Milligan-Morgan 手术联合痔动脉结扎术在Ⅲ ~ Ⅳ度混合痔治疗中的应用
李斌 李轩 张琼 赵文鹏
[摘要]目的觀察 Milligan-Morgan 手术联合痔动脉结扎术在治疗Ⅲ~Ⅳ度混合痔中的临床疗效。方法纳入2020年1—10月在武警甘肃省总队医院外二科收治的56例Ⅲ~Ⅳ度混合痔患者作为研究对象,将患者随机分为观察组(n=28)和对照组(n=28),观察组采用 Milligan-Morgan 手术联合痔动脉结扎术,对照组采用传统 Milligan-Morgan 手术。比较两组术中指标、术后并发症及复发情况。结果两组患者手术时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05),观察组术中出血量少于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05);两组在术后第1、3、7天疼痛评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05);观察组术后出血及肛缘水肿发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05);两组患者术后尿潴留及1年复发率比较差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。结论采用 Milligan-Morgan 手术联合痔动脉结扎术治疗Ⅲ~Ⅳ混合痔与传统 Milligan-Morgan 手术相比,能显著减少术中出血量,减少术后出血及肛缘水肿发生率;联合术式并不增加手术时间、患者术后疼痛程度及尿潴留发生率。
[关键词]混合痔;痔切除术; Milligan-Morgan;痔动脉结扎术
[中图分类号] R657.1+8 [文献标识码] A [文章编号]2095-0616(2022)08-0133-05
Milligan-Morgan procedure combined with hemorrhoidal artery ligation in the treatment of Ⅲ-Ⅳ degree mixed hemorrhoids
LI Bin LI Xuan ZHANG Qiong1 ZHAO Wenpeng1
1. Department of Surgery Ⅱ , Gansu Corps Hospital of the Chinese Armed Police Forces, Gansu, Lanzhou 730050, China;2. Department of Internal Medicine Ⅰ , Gansu Corps Hospital of the Chinese Armed Police Forces, Gansu, Lanzhou 730050, China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of Milligan-Morgan procedure combined with hemorrhoidal artery ligation in the treatment of Ⅲ-Ⅳ degree mixed hemorrhoids. Methods A total of 56 patients with Ⅲ-Ⅳ degree mixed hemorrhoids admitted to the Department of Surgery Ⅱ in the Gansu Provincial Corps Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces from January 2020 to October 2020 were included as study subjects. These patients were randomly divided into the observation group (n=28) and the control group (n=28). The observation group was treated with Milligan-Morgan procedure combined with hemorrhoidal artery ligation, while the control group was treated with traditional Milligan-Morgan procedure only. The two groups were compared in terms of intraoperative indicators, postoperative complications and relapse. Results There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in surgical duration (P >0.05). The intraoperative bleeding volume in the observation group was less than that in the control group, with statistically significant difference (P <0.05). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the pain level on the first, third and seventh postoperative days (P >0.05). The incidences of postoperative bleeding and anal edge edema in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P <0.05). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of the incidence of postoperative urinary retention and the 1-year relapse rate (P >0.05). Conclusion Compared with the traditional Milligan-Morgan procedure, the combination of Milligan-Morgan procedure and hemorrhoidal artery ligation can more significantly reduce intraoperative bleeding volume and the incidences of postoperative bleeding and anal edge edema in the treatment of Ⅲ-Ⅳ mixed hemorrhoids. In addition, such a combination does not increase the surgical duration as well as the pain level and the incidence of urinary retention after surgery.
[Key words] Mixed hemorrhoids; Hemorrhoidectomy; Milligan-Morgan; Hemorrhoidal artery ligation
痔是肛肠科最常见的良性疾病,根据中国成人常见肛肠疾病流行病学调查结果显示,我国痔病的患病率为49.14%,患病人数占所有肛肠疾病人数的98.09%[1]。Ⅲ~Ⅳ度内痔大多为混合痔,常伴有出血、疼痛、肛内肿物脱出、肛门坠胀感[2]。对患者日常生活及工作影响较大,保守治疗常常效果不佳。根据2018年美国结直肠外科医师学会痔病管理临床实践指南[3],非手术治疗失败的患者和Ⅲ/Ⅳ级痔患者推荐手术治疗。为了达到更好的治疗效果,减少术后并发症,本研究在行 Milligan-Morgan 手术(Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy, MMH)时先在直视下行痔动脉结扎术(hemorrhoid artery ligation, HAL),现将这种联合术式与单纯行 Milligan-Morgan 手术患者进行比较分析,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
纳入2020年1—10月在武警甘肃省总队医院外二科收治的56例Ⅲ~Ⅳ混合痔患者作为研究对象,将患者随机分为观察组(n=28)和对照组( n=28)。观察组男12例,女16例;年龄20~68岁,平均(37.5±11.4)岁;病程6个月至10年,平均(5.1±1.6)年;痔分度:Ⅲ度16例,Ⅳ度 12例。对照组男15例,女13例;年龄21~70岁,平均(42.1±12.3)岁;病程7个月至12年,平均(4.8±1.7)年;痔分度:Ⅲ度18例,Ⅳ度10例。两组性别、年龄、病程及痔分度比较,差异无统计学意义( P >0.05),具有可比性。本研究经医院医学伦理委员会批准。患者知晓本研究内容并签署知情同意书。
纳入标准:①符合2010年修订的《痔诊断和治疗指南》[4];②年龄18~70岁;③临床资料完整。排除标准:①伴有精神类疾病;②伴有活动性炎症肠病及直肠肛管恶性肿瘤;③合并重要脏器功能不全或凝血功能障碍;④妊娠或备孕者;⑤有严重腹泻或便秘者;⑥既往有肛门直肠手术史。
1.2 方法
术前20∶00后禁食,肠道准备。麻醉为腰麻。采用截石位,在臀部下放软垫适当抬高。
对照组:常规碘伏消毒术区,铺无菌巾单。适度轻柔扩肛2~4指。观察痔核大小及分布。初步规划要保留的皮桥部位、数目及切口的位置。血管钳夹痔核基底部向外牵拉,在痔核顶部钳夹第2把血管钳。牵拉两把血管钳充分暴露痔核,将基底部血管钳向上提起,“V”型切开临近肛缘皮肤,将痔与组织其下的肛门括约肌逐步分離,切除痔块至齿状线上方内痔基底部,用2-0可吸收线缝扎并分离其顶端,避免将肛门内括约肌缝入。切除大部分痔核,其余残端还纳肛内。同样的方法切除其余痔核,各个切口之间保留足够皮桥,创面彻底止血。油纱包绕橡胶管做成排气管塞入肛管。外固定敷料。
观察组:在行外剥内扎之前,通过半圆形肛门镜观察较大母痔,在齿状线上方约2~4 cm 处用食指扪及较明显痔动脉搏动,用2-0可吸收缝线“8”字缝扎痔动脉,缝合深度为黏膜下层。其余步骤同对照组。
术后处理:两组术后处理相同。嘱患者术后2 h 禁食禁饮,常规予以抗生素静脉滴注1~2 d 预防感染。每日换药1次,观察伤口。用太宁栓(西安杨森制药有限公司,国药准字 H20083150)、马应龙痔疮栓(马应龙药业集团股份有限公司,国药准字 Z44021461)纳肛。术后第2日开始坐浴,3次/d,便后加1次。
1.3 观察指标及评价标准
(1)术中指标。①手术时间:自消毒铺巾完毕开始至肛周外固定敷料结束。②术中出血量:采用纱布称重法进行估算。(2)术后并发症。①术后疼痛,疼痛程度依据视觉模拟评分法(VAS)[5]进行评价:0分为无痛;1~3分为轻微疼痛,不需处理;4~6分为中度疼痛,尚能忍受,需口服镇痛药物;7~10分为重度疼痛,疼痛剧烈,影响休息,需肌内注射止痛药物。分别评价术后第1、3、7天术区疼痛程度。②术后出血。③术后肛缘水肿。④术后尿潴留。
(3)术后复发率:术后随访1年,记录复发情况。
1.4 统计学方法
使用 SPSS 19.0统计学软件进行数据处理,计量资料用均数±标准差( x ± s)表示,采用 t 检验,计数资料用[n (%)]表示,采用χ2检验, P <0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
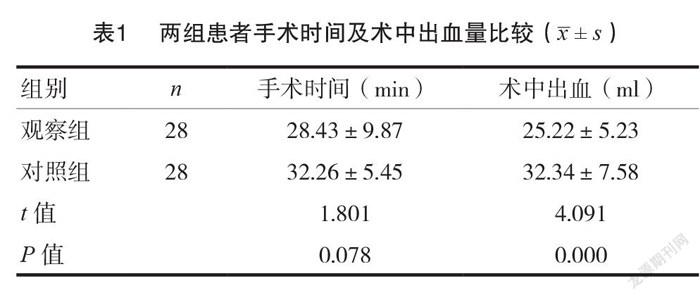
2.1 两组患者手术时间及术中出血量比较
两组患者手术时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。观察组术中出血量低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05)。见表1。
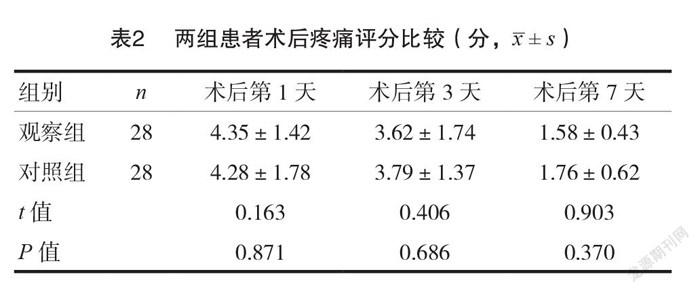
2.2 两组患者术后疼痛评分比较
两组术后第1、3、7天疼痛评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05),见表2。
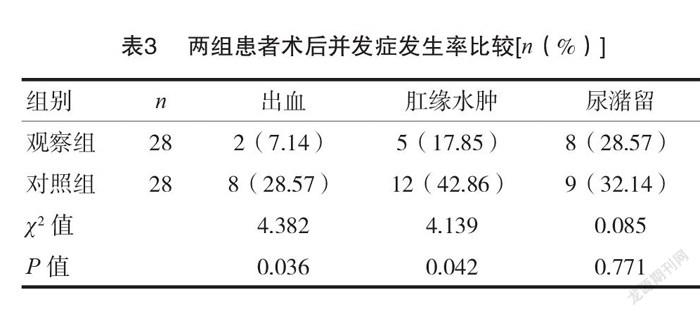
2.3 两组患者术后并发症发生率比较
观察组的术后出血、肛缘水肿发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05)。两组在术后尿潴留发生率差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。见表3。
2.4 两组患者术后复发率比较
两组术后随访1年,各有1例失访病例,观察组无复发,对照组有1例复发。两组复发率比较差异无统计学意义(P=1.000)。
3讨论
Milligan-Morgan 手术是目前应用最广泛的 Ⅲ~Ⅳ度痔治疗手术方式,疗效确切、复发率低,但出血量多、疼痛明显、恢复时间长[6]。目前 Milligan- Morgan 手术仍被认为是Ⅲ或Ⅳ级混合痔手术的“金标准”[7]。痔动脉结扎术在1995年由 Morinaga 提出[8]。相比传统手术,痔动脉结扎术后患者疼痛轻、出血少、恢复快,但复发率高。Giordano 等[9]研究发现痔动脉结扎术后1年以上痔的脱垂复发率为10.8%,出血复发率为9.7%,Ⅳ期痔的复发率更高。Ahmad 等[10] 认为痔动脉结扎术在Ⅰ~Ⅱ度内痔治疗效果更好。单纯痔动脉结扎术仅对出血性痔疗效较好,对脱垂痔疗效欠佳,痔核萎缩仅是血管断流后所产生的病理性改变[11-12]。痔动脉结扎术多使用多普勒探头定位并结扎痔动脉。也可以不借助多普勒探头仅通过手指触诊结扎痔动脉。多篇文献报告直视下痔动脉结扎术同多普勒引导下痔动脉结扎术相比,在症状改善方面以及疼痛、出血、脱垂等并发症方面无显著差异,且对设备要求低,操作相对简单[10,13-14]。
Milligan-Morgan 手术需要剥离痔核,开放创面,同时存在多个切口,术中出血量较多。本研究在行 Milligan-Morgan 手术时先在直视下行痔动脉结扎术,临床观察发现,能明显减少术中出血,同对照组相比差异有统计学意义(P <0.05)。而观察组同对照组相比并没有明显增加手术时间,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。混合痔术后出血多为少量渗血,只需按压止血即可,如出现喷射状出血,按压无法止血,则需再次探查并缝合结扎出血点。Haksal等[15]报告206位行 Milligan-Morgan 手术患者在术后前7天有24例有出血症状,其中2例再次行手术止血。本研究中观察组有2例有术后出血症状,低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05)。两组中只有对照组有1例于术后第8天出现明显喷射状出血,再次手术探查并缝扎出血点。
本研究发现观察组与对照组在术后第1、3、7天疼痛评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。观察组虽然联合两种术式,并没有增加患者术后疼痛。 Medina-Gallardo 等[16]的研究认为 Milligan-Morgan 术后约22.2%的病人需要服用阿片类镇痛药,而术后阿片类镇痛药的使用与术中切除痔核的数量无关。混合痔术后疼痛管理目前仍没有统一标准,应该根据患者的情况制订个体化方案,以减少患者痛苦,提高术后满意度。
肛缘水肿是混合痔术后常见并发症,董文双等[17]研究显示,混合痔外剥内扎术后肛缘水肿的发生率为38.58%,也有文献报告混合痔术后肛缘水肿发生率高达65.71%[18]。本研究中观察组发生率为17.8%,对照组发生率为42.8%。观察组肛缘水肿发生率明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05),而2组中发生重度肛缘水肿的病例均为环状混合痔,说明术式并不是术后肛缘水肿的唯一影响因素。文献报道环状混合痔、手术操作不当、术后排便异常(便秘或腹泻)、术后疼痛情况等4个因素是 Milligan- Morgan 手术后肛缘水肿的独立危险因素[17,19]。
尿潴留也是混合痔术后常见并发症,本研究中两组尿潴留发生率差异无统计学意义(P >0.05),共有17例患者(30.36%)发生尿潴留。文献报道男性患者在术后发生尿潴留比女性更常见,超过三分之一的痔切除术患者术后出现尿潴留,而切除痔核数量越多,发生尿潴留的概率越大[20]。
两组患者均术后随访1年,观察组无复发,对照组有1例复发,两组患者复发率差异无统计学意义( P >0.05)。而赵文召等[21]在 Milligan-Morgan 术中进行痔动脉结扎,术后随访1~2年,观察组无复发,对照组复发率为15.6%。提示Milligan—Morgan术中进行痔动脉结扎能降低术后复发率。痔的复发和痔切除时需保留足够的皮桥而保留下来部分痔静脉有关,随着时间延长,压力增加以及侧支循环形成,继而发展成有症状的痔1221。痔动脉结扎术通过结扎阻断痔供血,从而使痔组织萎缩。当痔动脉结扎术联合Milligan—Morgan手术时,在尽量切除痔核的基础上结扎痔动脉,使少量残留痔静脉逐渐萎缩,降低术后复发率。
本研究的不足包括样本量较少、术后随访时间较短;入组患者手术并非同一组医师完成,在操作熟练程度及规范性上存在差异。所得结果具有局限性,后续可行进一步研究以改进。
综上所述,Milligan-Morgan手术联合痔动脉结扎术在治疗III~IV度混合痔同传统Milligan—Morgan手术相比,能减少术中出血量,降低术后出血及肛缘水肿发生率,联合术式并不增加手术时间、患者术后疼痛程度及尿潴留发生率。具有良好的临床应用价值。
[参考文献]
[1] 田振國,陈平,韩宝 . 中国成人常见肛肠疾病流行病学调查主要结论与建议 [C]. 郑州:中医药学会肛肠分会 2015 年学术年会暨全国流调行业发布会,2015:20-21.
[2] GuttenplanM.The evaluation and office management of hemorrhoids for the gastroenterologist[J].Current Gastroenterology Reports,2017,19(7):1-8.
[3] Davis BR,Lee-Kong SA,Migaly J,et al.The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons clinical practice guidelines for the management of hemorrhoids[J]. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum,2018,61(3):284-292.
[4] 美囯结直肠外科医师协会标准化工作委员会 . 痔诊断和治疗指南(2010 修订版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志,2012,11(3):243-247.
[5] 徐城,杨晓秋,刘丹彦 . 常用的疼痛评估方法在临床疼痛评估中的作用 [J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2015,21(3):210-212.
[6] He P,Chen H.Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids with Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in the treatment of prolapsed hemorrhoids[J].Chinese Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery,2015,18(12):1224-1230.
[7] Gallo G,Martellucci J,Sturiale A,et al.Consensus statement of the Italian society of colorectal surgery(SICCR): management and treatment of hemorrhoidal disease[J].Techniques in Coloproctology,2020,24(2):145-164.
[8] Morinaga K,Hasuda K,Ikeda T.A novel therapy for internal hemorrhoids: ligation of the hemorrhoidal artery with a newly devised instrument (Moricorn) in conjunction with a Dopplerflowmeter[J].Am J Gastroenterol,1995,90(4):610-613.
[9] Giordano P,Overton J,Madeddu F,et al.Transanalemorrhoidal dearterialization: a systematic review[J].Dis Colon Rectum,2009,52(9):1665-1671.
[10] Ahmad A,Kalimuddin M,Sonkar AA,et al.A Randomized Clinical Study to Compare the Outcome of Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (HAL) Procedure with and without Doppler Guidance in Grades Ⅰ - Ⅲ Hemorrhoidal Disease[J].Indian Journal of Surgery,2020:1-5.
[11] 王業皇,王元钊,章阳 . 超声多普勒引导下痔动脉结扎术的临床观察 [J]. 中国肛肠病杂志,2006,26(5):11-13.
[12] 林晖 . 痔动脉治疗的再认识与术式创新研究概况 [J].中国中西医结合外志,2019,25(1):109-113.
[13] Naqvi SRQ,SS QN,Rashid MM,et al.Haemorrhoidal Artery Ligation Operation Without Doppler Guidance[J].Journal of Ayub Medical College,Abbottabad: JAMC,2018,30(4):S664-S667.
[14] Schuurman JP,BorelRinkes IH,Go PM.Hemorrhoidal artery ligation procedure with or without Doppler transducer in grade Ⅱ and Ⅲ hemorrhoidal disease: a blinded randomized clinical trial[J].Ann Surg,2012,255(5):840-845.
[15] Haksal MC,Çiftci A,Tiryaki Ç,et al.Comparison of the reliability and efficacy of LigaSure hemorrhoidectomy and a conventional Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in the surgical treatment of grade 3 and 4 hemorrhoids[J].Turkish Journal of Surgery,2017,33(4):233.
[16] Medina-Gallardo A,Curbelo-Peña Y,De Castro X,et al.Is the severe pain after Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy still currently remaining a major postoperative problem despite being one of the oldest surgical techniques described? A case series of 117 consecutive patients[J].International Journal of Surgery case reports,2017,30:73-75.
[17] 董文双,师文霞,轩晶晶 . 混合痔外剥内扎术后患者肛缘水肿发生状况及其影响因素 [J]. 中国肛肠病杂志,2021,41(1):30-32.
[18] 付欢欢,余苏萍 . 超声刀加皮桥横向转移治疗环状混合痔的临床疗效 [J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2016,24(8):1293-1297.
[19] 向广阳,欧昌柏,张晓威,等 . 混合痔行外剥内扎术后肛缘水肿的相关危险因素分析 [J]. 中国医药指南,2020,18(14):38-40.
[20] Ng KS,Holzgang M,Young C.Still a case of “no pain, no gain”? An updated and critical review of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management options for hemorrhoids in 2020[J].Annals of Coloproctology,2020,36(3):133.
[21] 赵文召,赵治国,杨俊川,等 . 直视下痔动脉结扎在痔 Milligan-Morgan 手术中的临床应用 [J]. 中国肛肠病杂志,2013,33(12):32-34.
[22] 王杉 . 痔的外科治疗 [M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:133-134.
(收稿日期:2021-11-22)

