血脂水平与子宫内膜异位症关系的Meta分析
姬笑影 任琛琛 杨立 朱远航 李飞燕 杨欣 郑娅婷

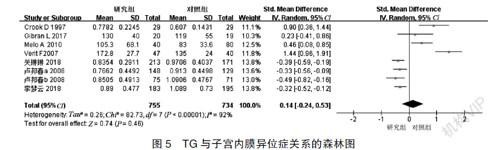
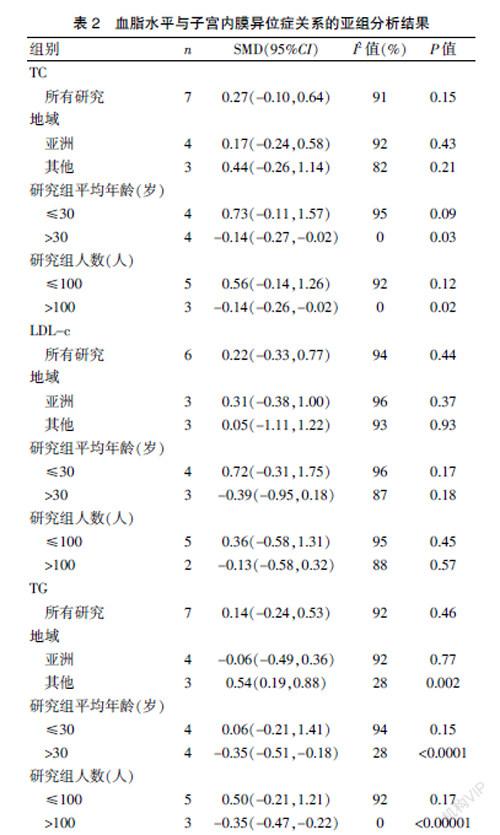
[摘要] 目的 探討人的血脂水平与子宫内膜异位症之间的关系。 方法 在线检索Pubmed、Web of Science、Scopus、中国知网、万方、维普数据库,收集人血脂水平与子宫内膜异位症相关性的研究,检索时间为建库至2020年12月。对其进行质量评估和数据提取后,应用RevMan5.3进行Meta分析。 结果 纳入文献7篇,共包括755例子宫内膜异位症患者,734例对照者。Meta分析结果:剔除异质性较高文献后,子宫内膜异位症患者HDL-c高于对照组,差异有统计学意义[SMD=0.36,95%CI(0.24,0.49),P<0.00001,I2=46%]。总胆固醇[SMD=0.27,95%CI(-0.10,0.64),P=0.15,I2=91%]、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[SMD=0.22,95%CI(-0.33,0.77),P=0.44,I2=94%]及三酰甘油[SMD=0.14,95%CI(-0.24,0.53),P=0.46,I2=92%]与子宫内膜异位症发病无相关性,且因异质性较大,行亚组分析发现纳入文献的地域、年龄、样本量均可能为异质性来源而影响结果。 结论 血脂水平可能与子宫内膜异位症相关,较高的高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平可能是子宫内膜异位症发生的危险因素,总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇及三酰甘油水平与子宫内膜异位症的关系尚需进一步证实。
[关键词] 子宫内膜异位症;血脂;胆固醇;三酰甘油;Meta分析
[中图分类号] R711.71 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0004-06
Meta-analysis of relationship between blood lipid levels and endometriosis
JI Xiaoying REN Chenchen YANG Li ZHU Yuanhang LI Feiyan YANG Xin ZHENG Yating
Department of Gynecology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the relationship between the level of blood lipid and endometriosis in human. Methods Online retrievals of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases were conducted to collect the studies on the correlation between the human blood lipid level and endometriosis. The retrieval period was from the establishment of the database to December 2020. After quality assessment and data extraction, Meta-analysis was performed by using RevMan5.3. Results Seven studies were included, including 755 patients with endometriosis and 734 controls. Results of Meta-analysis: HDL-c was higher in endometriosis patients than that in patients in the control group after literatures with higher heterogeneity were excluded, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD=0.36, 95%CI (0.24, 0.49), P<0.00001, I2=46%]. No correlations with the incidence of endometriosis were observed in total cholesterol [SMD=0.27, 95%CI (-0.10, 0.64), P=0.15, I2=91%], low density lipoprotein cholesterol [SMD=0.22, 95%CI (-0.33, 0.77), P=0.44, I2=94%] and triglycerides [SMD=0.14, 95%CI (-0.24, 0.53), P=0.46, I2=92%], which were caused by great heterogeneity. The region, age and sample size of the included literatures were all likely to influence the results due to their heterogeneity, which was found by subgroup analysis. Conclusion The blood lipid level may be related to endometriosis, and high HDL cholesterol level may be a risk factor for the occurrence of endometriosis. The relationship between total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels and endometriosis needs to be further confirmed.

