Comparison of clinical outcomes of astigmatic correction using Toric intraocular lens
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Clinical data shows that 40%-45% of patients undergoing cataract surgery have more than 1 diopter (D) of corneal astigmatism[1-2], which would inevitably affect the visual quality of patients, if not corrected. Since its introduction in 1994, Toric intraocular lens (Toric IOL) has been widely used with accurate and stable effect of correcting corneal astigmatism[3-6]. Toric IOL is designed with a complex curved surface with a clear axial marker line on the intraocular lens, aiding its accurate implantation for the correction of the corneal astigmatism. The rotational stability of any IOL is a crucial factor that affects the long-term outcomes after Toric IOL implantation. Recent studies have shown, that the majority of IOL rotations occur immediately after surgery when the capsular bag is still open[7]. Even a slight rotation can lead to a sharp decline in the astigmatism correction ability of Toric IOL, for example, 1 degree of rotation will cause 3.3% loss of the Toric IOL’s astigmatism correction ability[8]. At present, many kinds of Toric IOLs are widely available clinically, but only limited studies and data are available to compare their clinical outcome. In this study, we used two widely used Toric IOLs in the clinic, Rayner’s 623T (which entered the Chinese market in 2014) and Alcon’s AcrySof Toric, and compared the clinical outcomes three months after implantation in order to provide better options for patients.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
EthicalApprovalThe study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Peking University Third Hospital (No.457-02,2019). All patients had been fully informed of the purpose and methods of the present study and provided written informed consent from themselves.
GeneralInformationThe medical records of 35 cataract patients (50 eyes) with corneal astigmatism who underwent ophthalmic surgery from April 2019 to July 2019 in Peking University Third Hospital were retrospectively analyzed. All patients had preoperative corneal astigmatism with the rule ≥1.5 D or corneal astigmatism against the rule ≥0.75 D and underwent cataract phacoemulsification combined with Toric IOL implantation. Among them, 25 eyes of 20 cases were implanted with Rayner 623T, while 25 eyes of 15 cases were implanted with Alcon AcrySof Toric IOL. Among all the cases, patients undergoing binocular surgery received the same brand of IOL for both eyes. The Rayner 623T optics range of sphere and cylinder power in general are -10.0 D to 24.0 D and 1.0 D to 11.0 D respectively. The Alcon Acrysof Toric optics range of spherical equivalent refraction and cylinder power in general are 6.0 D to 30.0 D and 1.0 D to 6.0 D respectively.
Inclusion criteria: patients diagnosed with age-related cataract, preoperative corneal astigmatism with the rule ≥1.5 D or corneal astigmatism against the rule ≥0.75 D. The corneal astigmatism was measured by optical coherence biometrics (IOL Master 500; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Jena, Germany) which measure the anterior corneal astigmatism. Exclusion criteria: patients with irregular corneal astigmatism, corneal leukoplakia, glaucoma, fundus diseases, history of previous intraocular surgery, high myopia, abnormal suspensory ligament and any other ocular pathology.
PreoperativeExaminationAll patients underwent preoperative routine cataract examinations, including visual acuity, non-contact intraocular pressure, slit lamp examination, fundus examination, Ophthalmic B-ultrasound, ophthalmic infiltrative A-ultrasound, IOL Master and corneal topography (Pentacam; Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany). The ophthalmic parameters used to calculate the IOL dioptric amount and axis were mainly from the measurement results of the IOL Master. In patients where the refractive medium was highly turbid and the IOL Master could not measure the axial length, the immersion A-ultrasound was used to measure the optic axis. Pentacam was used to determine the regularity of corneal astigmatism and the amount and meridian of astigmatism on the posterior surface of the cornea. Two groups of on-line Toric IOL calculators (https://www.raytrace.rayner.com) and (https://www.acrysoftoriccalculator.com) were used to obtain the model of Toric IOL and the targeted implant axis of IOL by inputting relevant data such as the corresponding axial length, corneal curvature on the anterior surface, surgically induced astigmatism and position and size of the incision. The intraoperative digital real-time navigation system (Callisto eye; Carl Zeiss meditec, Jena, Germany) was used to mark the actual incision and the targeted implant axis of IOL. All surgeries were performed by the same surgeon and surgeon induced astigmatism used the personalized value obtained through preliminary calculation, which was 0.60 D in this study.
SurgicalProceduresBoth groups were treated with cataract phacoemulsification combined with Toric IOL implantation. Intraoperative real-time navigation system was used to perform conventional phacoemulsification through the 3.2 mm corneoscleral limbal incision at 12 o’clock and 0.8 mm transparent corneal incision at 3 o’clock. Continuous circular capsulorrhexis was performed and achieved with a size of about 5.5-6.0 mm in all cases. IOL was implanted into the capsular bag, immediately after complete absorption of the viscoelastic agent from the capsular bag and the anterior chamber. With the help of the intraoperative navigation system, the IOL was adjusted to the targeted implant axis and the incision was made watertight. The models of Alcon AcrySof Toric IOL used in this study included SN6AT2-T7 (16.0 D-25.0 D of spherical power; and 1.0 D-4.5 D of cylindrical power). The diopter of cylindrical power of Rayner 623T IOL ranged from 1.0 D-3.5 D, and spherical power ranged from 15.0 D-23.0 D.
PostoperativeFollow-upThe patients were followed for uncorrected distance visual acuity (UCDVA), best corrected distance visual acuity (BCDVA), residual astigmatism, contrast sensitivity (CS), objective visual quality (including modulation transfer function cut off (MTF cut off), Strehl ratio (SR), objective scatter index (OSI), the objective visual acuity under different contrast (VA100/VA20/VA9)), rotational degree of IOL and national eye institute 25-item visual function questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25) score (Table 1) 3mo after surgery. The contrast sensitivity tester (CSV-1000; Vector Vision, Ohio, America) was used to test the contrast sensitivity while the dual channel objective visual quality tester (OQAS II; Visiometrics, Barcelona, Spain) was used to check the objective visual quality. Taking Rayner 623T as an example, the measurement method of IOL rotational degree was as follows: after dilating the pupil, a digital camera was used under the slit lamp to take color images of the anterior segment under the red light reflection, and the axial markers on the IOL were clearly visible (Figure 1). The image processing software (Photoshop CC 2019 version; adobe, California, USA) was used to mark the axis (Figure 2 green line) and the horizontal line (Figure 2 blue line) of IOL. The angle of IOL axis (green line) was determined by the angle measuring tool provided by the software, which was compared with the intended axis to confirm the degree of rotation 3mo after surgery.

Table 1 Item analysis of NEI VFQ-25
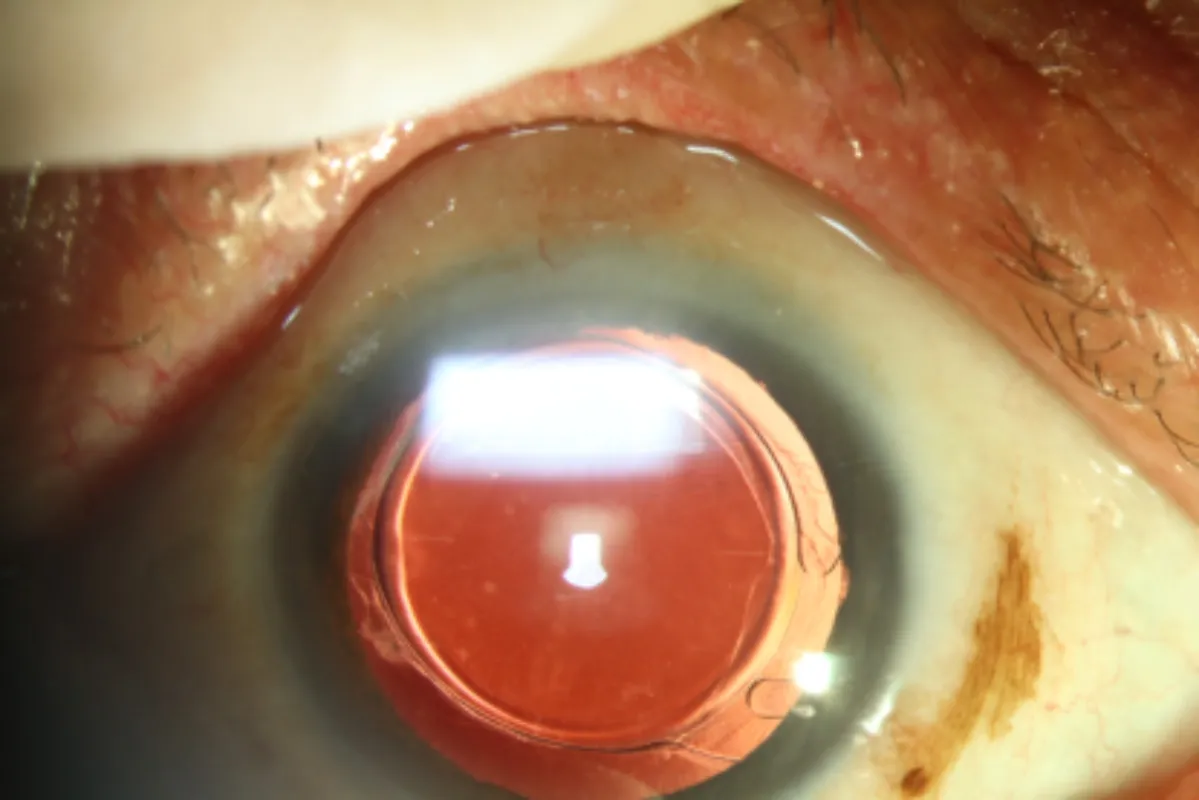
Figure 1 The color image of anterior segment under slit lamp 3mo after surgery IOL axial marker was clearly visible (the marker line was at approximate horizontal position).
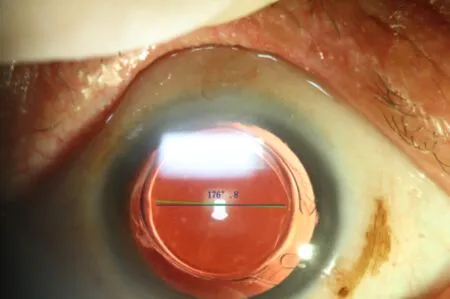
Figure 2 Measurement of IOL axis 3mo after surgery by the software (the green line is the IOL axis shown by the IOL marker line, the blue line is the horizontal line, and the software automatically generates the angles of the two).
VectorAnalysisWe performed vector analysis using the Alpins method, facilitated by the ASSORT program version 5.04 (Assort Pty., Ltd., Victoria, Australia). Target induced astigmatism (TIA) means the astigmatic change in the magnitude and axis the surgery intended to correct. Surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) means the amount and axis of the astigmatism the surgery actually induced. Difference vector (DV) means the induced astigmatic change by the magnitude and axis that would enable the initial surgery to achieve its intended astigmatic target (Figure 3). That means the difference vector is the actual measured postoperative refraction remaining after the surgery. Correction index was calculated by determining ratio of SIA to TIA (correction index is preferably 1.0; if correction index >1.0 overcorrection occurred and if correction index <1.0 undercorrection occurred).

Table 2 Demographics and clinical information of patients included in this study

Figure 3 Vector plots.
Absolute angle of error is the angle described by the vectors of SIA versus TIA. Index of success was calculated by dividing DV by TIA, representing a relative measure of success (index of success is preferably 0).
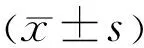
RESULTS
PreoperativeClinicalInformationofPatientsintheTwoGroupsThere were no significant differences in the patient demographic and clinical data including the age, gender, left or right eye, UCDVA, BCDVA, manifest refraction, corneal astigmatism, axial length and IOL spherical or cylinder power between the two groups (P>0.05) as shown in Table 2.
VisualAcuity,Refraction,RotationalStabilityandVisualQualityAll patients’ surgeries were without any significant complications and were followed up for 3mo and no patient required a repeated surgical correction to adjust IOL axis due to visual quality or postoperative lens rotation. There was a statistically significant (P<0.05) improvement in the UCDVA and BCDVA of patients in both groups postoperative compared to preoperative. Moreover, the IOL cylinder power was obviously decreased after surgery compared with that before surgery (P<0.05), which indicated that both brands of Toric IOL could effectively improve patients’ vision and correct astigmatism (Figure 4). The rotational stability of Toric IOL in two groups are as follows: in Rayner group, 80% of the patients rotated below 5° and 20% of the patients (5 eyes) rotated between 5° and 10°, with an average of rotational degree of (3.5±1.6)° while in Alcon group, 76% of the patients rotated below 5° and 24% of the patients (6 eyes) rotated between 5° and 10°, with an average of rotational degree of (4.0±2.1)° (P>0.05). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in UCDVA, BCDVA, residual astigmatism, IOL rotational stability, contrast sensitivity, objective visual quality and VFQ-25 scale score (Table 3) after 3mo of surgery (P>0.05).
VectorAnalysisVector analysis was performed 3mo after surgery (Table 4). The TIA vector was 2.02±0.55 D in the Rayner group and 2.19±0.77 D in the Alcon group. No statistically significant difference in average TIA vector nor average SIA vector (P>0.05) was found between the two groups. The average DV for the Rayner and Alcon groups were 0.56±0.22 versus 0.53±0.26, respectively, and also, no statistically significant difference was found (P>0.05). The mean correction index were 1.01±0.31vs1.03±0.30, respectively, reflecting light overcorrection in both groups (P>0.05). Other vector analysis parameters had no statistically significant difference between groups (P>0.05).
DISCUSSION
Several traditional and surgical clinical therapies are available for the correction of corneal astigmatism. Many kinds of IOLs are available which are designed with multiple characteristics for the improvement of the clinical outcomes including visual acuity, correction of astigmatism, and rotational stability. Toric IOLs are increasingly used to correct corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery and have greatly improved post-operative visual performance. In addition to the implantation of Toric IOLs, transparent corneal incision release is more commonly used. However, due to the requirements for the position of the surgical incision, the limitation of the astigmatism correction, and the poor predictability of the postoperative effect[9], surgeons prefer to choose a method that can treat corneal astigmatism while performing routine cataract surgery procedures. With growing interests in reducing undesirable residual astigmatism, a well-designed Toric IOLs greatly improves the postoperative visual quality and surgical satisfaction of patients[10], and are considered as the best way for the treatment of cataract with corneal astigmatism.

Figure 4 Refractive outcomes at 3mo postoperatively A: Uncorrected distance visual acuity; B: Uncorrected distance visual acuity vs best corrected distance visual acuity; C: Spherical equivalent refraction accuracy; D: Postoperative refractive cylinder.

Table 3 Visual quality analysis at 3mo postoperatively

Table 4 Vector analysis of astigmatism at 3mo postoperatively(Mean±SD)
Accurate preoperative biometry is the basis of the calculation of Toric IOL cylinder power and targeted implant axis. The measurements for axial lengths are limited, but there are many methods available for the measurement of corneal curvature. Kimetal[11]have found that there was no statistical difference in the corneal curvature measured by the keratometer, IOL Master and Pentacam corneal topography, and there was no statistical difference in the calculated IOL cylinder power and the targeted implant axis by the Toric IOL calculation formula. In this study we used the most commonly used optical biometer-IOL Master to measure the corneal curvature.
Many Toric IOLs are available with different characteristics, such as Tecnis, Precizon, AT Torbi 709, Acrysof Toric and Rayner 623T with monofocal design[12-13]. They all performed well in correcting corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. Our aim was to compare the clinical outcomes of Rayner 623T in comparison with Alcon Acrysof Toric, a widely used IOL. Rayner 623T has closed-loop haptics and is aberration free. Alcon Acrysof Toric has open-loop C haptics and has anterior Toric surface with a proprietary wavefront-designed Toric aspheric optic, resulting in negative spherical aberration. Both Toric IOL have two reference marks on the axis of the cylinder of their surface. Although their IOL characteristics are definitely different, their postoperative clinical results for many parameters were similar to each other.
The postoperative UCDVA is the most direct and important index used to evaluate the success of cataract surgery, and in our study the postoperative UCDVA in Rayner group was 0.17±0.20. The postoperative residual astigmatism is the objective index indicated to evaluate the astigmatism correction effect of Toric IOL and the average residual astigmatism in Rayner group was (-0.57±0.24) D. A study conducted by Alberdietal[14]showed that the postoperative UCDVA after the implantation of Rayner Toric IOL in 27 cases was 0.10, and the residual astigmatism was -0.52 D, which was consistent with results of this study.
The rotational degree of IOL reflects the stability of Toric IOL in the capsule. In order to achieve a good postoperative effect, the axial rotation of Toric IOL should be controlled within 5°[15]. In this study, 80% of patients in the Rayner group rotated below 5° and 20% of patients (5 eyes) rotated between 5° and 10°, with an average rotational degree of (3.5±1.6)°. 76% of patients in the Alcon group rotated below 5° and 24% of patients (6 eyes) rotated between 5° and 10°, with an average rotational degree of (4.0±2.1)°. By reviewing the literature, a study by Entabietal[16]showed that the average postoperative rotational degree of Rayner 623T was 3.44°, and the range of rotational degree was 0°-12°. In another study, Mendicuteetal[17]found that Alcon Acrysof Toric had better rotational stability, and the rotational degree was all below 12°, which was consistent with results of this study. Both brands of Toric IOLs adopted a one-piece design to increase the rotational stability of IOL. Correspondingly, the three-piece Toric IOL has poor rotational stability, with about 41% of the postoperative rotational degree greater than 10°[18], and therefore not recommended and was gradually withdrawn from the market. Recent studies have shown that the area of capsulorhexis, axial length and lens thickness were positively correlated with Toric IOLs’ early postoperative rotational stability[19-20], and a capsulorhexis within 5.8 mm had an important significance in improving rotational stability[21], while for the long-term, reducing the polishing of anterior capsule may improve the rotational stability of a Toric IOL[22]. In our study, we performed capsulorrhexis of about 5.5-6.0 mm and avoided unnecessary polishing of anterior capsules. The above surgery technique may partially explain the IOLs’ rotational stability described in our study results. As for Rayner 623T, in addition to its one-piece design, the excellent rotational stability of Rayner 623T is due to its unique anti-vaulting haptic (AVH) loop design. The total length of IOL is 12.5 mm and when the diameter of the capsule is ≥12.5 mm, the loop is fully extended. When the diameter of the capsule shrinks to 10.5 mm after surgery, the outer loop begins to resist the pressure generated by the capsule contraction. As the diameter of the capsule reaches 10 mm, the outer loop begins to contact with the inner loop, generating an additional progressive support force, and when the diameter of the capsule reaches 9.5 mm, the outer loop is in full contact with the inner loop, and the contact between the top of the loop and the optical part produces a strong supporting force to resist the impact of the capsule contraction on IOL.
The National Eye Institute 25-Item Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25) can quickly and accurately determine the quality of life related to visual function of patients through more than 20 questions, and thus is widely used in clinical and scientific research of ophthalmology. The scores of Rayner group and Alcon group were both high and showed no statistical difference, reflecting the good postoperative visual related quality of life in the two groups. In addition, there was no statistically significant difference in contrast sensitivity or objective visual quality at each spatial frequency between the twogroups 3mo postoperative (P>0.05). Moreover, there are nearly no complaints of visual disturbance 3mo postoperative, with only 1 eye with glare in Rayner group and 2 eyes with halos in Alcon group. We have seen that both Toric IOLs are equally beneficial and precise in the correction of residual astigmatism after cataract surgery, and was ascertained with good rotational stability, postoperative visual function, and high visual quality of life for patients. As far as we know, this is the first time NEI VFQ-25, contrast sensitivity and objective visual quality have been simultaneously introduced into studies to investigate the clinical effect of Toric IOL, providing more dimensional evidence to support the evaluation of postoperative visual quality and quality of life of patients.
There are still some shortcomings in this study:1) The sample size is small and needs to be expanded; 2) All patients have underwent a detailed and necessary preoperative ophthalmic examination as possible, but due to the limited availability of examination equipment, it was not possible to measure and compare the size of the lens capsule in the two groups before the surgery. Since the size of the capsule can affect the rotational stability of Toric IOL, in the future studies, the measurements of capsule size can be carried out to improve the preoperative measurements; 3) In the measurement of rotational degree of IOL, it is always ideal to compare the IOL axial position immediately after surgery and 3mo postoperative, but the IOL cannot be placed on the targeted implant axis calculated before surgery due to a variety of subjective and objective reasons. Because we used the intraoperative navigation system, the intraoperative axial position anchoring was very accurate, and at the end of the surgery, the operator repeatedly confirmed that the IOL marker line has been placed in the targeted implant axis. Therefore, from the perspective of patients maximum benefit, photographs of anterior segment under slit lamp at sitting position at the end of the surgery were not taken, as we were worried that above operations may cause discomfort, and even increase the risk of postoperative infection in patients. Under conditions of good sterility and patient’s cooperation, photographs of anterior segment under slit lamp at sitting position at the end of the surgery can be taken to calculate the rotation axis of the IOL more accurately and scientifically.
In conclusion, both Rayner 623T and Alcon Acrysof Toric are equally beneficial to accurately correct the corneal astigmatism of cataract patients, and the postoperative visual quality, visual related quality of life score and intracapsular rotational stability of the two groups were high and comparable.

