Effects of Dendrobium candidum polysaccharides on microRNA-125b and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in diabetic cataract rats
Zi-Yang Chen,Qian Lan,Sheng Chen,Yan-Hong Hu*,Fa-Jie Ke,Jun Hu,Chun-Yan Feng,Ming-Xin Qi,Xiu-Rong Huang
1Comprehensive Clinic of Fujian Academy of Chinese Medicine,Fuzhou 350003,China.2Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Fuzhou 350122,China.3Department of Opthalmology,The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Traditional Chinese Medical University,Fuzhou 350003,China.
Abstract Background: Diabetic cataract is a common complication and a lens disorder in diabetes.Moreover, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide (DOP) is found to alleviate diabetes complications.Consequently, microRNA-125b and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways play significant roles in diabetes.However, the mechanism and the effect of DOP on diabetic cataract remains unknown.Methods: Wistar male rats were randomly assigned to the control, model, and DOP groups.Diabetes was induced with streptozotocin.Furthermore, DOP was orally given for 12 weeks.The Lens Opacities Classification System III was used to evaluate lens opacity by slit-lamp microscope.The lens was then harvested for testing the mRNA expression of microRNA-125b, ERK1, ERK2, Raf and Ras using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.The protein expression of ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras was detected using the Western blot analysis.The targets of microRNA-125b were predicted in miRWalk 2.0.These targets were obtained from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway.Results:The lens opacities of the rats in the control group were almost at C0N0.Moreover, the majority of the lens opacities in the model group were C3 to C4 and N1 to N2, and were mostly at C1 to C2 and N0 to N1 in the DOP group.The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).Furthermore, the microRNA-125b expression in the model group is significantly higher compared with the control group.Conversely, the microRNA-125b expression in the DOP group is significantly decreased (all P < 0.05).The mRNA expression of ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras in the model groups were upregulated compared with those of the control group.However, the ERK1 and Raf mRNA expressions of the DOP group were lower compared with the model group(all P < 0.05).The protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras in the model group was significantly increased compared with those of the control group.The protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras in the DOP group was significantly lower compared with the model group(all P < 0.05).Moreover, 3,378 genes of the microRNA-125b target were gained from the miRWalk.After Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways analysis in Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, 246 items were gained including Ras (rno04014) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (rno04010) signaling pathways.A positive correlation exists between microRNA-125b and mRNA expression of ERK1, ERK2, Raf and Ras (r = 0.940, 0.841, 0.666,and 0.768; all P < 0.05).Conclusion: DOP can alleviate the severity of the opacity of the lens in diabetic cataract rats via microRNA-125b and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Thus, microRNA-125b has something to do with the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Keywords: Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide; microRNA-125b; mitogen-activated protein kinase; diabetic cataract
Tradition
The Chinese herb Dendrobium candidum is honored as the first of nine Chinese divine medicine known as gold in medicine.The application of Dendrobium candidum has been recorded in Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica at the end of the Eastern Han Dynasty(25 C.E.–220 C.E.).Moreover,modern pharmacological studies have shown that Dendrobium candidum has many effects(e.g.,hypoglycemic and anti-aging).Its polysaccharide has a strong antioxidant activity.Consequently,Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide could reduce pentylenetetrazol-induced brain inflammation and seizures in rats with epilepsy by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Background
The number of diabetic patients continuously increases as the population ages and the living and eating habits change [1].Diabetic patients with eye complications (e.g., diabetic cataract, retinal hemorrhage, macular edema, and so on) are not uncommon.Many studies have shown that the microRNA (miRNA) expression in multiple organs and tissues of diabetic patients (e.g., the upregulation of miRNA-125bexpression in patients with type 2 diabetes) is different compared with normal people [2, 3].Some scholars have recently found different microRNA expression in the lens of diabetic patients[4–6].Moreover, miR-125b is involved in cataract formation [7].The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway is involved in many diseases including cataract development[8].Thus, a diabetic rat model was established by streptozotocin in this study to observe the miR-125b expression and MAPK signaling pathway in diabetic cataracts.
The Chinese herb Shihu (Dendrobium candidum) is honored as the first of nine Chinese divine medicine and is known as gold in medicine.The application of Dendrobium candidum has been recorded in Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica at the end of the Eastern Han Dynasty (25 C.E.–220 C.E.) [9].Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Dendrobium candidum has many effects(e.g., hypoglycemic and anti-aging).Its polysaccharide has a strong antioxidant activity[10].Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide (DOP) could reduce pentylenetetrazol-induced brain inflammation and seizures in rats with epilepsy by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway [11].The important regulatory targets on MAPK signaling pathways include extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK), Ras, Raf, and so on.In this study, the expression of miR-125b, ERK, Raf, and Ras in the lens of diabetic cataract model after DOP was detected.
MiRWalk2.0 involves 12 predicted algorithms (Targetscan,RNAhybrid, RNA22, PITA, Pictar2, miRWalk, Microt4, miRNAMap,miRDB, mirbridge, miRanda, and miRMap) [10].The target genes of miR-125b can be predicted in this platform.These targets are obtained from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG) pathway.At the same time, the correlation between miR-125b and ERK1, ERK2,Raf, and Ras mRNA expression was analyzed.Furthermore, this study illuminated the role of DOP and its potential mechanism in reducing diabetic cataracts.
Materials and methods
Diabetic rat model and groups
Wistar clean-grade male rats (180 ± 20 g) were provided by Fujian Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine(license number: SCXK (Min)2012-0001, China).The rats were kept and bred in the Animal Center at the Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine following the National Standards (Gb14925-2001).The ambient environment was set to a humidity of 60% ± 10% and a temperature of 25°± 1 °C.Ten rats were randomly chosen as the normal group, and the remaining 20 rats were subjected to the diabetes model.The diabetes model was induced by intraperitoneal injection of 60 mg/kg streptozotocin(S17049, Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., China).Consequently, the blood glucose was measured 72 h after injection.A value > 16.7 mmol/L was defined as diabetes.Diabetic rats were randomly assigned to groups with (10 rats) or without (10 rats) DOP treatment.
Ethics
This study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.These animal experiments were conducted following the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (approved number:FJATCM-IAEC2019014).
Preparation of DOP and DOP treatment
DOP was prepared by hot-water extraction and alcohol precipitation.Moreover, Dendrobium powder was added to distilled water at a ratio of 1:50.It was then placed in a water bath for 1.5 h at 85 °C.The filter residue was re-extracted twice.The filtrates were combined and concentrated to a certain volume, and anhydrous ethanol was slowly added with continuous stirring.Samples were left for extraction overnight at 4 °C when the alcohol concentration of the mixture reaches 80%.Finally, they were filtered and freeze-dried.DOP was gained and its yield was about 15%.Moreover, glucose dried to constant weight was used as standard.The DOP purity was > 85%.DOP powder (200 mg; Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd.,China) was dissolved in 10 mL sterilizing injection water.DOP was given by perfusion at a dose of 0.1 g per kilogram twice daily for 12 consecutive weeks.The DOP dosage was determined based on the experience of previous studies (accepted by China Journal of Chinese Ophthalmology).An equivalent volume of distilled water was used as control.All rats were fasted for 12 h after the last administration.All rats were then executed by spinal cord dislocation, and the lens was harvested.
Lens opacity
The Lens Opacities Classification System II [12] was used to evaluate lens opacity using a slit-lamp microscope.The system by Chylack Jr.uses a set of colored slit-lamp and retroillumination transparencies to grade different degrees of nuclear, cortical, and subcapsular cataracts.
Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis
The total RNA of the lens was obtained using Trizol reagent, RNAiso Plus (Takara, 9109, Japan).Subsequently, miRNA was reversed to cDNA by PrimeScriptTM RT reagent kit (Takara, RR037A, Japan).Moreover, ChamQ SYBR® qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, Q311-02/03,China)was applied to detect the expression of miR-125b, ERK1,ERK2,Raf, and Ras in quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis.After 30 s of 95 °C predenaturation, 40 cycles were entered: 95 °C, 10 s; 56 °C, 30 s; 72 °C, 30 s; 95 °C, 15 s; 60 °C, 1 min;95 °C, 15 s; and 60 °C, 15 s.Furthermore, U6 was utilized as an internal control, and the 2−ΔΔCtmethod was used to normalize the target gene expression levels.Primer sequences were as follows (Table 1).

Table 1 Primer sequences
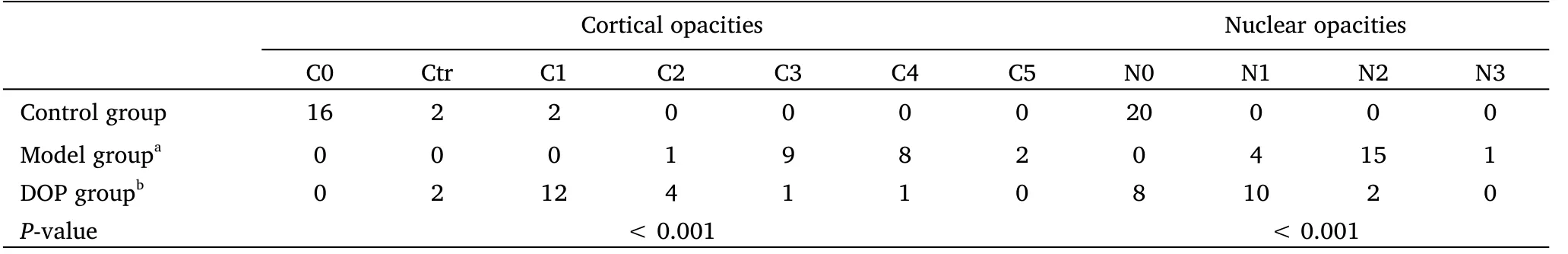
Table 2 Effect of DOP on lens opacity in diabetic rats
Western blot analysis
Total tissue proteins were isolated from the lens using a protein extraction kit (Keygen, KGP702, China).Protein concentrations were determined using a bicinchonininc acid protein assay kit (Thermo,23227, USA) and separated via 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.The protein bands were then electrotransferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Millipore,IPVH00010, USA).Thereafter, the membranes were blocked in 5%skimmed milk and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h and overnight at 4 °C with the following rabbit antirat primary antibodies against Ras(1:1,000), Raf 1 (1:1,000), ERK1 + ERK2 (1:1,000), and GAPDH
(1:1,000; all obtained from Abcam, UK).Additionally, the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat antirabbit secondary antibody (Proteintech, USA) for 1 h at 37 °C followed by treatment with ECL (Bio-Rad, USA), and the intensity of protein bands were detected using Image Lab™Software (Bio-Rad,USA).
Prediction of regulatory mechanisms between miR-125b
The miRNA-mRNA interactions were identified by miRWalk 2.0 [13],which involves 12 predicted algorithms (Targetscan, miRWalk,RNAhybrid, RNA22, PITA, Pictar2, Microt4, miRNAMap, miRDB,mirbridge, miRanda, and miRMap).In this web, this study predicted the targets of miR-125b.These targets were obtained from the KEGG pathway.KEGG pathways with aP-value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Statistical analysis
The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences,version 21.0(IBM, USA)was utilized to analyze the data.The Kruskal-Wallis H rank-sum test was used to analyze the differences of lens opacities.Single-factor analysis of variance was used in comparing between groups, and the least significant differences and Student-Newman-Keuls tests were used in a pairwise comparison.The correlation used the two-sided Pearson correlation coefficients and thez-test.Moreover,P< 0.05 was defined as significant.
Result
The severity of lens opacity
The lens opacity of the rats in the control group was almost C0N0; the majority of the lens opacities in the model group were C3 to C4 and N1 to N2, and was mostly at C1 to C2 and N0 to N1 in the DOP group.The lens opacities in the model group were higher compared with the control group.Conversely, the lens opacities in the DOP group were lower compared with the model group.The difference was statistically significant (P<0.001) (Table 2 and Figure 1).
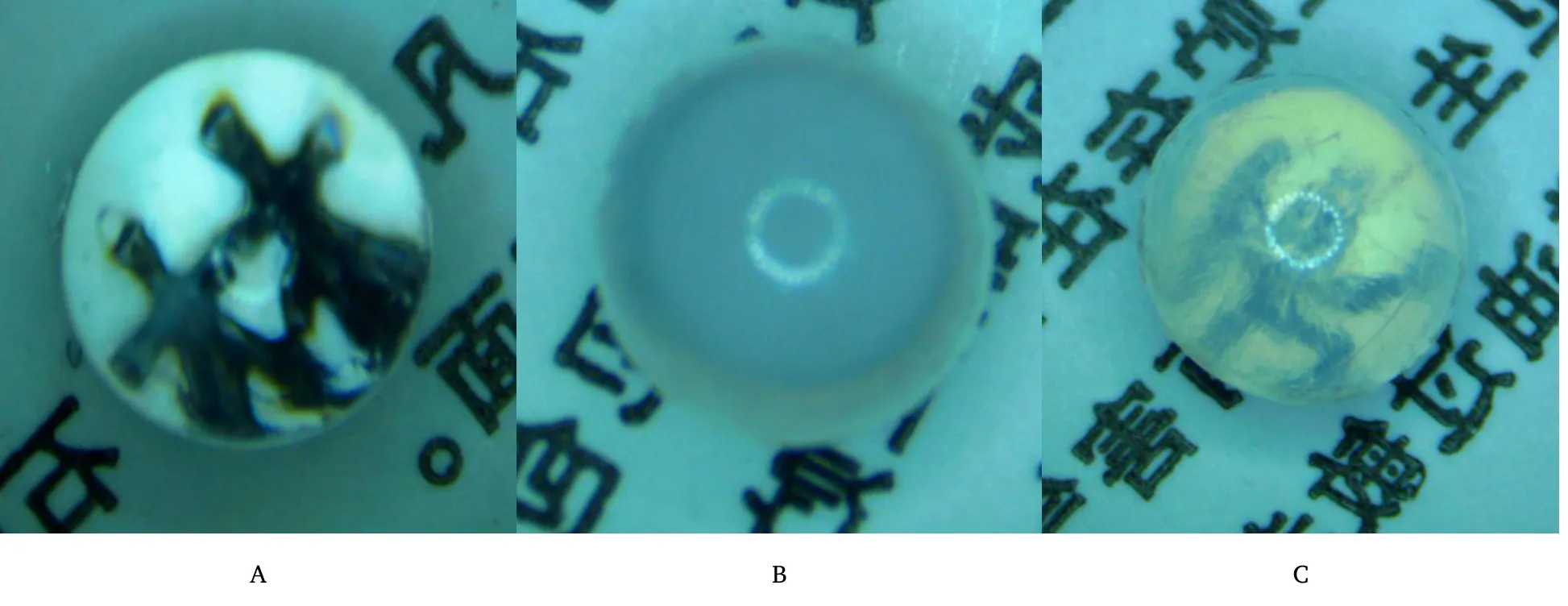
Figure 1 DOP alleviates the lens opacity in diabetes model rats.A The lens were harvested from the control group.It was transparent and the word in the newspaper can be seen.B This lens was gained from the model group.It was so opaque that no word can be seen.C The lens in the DOP group presented with mild opacity and the black word could be seen.DOP, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide.
The mRNA expression of miR-125b in the lens of the three groups by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis
The mRNA expression of miR-125b in the model group was significantly higher compared with that of the control group.Moreover, the expression in the DOP group significantly decreased compared with the control and model groups (allP< 0.05) (Figure 2).
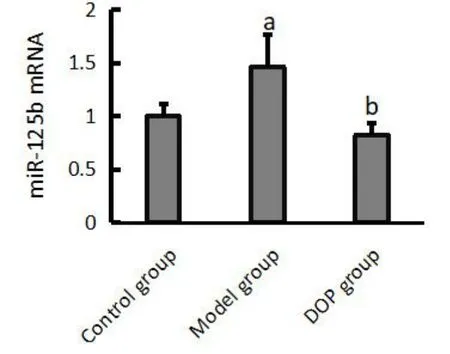
Figure 2 mRNA expression of miR-125b in the lens.a, compared with the control group, P < 0.05; b, compared with the model group,P <0.05; DOP, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide.
The mRNA and protein expression of key gene in MAPK signaling pathway
The ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras mRNA expression in the model group was upregulated compared with those of the control group(P< 0.05).However, the mRNA expression of ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras in the DOP group was downregulated compared with those of the model group.Consequently, a significant difference in ERK1 and Raf mRNA expression exists in the DOP and model groups (P< 0.05).Moreover,no significant difference in ERK2 and Ras mRNA expression exists in the DOP and model groups(P> 0.05) (Figure 3).
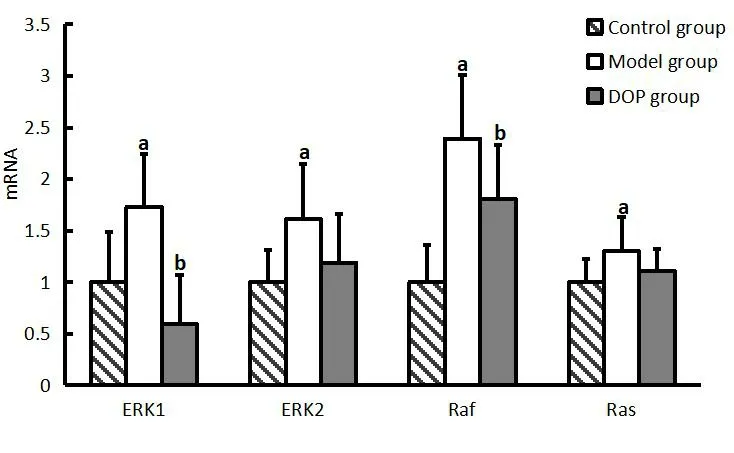
Figure 3 ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras mRNA expression in the lens.a, compared with control group, P < 0.05; b, compared with model group, P < 0.05.ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinases; DOP,Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide.
The protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras in the model group was significantly increased (allP< 0.05) compared with the control group.Conversely, the protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras in the DOP group was significantly lower compared with the model group(allP< 0.05) (Figure 4).
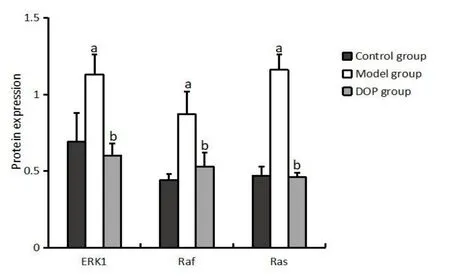
Figure 4 The protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras.a,compared with the control group, P < 0.05; b, compared with the model group, P < 0.05.ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinases;DOP, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide.
Prediction of miR-125b regulating signaling pathway
Of the genes associated with miR-125b, 3,378 target genes were obtained from the miRWalk.Moreover, 246 items were gained after KEGG pathways analysis in Gene Set Enrichment Analysis.TheP-value < 0.05 was shown in Table 3.It includes MAPK (rno04010)and Ras (rno04014) signaling pathways.Moreover, 32 and 29 miR-125b-related targets focused on MAPK and Ras signaling pathways,respectively.
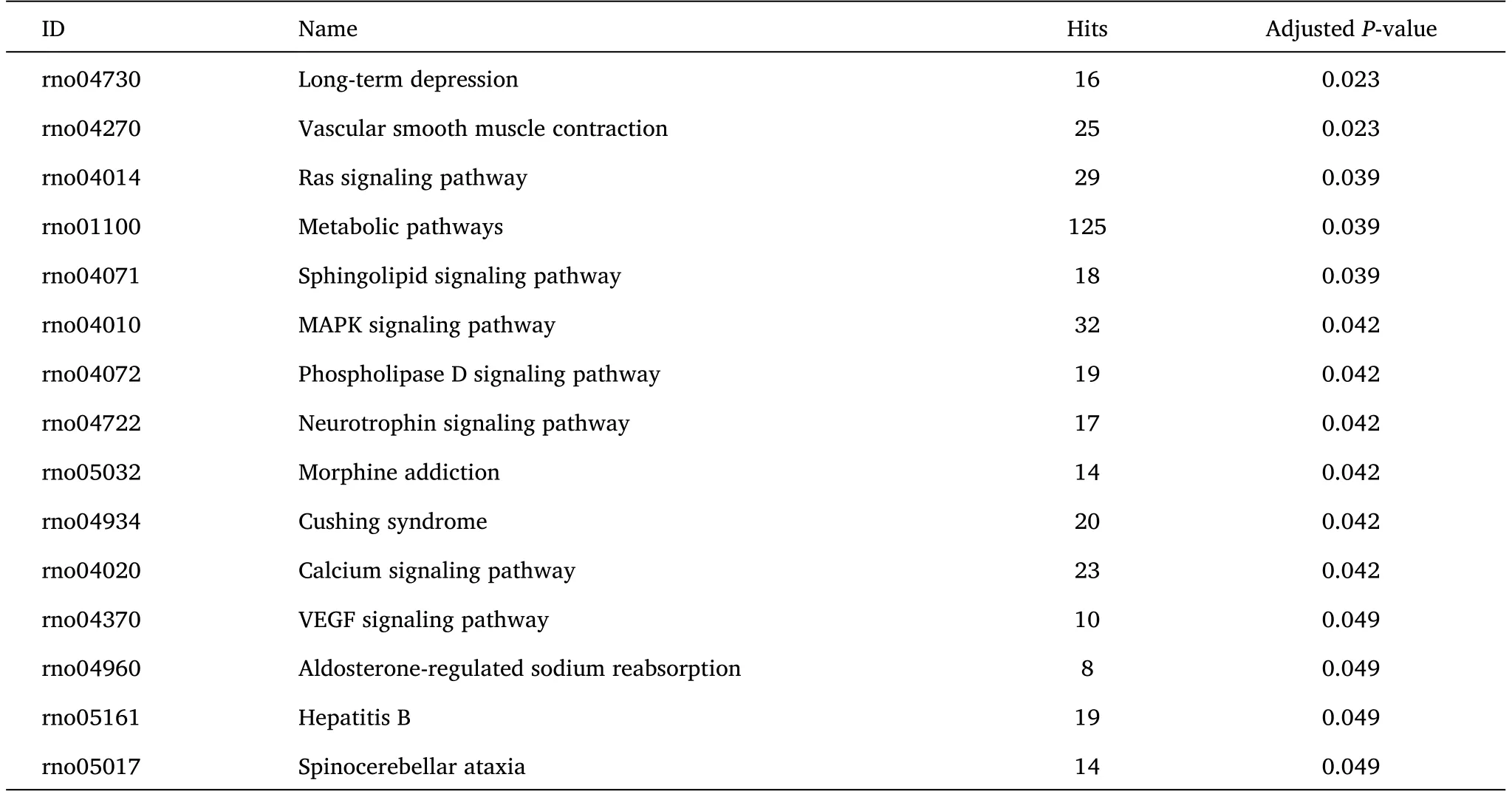
Table 3 KEGG pathways analysis
The correlation between miR-125b and ERK1, ERK2,Raf, and Ras mRNA
The correlation between the expression level of the miR-125b and four targets is shown in Figure 5.All positive correlations were noted between miR-125b and mRNA expression of ERK1, ERK2, Raf and Ras(r= 0.940, 0.841, 0.666, and 0.768; allP< 0.05).
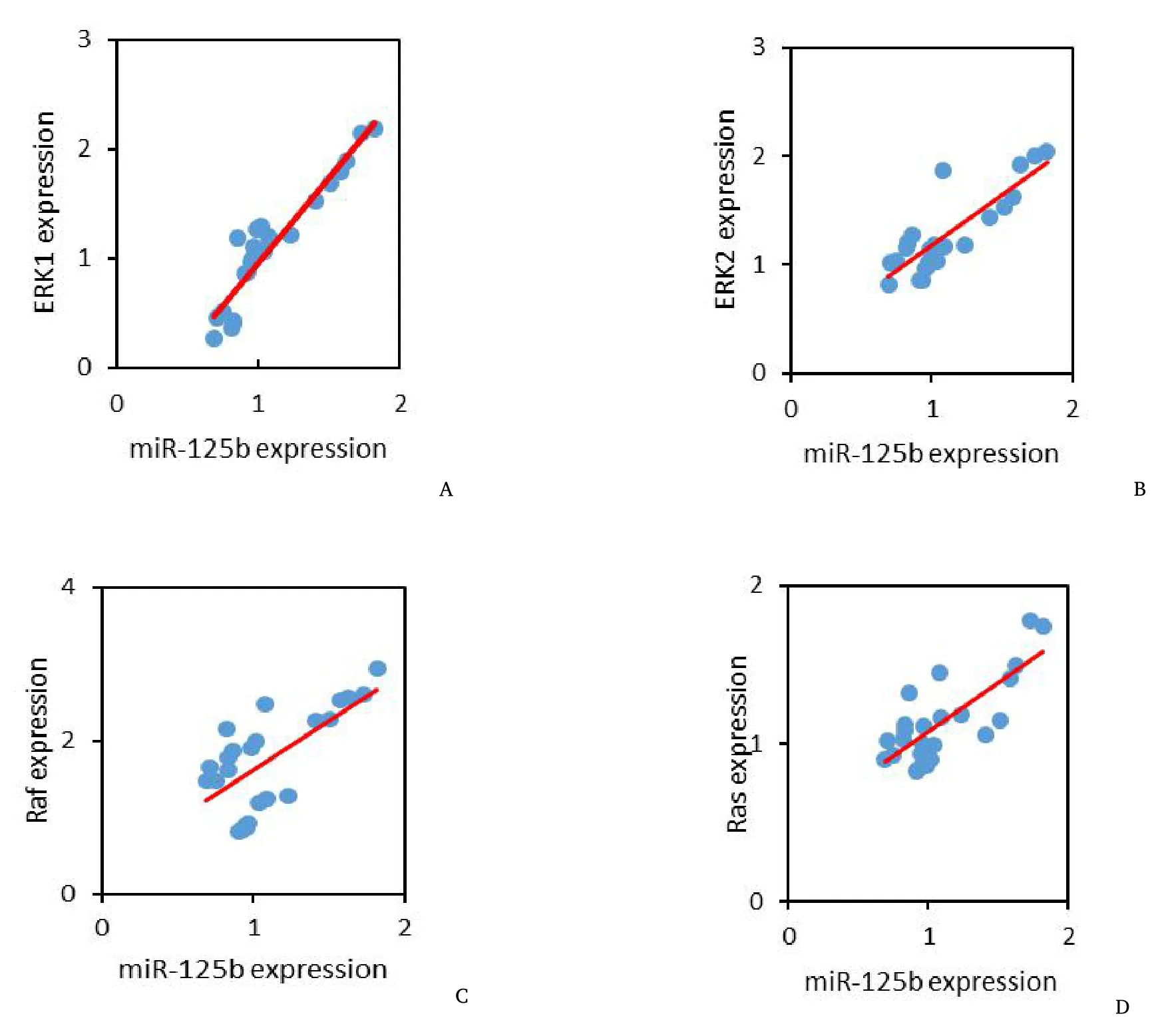
Figure 5 The relationship between miR-125b, ERK1,ERK2, Raf, and Ras mRNA.ERK1, extracellular regulated protein kinases 1.
Discussion
Diabetic cataracts are not uncommon, and their mechanism is still unclear.Dendrobiumhas many effects (e.g., hypoglycemic and
anti-aging) and was used to treat diabetes and its complications (e.g.,liver metabolism disorders [14] and diabetic cataract [15]).Consequently, the different active components ofDendrobiumwere identified to delay the process of lens opacity [16].This study also showed that DOP can alleviate the opacity of diabetic cataracts.
Studies have shown that the expression of miR-125b upregulates in patients with type 2 diabetes or cataract [2, 7].This study established by streptozotocin a model of diabetic cataract rats.Moreover, the higher miR-125b expression in the lens of the model groups was observed.However, DOP can downregulate the mRNA expression of miR-125b in the DOP group.The miR-125b may be a target for DOP alleviating the lens opacity.The expression of three main targets in MAPK signaling, ERK, Raf, and Ras were tested in this study.The ERK1, ERK2, Raf, and Ras mRNA expression was upregulated in the model group.However, it was downregulated in the DOP group.The protein expression of ERK1, Raf, and Ras in the model group was significantly increased compared with that of the control group.Furthermore, the protein expression of the ERK1, Raf, and Ras DOP group was significantly lower compared with that of the model group.Thus, DOP can alleviate cataracts via the MAPK signaling pathway.
Studies have found that miR-125b is closely associated with ERK and Raf signaling pathways in different diseases [13, 17, 18].The potential signaling pathway in miRWalk 2.0 identified miR-125b-regulated potential signaling pathways.MiR-125b can regulate the MAPK signaling pathway.The miR-125b mRNA expression was found to correlate with ERK1, ERK2, Ras, and Raf through the correlation analysis.Although some studies indicated that the MAPK signaling pathway plays a significant role in diabetic cataracts [8].The relationship that miR-125b can regulate MAPK signaling pathway in diabetic cataracts was rarely reported.This study preliminarily showed that miR-125b had something to do with the MAPK signaling pathway in the lens of diabetic rats.DOP may mediate miR-125b and MAPK signaling pathways to alleviate cataracts.
This study has some limitations.Specifically blocking the miR-125b expression in animals is difficult.Thus, more cell experiments should be done to identify whether the possibility that miR-125b regulates MAPK signaling in diabetic cataracts exists.
Conclusion
DOP can alleviate the severity of the lens of the opacity of diabetic cataract rats.Moreover, it may be via miR-125b and MAPK signaling pathways.Thus, miR-125b has something to do with the MAPK signaling pathway.
 Traditional Medicine Research2021年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2021年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The protective effect of a standardized hydroalcoholic extract of Prosopis farcta(Banks&Sol.)J.F.Macbr.fruit in a rat model for experimental ulcerative colitis
- Neuroprotective effect and mechanism of daidzein in oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury based on experimental approaches and network pharmacology
- Understanding the prevention and cure of plagues in Daoist medicine
- Efficacy of Xianglian pill for antibiotic-associated diarrhea:a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
- Research advances concerning the mechanism of glucocorticoid resistance in relation to traditional Chinese medicine for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Light and color therapy: the role of light and color in architecture from the perspective of traditional Persian medicine
