PCT联合NEWS预警评分在诊断多发伤后MODS中的应用
余元霞 陈志明 李俊丽 马建
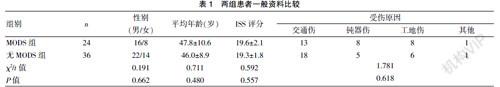
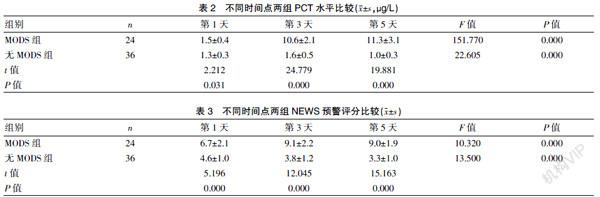
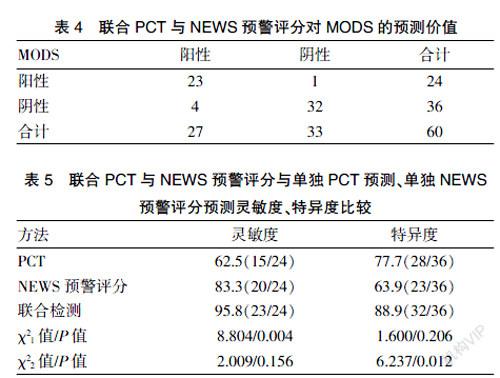
[摘要] 目的 探討PCT联合NEWS预警评分在诊断多发伤后MODS中的应用。 方法 选择2018年5月至2020年5月在我院急诊科治疗的多发伤患者60例的临床资料进行回顾性分析,根据是否发生MODS分为MODS组(24例)与无MODS组(36例)。比较入住急诊科后第1、3、5天PCT水平与NEWS预警评分,分析PCT水平与MEWS预警评分对诊断多发伤后MODS的预测价值。 结果 ①入住急诊科第1、3、5天,MODS组PCT水平均显著高于无MODS组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。②入住急诊科第1、3、5天,MODS组NEWS预警评分均显著高于无MODS组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。③以1.5 μg/L为界值,PCT值预测MODS的灵敏度为62.5%(15/24),特异度为77.7%(28/36),曲线下面积AUC为0.708。④以6分作为分界值,NEWS预警评分预测MODS的灵敏度83.3%(20/24),特异度63.9%(23/36),AUC为0.811。⑤PCT联合NEWS预警评分预测MODS的灵敏度23/24(95.8%),特异度32/36(88.9%)。 结论 患者发生多发伤后,PCT与NEWS预警评分可作为预测MODS的相关指标,两者联合对预测MODS具有较高的预测价值。
[关键词] 降钙素原;NEWS预警评分;多发伤;多器官功能障碍综合征
[中图分类号] R641 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0102-04
Application of procalcitonin combined with National Early Warning Score in the diagnosis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome after multiple trauma
YU Yuanxia CHEN Zhiming LI Junli MA Jian
Emergency Department,Zhejiang Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital (Hangzhou Red Cross Hospital), Hangzhou 310003, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application of procalcitonin (PCT) combined with National Early Warning Score (NEWS) in the diagnosis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) after multiple trauma. Methods The clinical datas of 60 patients with multiple trauma treated in the emergency department of our hospital from May 2018 to May 2020 were analyzed retrospectively.According to the occurrence of MODS,the patients were divided into MODS group (n=24) and non-MODS group (n=36). PCT levels and NEWS scores on the 1st,3rd and 5th day after admission to the emergency department were compared,and the predictive value of PCT levels and MEWS scores in the diagnosis of MODS after multiple trauma were analyzed. Results On the 1st,3rd and 5th day after admission to the emergency department,the level of PCT in MODS group was significantly higher than that in non-MODS group and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). On the 1st, 3rd and 5th day after admission to the emergency department, the NEWS score of MODS group was significantly higher than that of non-MODS group and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). With 1.5 μg/L as the cutoff value,the sensitivity of PCT value for predicting MODS was 62.5% (15/24),the specificity was 77.7% (28/36), and the area under the curve AUC was 0.708. ④With 6 points as the cut-off value,the sensitivity of NEWS score to predict MODS was 83.3% (20/24), the specificity was 63.9% (23/26) and AUC was 0.811.⑤The sensitivity and specificity of PCT combined with NEWS to predict MODS were 23/24 (95.8%) and 30/36 (88.9%), respectively. Conclusion After the occurrence of multiple trauma, PCT and NEWS can be used as related indexes to predict MODS, and their combination has high predictive value for MODS.

