Influence of Tuina plus oxiracetam on serum inflammatory factors and oxidative stress in mild vascular dementia patients
GU Nan (谷楠), FAN Yuexian (范月先), ZHOU Ling (周玲), ZHANG Yan (张岩), BAI Weijie (白卫杰), LI Yanfeng (李延峰),YANG Liyun (杨丽芸), LI Jinlong (李进龙)
1 Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
2 Hebei Province Special Care Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
3 The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Cognitive Dysfunction; Dementia, Vascular; Activities of Daily Living; Oxidative Stress;Inflammatory Factors
Vascular dementia (VD), the second most common form of dementia only after Alzheimer disease,accounts for approximately 1/5 of the population affected by dementia[1]. Its main clinical symptoms include problems with cognition, language, memory,calculation, and judgment[2], burdening the patients,their families, and the whole society. To date, we are still unable to understand VD’s pathogenesis fully. Yet,some theories hold that numerous factors like blood-brain barrier destruction, cerebral hypoperfusion,cerebral hypometabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammatory reactions all play a role in the process[3-5].Oxiracetam is a brain development supplement commonly used to help with cognitive and memory dysfunctions[6]. Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage)therapy can influence the metabolic process, regulate immune function, modulate vascular endothelial function, and maintain normal blood circulation[7-9]. This study observed the efficacy of combining Tuina and oxiracetam to treat mild VD and explored the plausible mechanism of action. The results are presented as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria in Western medicine referred to the criteria for VD in the fourth edition ofDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders[10]; the diagnostic criteria in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)were in line with the criteria for dementia due to Qi and blood stagnation in theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[11]. Clinical symptoms and signs and tests like magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) were incorporated to make the final diagnosis.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Met the diagnostic criteria in both the TCM and Western medicine; aged 40 to 80 years old without gender preference; with a history of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease such as cerebral stroke and atherosclerosis but was conscious; multiple infarctions found by head CT or MRI examination; rated as mild by Hasegawa dementia scale; the patient or his family signed the informed consent form.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Mental disorders caused by psychosis or other reasons; coupled with brain diseases such as brain trauma, brain tumor, or encephalitis; and severe organic disorders involving the heart, lungs, liver, or kidney.
1.4 Dropout criteria
Those withdrew due to force majeure; those with poor compliance and unable to stick with the treatment protocol.
1.5 Statistical methods
The SPSS version 22.0 statistical analysis software was used for data analysis. Counting data were expressed as case numbers or percentages and analyzed using the Chi-square test. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s) if normal distribution and homogeneity of variance were satisfied, and thet-test was adopted. Differences were recognized as statistically significant whenP<0.05.
1.6 General data
A total of 96 mild VD patients were recruited who visited Hebei Province Special Care Hospital during February and November of 2019. They were divided into two groups using the random number table method, with 47 cases in the observation group and 49 in the control group. The general data were statistically equal between the two groups (P>0.05), suggesting comparability (Table 1).
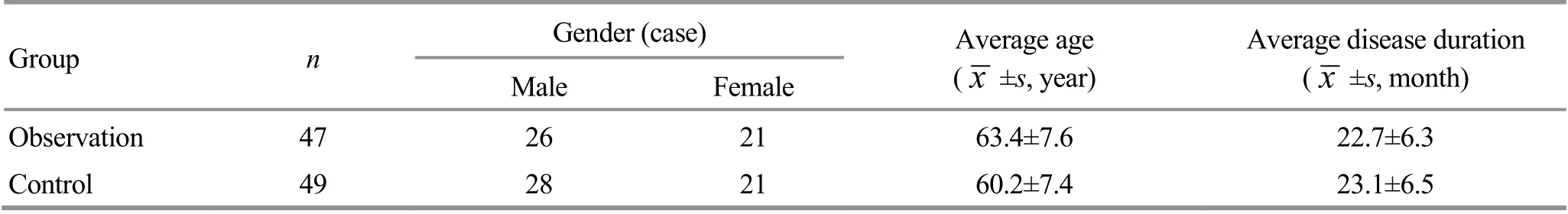
Table 1. Comparison of the clinical materials between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
The two groups of patients received the same routine treatments for blood pressure, glucose, lipids,anti-platelet agglutination, etc.
2.1 Observation group
2.1.1 Medications
Oral administration of oxiracetam [State Food and Drug Administration Approval No. WS-1006 (X-751)-2002-2014Z, Hunan Jianlang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,China], 800 mg each time for 30 d on end.
2.1.2 Tuina
Points: Xinshu (BL15), Feishu (BL13), Ganshu (BL18),Pishu (BL20), Shenshu (BL23), Taixi (KI3), Sanyinjiao(SP6), Zusanli (ST36), Guanyuan (CV4), Qihai (CV6),Zhongwan (CV12), Baihui (GV20), Yintang (GV29),Shenting (GV24), and Sishencong (EX-HN1).
Method: The patient took a prone position. The physician first Rou-Kneaded the back for 1-2 min till the back gave out heat. Then Dian-Digital An-Pressed Xinshu (BL15), Feishu (BL13), Ganshu (BL18), Pishu(BL20), and Shenshu (BL23) for 3-5 min (Figure 1a),followed by Nie-Pinching the spine 5-9 times to make the patient get a feeling of soreness, distension, or heat generation (Figure 1b). Afterward, the patient lay on his back. The physician Anrou-Pressed and Kneaded Taixi(KI3), Sanyinjiao (SP6), and Zusanli (ST36) for 2 min till the heat sensation reached Yongquan (KI1), (Figure 1c),then Rou-Kneaded the abdomen for 3-5 min and An-Pressed Guanyuan (CV4), Qihai (CV6), and Zhongwan (CV12), 2 min for each point, till the heat sensation penetrated inward (Figure 1d); conducted one-thumb Tui-Pushing at Baihui (GV20), Yintang(GV29), Shenting (GV24), and Sishencong (EX-HN1), 1-2 min for each point (Figure 1e-Figure 1g). Finally, the patient took a sitting position. The physician Na-Grasped Wujing 9 times (Figure 1h). The Tuina treatment was offered three times a week, lasting for 30 d.
2.2 Control group
The control group received the same medication treatment as the observation group, with the same dosage and duration.

Figure 1. Tuina manipulations
3 Observation of Outcomes
3.1 Outcome measures
3.1.1 Serum detection
Cubital fossa vein blood was drawn to collect serum from each patient before and after treatment. The contents of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were determined using kits.The glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) content was tested using the non-enzymatic reaction method. The test kits were provided by Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China. The double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the levels of interleukin (IL)-1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-6, and IL-8. The IL-1 test kit came from Lifkey BioMeditech, USA; the kits for TNF-α,IL-6, and IL-8 were from Diaclone, France. All the tests were performed by the Laboratory Department of Hebei Province Special Care Hospital.
3.1.2 Hemodynamic parameters
We adopted the Digi-Lite transcranial Doppler analyzer and Digi-Lite IP neural ultrasonographic system to observe the systolic velocity (Vs), mean velocity (Vm),and pulsatility index (PI) of the middle cerebral artery.The Digi-Lite transcranial Dopper analyzer was manufactured by RIMED, Israel.
3.1.3 Cognitive function rating
One same staff was in charge of evaluating the cognitive function using the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) with a maximum score of 30 points. The higher the score, the better the cognitive function. The activities of daily living (ADL) scale was used to assess patients’ daily living abilities. The maximum score is 100 points: 61-99 points for mild dysfunction but still being capable of managing basic everyday activities; 41-60 points for moderate dysfunction and in need of certain help for everyday life;21-40 points for severe dysfunction and being dependent on others for daily life; <20 points for entirely disabled and dependent on others.
3.2 Results
3.2.1 Comparison of the oxidative stress level
Before treatment, the two groups had no significant between-group differences in MDA, SOD, or GSH-Px(P>0.05). After treatment, the level of MDA dropped(P<0.05), and the levels of SOD and GSH-Px increased(P<0.05) in both groups. The level of MDA was significantly lower (P<0.05), and the levels of SOD and GSH-Px were notably higher in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). The details are shown in Table 2-Table 4.
3.2.2 Comparison of the inflammatory factor levels
Before treatment, there were no significant differences in IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, or IL-8 between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment, the levels of serum IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 dropped in both groups(P<0.05) and were notably lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). The data are detailed in Table 5-Table 8.
Table 2. Comparison of the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) before and after treatment ( ±s, μmol/L)
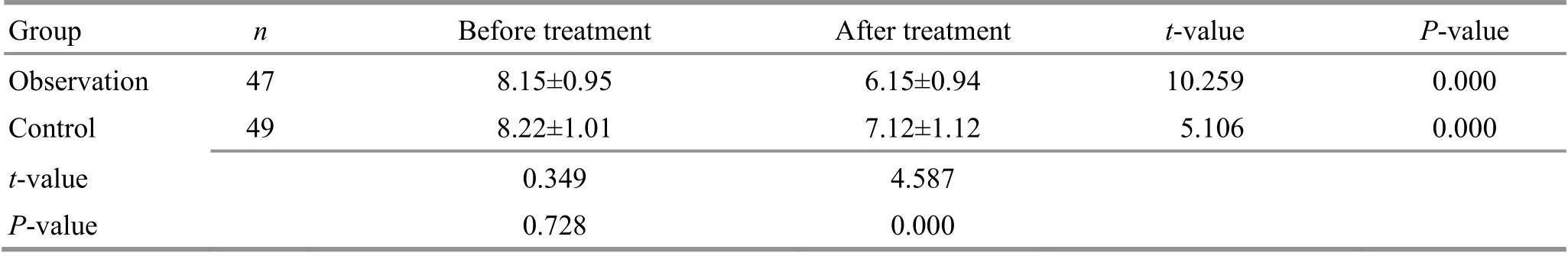
Table 2. Comparison of the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) before and after treatment ( ±s, μmol/L)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 8.15±0.95 6.15±0.94 10.259 0.000 Control 49 8.22±1.01 7.12±1.12 5.106 0.000 t-value 0.349 4.587 P-value 0.728 0.000
Table 3. Comparison of the level of superoxide dismutase (SOD) before and after treatment ( ±s U/mL)

Table 3. Comparison of the level of superoxide dismutase (SOD) before and after treatment ( ±s U/mL)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 72.46±8.78 87.76±11.40 -7.290 0.000 Control 49 73.20±9.53 81.42±10.45 5.106 0.000 t-value 0.395 -2.842 P-value 0.694 0.005
Table 4. Comparison of the level of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) before and after treatment ( ±s U/mL)

Table 4. Comparison of the level of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) before and after treatment ( ±s U/mL)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 77.67±9.75 93.45±12.46 -6.838 0.000 Control 49 76.50±9.68 84.98±11.23 -4.004 0.000 t-value -0.590 -3.501 P-value 0.557 0.001
Table 5. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-1 before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)

Table 5. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-1 before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 32.12±3.05 25.06±2.16 12.950 0.000 Control 49 32.06±3.02 28.76±3.14 5.302 0.000 t-value -0.097 6.690 P-value 0.923 0.000
Table 6. Comparison of the level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)

Table 6. Comparison of the level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 40.59±7.52 34.12±7.25 4.289 0.000 Control 49 40.74±7.49 38.67±7.35 1.381 0.171 t-value 0.098 3.052 P-value 0.922 0.003
Table 7. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-6 before and after the treatment ( ±s ng/L)

Table 7. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-6 before and after the treatment ( ±s ng/L)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 32.34±1.32 25.12±1.73 23.047 0.000 Control 49 31.63±1.34 29.25±1.36 8.725 0.000 t-value -2.614 13.033 P-value 0.010 0.000
Table 8. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-8 before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)
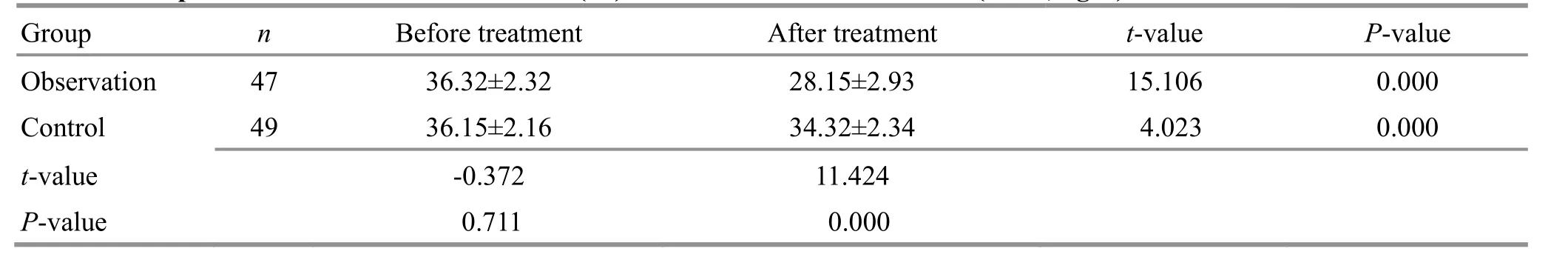
Table 8. Comparison of the level of interleukin (IL)-8 before and after treatment ( ±s ng/L)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 36.32±2.32 28.15±2.93 15.106 0.000 Control 49 36.15±2.16 34.32±2.34 4.023 0.000 t-value -0.372 11.424 P-value 0.711 0.000
3.2.3 Comparison of the hemodynamic levels
Before treatment, there were no significant differences in the hemodynamic parameters Vs, Vm, or PI between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment,the levels of Vs and Vm increased (P<0.05), and the level of PI decreased (P<0.05) in both groups; compared with the control group, the levels of Vs and Vm were higher (P<0.05), and the PI was lower (P<0.05) in the observation group. Please find details in Table 9-Table 11.
3.2.4 Comparison of the cognitive function and ADL scores
Before treatment, the MMSE and ADL scores were statistically equal between the two groups (P>0.05).After treatment, the MMSE and ADL scores rose significantly (P<0.05) in both groups and were higher in the observation group than in the control group(P<0.05). The details are shown in Table 12 and Table 13.
Table 9. Comparison of the systolic velocity (Vs) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s cm/s)

Table 9. Comparison of the systolic velocity (Vs) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s cm/s)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 80.16±8.67 97.45±9.78 -9.068 0.000 Control 49 80.24±8.14 89.25±8.94 -5.216 0.000 t-value 0.047 -4.291 P-value 0.963 0.000
Table 10. Comparison of the mean velocity (Vm) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s cm/s)

Table 10. Comparison of the mean velocity (Vm) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s cm/s)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 48.46±6.03 67.21±6.32 -14.716 0.000 Control 49 48.76±5.67 56.49±6.43 -6.312 0.000 t-value 0.251 -8.234 P-value 0.802 0.000
Table 11. Comparison of the pulsatility index (PI) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s)
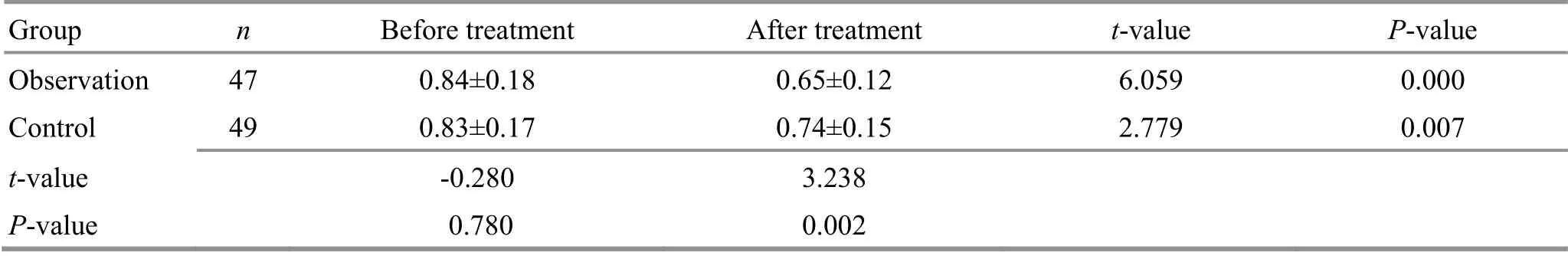
Table 11. Comparison of the pulsatility index (PI) of the middle cerebral artery before and after treatment ( ±s)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 0.84±0.18 0.65±0.12 6.059 0.000 Control 49 0.83±0.17 0.74±0.15 2.779 0.007 t-value -0.280 3.238 P-value 0.780 0.002
Table 12. Comparison of the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) score before and after treatment ( ±s point)

Table 12. Comparison of the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) score before and after treatment ( ±s point)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 14.62±2.15 20.17±3.74 -8.820 0.000 Control 49 14.57±2.15 16.43±3.22 -3.363 0.001 t-value -0.114 -5.258 P-value 0.910 0.000
Table 13. Comparison of the activities of daily living (ADL) score before and after treatment ( ±s point)

Table 13. Comparison of the activities of daily living (ADL) score before and after treatment ( ±s point)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 47 35.23±5.63 68.93±6.23 -27.514 0.000 Control 49 35.54±5.05 59.56±5.76 -21.950 0.000 t -value 0.287 -7.656 P-value 0.775 0.000
4 Discussion
VD is a type of cognitive dysfunction due to cerebral ischemia and hypoxia, mainly affecting the elderly. As the aging problem is getting more serious, VD, a common geriatric disease, urgently requires more effective treatments. TCM classifies VD under“dementia”, “forgetfulness”, or “dullness”, holding that its pathogenesis mechanism is excess in the superficial and deficiency in the root. More specifically, Yang deficiency and Zang-Fu organs deficiency are the root cause, and blood stasis is the superficial cause. Thus,the superficial and the root causes must be treated simultaneously.
Points-based Tuina therapy is a practical approach for VD[12]. Our study mainly treated points from Yang meridians in the Tuina treatment protocol, in which strengthening and protecting the Yuan-Primordial Qi was also stressed[13]. According to this protocol, the physician began treatment by Anrou-Pressing and Kneading the back to enhance the therapeutic efficacy.Research shows that applying Tuina manipulations to the back can strengthen immune function[14]. Dian-Digital An-Pressing the Back-Shu Points of the five Zang organs, Nie-Pinching the spine, and Rou-Kneading Guanyuan (CV4), Qihai (CV6), and Zhongwan (CV12) can regulate and unblock the Zang-Fu organs and the Conception and Governor Vessels[15]. Spleen and stomach are the sources of acquired constitution and generation of Qi and blood. Treating the Back-Shu Points of the five Zang organs together with Zusanli(ST36) and Zhongwan (CV12) can reinforce the spleen,harmonize the stomach, support the healthy Qi, and consolidate the foundation[16-17]. Rou-Kneading Guanyuan (CV4), Qihai (CV6), Taixi (KI6), and Sanyinjiao(SP6) can reinforce Qi to consolidate the foundation and strengthen the kidney to reinforce the essence.Na-Grasping Wujing and One-thumb Tui-Pushing Baihui(GV20), Yintang (GV29), Shenting (GV24), and Sishencong (EX-HN1) can improve Qi-blood circulation in the brain[18-19]. So, this treatment protocol can support the healthy Qi, consolidate the foundation,activate blood flow, unblock meridians, and treat both the superficial and the root.
VD is a progressive disease associated with cerebral hypoperfusion. In addition, vascular risk, diabetes, and hypertension make middle-aged adults more likely to develop VD[20-22]. The brain is especially vulnerable to oxidation, and neurons are sensitive to oxidative injuries[23]. MDA is a type of lipid peroxide produced in the metabolism of oxygen free radicals. The crosslinking polymerization of MDA and lipoproteins will destroy the synthesis of proteins, affecting cognitive function[24].
SOD and GSH-Px can eliminate oxygen free radicals and protect neurons, playing a significant role in maintaining the dynamic balance of oxygen free radicals.Cerebral ischemic and reperfusion injuries evoke the endothelial cells and the surrounding neurons, trigger inflammatory cascades, and release a large number of inflammatory factors, resulting in the accumulation of inflammatory factors and metabolites in the injured brain tissues, re-blocking the involved brain vessels, and restricting backflow. White blood cells can further release proteinases that directly damage brain tissue[25].TNF-α and IL-6 are proinflammatory factors that activate macrophages, lymphocytes, immunocytes, and structural cells (including astroglia and neurons) to cope with infection or injuries. These two factors may initiate inflammatory cascades and cause secondary brain injuries[26]. At the same time, they can boost neural cells to produce inducible nitric oxide synthase and damage neurons through nitro-oxidative stress[27-28]. Moreover,they can also directly injure cholinergic cells and induce cholinergic dysfunction[29], consequently leading to VD.TNF-α can cause cerebral microvascular endothelial dysfunction and disrupt the blood-brain barrier, leading to VD. IL-1 and IL-8 mainly participate in immune responses to induce inflammatory reactions and subsequent cerebral ischemia and hypoxia, resulting in VD. Besides, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes,and atherosclerosis all play a role in the development of VD[30]. Therefore, the main principle in treating VD should be activating blood flow to resolve stasis,supplement Qi and awaken the brain[31].
In this study, the serum MDA content dropped, the SOD and GSH-Px contents elevated, and the levels of serum IL-1, TNF-α, and IL-8 decreased after treatment in both groups. The results demonstrate that Tuina plus oxiracetam or oxiracetam alone can reduce stress-induced injuries and inflammatory reactions in VD patients. Besides, the Vs and Vm increased, the PI decreased, and the MMSE and ADL scores increased after treatment in both groups, and more significant changes were found in the observation group.Therefore, it is indicated that points-based Tuina therapy plus oxiracetam can improve cerebral blood supply, daily living abilities, and cognitive function in VD patients. Its efficacy wins out that of oxiracetam alone.The results also suggest that the mechanism of Tuina therapy in treating VD may be associated with the reduction of oxidative stress-induced injuries and inflammatory reactions via up-regulating the peripheral blood SOD, GSH-Px levels, and down-regulating the MDA, IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 levels.
In summary, points-based Tuina therapy plus oral oxiracetam can improve cerebral blood supply, every living ability, and cognitive function in mild VD patients.Furthermore, its mechanism is plausibly related to reducing oxidative stress-induced injuries and inflammatory reactions. Nevertheless, the mechanism needs to be further detailed using large-scale clinical trials.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine(河北省中医药管理局项目, No. 2017002).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 29 July 2020/Accepted: 12 January 2021
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年4期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年4期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Study on the mechanism of moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Study on the relationship between relieving energy crisis in myofascial trigger points with An-Pressing manipulation and AMPK/PGC-1α pathway activation
- Regulatory effect of acupuncture on electrical activity level of optic cortex in amblyopia model rats
- Effects of acupuncture on nutritional status in patients in a persistent vegetative state:a prospective randomized controlled study
- Clinical observation of acupuncture plus acupoint sticking therapy for insomnia and its influence on subjective and objective sleep indicators
- Clinical observation of warm needling moxibustion plus lumbar traction for lumbar disc herniation
