Zinc carnosine-based modified bismuth quadruple therapy vs standard triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized controlled study
INTRODUCTION
Since its first successful culture in the laboratory almost 40 years ago,() infection and gastric diseases have been a source of debate among medical professionals and scientists[1,2]. This bacterium, which is among very few organisms that can survive in the human stomach, has gained much reputation, mostly as a harmful bacterium, based on its association with various gastroduodenal diseases[3].is a highly prevalent helical shaped gram-negative bacterium that colonizes and infects the human gastric mucosa in approximately more than 50% of the world’s population[4]. One conducted cross-sectional study in the United Arab Emirates revealed that the prevalence ofamong healthy children and adults was 40%[5]. Infection can, at a minimum, cause gastritis and is a prominent etiologic agent of gastric and duodenal ulcer diseases, gastric adenocarcinoma and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma[2,6,7]. The development of peptic ulcers arises in about 10%-20% of patients infected with, while advancement to gastric cancer occurs in 1%-3% of cases[8].
The first and second times her sisters did not notice this, but when it happened continually, they remarked it and said, Something is the matter with Little Two-eyes, for she always leaves her food now, and she used to gobble up all that was given her
Triple therapy (TT), which includes a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and two antimicrobial agents (clarithromycin and amoxicillin or metronidazole) prescribed for 10 to 14 d, has been the standard first-line eradication therapy since 1996[9]. However, due to the increased rate of clarithromycin or metronidazole resistance, standard TT has been often ineffective in regions with high antibiotic resistance[10,11]. In fact, one systematic review and meta-analysis revealed a high resistance rate (≥ 15%) ofto clarithromycin and metronidazole in World Health Organization regions[12]. This has led to a detrimental effect on the efficacy of the triple treatment regimen, as its eradication response now falls considerably short between 50%-70%[13]. This is considered far below the minimal acceptable level of intention-to-treat (ITT) eradication rate (> 80%) as recommended by Maastricht guidelines[14]. As a result, four-drug regimens (quadruple, sequential, concomitant and hybrid) and levofloxacincontaining therapies have been studied with variable success[15,16]. Later on, a bismuth based treatment, now known as bismuth quadruple therapy, was suggested as an alternative initial therapy option, especially in regions where high rates of antibiotic resistance exist[13].
Studies have shown that the efficacy of bismuth intreatment regimens is mainly associated with its bactericidal effect against[17]. Various means that aid bismuth to exert such a role have been proposed[18]. Ultrastructural studies showed that bismuth bind the bacterial wall and periplasmic membrane, thus forming complexes[19]. Moreover, experiments revealed that bismuth is capable of inhibiting various enzymes ofsuch as urease, phospholipase and catalase[20]. One other mechanism through which bismuth exerts its anti-actions is by inhibiting the pathogen’s protein and adenosine triphosphate synthesis and preventing its adherence to the gastric mucosa[21]. Bismuth compounds also protect the gastric mucosa and aid in ulcer healing[22]. No resistance of strains ofto bismuth has been reported yet.
And I will own, that when people saw my father perched up in front of the omnibus of death, dressed in his long, wide, black cloak, and his black-edged, three-cornered hat on his head, and then glanced at his round, jocund6 face, round as the sun, they could not think much of sorrow or the grave
We, hereby, present a study that compares the eradication responses ofobtained from a standard TT regimena modified one that constitutes a standard TT regimen enforced by two adjuvants: Bismuth subcitrate and the nutritional supplement zinc carnosine (modified bismuth quadruple therapy or MBQT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
In this prospective study, we aimed to tackle the issue of increased failure rate of standard antimicrobial therapies by combining the benefits and positive effects of both bismuth compound and zinc carnosine in a single regimen protocol. The latter was used to enhance the effect of antimicrobial therapy in eradicatinginfection, while at the same time maintaining a safe profile of the regimen with good patient compliance to the treatment course. In fact, our study was able to show that adding bismuth subcitrate and zinc carnosine to the standard therapy was associated with an increase in negative UBT results, leading to a better eradication rate ofin that subgroup of patients.
Though she was flustered5() , and the invitation came at such short notice, Diana accepted. She and her roommate, Carolyn Bartholomew, hurried to dress and prepare Diana for her big date. The evening was a success, and an invitation to party on the royal yacht came soon after……
Clinical trial
The enrolled patients were randomized by drawing a sealed envelope that contained pre-assigned treatment instructions. They were allocated to one of the following two groups. Group A (TT group) received esomeprazole 40 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and amoxicillin 1 g and all the medications were given twice daily for subsequent 14 d. On the other hand, group B (MBQT group) received zinc carnosine (gastrozin) 75 mg and bismuth subcitrate 240 mg in combination with esomeprazole 40 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg and amoxicillin 1 g. All the later medications were given twice daily for subsequent 10 d. Compliance with medication was checked immediately after stopping the treatment by counting the number of returned pills. Four weeks after cessation of the eradication therapy, a repeated UBT was done.
Outcomes and statistical analysis
Your husband, said Little Thumb, is in very great danger, being taken by a gang of thieves, who have sworn to kill him if he does not give them all his gold and silver. The very moment they held their daggers55 at his throat he perceived me, and desired me to come and tell you the condition he is in, and that you should give me whatsoever he has of value, without retaining any one thing; for otherwise they will kill him without mercy; and, as his case is very pressing, he desired me to make use (you see I have them on32) of his boots, that I might make the more haste and to show you that I do not impose upon you.
RESULTS
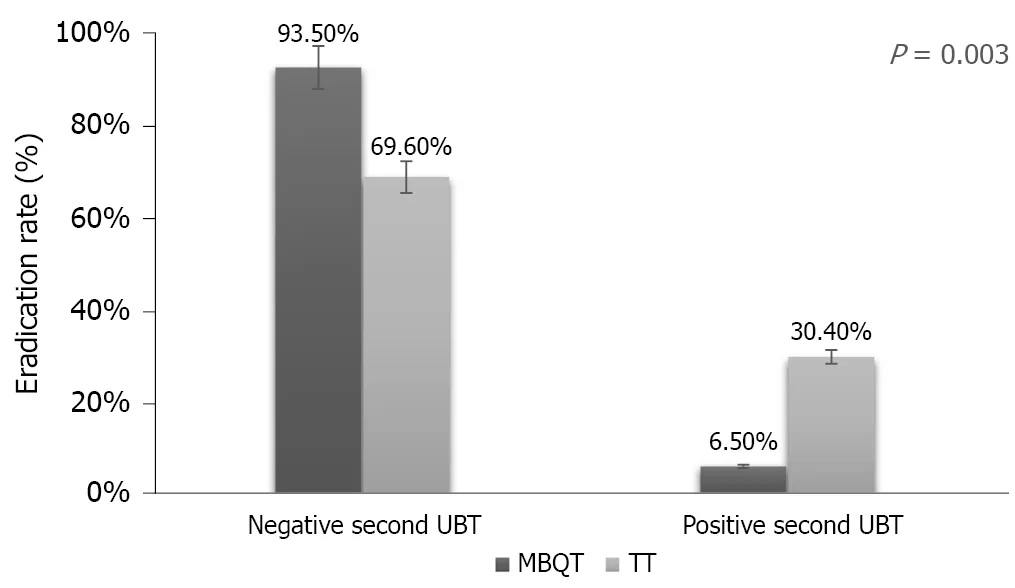
In this study, there were a total of 92 subjects of which 62 (67.4%) were males and 30 (32.6%) were females. Ages ranged from 19 to 56 years (mean of 31.88 ± 8.09 years). Most patients (60.9%) were Asian. This was followed by Arab (28.3%) and African (10.9%). Most subjects (81.5%) were non-smokers. Body mass index ranged from 17.20 to 43.70 kg/m(mean of 26.37 ± 4.12 kg/m). Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the two tested groups. Of the two types of therapy, there were 46 (50%) individuals in the MBQT group and 46 (50%) in the TT group (= 0.003). Among subjects in the MBQT group, 43 tested negative on the repeated UBT test and 3 tested positive. In the TT group, 32 tested negative and 14 tested positive (Figure 1).
Another potential adjuvant therapy that has been evaluated to enhance the eradication ofis polaprezinc (PZ). PZ, a chelated compound composed of Lcarnosine and zinc, is a mucosal protective agent[23] that has been used worldwide as a treatment for ulcers[24]. PZ prevents the formation of gastric mucosal lesions and mucosal cell damage induced by-associated gastritis in a dose-dependent manner[25,26]. This role has been attributable to various properties possessed by PZ such as stimulating the production of mucus, exerting its stabilizing-membrane activity and having an antioxidant action[27-30]. Moreover, some studies revealed that PZ led to an improvement in eradication rates of[31,32] by inhibiting the growth of, in addition to impeding its urease activity and adhesion to gastric mucin.
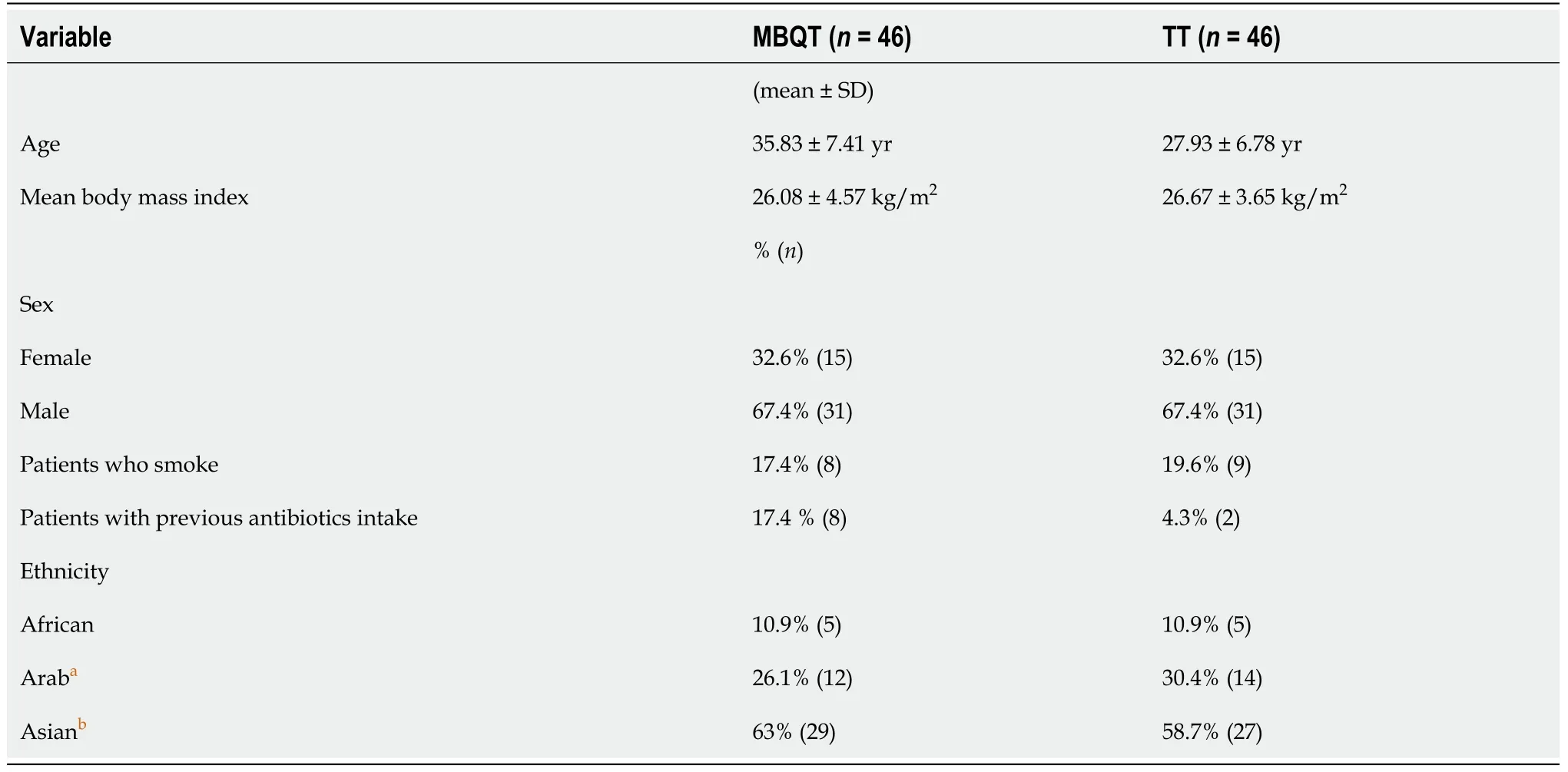
Binary logistic regression models were fitted in order to determine the efficacy of the MBQT in the eradication ofcompared with the standard TT. All assumptions of logistic regression were met. Of the predictor variables, only three were statistically significant: Nationality, smoking and therapy type (Table 2).
In conclusion, our study provides more evidence that 10-d modified B-quadruple therapy is a safe and effective therapeutic option for eradicatinginfection. This significant rate of success should promote such therapies to be considered as first line option in place of the old and declining TT protocol.
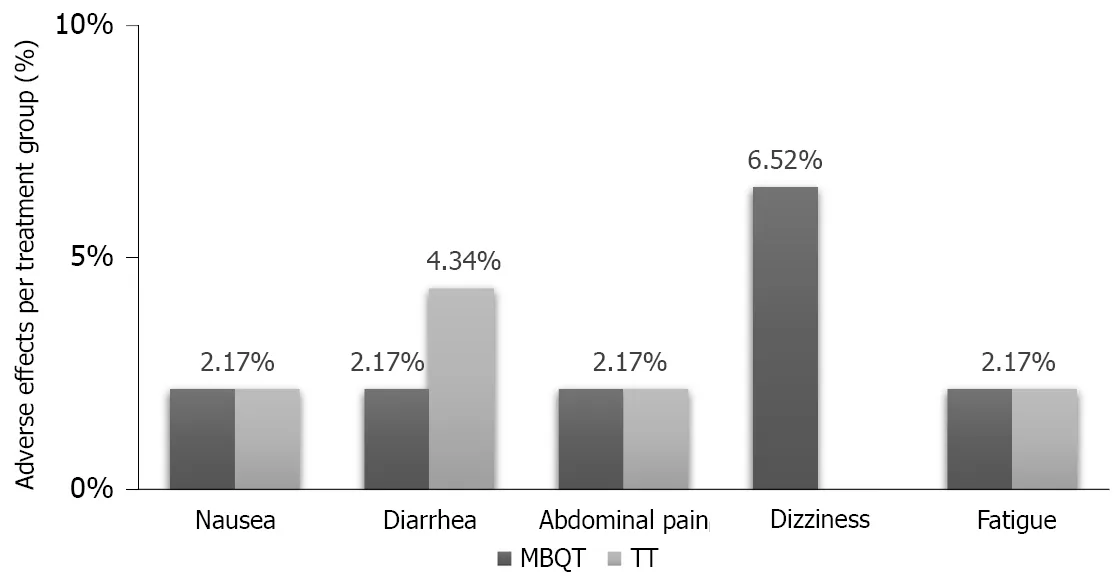
There were some adverse events that occurred in each of the two types of therapies. In the MBQT group, there was one occurrence (2.17% each) of nausea, abdominal pain and fatigue and three occurrences (6.52%) of dizziness. On the other hand, the TT group reported one occurrence (2.17% each) of nausea, diarrhea and fatigue and two occurrences (4.34%) of abdominal pain (Figure 2).
DISCUSSION
The present study was a prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled trial performed between 2018-2019. Physicians were not blinded to which treatment the subjects received. The patient population comprised 92 consecutive outpatients who presented to outpatient clinic with dyspepsia symptoms and were found to haveinfection.infection was diagnosed byC urea breath test (UBT) and reassessed 4 wk after the completion of the assigned treatment. The exclusion criteria were: Age < 18 years, existence of severe concomitant diseases, use of medications effective againstsuch as bismuth compounds, PPIs, or antibiotics during the last 3 mo, history of gastroduodenal surgery, pregnancy or lactation, chronic corticosteroid or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, history of allergy to PPI, macrolides or penicillin, alcohol abuse or drug addiction. Prior to enrolment, a written informed consent was obtained from all patients. This study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of NMC specialty hospital.
The recent Kyoto global consensus categorized-induced gastritis as an infectious disease and recommended performingeradication before premalignant changes develop to prevent gastric carcinogenesis[33]. However, the previously assigned first-line choice foreradication, which is a clarithromycin-based TT, has become a subject of argument in the medical field due to the worldwide growing resistance to clarithromycin, especially in developing countries[13]. In fact, several regimens have been proposed to overcome this critical concern. One of these regimens that added bismuth as adjuvant to other antimicrobial agents was found to exert synergistic effect that improved eradication rates by almost 30%[34]. In another clinical trial in China, a bismuth-quadruple therapy achieved a 92.7% eradication ofby ITT analysis[35]. Our study confirms the latter reports on a better eradication rate of the infection with MBQT. Recent studies from other countries suggested that the use of B-quadruple therapy is remarkably effective even in the presence of antibiotic resistance and prior treatment failures[36,37]. On the other hand, a 10-d course of quadruple therapy, consisting of the mucoprotective agent sofalcone added to rabeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin, demonstrated satisfactory treatment outcome witheradication rate being not less than 94% on the PP basis[31]. In addition to this, the concomitant use of PZ with TT regimen had previously shown promise in increasing the eradication rate ofinfection. In 1999, Kashimura[31] revealed thateradication rate can be significantly increased from 77.4% to 94.3% when PZ is added to the TT. In a more recent study, Tan[38] (2017) reported that the combined use of PZ with TT improved the eradication rate ofby 18.4% (ITT analysis) and 19.7% (PP analysis). This has been further validated by the results of our study where eradication rates were higher by 23.9% in MBQT group in comparison with that of TT group. Indeed, this points out the added benefit of using PZ concomitantly with bismuth in increasingeradication rates. However, further studies are needed to compare and evaluate the efficacy of PZ solelywhen combined with bismuth for the eradication of.
Many factors may affect eradication efficacy such as the physical structure of the patient, smoking habits, adherence to the prescribed regimen, genetic predisposition of cytochrome p450 2C19, which metabolizes PPIs, and frequency of strains resistant to antimicrobials[39,40]. In the present study, there were no significant differences in the baseline characteristics among the trial arms. Although the susceptibility ofto antibiotics was not assessed in our study, the risk of antibiotic resistance was minimized by excluding patients who had taken previous treatments effective against the organism. In addition to that, our study also showed that being a smoker increased the risk of treatment failure by 5-fold, which comes in concordance with other studies revealing the negative effect of smoking on the eradication rate[41,42]. Another interesting finding was ethnic variability regarding eradication success, where being of Arabic ethnicity increased the odds of eradication success. This could be pertained to ethnic disparities in dietary intake. Hołubiuk[43] revealed promising data regarding the antiactivity of certain food products present in fruits and vegetables, which is highly consumed in the Middle East[44]. Moreover, another possible factor that may account for such difference is the variability of antibiotics resistant strains among ethnicities or countries due to antibiotics abuse and use. However, the small sample size of our studied population questions the true significance of this finding.
In terms of safety, there has been concerns for bismuth induced neurotoxicity, mostly associated with chronic use[45]. However, in our trial, no bismuth related adverse effects were noted in the MBQT group. In addition, all-cause adverse events in both groups were tolerable and minor and had no influence on patient compliance.
ONCE there was a gentleman1 who married, for his second wife, the proudest and most haughty1 woman that was ever seen. She had, by a former husband, two daughters of her own humor, who were, indeed, exactly like her in all things. He had likewise, by another wife, a young daughter, but of unparalleled goodness and sweetness of temper, which she took from her mother,2 who was the best creature in the world.
By performing in depth analysis of our study, several limitations were found. Firstly, our study would have benefited from an analysis ofcultures and antibiograms. This was not feasible for technical and financial causes; hence, the exact role of antibiotic resistance (namely to clarithromycin) in eradication failure could not be evaluated. Another limitation was the study’s lack of double blinding and longterm follow-up period. A third technical limitation was the restricted availability of bismuth, which led to a smaller sample size than what we initially planned. Finally, the information on prior macrolide use was collected from patients using a questionnaire and may have therefore been subject to recall bias.
The rate of resistance of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection has been increasing worldwide. It is necessary to consider new alternatives to overcome the failure of H.pylori eradication rate.
CONCLUSION
Patients who received TT were 11 times more likely to have a positive UBT than those who received MBQT [adjusted odds ratio (aOR) = 11.44,= 0.004, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.179-60.07]. Moreover, Arabs were more likely to obtain negative UBT than Asians (aOR = 0.19,= 0.019, 95% CI 0.019-0.696). Furthermore, smoking seemed to increase the odds of persistentby 5-fold (aOR = 5.12,= 0.049, 95% CI: 1.005-26.097).
All data entry and statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS version 26.0 for Windows (SPSS, Armonk, NY, United States). The cure rate was then calculated for each arm. Chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test and independent-samples-test were used to compare the major outcomes between these groups.cure rate was evaluated by per protocol (PP) analysis. PP analysis included all patients who took at least 80% of each study medication as prescribed and returned for assessment ofcure. Multivariable analysis adjusted for sex, age, body mass index, smoking habits, previous antibiotics intake and ethnicity was performed. Avalue less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The nearer she approached the more miserable44 it appeared, and at length she saw a little old woman sitting upon the door-step, who said grimly: Here comes one of these fine beggars who are too idle to do anything but run about the country! Alas! madam, said Celandine, with tears in her pretty eyes, a sad fate forces me to ask you for shelter
Research motivation
There is shortage in reports on whether zinc carnosine is effective against H. pylori eradication.
Research objectives
Investigate the effect of triple therapy (TT) vs modified bismuth quadruple therapy against H. pylori eradication rate.
It was her, the young girl who came by every day to give him apples. After 12 years, after the war and in another country.....they had met again. What are the odds(,)? He proposed to her on that very night and told her he d never again let her go. They are still happily married today.
Research methods
Ninety-two patients with dyspepsia symptoms and positive 13C-urea breath test were randomly assigned in to the following two groups: TT group treated for 14 d using esomeprazole (40 mg twice daily), amoxicillin (1 g twice daily) and clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily). On the other hand, the modified bismuth quadruple therapy fortified with zinc carnosine was prescribed a 10-d of TT in addition to bismuth subcitrate (240 mg twice daily) and zinc carnosine (75 mg twice daily). A 13C-urea breath test was repeated after 4 wk from the completion of the eradication therapy.
Research results
The eradication rate was higher in the modified bismuth quadruple therapy group compared to that of the standard TT group (P = 0.003).
Research conclusions
Ten-day modified bismuth quadruple therapy is a safe and effective regimen for eradicating H. pylori infection.
Research perspectives
The first-line therapy for H. pylori eradication should be re-evaluated. Alternative regimens with higher eradication of H. pylori should be further investigated.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年1期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年1期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutation, infectivity,transmission, and vaccine resistance
- Clinical manifestations and prenatal diagnosis of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy: A case report
- Lunate dislocation with avulsed triquetral fracture: A case report
- Protein-losing enteropathy caused by a jejunal ulcer after an internal hernia in Petersen's space: A case report
- Eustachian tube teratoma: A case report
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in pregnancy: A case report
