PCI治疗STEMI发生再灌注损伤的危险因素分析
张欣 李小玲

[关键词] 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死;PCI;心肌缺血后再灌注损伤;危险因素
[中图分类号] R542.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0010-03
Analysis of risk factors of reperfusion injury of STEMI treated by PCI
ZHANG Xin LI Xiaoling
Department of Cardiology, Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310012, China
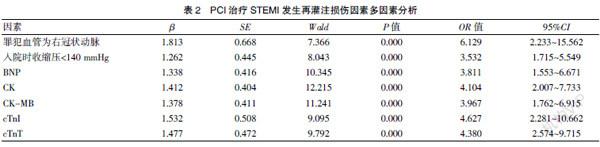
[Abstract] Objective To explore the risk factors of reperfusion injury of STEMI treated by PCI. Methods The clinical data of 162 STEMI patients who underwent PCI treatment in our hospital from January 2018 to June 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. The patient′s general information and clinical data were recorded,including patient gender, age, smoking history, BMI, history of hypertension, history of diabetes, history of stroke, family history of cardiovascular disease, time from onset to treatment, blood vessels of the offender, blood pressure, BUN, Scr, BNP, CK, CK-MB, TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C at admission, the FBG, cTnI, cTnT the next day after surgery.Single factor and multiple factors were used to analyze the influencing factors of reperfusion injury in STEMI treated by PCI. Results ①Univariate analysis showed that the culprit′s vessel was the right coronary artery, and the incidence of IRI was higher in patients with systolic blood pressure <140 mmHg at admission(P<0.05), the levels of BNP, CK, CK-MB, cTnI, cTnT in the IRI group were higher, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).②The results of multivariate analysis showed that the culprit′s blood vessel being the right coronary artery and the systolic blood pressure<140 mmHg on admission, BNP, CK, CK-MB, cTnI, and cTnT levels were independent risk factors for reperfusion injury in STEMI treated with PCI(OR=6.129, 3.532, 3.811, 4.104, 3.967, 4.627, 4.380, P<0.05). Conclusion The risk factors for reperfusion injury in STEMI treated by PCI include the culprit′s blood vessel being the right coronary artery, decreased systolic blood pressure at admission, and levels of BNP, CK, CK-MB, cTnI, and cTnT.This study indicates that the severity of the patient′s disease is closely related to reperfusion injury.
[Key words] Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PCI; Reperfusion injury after myocardial ischemia; Risk factors
急性心肌梗死仍然是嚴重威胁生命的疾病之一。ST段抬高型心肌梗死(ST segment elevation myocardial infarction,STEMI)是指具有典型的缺血性胸痛、持续超过20 min、血清心肌坏死标记物浓度升高并有动态演变、心电图具有典型的ST段抬高的一类急性心肌梗死。经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(Percutaneous coronary intervention,PCI)是指经心导管技术疏通狭窄甚至闭塞的冠状动脉管腔,改善心肌血流灌注的治疗方法,是目前临床上救治急性心肌梗死的有效方法之一[1-2]。再灌注损伤是指缺血的组织在恢复血液灌注后导致再灌注区细胞及局部血管网出现病理生理变化,导致组织进一步损伤。PCI后发生心肌缺血后再灌注损伤(Ischemi-reperfusion injury,IRI)降低再灌注的治疗效果,影响患者预后[3-4]。目前认为冠状动脉狭窄率、再灌注前低血压等与患者发生再灌注损伤有关[5]。本研究通过回顾性分析STEMI行PCI治疗患者的临床资料,分析发生再灌注损伤的影响因素,以期为临床预防提供参考,现报道如下。

