245例心脏外科手术患者术后急性肾损伤的危险因素分析
钟美容 张丹凤

[關键词] 心脏外科手术;急性肾损伤;危险因素;输血
[中图分类号] R692 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0035-06
Risk factors analysis of acute kidney injury in 245 patients undergoing cardiac surgery
ZHONG Meirong1 ZHANG Danfeng2
1.Department of Nephrology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China; 2.Department of Anesthesiology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China
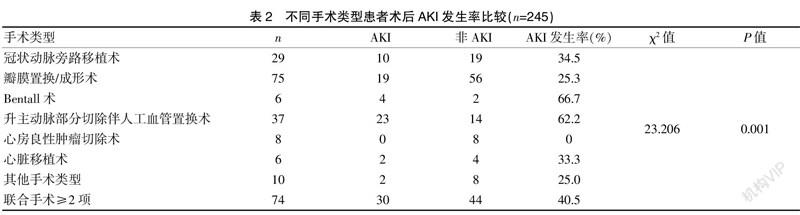
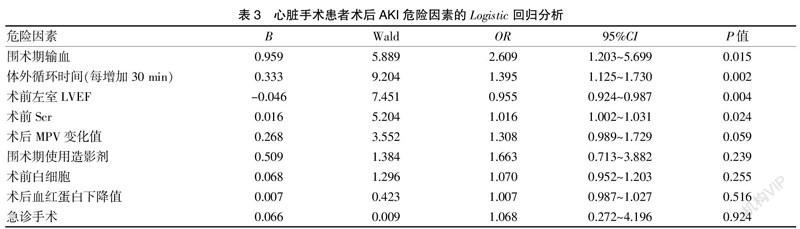
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the incidence rate and risk factors of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients undergoing cardiac surgery in Fujian Medical University Union Hospital. Methods The clinical data of 245 patients undergoing cardiac surgery in Fujian Medical University Union Hospital from January to April 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. Univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis were used to screen the risk factors of postoperative AKI. Results It was found that there was 90 patients (36%) showing AKI among the 245 patients, and the incidence rate of AKI stage 1, AKI stage 2 and AKI stage 3 was 20.4%, 7.3% and 9.0% respectively; 19 patients(7.8%) needed renal replacement therapy. The univariate regression analysis result indicated that the preoperative left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), the cardiopulmonary bypass time, the emergency operation, the application of contrast medium in perioperative period, the blood transfusion in perioperative period, the preoperative creatinine level, preoperative white blood cell level and decreased value of postoperative hemoglobin, and the changing value of postoperative mean platelet volume were related to AKI after cardiac surgery. The multivariate Logistic regression analysis result indicated the blood transfusion in perioperative period (OR=2.609, 95%CI: 1.203-5.699, P=0.015), the long cardiopulmonary bypass time (OR=1.395, 95%CI: 1.125-1.730, P=0.002), and the high level of preoperative creatinine (OR=1.016, 95%CI: 1.002~1.031,P=0.024) were independent risk factors of postoperative AKI, and the high preoperative left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (OR=0.955, 95%CI: 0.924-0.987, P=0.004) was a protective factor of AKI. Conclusion Postoperative AKI is one of the common complications in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Improving perioperative cardiac and renal function and reducing the need for intraoperative blood transfusion are feasible measures to reduce the incidence rate of AKI after cardiac surgery.

