基于Petri网基础标识的分散式故障诊断方法研究
葛 瑜,王晓静,朱光辉,3,王红艳
基于Petri网基础标识的分散式故障诊断方法研究
葛 瑜1,王晓静2,朱光辉1,3,王红艳1
(1.许昌学院电气与机械工程学院,河南 许昌 461000;2.河南轻工职业学院机电工程系,河南 郑州 450008;3.澳门科技大学系统工程研究所,澳门 999078)
电子信息技术的飞速发展催生了很多包含众多组件的复杂系统,故障诊断技术致力于及时、准确地检测这些系统中的故障,从而为快速恢复系统功能提供重要支撑。基于Petri网数学模型提出分散式的故障诊断方法,分别针对分散式架构中的诊断站点和协调者设计故障诊断算法,并提出相应的诊断协议。站点诊断算法基于Petri网基础标识和基础向量构建,避免穷举所有与观测序列一致的变迁序列,有效提高诊断效率。提出的分散式诊断方法比传统的集中式方法具有更高的计算效率和更好的稳定性。相对于其他已存在的分散式方法,该方法具有更小的Petri网结构假设限制和更广的适用范围。
Petri网;故障诊断;分散式结构;离散事件系统
0 引言
随着信息技术的飞速发展,涌现了很多组件繁多、功能复杂的电子系统,如高压输电系统、智能交通系统、分布式软件系统等,这些系统的复杂性增大了故障发生的风险。故障扰乱系统原定的运行流程,降低生产效率,甚至导致发生重大生产事故。故障诊断致力于及时、准确地识别故障的数量和位置,从而为快速恢复系统正常功能提供重要支撑。
为给故障诊断提供理论指导和定性分析,许多基于模型的故障诊断方法被提出[1-4]。最近几十年,基于离散事件系统(Discrete Event System)模型的故障诊断方法被广泛研究,形成了丰富的理论成果[5-14]。Petri网是一种典型的离散事件系统模型,具有清晰的图形化描述和准确的数学定义,许多现实系统可以抽象建模为Petri网模型。本文基于Petri网模型提出一种分散式的(decentralized)故障诊断方法。
文献[14]首次提出面向离散事件系统的故障诊断方法,使用自动机建模系统,并用不可观事件表示系统故障,通过构建诊断器判定故障的可诊断性并进行故障诊断。为了缓和自动机建模中的状态爆炸问题,许多文献基于Petri网模型研究故障诊断问题。
文献[15]通过监测与P不变量关联的库所中的托肯数从而诊断核力发电厂中的故障。文献[16]扩展文献[14]中的自动机方法,通过构建一个Petri网诊断器进行加标Petri网的在线故障诊断。文献[17-18]基于Petri网模型提出高效的电力系统故障诊断方法。为了进一步提高Petri网模型下的故障诊断效率,提出了许多基于基础标识或线性规划的方法。
文献[19]首次提出Petri网基础标识的概念,并在此基础上设计Petri网的故障诊断算法,避免了穷举与观测序列一致的所有变迁序列,提高了诊断效率。之后,许多基于基础标识的诊断方法被进一步研究和应用。文献[20-21]基于基础标识提出基础可达图的概念,基础可达图避免了穷举所有可达结点,有效提高诊断效率。文献[22-24]基于Petri网状态等式设计用于故障诊断的整数线性规划模型,通过为规划模型分配不同的目标函数计算故障诊断结果。
上述诊断方法均基于集中式结构进行设计,只有一台计算设备用于故障诊断,当系统规模较大时,此种结构不能保证诊断的及时性和有效性。为了缓和此种情况,提出一些基于分散式结构的故障诊断方法。文献[25]基于基础标识提出加标Petri网的分散式诊断方法,设计三种不同的诊断协议,并依次提出相应的诊断算法。文献[26]扩展文献[22]中的方法到分散式场景,分散式场景中的每个站点通过求解不同的整数线性规划问题计算诊断结果。
本文基于加标Petri网模型提出分散式的故障诊断方法,分散式结构包含多台具有相同计算能力的诊断站点,站点并行运行,各自计算其诊断结果,然后由协调者收集各站点的诊断数据并做出最终诊断。本文提出的分散式诊断方法利用多台诊断设备对系统进行并行诊断,保证了复杂系统故障诊断的及时性和有效性。主要贡献如下:
(1) 提出的分散式诊断方法相对于传统集中式方法[3,19-23]具有更高的计算效率和稳定性;
(2) 相比其他分散式方法[25-26],提出的方法不需要遵守特定的假设限制,扩大了方法的适用范围。
1 基本定义


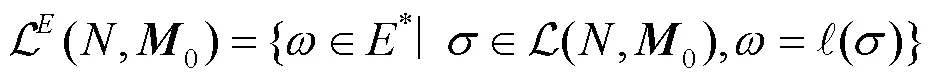
2 问题陈述
故障诊断依据观测到的系统输出推断系统中的故障数量和位置。依据不同的诊断架构,故障诊断分为集中式诊断和分散式诊断。集中式诊断使用单个诊断器,诊断算法更易设计和实施,但由于单个诊断器计算能力有限,不适用于大规模系统。分散式诊断包含多个计算能力相同的诊断器,并行计算诊断结果,有效提高大规模系统的诊断效率,保证诊断的及时性。
2.1 问题场景
本文基于加标Petri网数学模型,提出一种分散式的故障诊断方法,适用于如图1所示的应用场景。

图1 应用场景
图1所示的应用场景包含三部分主体,分别为:
(1) 系统。建模为加标Petri网数学模型,其输出表现为一串标签序列。
(2) 诊断站点1和2。分别可以观测到一部分系统输出(观测区域可能重叠),它们合作观测整个系统;每个站点具备较强的计算能力,依据观测数据计算各自的诊断结果,并发送诊断结果到协调者。
(3) 协调者。具备较弱的计算能力,通过诊断协议与诊断站点交互数据,并根据站点的局部诊断结果计算最终的全局诊断结果。
2.2 问题定义
在Petri网模型下,分散式诊断框架如图2所示,上述问题场景中的系统、诊断站点和协调者分别对应于下述(1)、(2)、(3)。
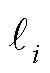

图2 分散式诊断框架
假设1 是Petri网故障诊断方法经常遵循的假设,主要作用为:(1) 防止系统运行在一个由不可观变迁组成的环里,从而导致站点永远观测不到系统输出;(2) 为Petri网在不可观子网中的可达性提供充要条件。用于表示站点诊断结果的诊断器定义如下所述。
3 问题求解
3.1 站点诊断算法

其对应的触发向量集定义为
最小触发向量集定义为

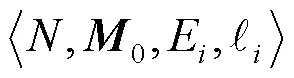
其中,

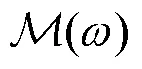
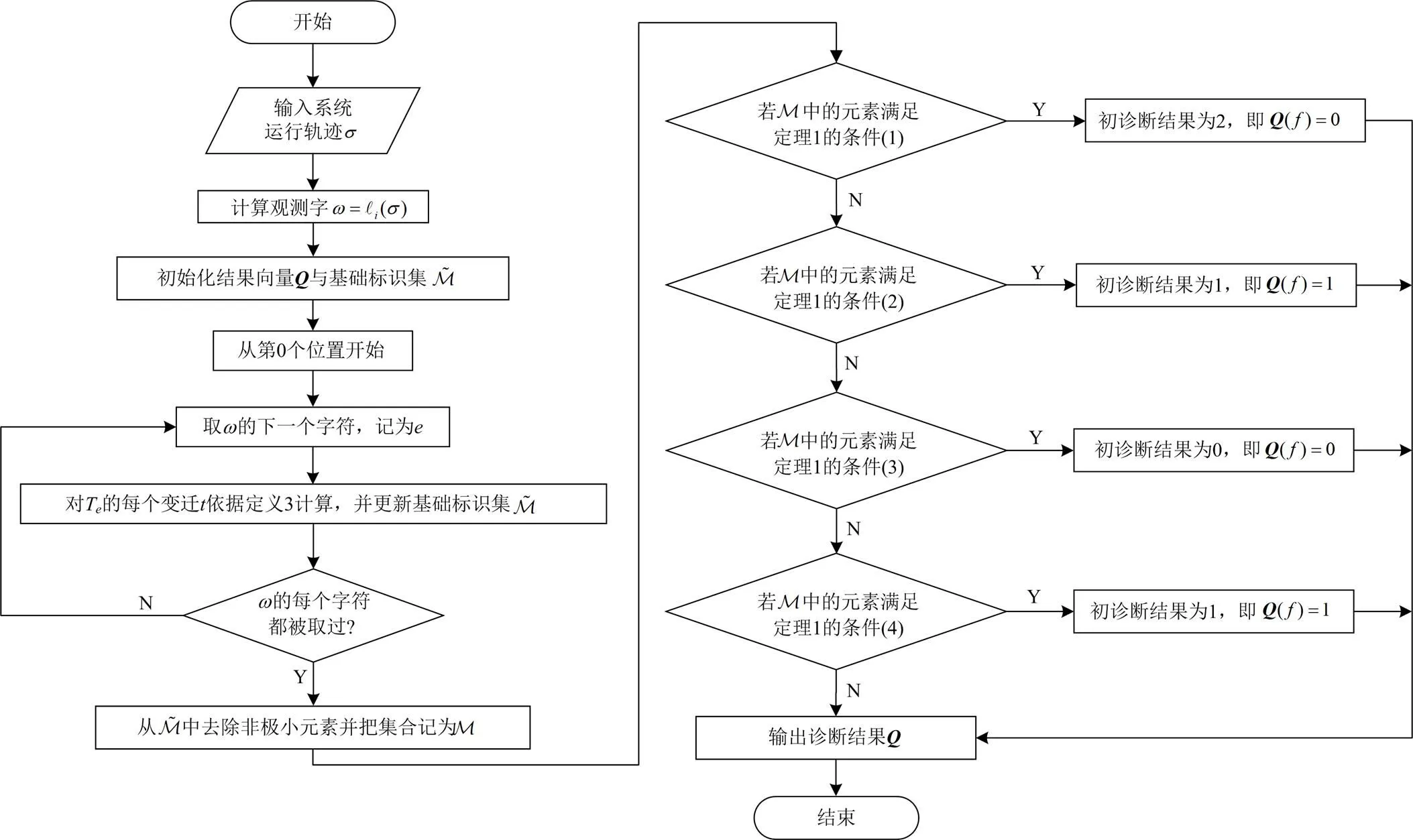
图3 站点诊断算法流程图
(4) 对所有变迁
3.2 诊断协议与协调者诊断算法
诊断协议约定了诊断站点和协调者之间的通信内容和格式,协调者依据诊断协议接收站点的局部诊断结果,计算全局诊断结果。诊断协议与协调者可由图4描述。
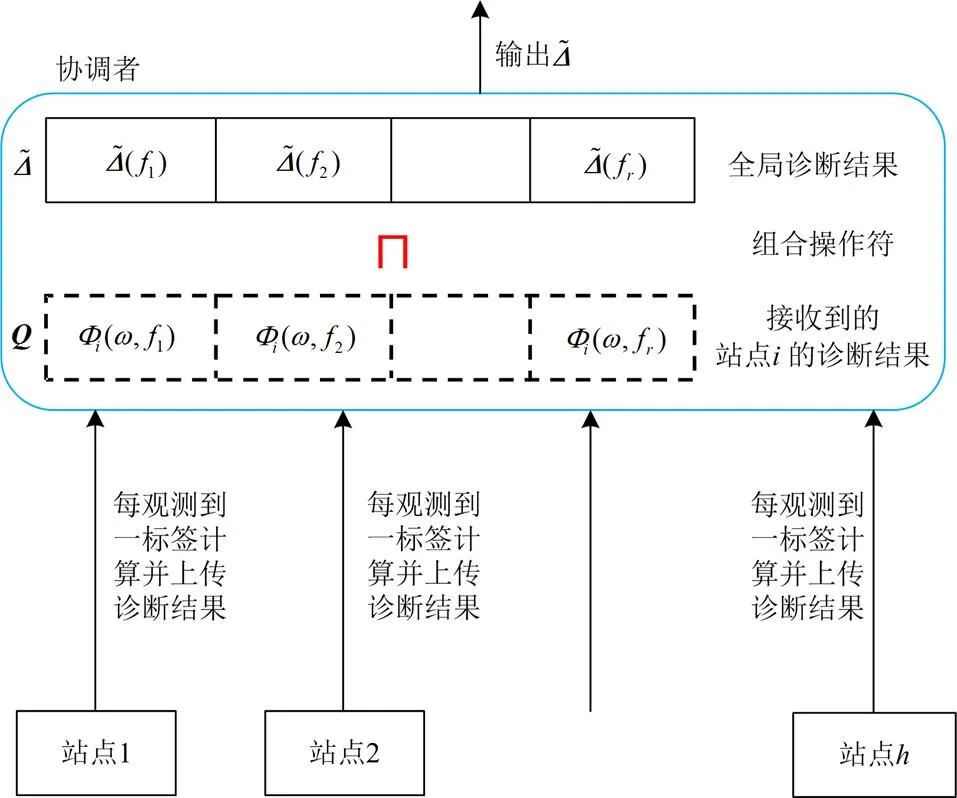
图4 诊断协议


表1 二元操作符
综上所述,协调者的诊断流程如算法2所示。
算法2:协调者诊断算法
(2) 等待直到接收到局部诊断结果
(6) 返回行(2)
4 集中式与分散式方法对比
单个诊断站点本质上以调用集中式诊断算法的方式工作,当多个诊断站点基于分散式架构诊断系统时,可从分散式诊断结果推理出集中式诊断结果。
5 仿真
图5所示的加标Petri网模拟了一个生产螺丝和螺母的生产线,共分成三部分:左边部分为原材料运输部分,右上部为螺丝生产线,右下部为螺母生产线。


图5 生产螺丝和螺母的产品线Petri网模型
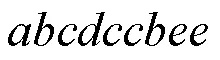
表2 仿真结果
Table 2 Simulation result
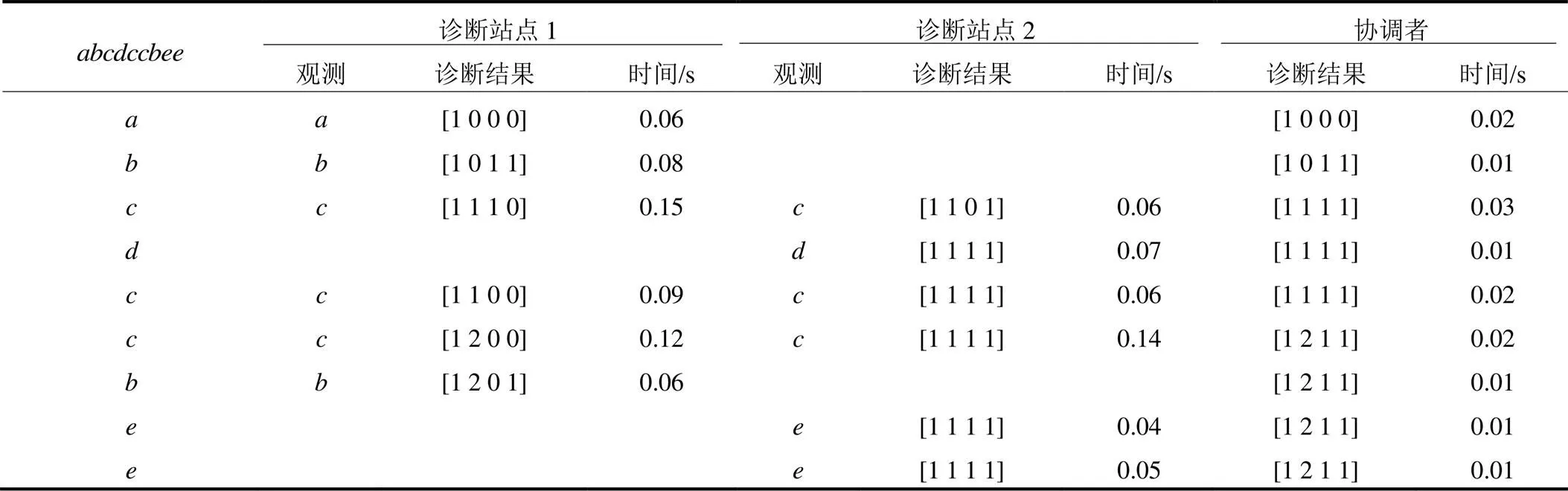

表3 不同方法运行时间对比(以s为单位)
更形象化的对比结果如图6所示,在相同观测标签数量情况下,文献[3]、文献[21]和文献[23]中方法的计算时间明显长于本文,并且随着观测标签数量的增多,它们的计算时间均呈现逐渐增长的趋势,而本文提出的方法的计算时间不会增长。
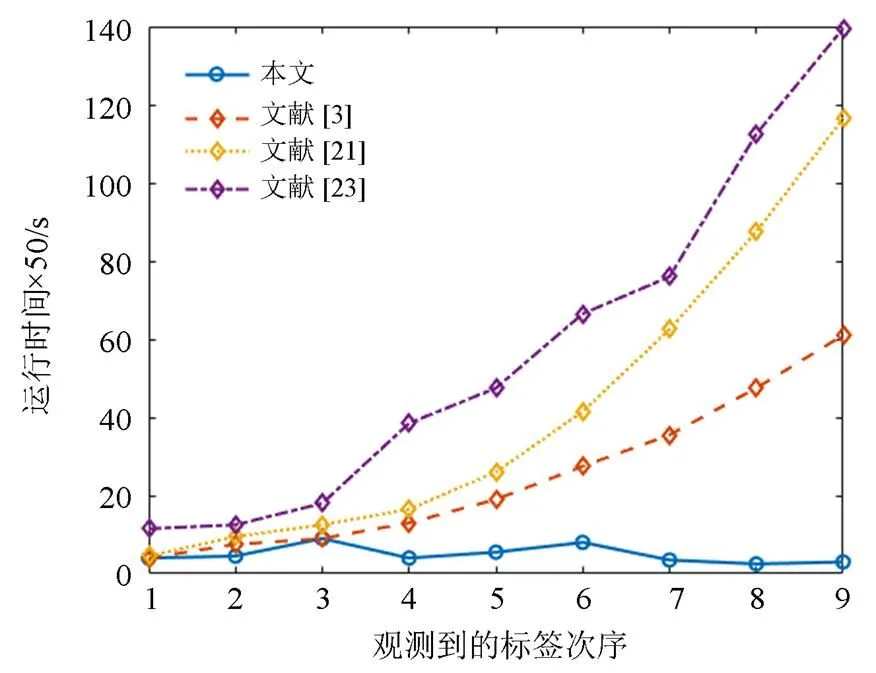
图6 不同方法运行时间对比
6 结语
基于加标Petri网数学模型提出分散式架构下的故障诊断方法,相对于传统的集中式诊断,分散式方法包含多个诊断站点,保证了诊断的及时性和有效性。文中提出的诊断协议比其他分散式协议具有更少的假设限制,扩展了诊断方法的适用范围。
[1] 魏勇, 崔俊彬, 刘辛彤, 等. 基于改进动态故障树的电力系统广域保护通信系统可靠性分析方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(23): 171-177.
WEI Yong, CUI Junbin, LIU Xintong, et al. A reliability analysis method power system wide area protection communication system based on an improved dynamic fault tree[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(23): 171-177.
[2] 何宁辉, 朱洪波, 李秀广, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络和假设检验的变压器故障诊断[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36(6): 20-27.
HE Ninghui, ZHU Hongbo, LI Xiuguang, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis based on Bayesian network and hypothesis testing[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2021, 36(6): 20-27.
[3] ZHU G, FENG L, LI Z, et al. An efficient fault diagnosis approach based on integer linear programming for labeled Petri nets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 66(5): 2393-2398.
[4] XIA Y, GOU B, XU Y. A new ensemble-based classifier for IGBT open-circuit fault diagnosis in three-phase PWM converter[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2018, 3(4): 364-372.
[5] CASSANDRAS C G, LAFORTUNE S. Introduction to discrete event systems[M]. New York: Springer, 2009.
[6] 李欣悦, 李凤婷, 尹纯亚, 等. 直流双极闭锁故障下送端系统暂态过电压计算方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(1): 1-18.
LI Xinyue, LI Fengting, YIN Chunya, et al. Transient overvoltage calculation method of HVDC sending-end system under DC bipolar blocking[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(1): 1-18.
[7] LAFORTUNE S, LIN F, HADJICOSTIS C N. On the history of diagnosability and opacity in discrete event systems[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2018, 45(1): 257-266.
[8] 孙湛冬, 焦娇, 李伟, 等. 基于改进蚁群算法的电力云数据中心任务调度策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50(2): 95-101.
SUN Zhandong, JIAO Jiao, LI Wei, et al. A task scheduling strategy for a power cloud data center based on an improved ant colony algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50(2): 95-101.
[9] 方如举, 葛瑜, 孙伟, 等. 基于WSNs的智能配电网通信数据传输带宽的优化分配策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(23): 88-95.
FANG Ruju, GE Yu, SUN Wei, et al. Transmission bandwidth optimal allocation strategy of communication data for a smart distribution grid based on WSNs[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(23): 88-95.
[10]胡列翔, 王蕾, 董明枫, 等. 基于改进时间约束Petri网的综合能源系统运行优化及可靠性评估[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53(10): 123-132, 139.
HU Liexiang, WANG Lei, DONG Mingfeng, et al. Operation optimization and reliability evaluation of integrated energy system based on improved timing constraint Petri net[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53(10): 123-132, 139.
[11]刘久富, 刘文良, 周建勇, 等. 改进的部分可观Petri网系统在线故障诊断器设计[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(7): 866-872.
LIU Jiufu, LIU Wenliang, ZHOU Jianyong, et al. An improved design of online fault diagnosis for partially observed Petri net systems[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(7): 866-872.
[12]阙蔡雄, 刘富春, 赵锐, 等. 基于Petri网诊断器的离散事件系统模式故障的在线诊断[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(7): 1621-1627.
QUE Caixiong, LIU Fuchun, ZHAO Rui, et al. On-line pattern diagnosis of discrete event systems with Petri net diagnosers[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(7): 1621-1627.
[13]杨雯, 刘元琦, 吴小忠, 等. 计及死区故障的3/2接线变电站的Petri网故障诊断方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45(20): 29-37.
YANG Wen, LIU Yuanqi, WU Xiaozhong, et al. A fault diagnosis method of 3/2 connection substation based on Petri nets with dead-zone fault taken into account[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45(20): 29-37.
[14]SAMPATH M, SENGUPTA R, LAFORTUNE S, et al. Diagnosability of discrete-event systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1995, 40(9): 1555-1575.
[15] PROCK J. A new technique for fault detection using Petri nets[J]. Automatica, 1991, 27(2): 239-245.
[16]GENC S, LAFORTUNE S. Distributed diagnosis of discrete-event systems using Petri nets[C] // Proceedings of International Conference on Application and Theory of Petri Nets, May 27, 2003: 316-336.
[17] 杨斐然, 于永进. 基于时间约束的分层模糊Petri网的配电网故障诊断[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(2): 99-106.
YANG Feiran, YU Yongjin. Fault diagnosis of distribution network based on time constrained hierarchical fuzzy Petri nets[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(2): 99-106.
[18] 陈伟伟, 吕盼, 纪凤坤, 等. 基于多维度检测与Petri网的变电站接地故障风险评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(23): 152-159.
CHEN Weiwei, LÜ Pan, JI Fengkun, et al. Risk assessment of substation grounding fault based on multidimensional detection and Petri net[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(23): 152-159.
[19]GIUA A, SEATZU C. Fault detection for discrete event systems using Petri nets with unobservable transitions[C] // Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, December 15, 2005, Seville, Spain: 6323-6328.
[20] CABASINO M P, GIUA A, SEATZU C. Fault detection for discrete event systems using Petri nets with unobservable transitions[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(9): 1531-1539.
[21] CABASINO M P, GIUA A, POCCI M, et al. Discrete event diagnosis using labeled Petri nets: an application to manufacturing systems[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2011, 19(9): 989-1001.
[22] DOTOLI M, FANTI M P, MANGINI A M, et al. On-line fault detection in discrete event systems by Petri nets and integer linear programming[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2665-2672.
[23]FANTI M P, MANGINI A M, UKOVICH W. Fault detection by labeled Petri nets in centralized and distributed approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2013, 10(2): 392-404.
[24]WANG Y, ZHU G, WU N. Fault diagnosis of backward conflict-free Petri nets by generalized markings[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8(2): 154871-154880.
[25] CABASINO M P, GIUA A, PAOLI A, et al. Decentralized diagnosis of discrete-event systems using labeled Petri nets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2013, 43(6): 1477-1485.
[26] CONG X, FANTI M P, MANGINI A M, et al. Decentralized diagnosis by Petri nets and integer linear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(10): 1689-1700.
Decentralized fault diagnosis of labeled Petri nets by basis markings
GE Yu1, WANG Xiaojing2, ZHU Guanghui1, 3, WANG Hongyan1
(1. School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Xuchang University, Xuchang 461000, China; 2. Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Henan Light Industry Vocational College, Zhengzhou 450008, China;3. Institute of Systems Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau 999078, China)
The rapid development of electronic information technology has spawned many complex systems which include a considerable number of components. Fault diagnosis aims to accurately detect faults in these systems in a timely manner, thus providing important support for the rapid recovery of system functions. This paper proposes a decentralized fault diagnosis approach based on Petri nets. Two algorithms for each diagnosis site and the coordinator in the decentralized architecture are provided. In addition, a diagnosis protocol used between diagnosis sites and the coordinator is developed. The diagnosis algorithm of each site is constructed based on Petri net basis markings and vectors. Thus, exhaustive enumeration of all transition sequences consistent with the observed label sequence is avoided, leading to better computational efficiency. The proposed decentralized diagnosis approach enjoys higher computational efficiency and better stability than the traditional centralized methods. Compared with existing approaches, that described here requires fewer assumptions on the structure of a net system and has broader applicability.
Petri net; fault diagnosis; decentralized structure; discrete event system
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220652
2022-05-05;
2021-07-04
葛 瑜(1973—),女,硕士,副教授,从事控制理论与应用方面的研究;E-mail:gy_73@163.com
王晓静(1976—),女,硕士,副教授,从事电气控制方面的研究;E-mail: oney139@163.com
朱光辉(1986—),男,通信作者,博士,讲师,从事离散事件系统理论与应用、信息安全方面的研究。E-mail: ghzhu@must.edu.mo
国家自然科学基金项目资助(62103349);河南省高等学校重点科研项目资助(21B470009)
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62103349).
(编辑 许 威)

