Efficacy of Xianglian pill for antibiotic-associated diarrhea:a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Xin Zhou,Rui Gao,Xiao-Bo Zhang,Tao Shen,Kun-He Xu
1School of Basic Medicine,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu 611137,China.
Abstract Background: Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is a clinical common symptom of antibiotics overuse and occurs in 5%–70% of adults.Xianglian pill has been traditionally considered as an efficient treatment of diarrhea and gastrointestinal diseases for thousands of years.However, no systematic review and meta-analyses have focused on its positive effects.Hence, this protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis was developed to evaluate the effect and clinical safety of Xianglian pill on treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea.Methods: All randomized controlled trials published in Chinese and English and assessed use of Xianglian pill for antibiotic-associated diarrhea will be included.Databases of PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Biomedical Literature, Wanfang, and Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database will be searched for randomized controlled trials from their inception until November 16, 2020.Primary outcomes will be the incidence of diarrhea and adverse events, and secondary outcomes will be bowel movements and microbiome characteristics.Two authors will extract data and assess the risk of bias independently.Risk ratio will be used to evaluate the results, and meta-analyses will be conducted using STATA 15.0 software.The review aims to demonstrate the effectiveness of Xianglian pill in the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Keywords: protocol; Xianglian pill; Chinese herbal; antibiotic-associated diarrhea; systematic review;traditional Chinese medicine
Tradition
Xianglian pill is a known classical prescription in Chinese history,which is composed of two herbal powders,namely,Coptidis RhizomaandAucklandiae Radixwhich is processed withFructus Evodiae(4:1,w/w).It was first recorded in theCollection of Formulas of Minister of Militarywritten by Li Jiang in the Tang Dynasty(written in 815 C.E.to 821 C.E.)and later officially revised inPrescriptions of Peaceful Benevolent Dispensaryin the Song Dynasty(written in 1107 C.E.to 1110 C.E.).This book is deemed as the first pharmacopoeia compiled by the government in the history of China,and many prescriptions recorded in the book are still widely applied in clinical practice.Xianglian pill is extensively administered in the treatment of gastrointestinal disease,hematochezia,enteritis,and bacillary dysentery and commended highly by famous Chinese doctors throughout the ages.
Background
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) is a common complication of overexposure to antibiotics, which cannot be explained by any other reasons [1].Epidemiological investigations have indicated that the occurrence of AAD usually varies from 5% to 39% [2].The main mechanism of AAD was considered an imbalance in intestinal flora due to the destruction of normal flora and excessive proliferation of conditionally pathogenic bacteria, interaction with the mucosal barrier, and intestinal immune system, which were induced by antibiotics [3].In recent decades, the incidence of AAD is gradually increasing globally because of the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics[4].Clinical symptoms of AAD usually take various forms, ranging from self-limiting diarrhea to severe pseudomembranous colitis,particularly inClostridium difficileinfections, which can be severe and even fatal [5].Infectious AAD caused byClostridium difficileovergrowth accounted for 10.0%–25.0% of AAD, which causes serious adverse reactions in older people, children, and people with low immunity, and the mortality rate can reach up to 24% [6, 7].The prevalence ofClostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in developing countries was higher than that in developed countries.The incidence rate ofClostridium difficileinfections among patients with diarrhea in Latin America and Asia were 19% and 12%, respectively, and that in China was up to 20% [8].
At present, the clinical management of AAD includes discontinuation or replacement of antibiotics, administration of antidiarrheal agents, antibiotic therapy, probiotics agent therapy, and clinical surgery [9].Probiotics is regarded as “live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host,” conferring advantages in counteracting AAD [10].However, because of the strain specificity of probiotics, heterogeneity in antibiotic dose, and clinical manifestation of various infections, the clinical efficacy of probiotics has been challenged [11].Therefore, an alternative therapy for ADD treatment is urgently needed.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has attracted wide attention because of its advantages in treating diarrhea over hundreds of years[12].As regards safety, TCM has attracted worldwide attention owing to its effectiveness on ADD and few adverse reactions [13].The Xianglian pill (XLP) is a known classical prescription in Chinese history, which is composed of two herbal powders, namely,Coptidis RhizomaandAucklandiae Radixwhich is processed withFructus Evodiae(4:1, w/w).It was first recorded inCollection of Formulas of Minister of Militarywritten by Li Jiang in the Tang Dynasty (written in 815 C.E.to 821 C.E.) and later officially revised inPrescriptions of Peaceful Benevolent Dispensaryin the Song Dynasty (written in 1107 C.E.to 1110 C.E.).It is a widely administered treatment of gastrointestinal disease, hematochezia, enteritis, and bacillary dysentery and commended highly by famous Chinese doctors throughout the ages [14].With the development of TCM, XLP is used clinically as a patent Chinese medicine to treat abdominal pain and diarrhea in recent decades (China Food and Drug Administration approved No.Z42020398) [15].In addition, XLP is applied in combination with other Western drugs to treat ulcerative colitis,contributing to highly improvement of its clinical efficacy [16].Modern studies have demonstrated that XLP possesses antimicrobial,anti-inflammatory, and analgesic activities [14].In addition,Coptidis RhizomaandRadix Aucklandiaehave been confirmed to exert various pharmacological activities (Figure 1).Coptidis Rhizomais a traditional Chinese medicine derived fromCoptis ChinensisFranch.Previous evidence have shown that it possesses various pharmacological activities, including antidiarrheal [17], anti-inflammatory [18],antimicrobial [19], anticancer [20], and antidiabetic activities [21].Radix Aucklandiaeis an extract of the Chinese herbAucklandia lappaapplied for preventing digestive disorder.Studies have demonstrated thatRadix Aucklandiaehas wide beneficial pharmacological effects involving anti-ulcer [22], anti-inflammatory [23], and anticancer activities [24].Meanwhile, a study confirmed the therapeutic effect of XLP on treating AAD by ameliorating intestinal microbiota disorders and reducing mucosal damage [14].However, consistent evidence about the positive AAD outcomes of XLP is currently insufficient.Thus,our objective was to systematically review the efficacy and safety of XLP in AAD prevention or treatment.

Figure 1 The whole plant of Coptidis Rhizoma,Radix Aucklandiae and their medicinal sites
Methods
Protocol registration
This current systematic review protocol was registered on INPLASY database with the number of INPLASY2020100112.Complete registration information is available on the website of the International DOI Foundation (https://doi.org/10.37766/inplasy2020.10.0112).The present protocol will be implemented according to the instructions of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses[25].
Criteria for included studies
Types of studies.Eligible studies are randomized controlled trials with high quality and have defined outcomes of diseases caused by antibiotics.Eligible randomized controlled trials mainly focused on the treatment and prevention of AAD,Clostridium difficileinfections,inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, nosocomial infections, acute pediatric diarrhea, and travelers’ diarrhea.The exclusion criteria will be as follows: diarrhea within the previous 30 days, record of a severe or generalized infection, history of severe chronic disease (e.g., cancer, tuberculosis, and inflammatory bowel disease), chronic gastrointestinal disorders, immune-deficient condition, allergy or hypersensitivity to any substance under investigation, exposure to laxatives, antidiarrheal drugs, or any probiotics within 14 days of randomization.In these trials, XLP was administered and compared with active, placebo, or no control group.
Types of patients.Participants (age 6 months to 80 years) are men and women who underwent antibiotic therapy for any reason as outpatients or inpatients.
Types of interventions.Interventions in the control group included blank, placebo, or routine drug therapy such as metronidazole and vancomycin for AAD.When XLP is modified by an additive Chinese herb, the syndrome-differentiation (it is the comprehensive analysis of clinical manifestations gained by observation, listening, questioning,and pulse analysis procedures, which is used to guide the choice of treatment) guideline of TCM is used to determine XLP as the primary herbal medicine.Moreover, intake of herbal foods, nutritional supplements, or no intervention will be ruled out.
Types of controls.Studies with control groups that received routine medication alone, health education, placebo, non-traditional Chinese active agents, or no treatment will be eligible for inclusion in the review.
Outcomes.Primary outcomes: (1) incidence of diarrhea or AAD as defined previously [26] (The consistency of stools was assessed based on “Bristol Stool Form Scale”.This is a seven-point scale that ranges from “separate hard lumps, like nuts” to “watery, no solid pieces” and shows important correlation between the scale scores of a subject’s stools and the measured whole-gut transit time [27].This scale is a water closet-relevant scale with seven items and descriptions written in simple language, which has been confirmed and recommended for research by an international working party [28].); (2) all types of adverse events, including bacteremia and meningitis [29].Secondary outcomes: (1) frequency of bowel movements (weekly mean number of bowel movements) [30];(2)vital signs(resting heart rate and blood pressure) and blood parameters (e.g., complete blood count,electrolytes, and glucose); (3) microbiome characteristics evaluated using a direct fecal smear, examined with Gram staining method, and analyzed using under a microscope [31].
Searching strategy
Literature search will be conducted not only in English databases but also in Chinese electronic platforms, including PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Chinese Biomedical Literature, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, VIP database for Chinese technical Periodicals, and Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform from database inception to November 2020.
The search strategy will use a keyword and free word combination.The keywords will include “Xianglian pill”, “diarrhea”, “antibiotic”,and “randomized controlled trials”.Two authors (Zhou X and Zhang XB) will take charge of this work independently.A sample searching strategy for PubMed is shown in Table 1, and an analogous template will be used for searching other relevant literatures.
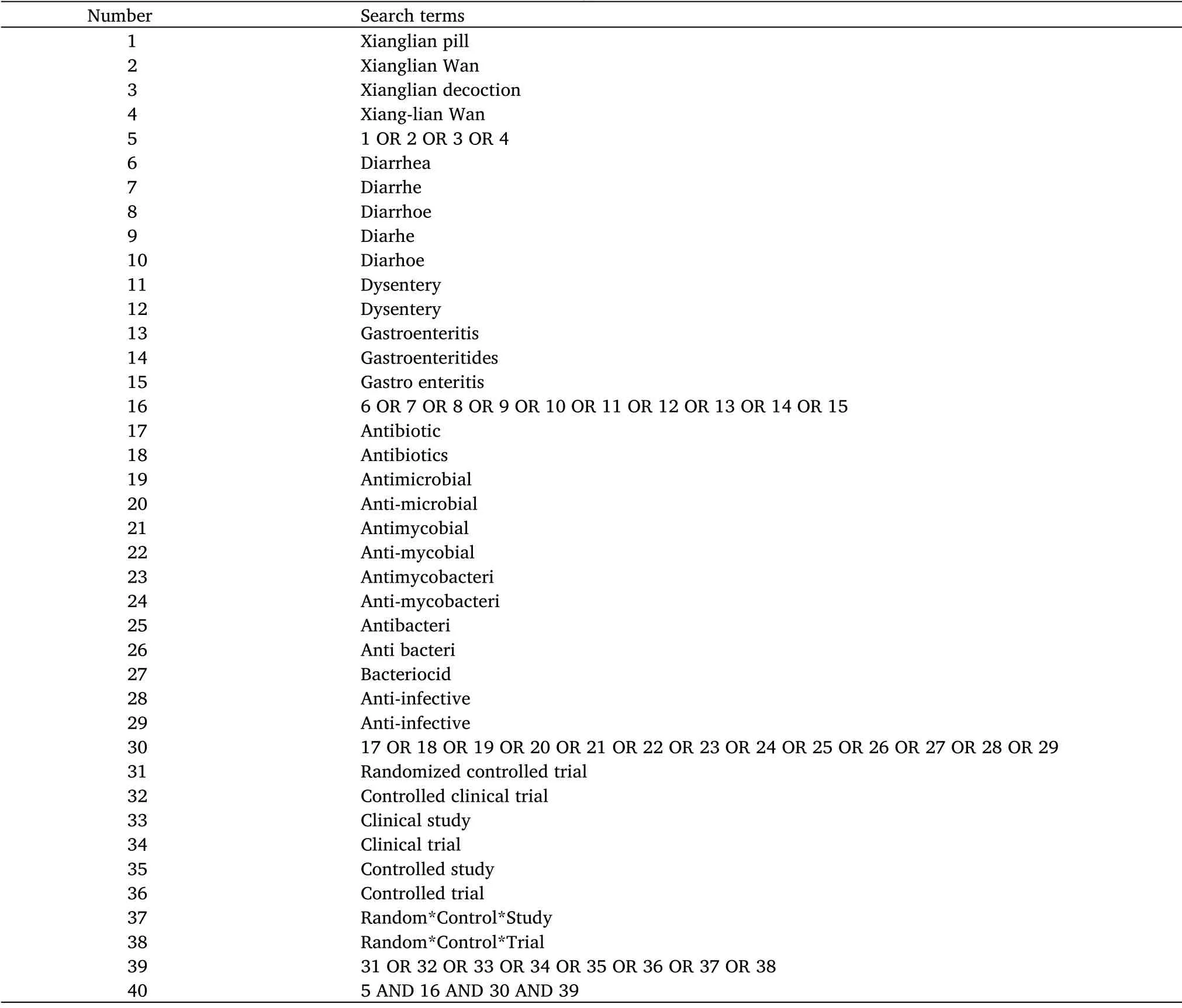
Table 1 Search strategy for PubMed database
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies.EndNote version 9.0 (Thomson Reuters, CA,USA) will be used to import the article and eliminate duplicates.Two authors (Zhang XB and Gao R) will independently extract information from each included trial according to pre-specified selection criteria.If these two authors cannot obtain an agreement, the selection process will be resolved by discussion with another author (Zhou X).The whole process including selecting articles and operating meta-analysis will be based on the instructions of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Flow chart of preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
Data extraction and management.The extracted content mainly includes author, publication time, article title, country where the study was conducted, language, study setting, study period, total number of people included in the study, diagnostic criteria for diarrhea, inclusion and exclusion standards for participants, patient characteristics (such as sex, age, diagnosis, and occupation), patient number in each group, presence/absence of intention, and efficacy data for analysis.If complete data are missing for some cases,data will be requested directly from the authors and extracted by using software.EndNote and Excel software will be used to extract data.
Assessment of risk of bias.Each eligible study will be evaluated by two researchers (Gao R and Fang RJ) to confirm the risk of bias for clinical trials in compliance with the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool[32].Domains of evaluation will include allocation concealment,blinding, incomplete statistics, selective outcome reporting, and other potential reasons of bias.The quality of items will be classified into three categories: “low risk of bias,” “unclear bias,” and “high risk of bias.” Disagreement will be assessed by consensus among authors.Evaluation database is created using Microsoft Excel, while images of bias risk will be drawn by RevMan 5.3 software.
Measures of treatment effect.Risk ratio will be applied in fixed-effects and random-effects models between the experimental and controls detected with 95% confidence intervals.Forest plots will function to evaluate the results, while the main outcomes, and secondary outcomes are summarized as risk ratios.Statistical analysis will be proceeded through STATA software (Stata Corp., College Station, Texas) and R studio (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Dealing with missing data.For articles with missing information,corresponding authors will be contacted directly through email or telephone.If information will still be incomplete, available data will be collected by outcome synthesis, and the influence of data loss will be comprehensively deeply.
Assessment of heterogeneity.HigginsI2test will be used to determine heterogeneity of the included studies, and heterogeneity will be expressed asI2value.Low statistical heterogeneity will be obtained whenI2< 50%.Heterogeneity will be considered meaningful ifI2≥ 50%.Sensitivity and subgroup analyses will be assessed based on the significance ofI2statistics to confirm the source of heterogeneity.
Assessment of reporting bias.Funnel plot will be employed to assess publication bias, while Egger method will be utilized to explore quantifications for the meta-analysis.
Data synthesis.Data will be obtained using the Cochrane Collaboration tool, which will be analyzed by RevMan software.If heterogeneity will remain low or not significant (I2< 50%), the fixed-effect model will be used.When heterogeneity will show significance (I2≥ 50%) among the included studies, the source of heterogeneity will be settled with meta-regression and subgroup analyses to eliminate the effect of important clinical heterogeneity, so the random-effects model will be employed.
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses.Subgroup analyses will be performed based on factors assessed by studies, such as AAD severity,age of the participants, drug forms (original or modified XLP), dosage of Chinese herbal medicines, and treatment of the control group.
Sensitivity analysis.Factors investigated by eligible recruited studies will be in the sensitivity analysis, in which sample size, missing data,and methodological heterogeneity will demonstrate the stability of outcomes.
Grading the quality of evidence.Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation will be used to evaluate the quality of included evidence.Quality of evidence will be determined in four levels: high,medium, low, and extremely low.
Discussion
AAD is considered a regular clinical complication of antibiotic therapy[33].With the widespread application of antibiotics on infectious diseases, the incidence of ADD remains high in clinical practice, which accounts for 5%–70%of adults[34].Antibiotics such as cephalosporin,clindamycin, and broad-spectrum penicillin are closely related to diarrhea [35].Many studies have shown that the mechanism of ADD is mainly attributed to abnormal intestinal microenvironment due to an imbalance in gut microbiota composition induced by antibiotics[6].Depletion of the gut flora due to antibiotics exposure may lead to the impairment of colonization resistance, causing extra intestinal infection and even inflammatory bowel disease outbreaks in most severe cases [36].In the treatment of ADD, Western medicine involved antibiotic therapy, administration of probiotics, and surgery,which have limitations and side effects [37].TCM has received wide attention because of its characteristics such as safe, effective,convenient to use, and less adverse reactions, which plays a crucial role in preventing and treating diseases [13, 37].XLP is a TCM preparation and has been administered to treat diarrhea for centuries.Recent literature has shown that XLP has positive effects by protecting the gastrointestinal tract, and evidence-based results demonstrated multilevel efficacy [14, 38].Therefore, a systematic study is needed to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of XLP in treating ADDS.The proposed study will summarize present studies systematically focusing on the curative effect and safety of XLP as treatment of ADD and to provide support for in-depth drug research and clinical trials in the future.
 Traditional Medicine Research2021年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2021年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The protective effect of a standardized hydroalcoholic extract of Prosopis farcta(Banks&Sol.)J.F.Macbr.fruit in a rat model for experimental ulcerative colitis
- Neuroprotective effect and mechanism of daidzein in oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury based on experimental approaches and network pharmacology
- Understanding the prevention and cure of plagues in Daoist medicine
- Effects of Dendrobium candidum polysaccharides on microRNA-125b and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in diabetic cataract rats
- Research advances concerning the mechanism of glucocorticoid resistance in relation to traditional Chinese medicine for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Light and color therapy: the role of light and color in architecture from the perspective of traditional Persian medicine
