The boron transporter SiBOR1 functions in cell wall integrity, cellular homeostasis, and panicle development in foxtail millet
Hailong Wang, Sha Tang, Hui Zhi, Lihe Xing, Haoshan Zhang, Chanjuan Tang, Eno Wang,Meicheng Zhao, Guanqing Jia, Baili Feng, Xianmin Diao,*
a State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology for Arid Areas, College of Agronomy, Northwest A & F University, Yangling 712000, Shaanxi, China
b Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
Keywords:Foxtail millet (Setaria italica)SiBOR1 Cell wall Panicle development Grain yield
ABSTRACT Boron (B) is an essential micronutrient for vascular plant growth. Both B deficiency and toxicity can impair tissue development in diverse plant species,but little is known about the effect of B on reproductive panicle development and grain yield.In this study,a mutant of Setaria italica exhibiting necrotic panicle apices was identified and designated as sibor1.Sequencing revealed a candidate gene,SiBOR1,with a G-to-A alteration at the seventh exon. Knockout transgenic lines generated by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and their associated protein-9 also had necrotic panicles, verifying the function of SiBOR1.SiBOR1 encoded a membrane-localized B efflux transporter,co-orthologous to the rice BOR1 protein. SiBOR1 was dominantly expressed in panicles and displayed a distinct expression pattern from those of its orthologs in other species. The induced mutation in SiBOR1 caused a reduction in the B content of panicle primary branches, and B deficiency-associated phenotypes such as thicker cell walls and higher cell porosity compared with Yugu 1. Transcriptome analysis indicated that differentially expressed genes involved in cell wall biogenesis, jasmonic acid synthesis, and programmed cell death response pathways were enriched in sibor1.qPCR analysis identified several key genes,including phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (SiPAL)and jasmonate-ZIM-domain (SiJAZ)genes,responsive to B-deficient conditions. These results indicate that SiBOR1 helps to regulate panicle primary branch development to maintain grain yield in S. italica. Our findings shed light on molecular mechanisms underlying the relationship between B transport and plant development in S. italica.
1. Introduction
Foxtail millet[Setaria italica(L.)P.Beauv]is a model species for functional genomics studies because of its small diploid genome(2n = 18, ~420 Mb), short life cycle, prolific seed production, and C4 photosynthesis [1]. Some identified genes function differently in Setaria than in rice and Arabidopsis [2–4]. Setaria italica is an ancient crop grown worldwide, especially in arid and semiarid regions of China and India [5]. It can be used as grain, forage, and bird feed. Yield, a key crop attribute, is determined by panicle length,seed setting,and primary branch length.Few genes associated with panicle development have been identified[6,7]and none have been verified using transgenic systems in S. italica.
Boron (B) is a micronutrient required for the optimum growth,development,yield,and quality of crops[8].Because the range of B concentrations separating deficiency from toxicity is narrow,proper B homeostasis is required for plant development [9–11]. B is present in soil mainly as uncharged boric acid, which can be taken up by roots from soil either passively or actively under Bdeficient conditions[12].Boric acid is relatively soluble and readily leached by rainfall. Thus, B deficiencies occur frequently in highrainfall areas such as those of southeastern Asia, including southeastern China[9]whereas excessive B accumulations are restricted mostly to arid and semiarid regions such as northern China,southern Australia, and the Middle East [13].
B participates in many metabolic and physiological processes in higher plants, including cell wall synthesis and lignification, cell wall structural maintenance, phenol metabolism, sugar transport,and carbohydrate metabolism [10]. B is able to crosslink with two rhamnogalacturonan-II(RG-II)pectic subunits via apiosyl residues to maintain cell wall stability[12].B deficiency also facilitates the accumulation of pectinolytic-related substances and lignin in mature cells, thereby inhibiting the formation and development of new tissues [14]. B deficiency in plants leads to seed abortion,brittle leaves, and cessation of root elongation [10,15]. B toxicity affects many cellular metabolic processes and causes DNA damage.Symptoms of B toxicity include chlorosis and necrosis at the tips of older leaves [16,17]. B thus plays a central role in plant development.
To ensure growth and reproduction under B deficiency, plants must continually take up B from the soil and deliver it to newly developing tissues [18]. When boric acid availability is limited,plants facilitate B uptake and transport using two different classes of B transporters:boric acid channels of the major intrinsic protein(MIP)family and borate transporters of the BOR family[19].Nodulin 26-like intrinsic proteins(NIPs)constitute one subfamily of MIPs.In Arabidopsis thaliana,rice(Oryza sativa),and maize(Zea mays),some NIP II subclass members, such as AtNIP5;1, OsNIP3;1, and Zmtls1,have been identified as influx B transporters that function in the uptake of B from soil to roots.Plants with mutations in these influx B transporters show reduced plant height, lower seed setting rate,and stiff leaves under B-deficient conditions [19–22]. Other NIPs involved in B uptake and distribution in Arabidopsis include AtNIP6;1, which contributes to B transfer from xylem to phloem and preferential distribution of B in young shoot tissues [23] and AtNIP7;1,which facilitates B uptake in developing anthers[24].
BOR proteins, which are involved in boric acid/borate export,function mainly in loading B into the xylem and thus aid the translocation of B from roots to shoots [25]. BOR proteins can respond to B deficiency and prevent the over-accumulation of B in root cells [26,27]. In Arabidopsis, AtBOR1 encodes an efflux B transporter that exhibits polar subcellular localization toward the stele side of roots [28]. The combined action of AtBOR1 and AtNIP5;1 can lead to the directional and radial transport of B from the soil to steles,contributing to the transportation of B from roots to shoots via the transpiration stream[29]. The redistribution of B in shoots is poorly understood. To avoid the overaccumulation of boric acid,AtBOR1 is rapidly ubiquitinated and transported to vacuoles for degradation when the cytosolic concentration of B becomes high [30]. Under B-deficient conditions, Atbor1 mutants display severe repression of apical dominance and reductions in root length, plant height, grain yield, and rosette leaf expansion compared with the wild type[31].In rice,Osbor1 mutants are characterized by reduced plant height and root length[32].Accumulation of OsBOR1 is increased under B deprivation.In maize,Zmbor1(Zmrotten ear[Zmrte])mutants show more severe defects than the wild type under B deficiency, in the form of shorter tassels and fewer branches [33,34]. Zmbor1bor2 double mutants display increased defects and die after a few weeks in B-deficient soil[34]. In rice and maize, all growth defects caused by defective BOR proteins can be cured by increasing the B supply. Homologs of AtBOR1 in other species, such as Vitis vinifera (VvBOR11) [35]
Citrus macrophylla (CmBOR1) [36] and Brassica napus (BnaC4.BOR1;1c) [37] also function as efflux B transporters. The function of BOR1 is thus conserved across different species.
Other BORs are also involved in B transport. For example,AtBOR2, which is expressed in root cap and epidermal cells, is involved in the loading of B into secretory vesicles to promote BRG-II cross-linking and root development [26,38]. In barley and wheat, strong expression of HvBOR2 and TaBOR2 reduced the content of B in roots, improving the degree of B tolerance [39,40].AtBOR4 shows weak polar localization in root epidermal cells,with more B accumulated in shoots and roots of Atbor4 mutants than in wild-type plants[27,41].OsBOR4,which is expressed specifically in pre-anthesis anthers and mature pollen in rice [42] promotes pollen germination and pollen tube elongation. BOR4 may thus function to relieve excess-B toxicity.
A previous study has revealed the regulatory roles of BOR1s played in regulating pollen sterility and floret development [33].In contrast, little research has been performed to elucidate the importance of BOR1s in controlling inflorescence architecture and grain yields in the grass family. In this study, we isolated a sibor1 mutant that showed many developmental defects, most notably reduction in the number of panicle primary branches and grain yield.Knockout transgenic lines generated using the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats(CRISPR)and CRISPRassociated protein-9 (Cas9) (CRISPR-Cas9) system verified the function of SiBOR1 in regulating panicle development. Transcriptome sequencing(RNA-seq)and quantitative real-time PCR(qPCR)analysis suggested that genes associated with cell wall biogenesis and jasmonic acid (JA) synthesis regulate cell wall formation, cell porosity, and cell death. Some of these pathway genes were also upregulated under B-deficient conditions. SiBOR1 thus contributes to primary branch development, maintaining grain yield in S. italica.The findings of this study shed light on molecular mechanisms involved in B transport in plant development in S. italica.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plant materials and growth conditions
The sibor1 mutant was isolated after multiple generations from the ethylmethane sulfonate(EMS)treated cultivar Yugu 1,the reference genome line of S.italica[43].The mutant was backcrossed with Yugu 1 three times,and the resulting recessive plants were used for subsequent experiments. Individual sibor1 mutant and wildtype Yugu 1 used for agronomic trait analysis,foliar application experiments, and transcriptome sequencing were grown under natural field conditions in Beijing, China. Unhulled fully-filled grains were harvested and dried.The grain width,grain length,and 1000-grain weight were measured with an automatic seed counting and analyzing instrument(Model SC-G,Wanshen Ltd.,Hangzhou,Zhejiang,China). Each data was collected from three repeats, with approximately 300 grains per repeat. For phenotypic analysis, Ci846 (an easily transformed Setaria line) and T3 homozygous sibor1stop(knockout transgenic) plants were grown in a greenhouse. Yugu 1 and sibor1 plants which used to measure shoot length(from the base of the first leaf to the top of the leaf cushion)and root length(of the main root),as well as used for qPCR,were grown in Hoagland’s medium containing two different B concentrations(0.5 and 50 μmol L-1).Data were collected from three repeats.
2.2. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and phloroglucinol staining
For SEM, inflorescences of Yugu 1 and the sibor1 mutant were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline for 2 h under vacuum. After washing with 130 mmol L-1NaCl and dehydration in an ethanol gradient, the samples were dried in a critical point dryer (CPD020, Balzers AG, Balzers, Switzerland)and coated with palladium/gold alloy, and imaged on a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi S3400N, Tokyo, Japan).
For TEM, uppermost stem nodes were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde, washed with 0.2 mol L-1phosphate buffer, fixed in 1%osmium tetroxide for 1 h,stained with uranyl acetate, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series,and embedded in resin.The resin blocks were sectioned with a diamond knife and the sections were observed under a transmission electron microscope (JEM 1230,JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). Inflorescences were also stained and embedded in resin;histological sections were stained with toluidine blue and observed under an optical microscope (DMLB, Leica, Wetzlar,Germany).
Uppermost stem nodes of Yugu 1 and sibor1 at the booting stage were subjected to phloroglucinol staining.Manually sliced sections were stained for 5 min with 1%phloroglucinol dissolved in ethanol,visualized with 40% HCl for 1 min, and observed under the optical microscope.
2.3. Whole-genome resequencing, candidate gene identification, and phylogenetic analysis
For whole-genome resequencing, two DNA pools were constructed using 30 individuals each of Yugu 1 and the recessive mutant sibor1. Resequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform (Illumina, Inc, San Diego, CA, USA). The MutMap+[44] method used for candidate-gene screening based on SNPindex values is described in our previous report [6].
For the phylogenetic analysis, BOR protein sequences were downloaded from Phytozome v12.ClustalW[45]was used for multiple sequence alignment. Mega7 [46] software was used for phylogenetic tree construction by neighbor-joining with 1000 bootstrap replications. Details of genes used for the phylogenetic analysis are presented in Table S1.
2.4. Measurements of boron (B) content and exogenous boric acid rescue
To measure the B contents, samples, including roots, basal leaves (the 10th and 11th leaves), middle leaves (the 5th and 6th leaves), flag leaves, uppermost internodes, panicle primary branches, and grains, were collected from Yugu 1 and sibor1 individuals at reproductive stage. All the samples were dried at 65 °C for 10 days and then ground into powder. The dry weights were measured. The samples were digested with 5 mL HNO3/HClO4(87:13, v/v) in a heating block. The residues were dissolved in 2%nitric acid and filtered before analysis.B concentrations in the samples were determined using inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, SPQ9700, Seiko, Tokyo, Japan). Data were collected from three repeats.
Plants used for B rescue of Yugu 1 and sibor1 were grown under natural field conditions(Haidian,Beijing,China).Plants were treated with foliar applications of different concentrations of B(10,50,150, and 300 mmol L-1or water alone) before the shooting stage.Each B concentration was applied to the same numbers of Yugu 1 and sibor1 plants for 10 days. Ci846 and T3 homozygous sibor1stopplants used for 10 mmol L-1B foliar applications were grown in a greenhouse.
2.5.SiBOR1 subcellular localization and transgenic vector construction
The coding sequence of SiBOR1 was cloned and inserted into a PAN580 vector and fused with green fluorescent protein (GFP) at the C terminus.The recombinant plasmid was co-transformed with membrane marker plasmids fused with red fluorescent protein(RFP) into S. italica leaf protoplasts. The GFP and RFP signals were detected with a confocal microscope (LSM700, Zeiss, Oberkochen,Germany). The primers used for this experiment are listed in Table S2.
To knock out SiBOR1 in S. italica, a pYLCRISPR-Cas9-MH vector was constructed using a target site in the second exon of SiBOR1 as described by Ma et al. [47]. The primers 100 CRISPR F/R were used to amplify the target sequence and combined with U-F/gR-R to fuse the target between the U6a promoter and the sgRNA. The primers U-GAL and Pgs-GG2 were used to amplify the entire OsU6a promoter–target sequence–sgRNA region. Primers used for amplification are listed in Table S2.
All the constructs were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105 for Ci846 transformation, using mature seeds as the explants.The detailed transformation and recovery methods were published recently [1]. In total, 20 individual transgenic plants and four positive genome-edited lines were produced.Transgenic T3 homozygous lines were used in further experiments.
2.6. Transcriptome sequencing and qPCR
Total RNA was extracted from inflorescences(<1 cm)of Yugu 1 and sibor1 and subjected to transcriptome sequencing. The RNAseq data were analyzed as in our previous study [48]. The raw sequencing data were uploaded to the BioProject database under the accession number PRJNA688579.The same samples were used for qPCR validation.Entire seedlings of Yugu 1 grown under different B concentrations (0.5 and 50 μmol L-1) were used for analysis of relative expression levels of several phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and plant hormone signal-transduction pathway genes. Cullin(Seita.3G037700)was used as a reference gene in the qPCR analysis.Total RNA was extracted from 1.0 g foxtail millet samples with a Pure Link RNA mini kit (cat. No. 12183018; Invitrogen, Carlsbad,CA, USA). Then, 5 μg RNA was used for cDNA synthesis (cat. No.6210A; TaKaRa, Otsu Shiga, Japan), and the cDNA was diluted 10-fold for use in qPCR. qPCR amplifications were performed using Fast Start Universal SYBR Green Master Mix (ROX) (cat. No.04913914001,Roche,Mannheim,Germany)on an Applied Biosystems 7300 Analyzer(Foster City,CA,USA).The qPCR reaction mixture was as follows: 0.1 mmol L-1primer, 25 μL SYBR mix, 2 μL dilute cDNA, and 21 μL H2O. The PCR conditions were as follows:95 °C for 1 min, followed by 25 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. There were three biological replicates per tissue and three technical replicates per sample. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2-ΔCTor 2-ΔΔCTmethod and Excel 2016 (Microsoft corporation, Redmond, Washington, USA) was used to calculate relative gene expression levels and standard deviation. The primers used for qPCR are listed in Table S2.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the foxtail millet panicle apical-abortion mutant sibor1

Fig.1. Phenotypes and agronomic traits of Yugu 1 and sibor1.(A)Phenotypes of Yugu 1 and sibor1 at the reproductive stage.Scale bar,6 cm.(B,C)Panicles(B)and flag leaves(C) of Yugu 1 and sibor1. Scale bars, 2.5 cm. (D) Apical, middle, and basal portions of primary branches of Yugu 1 (top) and sibor1 (bottom) panicles. (E,F) Inflorescences of Yugu 1 and sibor1 at different development stages. Scale bars, 2.5 cm. (G) Comparison of panicle length, flag leaf length, flag leaf width, number of primary branches per panicle, grain weight per panicle, and 1000-grain weight between Yugu 1 and sibor1. Values are means ± SD (n = 3).
No visible differences were detected between the sibor1 mutant and wildtype Yugu 1 during the vegetative stage under normal conditions. During the reproductive stage, necrosis was evident at the apices of sibor1 inflorescences,whereas the bases of inflorescences were generally normal and underwent grain setting and maturity as in the wild type(Fig.1D–F).Primary branch formation did not occur in middle inflorescence regions of sibor1 even though peduncles developed normally (Fig. 1E–F). The degree of panicle apical abortion of sibor1 mutant varied among planting environments (Shunyi, Haidian, and Changping in Beijing, China;Fig. S1A–C). Toluidine blue staining of the inflorescences (<3 mm) revealed that some cells at the apices of sibor1 peduncles and primary branches were necrotic, whereas the wild type showed normal inflorescence development during all stages(Fig. 2A, B). When inflorescence lengths reached nearly 1 cm,observation of manually sliced sections of inflorescences revealed that the whole apical peduncle and primary branches of sibor1 were necrotic.(Fig.2C,D).SEM observation indicated that the primary branch primordium was wrinkled and that primary branches could not be formed at the apices of early stage inflorescences in sibor1 (Fig. 2F, H); in contrast, the inflorescences of Yugu 1 developed normally (Fig. 2E, G). Thus, inflorescence development was impaired in the sibor1 mutant.
3.2. The mutation in the putative boron (B) transporter SiBOR1 is responsible for the panicle apical-abortion phenotype
To identify the candidate gene responsible for the observed phenotypes, the sibor1 mutant was crossed with the wild type Yugu 1.Plants in the F1generation showed normal panicle phenotypes.The segregation ratio of normal to mutant phenotypes in the BC1F2population was 3:1 (normal:mutant = 324:92, χ2= 1.846,χ20.05= 3.84), indicating that the sibor1 mutant phenotype is controlled by a single recessive gene. Bulked-segregant analysis sequencing was performed for separate pools of recessive and dominant individuals [49]. According to the sequencing results, the candidate gene was located in a 4.21–4.29 Mb interval on chromosome 3(Fig.3A).We next searched for SNPs with index values ≥0.9 in the pool of recessive individuals (SNPs were heterozygous in the dominant individual pool). Only one SNP matching this criterion was identified in the mapped interval. This SNP, which was located in the seventh exon of the gene Seita.3G333100,was a G-to-A alteration at 42,628,729 bp that was responsible for the change of a single amino acid (P241L) (Fig. 3B). Homolog annotations suggested that Seita.3G333100 encodes a B transporter, which was named SiBOR1.Phylogenetic analysis of BOR proteins of S. italica, rice, maize, sorghum, Arabidopsis, and Brachypodium distachyon revealed that SiBOR1 was orthologous to the rice B transporter OsBOR1 (Fig. 3C).In rice, Arabidopsis, and maize, BOR1 are associated with B efflux from root steles to xylem to maintain a stable B concentration. To further determine whether the above single amino acid mutation could affect the function of SiBOR1, protein sequences from several species were compared. The altered amino acid in SiBOR1, which was located in the seventh transmembrane helix, was conserved among rice, maize, Arabidopsis, and S. italica (Fig. 3D, E). The change in the amino acid due to the G-to-A alteration was responsible for the substitution of a straight carbon chain for an aromatic ring(Fig. 3F), suggesting that this amino acid is important for protein function. The disruption of SiBOR1 may have hindered the exploitation of B in the mutant plants.

Fig. 2. Sectioning and SEM analysis of Yugu 1 and sibor1 inflorescences. (A,B) Toluidine blue-stained of inflorescences of Yugu 1 and sibor1 at two stages of inflorescence development. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C,D) Manually sliced sections of inflorescences of Yugu 1 and sibor1. Scale bars, 2 mm for (C) and 1 mm for (D). (E–H) Scanning electron microscopy images of Yugu 1 and sibor1 inflorescences. (G,H) Primary branch primordium at the inflorescence apices of Yugu 1 and sibor1 (close-up views of the primary branch shown in E and F). Scale bars, 50 μm. pb, primary branch; pbp, primary branch primordium.
3.3. Reduction in B content in sibor1 mutants and rescue of panicle defects by exogenous boric acid application
To verify that the defective phenotypes resulted from a B deficiency in the mutant, the B contents of different tissues, including roots, basal leaves (10th and 11th leaves), middle leaves (5th and 6th leaves), flag leaves, uppermost internodes, panicle primary branches, and grains, from Yugu 1 and sibor1 plants, were tested at the reproductive stage. The B contents of basal leaves, middle leaves, flag leaves, uppermost internodes, and panicle primary branches of sibor1 were markedly lower than those in Yugu 1,whereas the B contents of roots and grains were unchanged.Thus,SiBOR1 influenced the distribution of B in leaves, internodes, and panicle branches.
To investigate whether B played a role in the defective panicle phenotype, the effect of exogenous B applied to leaves was measured. Application of water showed no effect on the phenotype of the sibor1 mutant (Fig. 4B). When 10, 50, or 150 mmol L-1B was applied to sibor1 plants, panicle lengths increased significantly(16.25, 18.00, and 16.00 cm, respectively) compared with 5.50 cm in the water control treatment(Fig.4C).Compared with sibor1 plants receiving the water treatment,the numbers of primary branches in different parts(apical,middle,and basal)of sibor1 panicles,as well as the grain-setting rates and grain weights in different parts (apical and middle), increased markedly during the 10,50, and 150 mmol L-1B treatments (Figs. 4D, S2A, B). In contrast to the mutant, these parameters were unchanged or only slightly increased in the wild type under the same B concentration conditions(Figs.4C,D,S2A,B).After application of 10 or 50 mmol L-1B,sibor1 panicle lengths, as well as grain weight and grain-setting rate in different panicle regions, were nearly the same as those of Yugu 1(Figs.4C,S2A,B).In both Yugu 1 and sibor1,primary branch number, grain-setting rate, and grain weight per panicle were markedly lower upon application of 300 than of 50 mmol L-1B(Figs. 4D, S2A, B), suggesting toxicity at the former concentration.Thus, the SiBOR1 mutation caused a reduction in B content and influenced panicle development in S. italica.
When plants were grown in Hoagland’s medium containing 0.5 μmol L-1B, the root length of the sibor1 mutant was 3.25 cm,significantly shorter than that of Yugu 1 (4.37 cm) (Fig. 4E, G). In contrast, no significant difference was observed between the root lengths of Yugu 1 and sibor1 grown under in 50 μmol L-1B conditions (Fig. 4F, G). The shoot length of sibor1 (1.66 cm) was also lower than that of Yugu 1 (1.89 cm) when plants were supplemented with 0.5 μmol L-1B (Fig. 4E, G), but equaled that of Yugu 1 under 50 μmol L-1B conditions (Fig. 4F, G). Thus, B deficiency inhibited root and shoot growth in S. italica.

Fig. 3. Candidate gene analysis. (A) Analysis of mutations between Yugu 1 and sibor1 based on BSA sequencing. (B) Gene structure diagram showing the location of the identified mutation site. 2039 is the position of the mutant site in SiBOR1 genome sequence. 241 is the position of the mutant site in the SiBOR1 amino acid sequence. (C)Phylogenetic tree of BORs from Arabidopsis,maize,rice,sorghum,Brachypodium distachyon,and S.italica.(D)Topological model of SiBOR1 from S.italica.The red star indicates the mutation site and the yellow cylinders represent transmembrane helices.(E)Comparison of amino acid residues of BOR1 proteins at the mutation site(red star)among Arabidopsis,rice,maize,and S.italica.The sequence region corresponding to the seventh transmembrane helix is indicated by the red box.(F)Comparison of SiBOR1 protein structures showing the structural effect of the observed amino acid substitution in sibor1 compared to Yugu 1 (SWISS-MODEL, https://swissmodel.expasy.org/). The red arrows indicate the mutation site.
3.4. Functional verification of SiBOR1 in S. Italica by CRISPR-Cas9 system
To validate the function of SiBOR1 in S. italica, the CRISPR-Cas9 system was used to knock out SiBOR1 in the background of Ci846,an easily transformed model cultivar.The target site was located in the sixth exon of SiBOR1 (Fig. 5A). In total, four positive genomeedited lines, each with a single A nucleotide inserted four nucleotides before the PAM sequence,were identified,and the insertions caused the early termination of the SiBOR1 protein. The lines obtained by selfing these four transgenic plants were designated as sibor1stop(Fig. 5A). When the T3homozygous sibor1stopplants(sibor1stop#1 and sibor1stop#2)and Ci846 plants were grown under normal conditions,the transgenic plants showed defective phenotypes similar to those of sibor1 plants (Fig. 5B): a necrotic apical peduncle, no primary branches at the apex of the inflorescence,shortened and wrinkled top leaves, and reduced plant height(Fig.5C–E).Foliar application of 10 mmol L-1B rescued these defective phenotypes (Fig. 5F). SiBOR1 is therefore the gene associated with the abnormal phenotype of the sibor1 mutant.
3.5. SiBOR1 encodes a plasma membrane protein, and is dominantly expressed in panicles
A 35S:SiBOR1-GFP vector was constructed and transformed into S. italica protoplast to analyze the subcellular location of SiBOR1.The SiBOR1 was localized at the plasma membrane, whereas the location of the control, 35S:GFP, was not specific (Fig. 6A).
To investigate the tissue-specific expression patterns of SiBOR1,26 different tissue samples from several developmental stages,including shoot elongation, booting, panicle developmental, flowering, and grain filling, were collected. The qPCR results showed that SiBOR1 was expressed preferentially in various panicle samples, including inflorescences, apical primary branches, and basal primary branches. During the vegetative growth stage, this gene was highly expressed in shoot tips but was relatively lowly expressed in roots, nodes, and leaves (Fig. 6B).
I got started. In the wee hours of Christmas morn, I finished the curtains, painted the walls and stepped back to admire my masterpiece. Wait-why not put rainbows and clouds on the walls to match the sheets? So out came my makeup6 brushes and sponges, and at 5 A.M. I was finished. Too exhausted7 to think about being a poor “broken home,” as statistics said, I went to my room and found Lisa spread-eagled in my bed. I decided8 I couldn’t sleep with arms and legs all over me, so I gently lifted her up and tiptoed her into her room. As I laid her head on the pillow, she said, “Mommy, is it morning yet?”
3.6. Lignin synthesis and plant hormone signaling influence cell wall integrity in sibor1
To identify molecular mechanisms associated with the function of SiBOR1 in foxtail millet, transcriptomes of inflorescences of sibor1 and Yugu 1 were compared. A principal-components analysis of the expression results for sibor1 and Yugu 1 showed a clear separation among genotypes,but limited differences were detected in the two components among the three experimental replications(Fig. 7A). Pairwise comparisons of gene expression profiles between sibor1 and Yugu 1 identified 2062 differentially expressed genes(DEGs;absolute log2FC value >1 and FDR ≤0.001)that may be regulated by SiBOR1. Among these DEGs, 95.9% were upregulated (Fig. 7B). GO enrichment analysis revealed that five main classes of GO terms were influenced in sibor1 relative to Yugu 1.Many genes involved in GO terms associated with cell wall formation and ion transport were differentially regulated.The phenylalanine -associated pathway, which can influence cell wall stabilization, was also enriched according to the KEGG analysis.Protein phosphorylation-associated genes were also enriched,reflecting the fact that phosphorylation is involved in many hormone and cell recognition regulatory processes. The expressions of several genes associated with programmed cell death(PCD)and defense response pathways were also changed in sibor1 compared with Yugu 1 (Fig. 7C). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that pathways involved in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, phenylalanine metabolism, and alphalinolenic acid metabolism were also enriched (Fig. 7D).

Fig.4. Comparison of B content between Yugu 1 and sibor1 and the results of B supplementation experiments.(A)B contents of Yugu 1 and sibor1 grown under natural field conditions of Haidian, Beijing, China.(B)Panicles from Yugu 1 and sibor1 plants supplemented with different concentrations of boric acid (10,50, 150,or 300 mmol L-1)or water alone(0 mmol L-1).Scale bar,6 cm.(C,D)Panicle lengths(C)and number of primary branches per panicle(D)in Yugu 1 and sibor1 under different B concentrations.(E–G) Shoot and root lengths under 0.5 and 50 μmol L-1 B conditions. Scale bar, 2.5 cm. *, P <0.05; **, P <0.01. Values are means ± SD (n = 3).
Other DEGs identified by KEGG and GO enrichment analyses included genes associated with plant-type secondary cell wall components, lignin metabolism, and phenylalanine metabolism,such as phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (SiPAL), cinnamoyl CoA reductase (SiCCR), cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (SiCAD), 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (Si4CL), laccases (SiLACs), and beta glucosidases (SiBGLUs), these genes are associated with lignin synthesis.MYB transcription factors(SiMYB4 and SiMYB43)that may regulate lignin synthesis were also included. Because lignin is a cell wall component, abnormal expression of these genes could result in structural instability of cell walls. Some genes involved in αlinolenic acid metabolism and response to JA signals were differentially regulated, including jasmonate-ZIM-domain (SiJAZ) and allene oxide synthase(SiAOS)genes.In regard to PCD-related pathways, genes functioning in repression of PCD, such as xylem cysteine peptidase (SiXCP), lesions simulating disease resistance 1(SiLSD1), and respiratory burst oxidase homologue D (SiRBOHD),were upregulated in sibor1. Among genes involved in the anion homeostasis pathway, several genes associated with calcium and phosphorus were upregulated, such as autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase(SiACAs),senescence-related gene 3(SiSRG3),and purple acid phosphatase 3 (SiPAP3) (Figs. 7E, S3A). The 17 genes in these pathways were selected for validation by qPCR.Consistent with the RNA-seq results, 13 were significantly upregulated in sibor1. They included SiPALs, Si4CL, and SiCAD, all acting in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway,and SiIAA14,SiETR2,and four SiJAZs associated with the plant hormone signal transduction pathway(Fig.S3B).To identify whether the 13 genes were also induced under B-deficient conditions,transcript levels of these genes in Yugu 1 and sibor1 under different B concentrations (0.5 and 50 μmol L-1) were measured.qPCR analysis of 10-day-old plants of Yugu 1 and sibor1 grown under sufficient-B (50 μmol L-1) and deficient-B (0.5 μmol L-1)conditions revealed that most SiPALs and SiJAZs were also induced under B-deficient conditions (Figs. S3C, 8A). Thus, lignin synthesis and JA signal transduction pathways function in response to Bdeficiency signals.
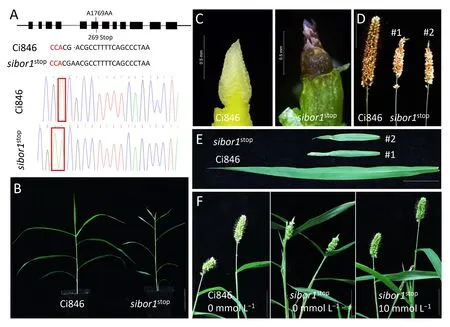
Fig.5. Phenotypic analysis of Ci846 and sibor1stop.(A)Diagram showing the location of the CRISPR-Cas9 edited site within the SiBOR1 gene and sequence traces of this region in Ci846 and sibor1stop.1769 means the position of the mutant site in SiBOR1 genome sequence.269 means the position of the mutant site in SiBOR1 amino acid sequence.(B–E) Images of whole plants (B), inflorescences (C), mature panicles (D), and flag leaves (E) of Ci846 and sibor1stop. In (D) and (E), #1 and #2 correspond to two different transgenic lines.(F)Phenotypes of Ci846 and sibor1stop under normal conditions and sibor1stop after foliar application of 10 mmol L-1 boric acid.(B,F)Scale bars,6 cm;(D,E)Scale bars, 2.5 cm.
As revealed by TEM, cell walls of xylem parenchyma in uppermost nodes of sibor1 were much thicker than those of Yugu 1(Fig. 8B–E), and xylem cells in sibor1 showed increased cell wall porosity(Fig.8F, G).To identify whether this abnormal phenotype was caused by elevated rates of lignin synthesis, phloroglucinol staining was used to analyze lignin content of the uppermost nodes. Enlarged vascular bundles in sibor1 were more strongly stained than those of Yugu 1(Fig.8H,I),which implied that the lignin content of sibor1 was higher than that of Yugu 1. Thus, the defective phenotype in sibor1 caused by lignin deposition influenced cell wall integrity.
4. Discussion
4.1. SiBOR1 is dominantly expressed in panicle and is responsible for panicle development in S. Italica
In many species, BOR1 has been shown to be a B efflux protein involved in loading B from parenchyma cells to xylem to maintain B homeostasis in roots and shoots[27,32].In the present study,no differences in B contents of roots and grain were observed between Yugu 1 and sibor1,whereas B contents of leaves,top internodes and panicle primary branches were significantly lower in sibor1 compared with Yugu 1(Fig.4A).These results differ from those of previous studies, which found that the B contents were reduced in roots of rice and rapeseed BOR1 mutants [32,37]. Consistent with the reduced B content of panicle primary branches,panicle defects in sibor1were the most prominent phenotypic differences from Yugu 1. Histological analysis and SEM revealed that the panicle defects in the mutant sibor1 were due to the failed development of inflorescence primary branches(Fig.2C,D).As a result,panicles of sibor1 were shorter,had fewer primary branches,and were more frequently aborted than those of Yugu 1 (Fig. 1B). The finding that exogenous boric acid application was able to rescue defective phenotypes (Fig. 4B) indicates that the mutation in SiBOR1 affected B utilization in panicles and thereby influenced panicle development.
In Arabidopsis, AtBOR1 is expressed in roots [50]. In rice, the accumulation of OsBOR1 transcripts is higher in roots than in shoots [32]. In maize, similar transcript levels of rte are observed in roots, leaves, tassels, and ears [33]. VvBOR1 in Vitis vinifera is expressed at higher levels in roots than in flowers [35]. In Citrus macrophylla, CmBOR1 is expressed in leaves, stems and flowers and has its highest accumulation in roots [36]. BnaC4.BOR1;1c in Brassica napus is expressed in roots, nodes, leaves, anthers, pistils,buds and flowers [37]. In all of these plant species, BOR1 genes are expressed either universally or mainly in roots. In S. italica,SiBOR1 is dominantly expressed in shoot tips and inflorescences during shoot elongation and booting stages. SiBOR1 was highly expressed in apical primary branches during different panicle developmental stages but expressed only at extremely low levels in roots, nodes, internodes and leaves (Fig. 6B). The dominant expression pattern of SiBOR1 in panicles thus implies that this gene has a major function in B transport and distribution in S. italica panicles.
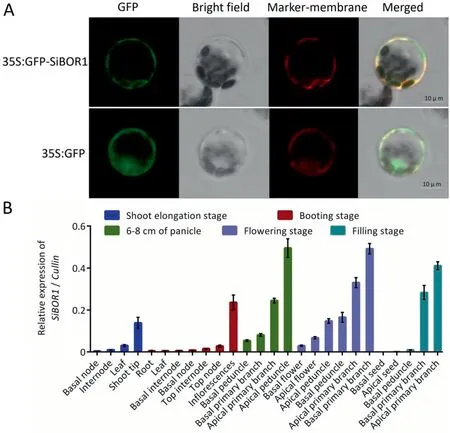
Fig. 6. Subcellular localization (A) and expression pattern (B) of SiBOR1 in different tissues of Yugu 1. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). Scale bars, 10 μm.
4.2. SiBOR1 regulates lignin synthesis, influencing cell wall stability
The mechanism responsible for defective cell walls under low-B conditions cannot be easily identified because the primary and secondary effects of B deficiency are unclear[10].Cross-linked B-RG-II complexes are required for the structural maintenance of cell walls[12] which are composed of cellulose, pectin, and lignin. B deficiency thus disrupts the organization and properties of plant cell walls[26].Lignin synthesis is regulated by various genes,including PAL,CCR,CAD,and 4CL[51].Transcription of these genes is induced under B-starvation conditions.As a result,cell wall lignin contents are increased [52]. In the maize rte mutant, rte is expressed in the vasculature, especially in the cells surrounding xylem and phloem[22]. Likewise, rice OsBOR1 is expressed in cells near the vasculature [32,35,40]. In the present study, TEM of uppermost nodes revealed that cell walls of xylem cells were thicker,and intercellular space was larger, in sibor1 than in the wild type (Fig. 8D, E).According to our RNA-seq results, many lignin synthesisassociated genes, such as PALs, were upregulated in sibor1(Fig.7E).qPCR analysis indicated that the expression of these genes was significantly changed between Yugu 1 and sibor1 (Fig. S3B).Phloroglucinol staining revealed that lignin deposition was much heavier in uppermost node xylem of the mutant(Fig.8H,I).When Yugu 1 and sibor1 were grown under B-deficient conditions(0.5 μmol L-1), these genes were also upregulated in comparison with their expressions under B-sufficient conditions (50 μmol L-1) (Fig. 8A). This result indicates that SiBOR1 can regulate lignin synthesis to maintain cell wall stability, which is consistent with results from Citrus [53].
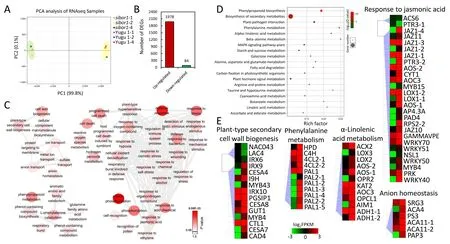
Fig. 7. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in sibor1 and Yugu 1. (A) Principal-components analysis plot of Yugu 1 and sibor1 transcriptome sequence data. (B) Numbers of upregulated and downregulated DEGs in sibor1 and Yugu 1. (C) Enriched GO terms of sibor1 and Yugu 1 DEGs. (D) KEGG pathway enrichment bubble diagram of the DEGs in sibor1 and Yugu 1.(E)Expression patterns of candidate genes in significantly enriched biological function categories.Each box represents a gene,and the color gradient represents the gene expression value.Gene ID and its expression value corresponding to each box are listed in Table S3.Values are means ± SD (n = 3). Inflorescences under 1 cm were used in experiments.
4.3. Panicle apical necrosis may be associated with JA-induced cell death via ROS-dependent mechanisms in foxtail millet in response to B deficiency

Fig.8. Relative expressions of candidate genes associated with lignin synthesis in S.italica and morphology of uppermost nodes.(A)Transcript levels of SiPALs under 0.5 and 50 μmol L-1 B conditions. The 2-ΔCT calculation method used for analysis. (B,C)Vascular bundles in Yugu 1 (B)and sibor1 (C). Red circles indicate xylem parenchyma.(D,E)Enlargements of areas in red circles showing xylem parenchyma cell walls in Yugu 1 (D) and sibor1 (E). The images shown in bottom right corner of D and E are the xylem parenchyma in B and C, respectively. (F,G) Cell porosity of Yugu 1 (F) and sibor1 (G). Cell porosities are indicated by dashed red circles. CW, cell wall. (H, I) Phloroglucinol staining of Yugu 1 and sibor1 uppermost nodes.Stained areas and enlarged vascular bundles are outlined in red and yellow,respectively.(B,C)Scale bars,10 μm;(D,E)Scale bars, 2 μm; (H, I) Scale bars, 1 mm.
The profiles of phytohormones, such as auxin, cytokinin (CK),ethylene, and abscisic acid, are also affected by low B concentrations [10,54–57]. B deficiency causes IAA and CK contents to decrease and increases the concentration of ethylene [58–60]. In the present study, IAA- and ethylene-associated genes, such as IAA14 and ETR2, also showed altered expression (Fig. S3C). JAassociated genes, including those encoding JA biosynthetic enzymes (such as lipoxygenase, allene oxide synthase, and allene oxide cyclase)as well as JA signaling pathway genes(such as JAZs),were also upregulated in sibor1 compared with Yugu 1(Fig.7E).In a recent study, JA was found to inhibit Arabidopsis root growth under low-B conditions [61]. In response to cell wall damage in Arabidopsis, JA accumulation induces the production of lignin and associated reactive oxygen species(ROS)[62].RBOHD-derived ROS act as a local and systemic signal for responding to pathogen infection [63,64]. RBOHD interacts with RBOHF to fine-tune ROS production during pathogen infection [64] and ROS signals can translate to downstream targets by oxidative signal-inducible1(OXI1), such as MAP kinase 3 (MAPK3) [65]. MID1 complementing-activity 1 (MCA1) can sense cell wall damage and accordingly regulate Ca2+uptake [66]. The above mentioned JAand ROS-associated genes were all differentially expressed in sibor1 compared with Yugu 1 (Figs. 7E, S3A). As a result, PCDrelated genes, such as SiXCP, SiLSD1, and SiRBOHD, were upregulated in sibor1 (Fig. S3A), suggesting that the apical abortion in the mutant may be a self-protective process ensuring adequate B supply for basal flower development in the panicle. SiBOR1 may thus influence cell homeostasis via JA- and ROS-related processes.This speculation sheds new light on the function of B in plant panicle developmental regulation.
4.4. B homeostasis affects S. italica development
Under limited or excess B conditions, many plant species show defective development. For example, B-deficient Arabidopsis mutants Atbor1-1 and Atbor2 show repressed rosette leaf expansion and display swollen, irregularly shaped root epidermal cells[26,31]. The Arabidopsis mutant Atbor4, which has a B content higher than that of the wild type, also displays inhibited shoot growth [67]. The rice dte1 mutant has reduced total B content and exhibits retarded growth [21]. These root and leaf defects are also evident in sibor1 under B-limited conditions. The low B content of the maize rte mutant causes shorter tassels, reduced branching, and sterile ears [33]. Maize rte rte2 double mutant plants exhibit leaf and ear defects and die during the vegetative stage in soils with low B contents [34]. In Brassica napus, knockdown of BnaC4.BOR1;1c lowers the accumulation of B in floral organs,resulting in thickened cell walls of stigma papilla cells,severe sterility, and seed yield loss [37]. In the present study, the mutant sibor1 showed abnormal panicle, root, and leaf development (Figs. 1A, S1A). Plant height, root length, leaf length, leaf width, panicle length, number of primary branches, and grain weight per panicle were significantly reduced in sibor1 in comparison with the wild type (Figs. 1G, S1F). The most marked differences between sibor1 and the wild type Yugu 1 were in the panicle. Bulked-segregant analysis sequencing and transgenic assays revealed an association between SiBOR1 and these phenotypic differences. B contents measurements and B application experiments showed that the mutation in SiBOR1 was responsible for the reduced B content of sibor1. These results suggest that B acts in S. italica development in a manner similar to its action in other plants.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Xianmin Diao:provided funding acquisition and project administration, characterized mutants.Baili Feng:provided funding acquisition and project administration.Hui Zhi:characterized mutants.Haoshan Zhang:generated transgenic plants.Hailong Wang:made the data collection and visualization, wrote and edited the manuscript.Lihe Xing:made the data collection and visualization.Sha Tang:made the data collection and visualization,wrote and edited the manuscript.Chanjuan Tang:provided technical assistance.Enbo Wang:provided technical assistance.Meicheng Zhao:provided technical assistance.Guanqing Jia:provided technical assistance.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFD1000700 and 2019YFD1000704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871692), the China Agricultural Research System(CARS06-13.5-A04), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data for this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.05.002.
- The Crop Journal的其它文章
- Brief Guide for Authors
- Cob color, an indicator of grain dehydration and agronomic traits in maize hybrids
- Effects of sgRNA length and number on gene editing efficiency and predicted mutations generated in rice
- Imbalance between nitrogen and potassium fertilization influences potassium deficiency symptoms in winter oilseed rape(Brassica napus L.)leaves
- ZmWRKY104 positively regulates salt tolerance by modulating ZmSOD4 expression in maize
- A novel genomic prediction method combining randomized Haseman-Elston regression with a modified algorithm for Proven and Young for large genomic data

