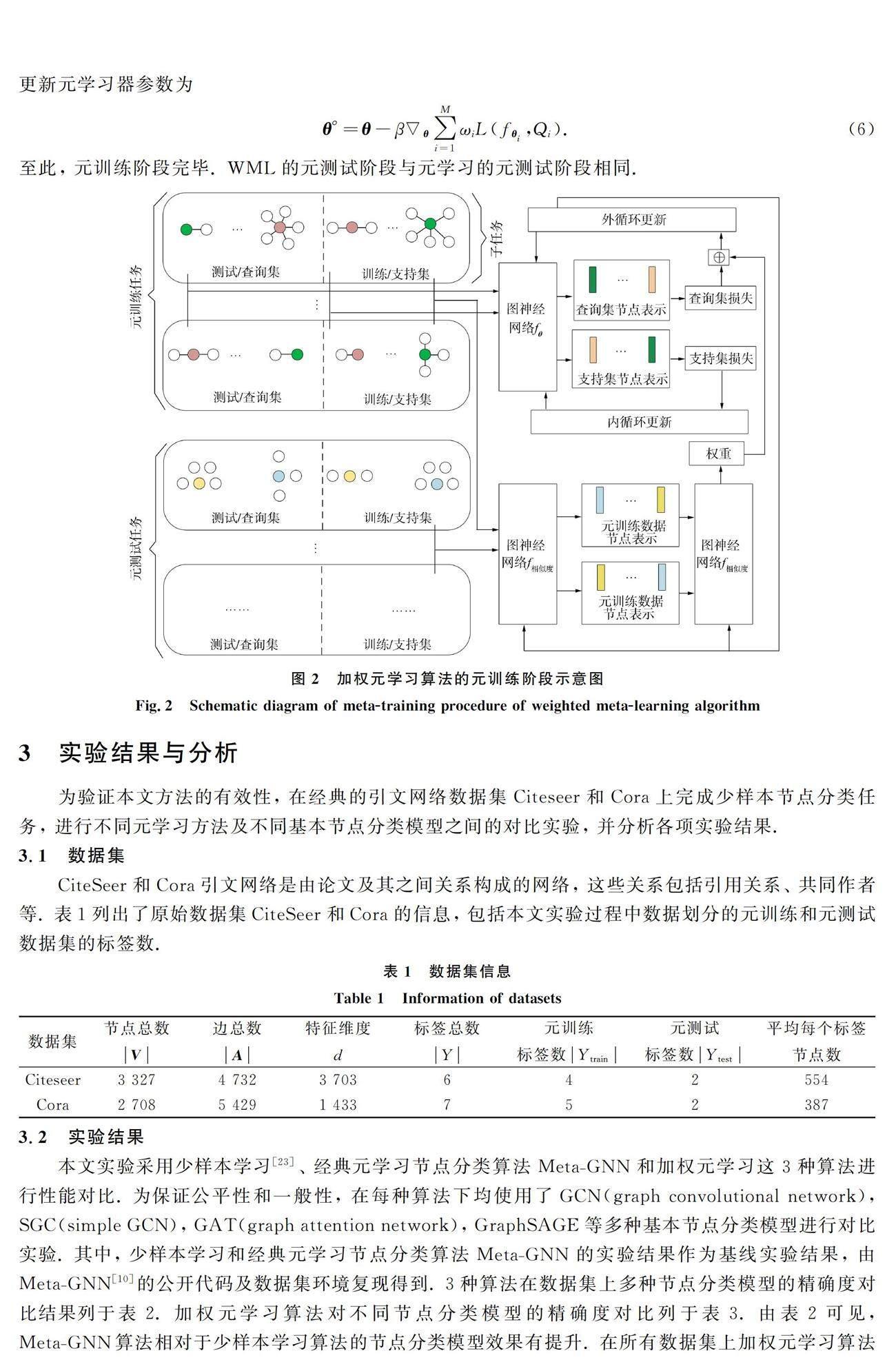
為解决上述问题,本文先利用欧氏距离[14]计算元学习子任务间样本特征的相似程度,捕获子任务间数据分布的差异程度,然后使用样本邻接矩阵计算子任务间样本子图结构的相似程度,捕获子任务间样本结构的差异程度,最后将这两种子任务间的信息转化为权重,融入元训练阶段,优化经典元学习算法. 实验结果表明,基于加权元学习的节点分类算法效果更好,分类更精确.
3 实验结果与分析
为验证本文方法的有效性,在经典的引文网络数据集Citeseer和Cora上完成少样本节点分类任务,进行不同元学习方法及不同基本节点分类模型之间的对比实验,并分析各项实验结果.
3.1 数据集
CiteSeer和Cora引文网络是由论文及其之间关系构成的网络,这些关系包括引用关系、 共同作者等. 表1列出了原始数据集CiteSeer和Cora的信息,包括本文实验过程中数据划分的元训练和元测试数据集的标签数.
3.2 实验结果
本文实验采用少样本学习[23]、 经典元学习节点分类算法Meta-GNN和加权元学习这3种算法进行性能对比. 为保证公平性和一般性,在每种算法下均使用了GCN(graph convolutional network),SGC(simple GCN),GAT(graph attention network),GraphSAGE等多种基本节点分类模型进行对比实验. 其中,少样本学习和经典元学习节点分类算法Meta-GNN的实验结果作为基线实验结果,由Meta-GNN[10]的公开代码及数据集环境复现得到. 3种算法在数据集上多种节点分类模型的精确度对比结果列于表2. 加权元学习算法对不同节点分类模型的精确度对比列于表3. 由表2可见,Meta-GNN算法相对于少样本学习算法的节点分类模型效果有提升. 在所有数据集上加权元学习算法中所有节点分类模型的效果都优于其他算法,在节点分类任务上性能更好. 由表3可见,加权元学习算法下,在所有节点分类模型中GAT模型的效果最好.
3.3 分离实验
为验证子任务间数据分布差异dist和子图结构差异struc的有效性进行分离实验. 实验结果如表4、 图3和图4所示. 其中WML-struc只使用struc计算权重; WML-dist只使用dist; 加权元学习二者均使用; MAML等权重,二者均不使用. 图3和图4中均使用GAT节点分类模型. 由表4及图3和图4可见,在所有的数据集上,MAML,WML-struc,WML-dist,WML的收敛精确度依次递增,表明dist和struc均能提升经典元学习算法的性能. 由于Citeseer和Cora都是一张图,数据划分后子图间结构差异较小,因此在本文实验中WML-dist比WML-struc效果好并不能证明dist比struc更重要.
综上所述,受注意力机制和直推式学习方法的启发,本文提出了一种基于加权元学习的节点分类方法,通过计算元学习子任务间数据分布差异和数据点的结构差异等子任务间信息,并转化为信息权重优化经典元学习元训练阶段的外循环更新过程,解决了经典元学习算法在元训练阶段外循环更新过程中等权重更新元学习器的问题.
参考文献
[1] CHENG G,LI R M,LANG C B,et al. Task-Wise Attenti
on Guided Part Complementary Learning for Few-Shot Image Classification [J]. Science China Information Sciences,2021,64(2): 1-14.
[2] LI X X,SUN Z,XUE J H,et al. A Concise Review of Recent Few-Shot Meta-Learning Methods [J]. Neurocomputing,2021,456: 463-468.
[3] 胡娟,杨厚群,杜欣然,等. 小样本学习在高分遥感影像分类与识别中的应用 [J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版),2022,34(3): 410-422.
(HU J,YANG H Q,DU X R,et al. Application of Small Sample Learning in Classification and Recognition of High Resolution Remote Sensing Images [J]. Journal of Chongqing
University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition),2022,34(3): 410-422.)
[4] 黄彭奇子,段晓君,黄文伟,等. 基于元学习的小样本图像非对称缺陷检测方法 [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版),2023,53(1): 234-240.
(HUANG P Q Z,DUAN X J,HUANG W W,et al. A Method of Detecting Unsymmetrical Defects in Small Sample Images Based on Meta-Learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University
(Engineering and Technology Edition),2023,53(1): 234-240.)
[5] HSU J Y,CHEN Y J,LEE H. Meta Learning for End-to-End Low-Resource Speech Re
cognition [C]//2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Piscataway,NJ: IEEE,2020: 7844-7848.
[6] WANG D S,YU J W,WU X X,et al. Improved End-to-End Dysarthric Speech Recognition via Meta-Learning Based Model Reinitialization
[C]//2021 12th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP). Piscataway,NJ: IEEE,2021: 1-5.
[7] FINN C,ABBEEL P,LEVINE S. Model-Agnostic Meta-Le
arning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks [C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. [S.l.]: PMLR,2017: 1126-1135.
[8] NICHOL A,SCHULMAN J. Reptile: A Scalable Metalearni
ng Algorithm [EB/OL]. (2018-05-08)[2021-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02999v1.
[9] NICHOL A,ACHIAM J,SCHULMAN J. On First-Order Meta
-Learning Algorithms [EB/OL]. (2018-05-08)[2021-12-15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02999.
[10] ZHOU F,CAO C T,ZHANG K P,et al. Meta-Gnn: On Few-Shot Node Classification in Graph Meta-Learning [C]//Proceedings of the 28th ACM
International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New York: ACM,2019: 2357-2360.
[11] HUANG K,ZITNIK M. Graph Meta Learning via Local Sub
graphs [J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2020,33: 5862-5874.
[12] CHUA K,LEI Q,LEE J D. How Fine-Tuning Allows for
Effective Meta-Learning [J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2021,34: 8871-8884.
[13] SHEN Z Q,LIU Z C,QIN J,et al. Partial Is Better Than All: Revisiting Fine-Tuning Strategy for Few-Shot Learning [C]//Proceedings o
f the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI,2021: 9594-9602.
[14] MORIN L,GILORMINI P,DERRIEN K. Generalized Euclid
ean Distances for Elasticity Tensors [J]. Journal of Elasticity,2020,138(2): 221-232.
[15] PIAO Y,LEE S,LEE D,et al. Sparse Structure Learn
ing via Graph Neural Networks for Inductive Document Classification [C]//Proceed
ings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI,2022: 11165-11173.
[16] DING K Z,LI J D,AGARWAL N,et al. Inductive Anomaly Det
ection on Attributed Networks [C]//Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Internatio
nal Conference on International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM,2021: 1288-1294.
[17] MAO Y Y,WANG N,ZHOU W G,et al. Joint Inductive and Tra
nsductive Learning for Video Object Segmentation [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway,NJ: IEEE,2021: 9670-9679.
[18] TAN Z,WANG S,DING K,et al. Transductive Linear Pro
bing: A Novel Framework for Few-Shot Node Classification [EB/OL]. (2022-11-11)[2022-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.05606.
[19] SHARMA K K,SEAL A. Spectral Embedded Generalized Mea
n Based k-Nearest Neighbors Clustering with S-Distance [J]. Expert Systems with Applications,2021,169: 114326-1-114326-10.
[20] DONG Y X,MA X J,FU T L. Electrical Load Forecasti
ng: A Deep Learning Approach Based on K-Nearest Neighbors [J]. Applied Soft Computing,2021,99: 106900-1-106900-15.
[21] KURANI A,DOSHI P,VAKHARIA A,et al. A Comprehensi
ve Comparative Study of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machines (SVM) on Stock Forecasting [J]. Annals of Data Science,2023,10: 183-208.
[22] ZOU Y,WU H J,GUO X Y,et al. MK-FSVM-SVDD: A Mu
ltiple Kernel-Based Fuzzy SVM Model for Predicting DNA-Binding Proteins via Support
Vector Data Description [J]. Current Bioinformatics,2021,16(2): 274-283.
[23] WANG Y Q,YAO Q M,KWOK J T,et al. Generalizing fr
om a Few Examples: A Survey on Few-Shot Learning [J]. ACM Computing Surveys (Csur),2020,53(3): 1-34.
(責任编辑: 韩 啸)

