A pilot allocation method for multi-cell multi-user massive MIMO system
LI Yiming ,DU Liping,2,* ,and CHEN Yueyun
1.School of Computer and Communication Engineering,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China;2.Wireless and Space Communication Laboratory,Shunde Graduate School of University of Science and Technology Beijing,Foshan 528000,China
Abstract: Pilot contamination can spoil the accuracy of channel estimation and then has become one of the key problems influencing the performance of massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems.This paper proposes a method based on cell classification and users grouping to mitigate the pilot contamination in multi-cell massive MIMO systems and improve the spectral efficiency.The pilots of the terminals are allocated onebit orthogonal identifier to diminish the cell categories by the operation of exclusive OR (XOR).At the same time,the users are divided into edge user groups and central user groups according to the large-scale fading coefficients by the clustering algorithm,and different pilot sequences are assigned to different groups.The simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the spectral efficiency of multi-cell massive MIMO systems.
Keywords:massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO),pilot allocation,cell classification,users grouping (UG),spectral efficiency.
1.Introduction
The feature of massive multiple input multiple output(MIMO) is that the base station (BS) has many antennas(tens or even hundreds) [1,2].As the key technology of the 5th generation (5G) wireless communication system[3−5],massive MIMO has many advantages such as high transmission rate,energy efficiency and spectral efficiency compared with the traditional MIMO technology[6−9].Its advantages rely mostly on the accuracy of channel state information (CSI).At present,the massive MIMO system generally uses pilots for channel estimation.A pilot sequence is inserted in the transmitting data,and the receiver performs channel estimation by using the received pilot symbols.Ideally,the massive MIMO system assigns each user a mutually orthogonal pilot sequence.When the coherence time is short,the length of the pilot sequence and the size of the pilot set are often limited.If the same pilot sequence is assigned to different users,it induces the estimation error of CSI,which is the problem of pilot contamination [10,11].The influence of pilot contamination on system performance in multi-cell massive MIMO systems was studied in [12,13].The research shows that the pilot contamination not only seriously affects the accuracy of the CSI,but also has a great influence on the downlink precoding of the system.Therefore,different pilot allocation strategies have been proposed to come up with the pilot contamination without increasing the transmit power and without changing the pilot structure.It is also an effective way to improve the spectral efficiency of the massive MIMO system.At present,pilot scheduling schemes include time-shifted pilots,superimposed pilot (SP),power control and users grouping.
The method of time-shifting pilots is to rearrange the transmission order of the uplink pilots of different cells in the frame structure [14,15].The zero-forcing (ZF) precoding algorithm and the time-shifted pilots method were used to mitigate pilot contamination in [16].Only one cell transmits pilots while the rest cells transmit data.However,when the users within different cells are very close,both data and pilots transmitted at the same time may cause interference and time synchronization is required.In [17],a partial-time-shifted pilot scheme was proposed.The scheme finds a better tradeoff between the users accommodation and orthogonality of pilots.However,it has stronger interference.
In the SP method,the pilots are periodically superimposed and transmitted on the data information in different time slots [18−20].In [21],a time-multiplexed pilot sequence is combined with SP to mitigate pilot contamination.The interference caused by transmitting the pilot together with the data will be greatly reduced.In [22],using the theory of structured compressive sensing (CS),the structured subspace pursuit (SSP) algorithm was proposed with low pilot overhead.
The power control method is that different user groups transmit pilots with controlled power in their time slots[23,24].A single-cell pilot power allocation method was proposed in [25].This method allocates the pilot power of each user to maximize the sum-rate of downlink under the condition of total pilot power constraints.In [26],the problem of pilot and data power allocation in multi-cell massive MIMO systems was studied,and a joint allocation scheme of pilot and data power was proposed.The total transmit power of the system is reduced based on the signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio (SINR) requirements and power constraints of each user.The method proposed in [27]defined the relative channel estimation error (RCEE) metric and used the expected value of RCEE to improve the minimum uplink achievable rate.In [28,29],the cells were separated into two groups while the pilot training phase was divided into two segments.Each group occupies one segment of pilot time slot,but the pilot contamination from all neighboring cells cannot be completely eliminated.The length of the time slot occupied by the pilot is twice as much as the conventional method.In [30],the cells were classified into three categories.The cells of each category are assigned orthogonal cell identification,which are added to the beginning of the pilot sequence.This method eliminates pilot contamination at the expense of the triple length of pilot time slot in the conventional method.
The method of users grouping (UG) is to allocate different pilots among user groups classified with different criteria to lower the pilot contamination [31−33].The traditional UG method uses the distance between users and the BS.Fang et al.[34]used the interference strength between BS in the target cell and the users of the interfering cells to classify the interfering cell into two categories.The first type performs optimal allocation of pilots,and the second type randomly allocates pilots.This method effectively improves the downlink sum-rate of the system,but the pilot contamination generated by the second type of cell is still relatively large.In [35],users were divided into edge user groups and central user groups by using large-scale fading coefficients.The central users multiplex the same pilots,while the edge users with poor channel quality use orthogonal pilots.This method reduces pilot contamination of edge users and improves the sumrate of the system with longer length of pilot time slot.
This paper proposes a method based on orthogonal cell identification and UG to reduce pilot contamination in the massive MIMO system.In the hexagonal cellular network structure,the cells are divided into two categories.Users in the cells are divided into two groups:central group and edge group.One-bit orthogonal cell identification is added to the beginning of the pilot sequence.The central group multiplexes the same pilots and the edge group is assigned orthogonal pilots.The contribution of the paper lies in the following:
(i) One-bit orthogonal identifier ahead the pilot sequence marks the cells into two categories.Combining one-bit orthogonal identifier with the UG can reduce the length of the pilot and then improve the spectral efficiency of the system.
(ii) We propose a new UG method based on the Euclidean distances of the large-scale fading coefficient which considers the space information in each category,the users are grouped by using the cluster algorithm.
The numerical simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively reduce inter-cell pilot contamination in multi-cell systems and improve the spectral efficiency.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we review the multi-cell massive MIMO system model and the influence of pilot contamination on the system.The proposed method,namely the pilot allocation method based on one-bit orthogonal identifier and UG,is discussed in Section 3.The simulation results are shown in Section 4.Section 5 concludes the paper.
2.System model
Fig.1 shows a multi-cell massive MIMO system model.There areLhexagonal cells in the cellular network,and each cell includes one BS equipped withMantennas,servingKsingle antenna users.In order to facilitate the analysis of the problem,the target cell is surrounded by six neighbor cells.We assume that the system uses the time division duplex (TDD) mode.Based on the channel reciprocity criterion,the channel information can be estimated according to the uplink pilot transmitted by the user.The ZF precoding is used at the BS.
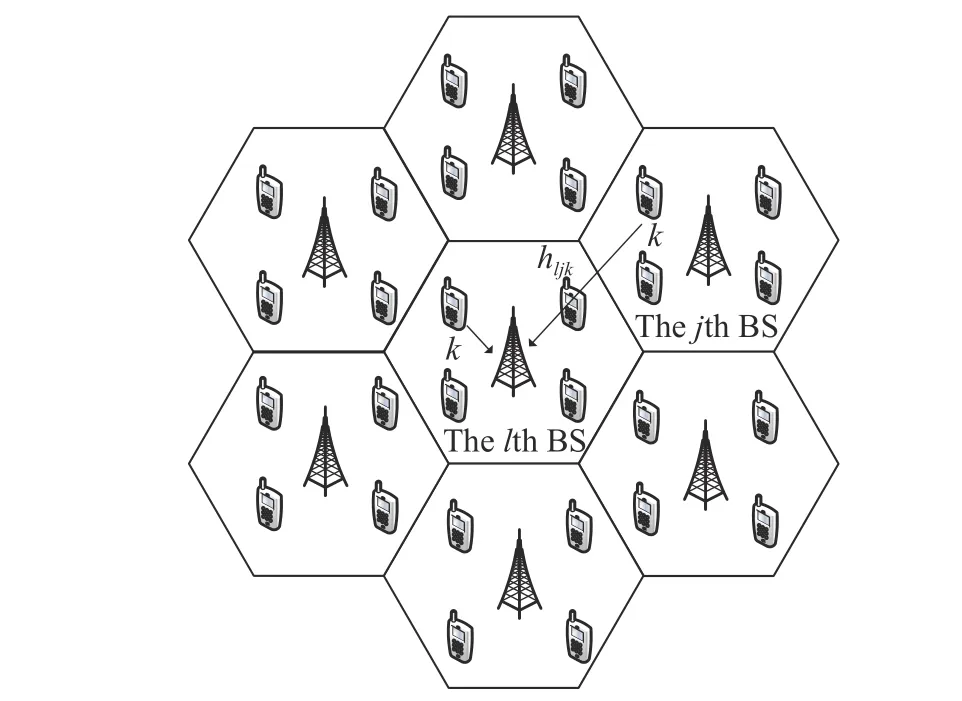
Fig.1 Multi-cell massive MIMO system model
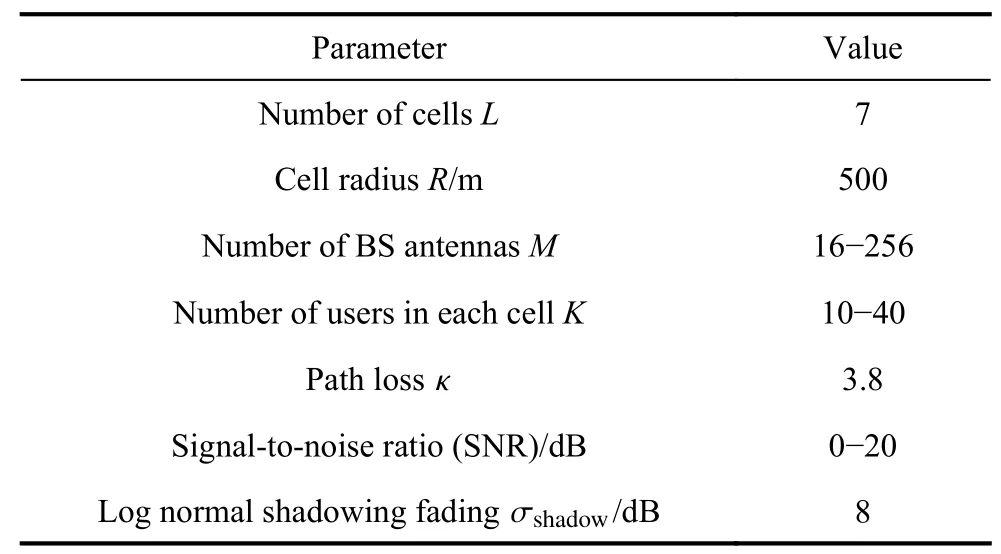
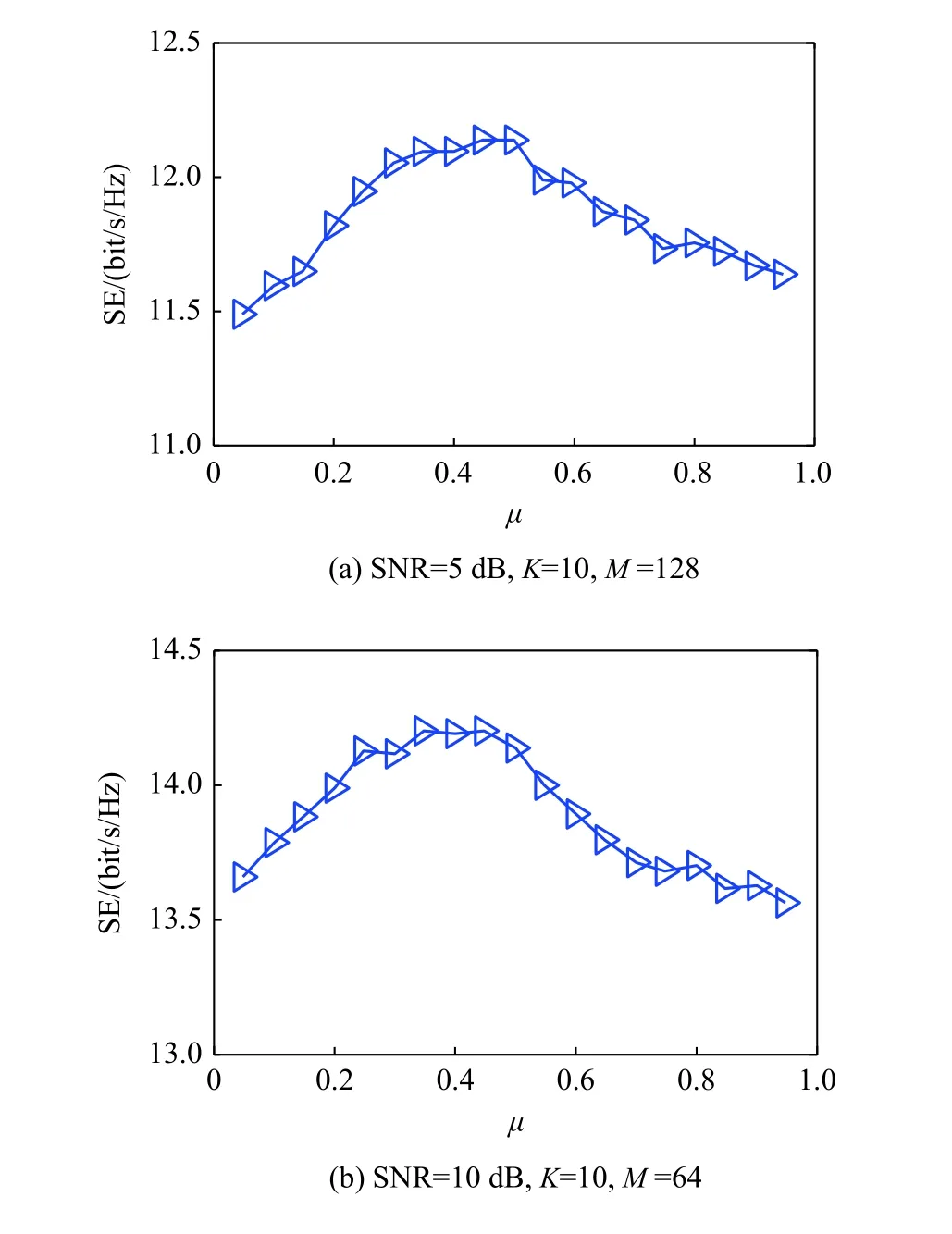
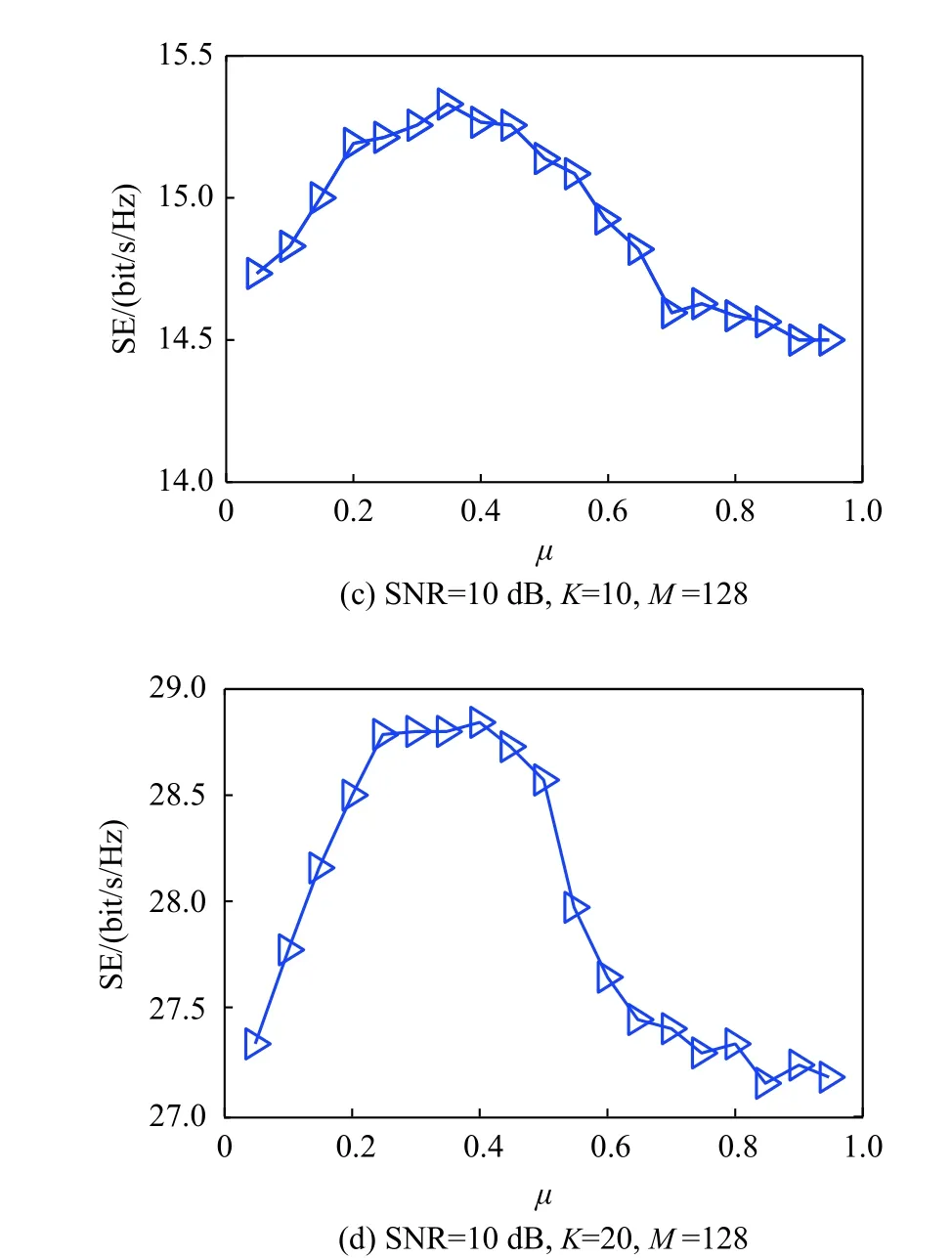
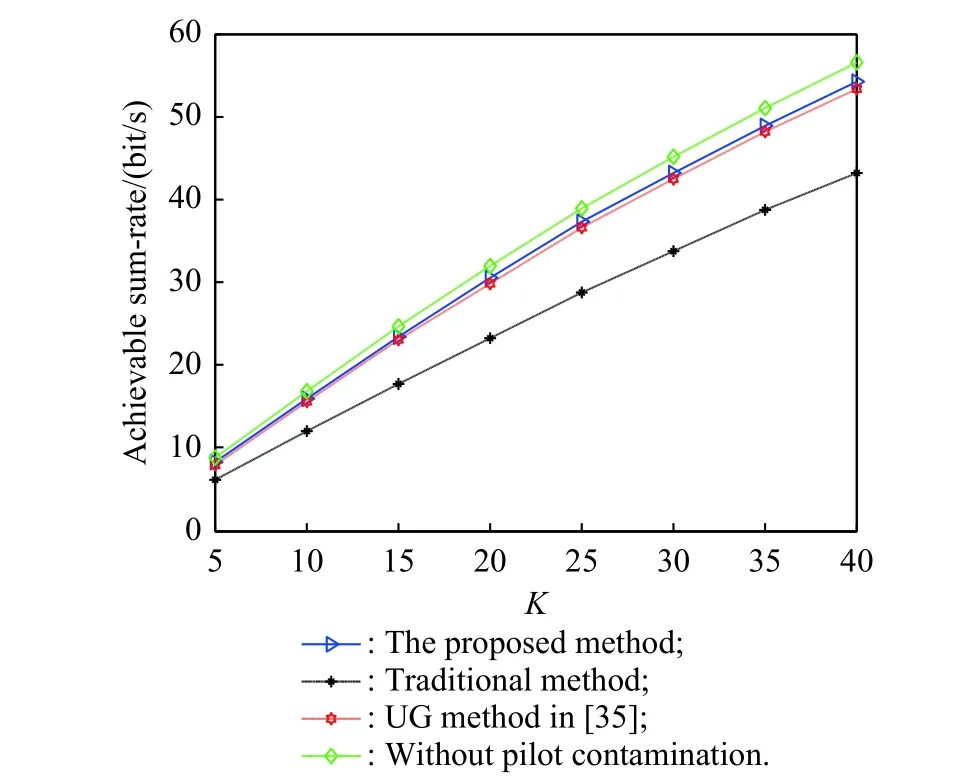
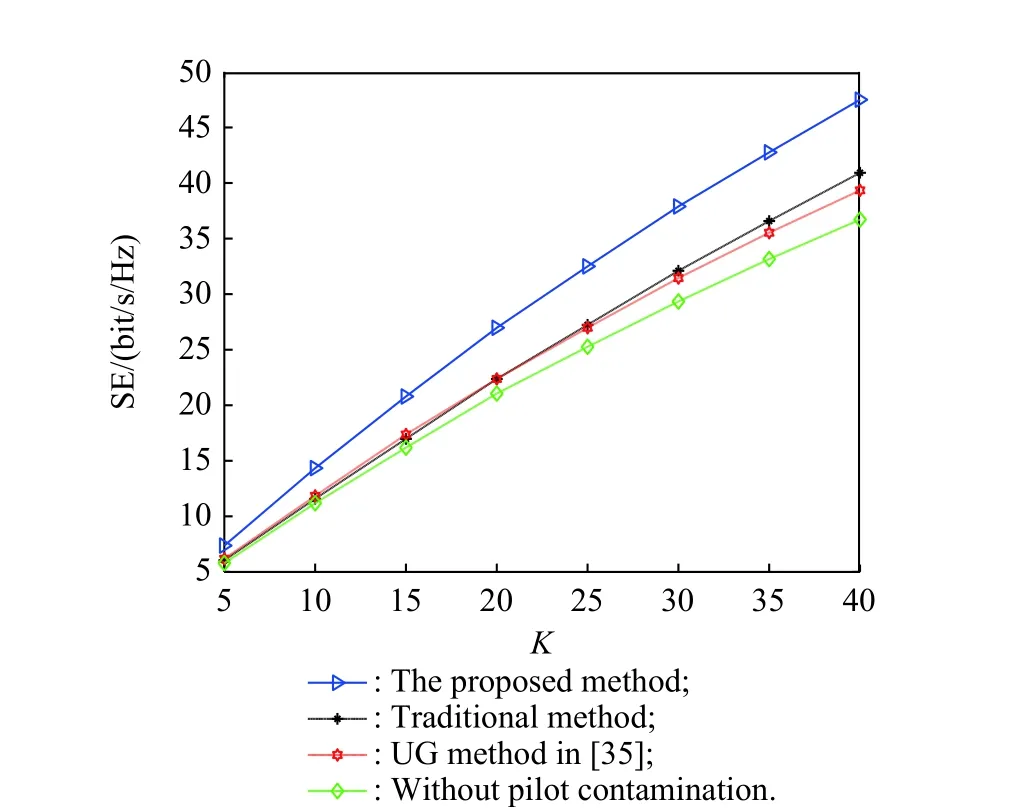
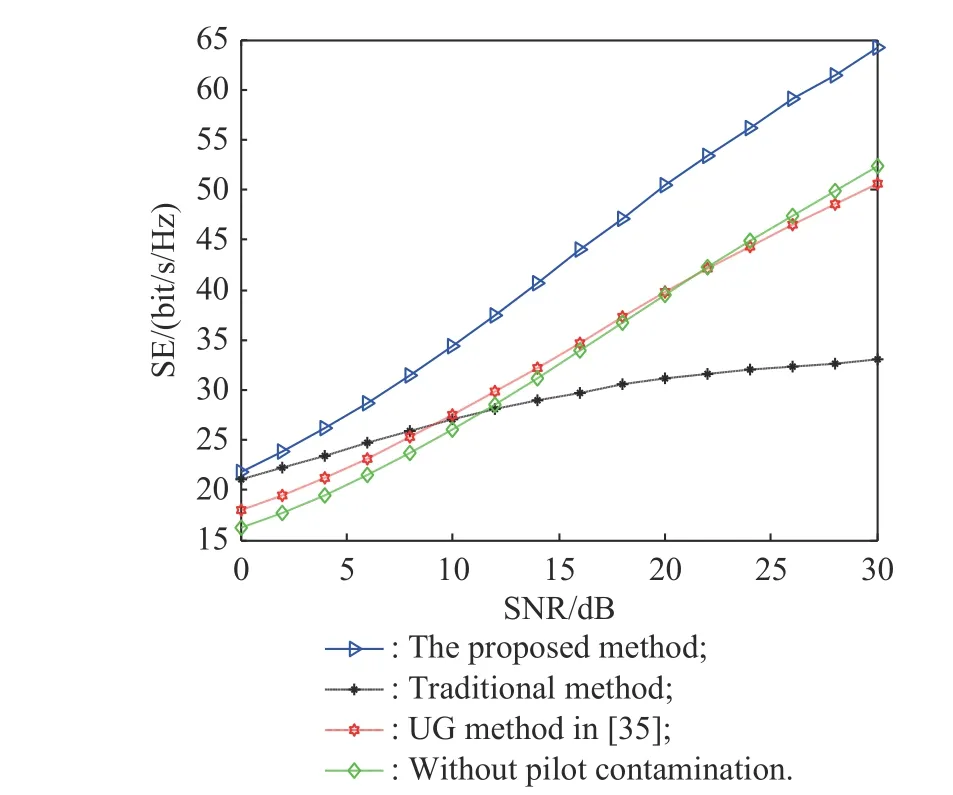
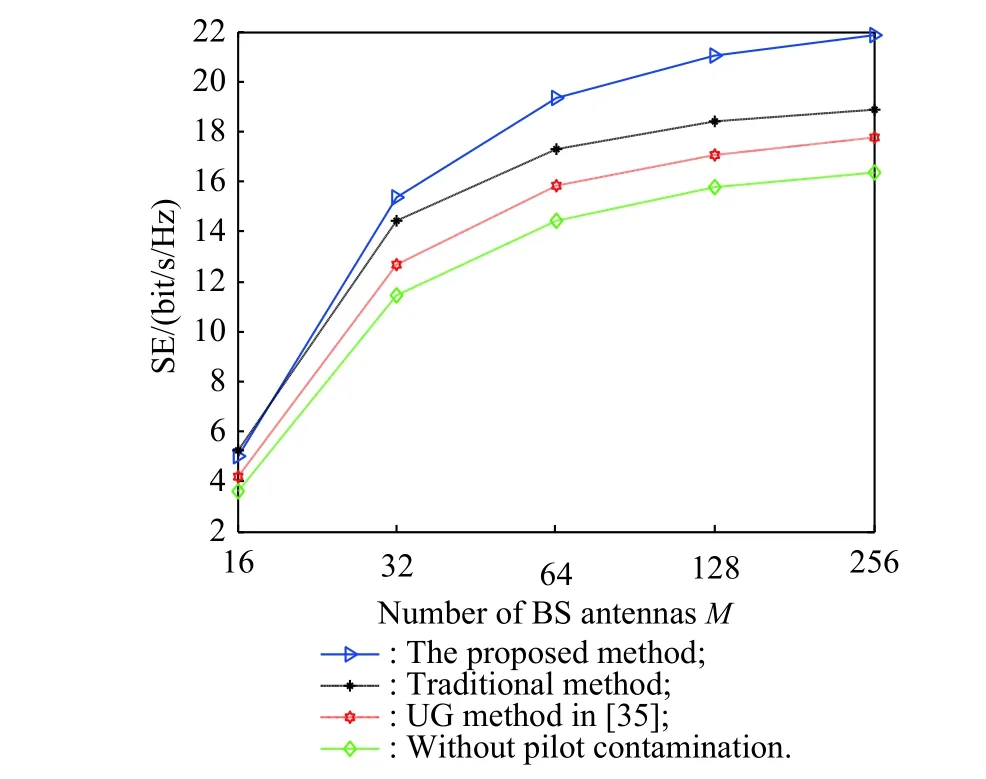
The channel quality is determined by the small-scale fading coefficient and the large-scale fading coefficient.Hl j∈CM×Kis the channel matrix between all users in thejth (1 All elements ofGl j∈CM×Kare independent identical distribution (i.i.d).glmjkis the small-scale fading coefficient between thekth user in thejth cell and themth antenna of thelth BS.We assume that the large-scale fading coefficients of a user to all antennas of the BS are the same because the distance between the antenna array is negligible compared with the distance between the users and the BS [36].Dl j∈CK×Kis a diagonal matrix.The elements ofDl j=[βl j1,βlj2,···,βljK]are the large-scale fading coefficient between thekth user in thejth cell and thelth BS: where κ (κ ⩾2) is the path loss index,Ris the radius of the cell,rl jkis the distance between thekth user in thejth cell and thelth BS,andzl jkrepresents the shadow fading and possesses a lognormal distribution 10lgzl jk∼CN(0,σshadow). For the unlink of the massive MIMO system,it is assumed that the pilot sequence transmitted by all users in thejth cell is φj=[θj1,θj2,···,θjK]T,while the pilot lengthThe training information received by the BS of thelth cell is whereppis the pilot transmit power,andNlis the additive white Gaussian noise in thelth cell.With the least square (LS) channel estimation,the estimation of CSI of the BS in thelth cell to the users in thejth cell is shown as For the downlink of the multi-cell massive MIMO system in the TDD mode,the received signalylkof thekth user in thelth cell can be expressed as wherepsis the BS transmit power,andxjnis the data sent by thejth BS to thenth user in the cell.Wjis precoding matrix of thejth cell,andwjnis thenth column ofWj∈CM×K. where the first item is the expected signal,and the other items represent inter-cell interference,channel estimation error,intra-cell interference and Gaussian white noise.xlkis the data of thelth BS sent to thekth user.psis the BS transmission power.wlkis thekth column ofWl.wjnis thenth column ofWj.We assumeThenTherefore,the SINR of thekth user in thelth cell is It can be seen from (12)−(14) that when the number of antennas approaches infinity,the spectral efficiency is related to the precoding matrix and the channel estimate.Since the precoding matrix is determined by the channel estimation,we can improve the accuracy of precoding by reducing the channel estimation error.From (5)−(7),the result of channel estimation is related to the large-scale fading coefficient and the pilots when the LS method is used.Therefore,when the large-scale fading coefficient is determined,the spectral efficiency of the system can be improved by designing the pilot allocation method. To reduce the pilot contamination,we group users of each cell into center users and edge users using the clustering algorithm which is based on large-scale fading coefficients of users.Here the Euclidean distances of large-scale fading coefficients are used to measure the space information between users and BS.The center users and the edge users are expressed asKjcandKje,respectively.The channel quality between thekth user and thejth BS as the square of the large-scale fading coefficient is The UG algorithm based on clustering can be described as follows: Step 1Preprocess the channel quality.If some channel qualitysjkis greater than the predetermined thresholdµ,this user is directly added to the central groupKjc,and its channel quality is removed fromSj. Step 2Randomly select two valuesscandsefromSjas the center of each group. Step 3Compute the Euclidean distances between each elements ofSjand the two centers.Divide each user inSjinto two groups according to whether it is close toscorse. Step 4Update the center of two new groupsscandseaccording to the mean of each group. Step 5Repeat Step 3 and Step 4 until the users in all groups no longer change,or (16) does not change significantly. Step 6Repeat Step 1 to Step 5 until all cells complete the users grouping. Because of the division of users in each cell,the pilot sequences are divided into two groupsP1andP2as well.The edge users of cells use the mutually orthogonal pilot sequence of groupP2,and the central users of cells share the pilot sequencesP1to reduce the extra pilot overhead. After the users are grouped,the pilot length τ′is wherea1,a2,···,aLis the number of users in the center group of each cell,andb1,b2,···,bLis the number of users in the edge group. We assume that there are seven cells in the massive MIMO system,and each cell hasKusers.The middle cell is the target cell.To further reduce the pilot contamination,all cells are classified into two categories,L1(yellow cells) andL2(blue cells).The pilot length of each user is τ,and one-bit orthogonal cell identificationsAi=[0,1](i=1,···,L) are allocated to each cell.As shown in Fig.2,L1is assigned 1,andL2is 0. Fig.2 One-bit orthogonal cell identifications allocated to two cell classifications The orthogonal identification is added to the beginning of the pilot sequence.In Fig.3,the one-bit orthogonal identifier is added to the head of the pilot sequence in the same cell category. Fig.3 Assignment of pilot in a time slot based on one-bit orthogonal identifier When the BS receives the uplink pilot of users,the one bit of the head of each pilot sequence is taken out to beB.Then perform an exclusive OR (XOR) operation betweenBand the one-bit identificationAi,which can be shown as If the result of (18) is 0,it indicates that the pilot received by the BS is from the same category of cell.Then the pilot is sent to the BS processor that performs downlink channel estimation and data precoding according to the received pilot.If the result is 1,it will consider the corresponding pilot from the other category,so the corresponding pilot signal is filtered out.In this way,the pilot contamination of the blue cells is eliminated,so the target cell is only contaminated by pilots of two neighboring cells. Therefore,our proposed method makes UG based on the clustering algorithm and the cell classification method based on the one-bit orthogonal identifier.It can be described as follows: Step 1Use the method in Subsection 3.2 to classify cells and assign the one-bit orthogonal identifier to users in each cell. Step 2Use the method in Subsection 3.1 to group users in each cell to obtain the center user groupsKjcand edge user groupsKje. Step 3Assign pilot sequencesP1andP2toKjcandKje,respectively. Step 4Add the pre-assigned one-bit orthogonal identifier to the beginning of the pilot sequence of users for each cell. In our proposed method,the pilots of the target cell are only contaminated by the pilots of users in the edge user group of two yellow neighboring cells,and the length of the pilot sequence τ can be expressed as whereaiis the number of central users in theith cell,andbiis the number of edge users in theith cell. The spectral efficiency of thelth cell of the proposed method can be expressed as The MSE per antenna of the LS estimation can be expressed as wherekjis thekth user in thejth cell.Whenkj∈Kje, In our proposed methods,the computational complexity is mainly made by three stages.The first stage is to directly list the users whose large-scale fading coefficient is larger than the preset threshold in the center group,and the complexity isO(K).The second stage is to classify the remaining users by using the clustering algorithm.The complexity isO(nKi ti),wherenis the number of categories (n=2),Kiis the number of remaining users after the first stage for theith cell,tiis the number of iterations.The complexity of the second stage can also be expressed asO(Ki ti).The third stage is that the base station takes out one bit of the head of each pilot sequence for XOR operation and the complexity isO(K). As for the UG method in [35],it needs two stages:the first stage is to calculate the mean of the maximum and the minimum of the square of the large-scale fading coefficient from the users to the base station in each cell,and its complexity isO(K);the second stage is to group users according to the mean,and the complexity isO(K). It can be seen from the analysis that the second stage makes the computational complexity of the proposed method slightly higher than the UG method in [35].The additional complexity is in proportion to the number of users in each cell and the iteration number of the clustering algorithm.From our experiment observation,the iteration number of the clustering algorithm is between 2 to 10,but it can dynamically classify users according to large-scale fading coefficients and obtain better results of UG. In this section,we will study the performance of the proposed scheme through Monte Carlo simulation.The system parameters are given in Table 1. Table 1 Basic parameters of system simulation Fig.4 shows the spectral efficiency of the target cell which changes with the predetermined threshold µ under diffident simulation parameters.The users are grouped based on the clustering algorithm.It is shown that the spectral efficiency (SE) first increases with µ and then decreases after it reaches the peak,and finally approaches a fixed value.It is known that the number of preselected central users decreases with µ.If µ is too small,more users are included into the pre-selected central users and some of them may be users with poor channel quality.When µ is large,some users with high channel quality may be not selected.Both cases can affect the clustering result.The SE reaches the maximum with µ ranging f rom 0.35 to 0.5 and trends to constant after µ=0.7. Fig.4 Predetermined threshold µ on the spectral efficiency of the target cell Fig.5 shows the achievable sum-rate of the target cell of our proposed method (cell classification and UG based on the clustering algorithm),the UG method in [35],the method without pilot contamination (the users in all cells use orthogonal pilot sequences) and the traditional method (each cell multiplexes the same pilot sequences)when the numbers of usersKincreases.The number of antennas is 128.The SNR is 10 dB.The predetermined threshold µ is 0.35.As the number of users increases,the achievable sum-rate of the four methods tends to increase.The proposed method and the UG method are close to the method without pilot contamination.The proposed method has a little better performance than the UG method,which indicates that these sum-rates of the two methods are similar. Fig.6 shows the SE of the target cell of our proposed method,the UG method in [35],the method without pilot contamination and the traditional method when the number of usersKincreases.The number of antennas is 128.The SNR is 10 dB.The predetermined threshold µ is 0.35.It is shown that the SE of the four methods increases with the number of users.The SE of these four methods is similar when the number of users is small.As the number of users increases,the advantages of the proposed method will be more obvious.It is known that the pilot length will increase with the number of users.The time slot of the UG method is maxis the number of users in each center group,andis the number of users in the each edge group by this method.The time slot of the method without pilot contamination is 7Kand the SE of this method is the least.From (18),the proposed method reduces the time slot occupied by transmitting pilots,then improves the SE. Fig.5 Influence of the number of users K on the achievable sumrate of the target cell Fig.6 Influence of the number of users K on SE of the target cell Fig.7 shows the spectral efficiency of the target cell of our proposed method,the UG method in [35],the method without pilot contamination and the traditional method when the SNR increases.The number of antennas is 128.The number of users in each cell is 15.The predetermined threshold µ is 0.35.It can be seen in Fig.7,the SE of the four methods increases with the SNR.The SE of our proposed method is better than that of the other three methods.The SE of the UG method is similar to the method without pilot contamination.The traditional method has the lowest SE with a high SNR. Fig.7 Influence of SNR on SE of the target cell Fig.8 shows the SE of the target cell of our proposed method,the UG method in [35],the method without pilot contamination and the traditional method when the antennas number increases.The SNR is 5 dB.The number of users in each cell is 15.The predetermined threshold µ is 0.35.The SE of four methods increases with the number of antennas from 16 to 256.The proposed method is better than the other three methods.Compared with the UG method,the SE of the proposed method is improved by 4 bit/s/Hz whenM=256. Fig.8 Influence of the number of antennas on SE of the target cell From the results of sum-rate and SE,the advantages of the proposed method are more obvious. This paper proposes a method based on the one-bit orthogonal identifier and UG to mitigate pilot contamination in multi-cell massive MIMO systems while improving the SE.The pilots between different categories of cells classified by the one-bit orthogonal identifier are filtered out.At the same time,users of each cell are grouped according to the large-scale fading coefficient to reduce pilot contamination between cells of the same category.The simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the SE of multi-cell massive MIMO systems.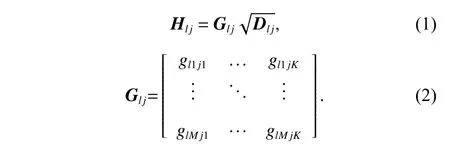
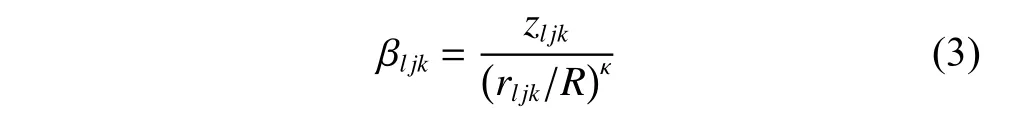
2.1 Channel estimation
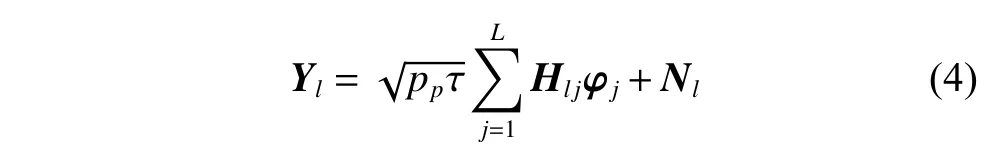
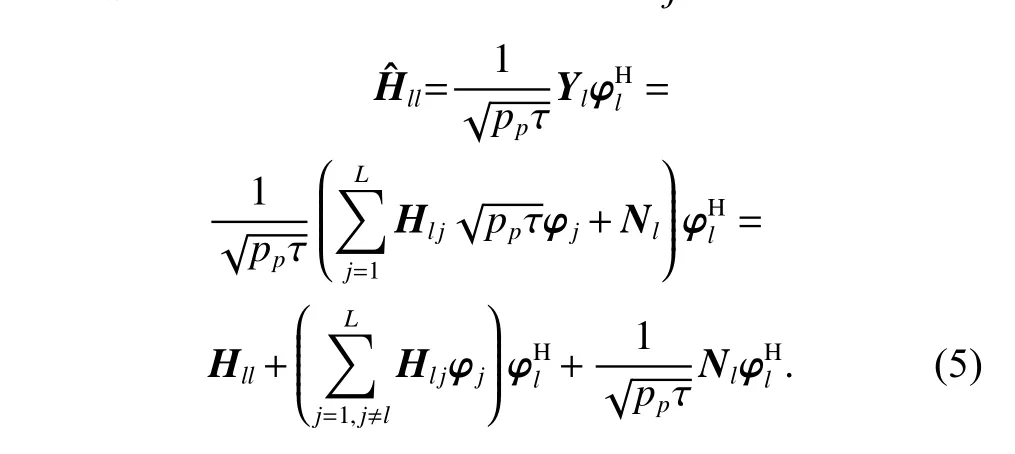

2.2 Downlink data transmission
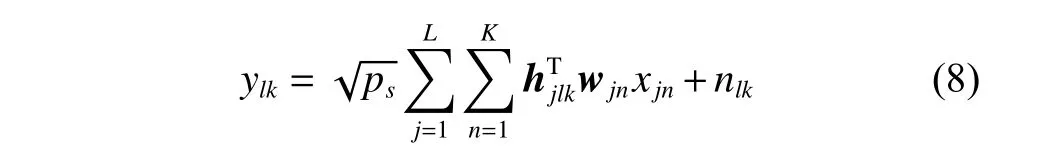


3.Pilot allocation method based on UG and one-bit orthogonal identifier
3.1 UG based on clustering algorithm
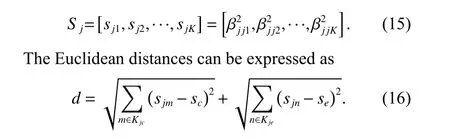


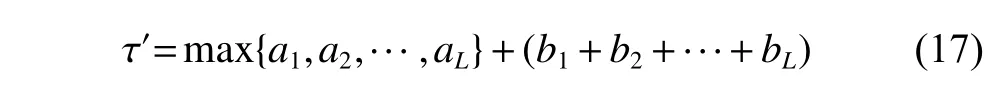
3.2 Cell classification method based on one-bit orthogonal identifier
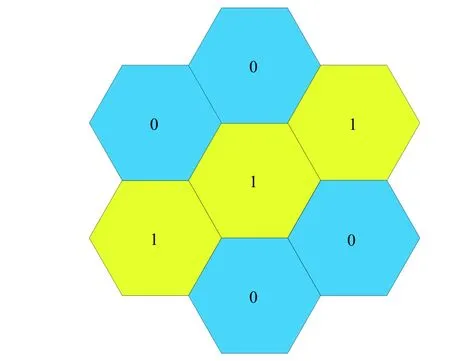
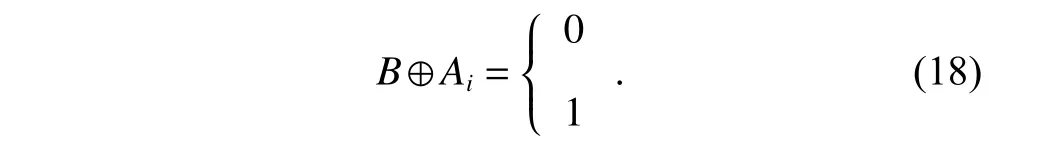
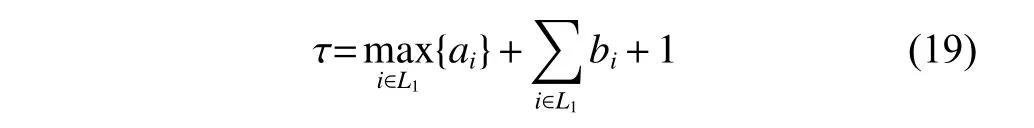
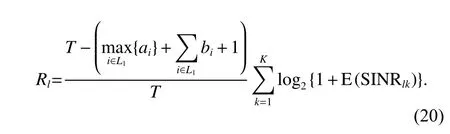
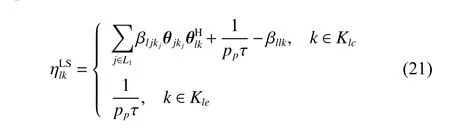
3.3 Computational complexity analysis
4.Simulation results
5.Conclusions
 Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2021年2期
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2021年2期
- Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics的其它文章
- Data-driven evolutionary sampling optimization for expensive problems
- A dual population multi-operator genetic algorithm for flight deck operations scheduling problem
- Observation scheduling problem for AEOS with a comprehensive task clustering
- An improved estimation of distribution algorithm for multi-compartment electric vehicle routing problem
- VCR-LFM-BPSK signal design for countering advanced interception technologies
- RFC:a feature selection algorithm for software defect prediction
