低氧环境下PLGA/胶原纤维支架对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成肌腱分化影响
姜杨 侯继野 张晓东 徐桂清 王玉 沈雷 吴雨轩

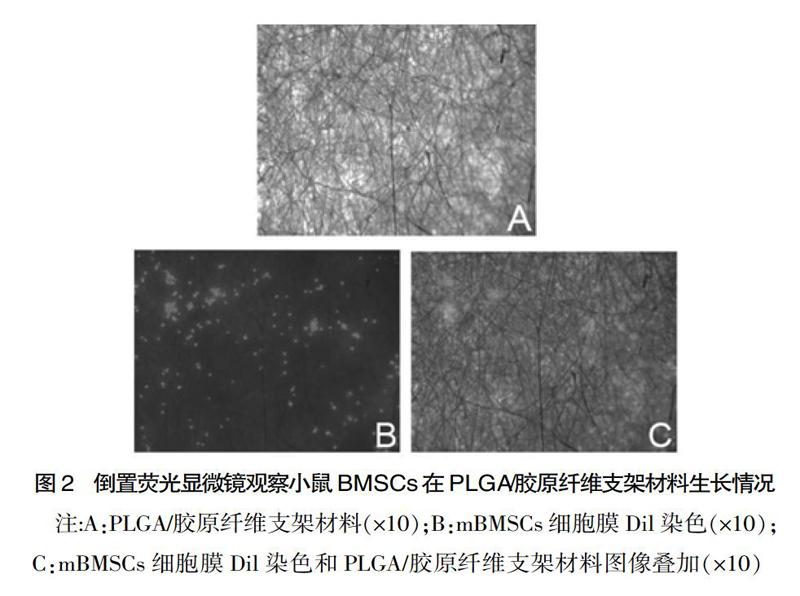
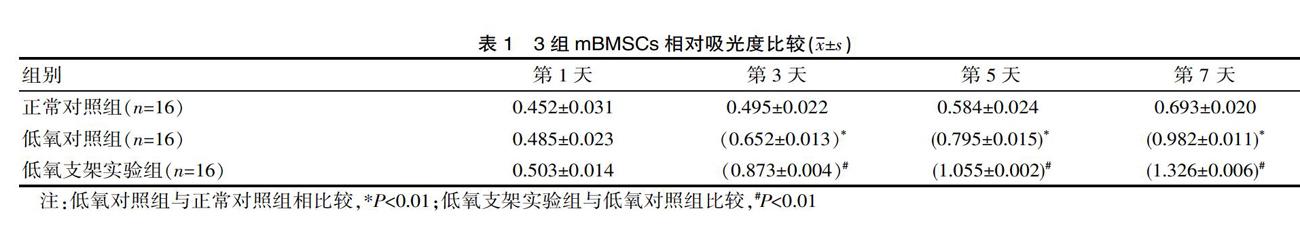
[摘要] 目的 探討低氧环境下PLGA/胶原纤维支架对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞(mBMSCs)增殖及成肌腱分化的影响。方法 利用静电纺丝技术制作出30组PLGA/胶原纤维支架,正常条件下培养的mBMSCs为正常对照组;以3%O2,5%CO2,92%N2建立细胞低氧模型,在低氧环境下培养mBMSCs为低氧对照组,mBMSCs种植在PLGA/胶原纤维支架为低氧支架实验组,各组均进行成肌腱分化诱导实验14 d。CCK-8实验检测3 d、5 d、7 d各组mBMSCs增殖的吸光度值,ELISA实验检测各组mBMSCs上清液肌腱细胞标志性蛋白Tenomodulin和Scleraxis含量。结果 在3 d、5 d、7 d观察点内,正常对照组、低氧对照组、低氧支架实验组mBMSCs吸光度值差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),第3 d、5 d、7 d观察点内,低氧对照组mBMSCs吸光度值均高于正常对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);与低氧对照组相比,低氧支架实验组3 d、5 d、7 d吸光度A值均分别增高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。在细胞低氧环境下,低氧支架实验组Tenomodulin蛋白(4.526±0.002)μmol/L和Scleraxis蛋白(3.752±0.004)μmol/L含量高于低氧对照组Tenomodulin蛋白(2.831±0.023)μmol/L和Scleraxis蛋白(2.457±0.032)μmol/L,低氧对照组Tenomodulin蛋白(2.831±0.023)μmol/L和Scleraxis蛋白(2.457±0.032)μmol/L含量高于正常对照组Tenomodulin蛋白(1.542±0.071)μmol/L和Scleraxis蛋白(1.136±0.056)μmol/L,3组对比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论 低氧环境下PLGA/胶原纤维支架可有效促进mBMSCs增殖和成肌腱分化。
[关键词] 细胞低氧;PLGA/胶原纤维支架;间充质干细胞;细胞增殖;成肌腱分化
[中图分类号] R329 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)11(a)-0001-05
Effects of PLGA/collagen Fiber Scaffold on the Proliferation and Tendon Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells under Hypoxia
JIANG Yang1, HOU Ji-ye2, ZHANG Xiao-dong1, XU Gui-qing1, WANG Yu1, SHEN Lei1, WU Yu-xuan3
1.School of Basic Medicine, Qiqihar Medical College, Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province, 161006 China; 2.Department of Intervention, Qiqihar Jianhua Hospital, Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province, 161006 China; 3.Department of Endocrinology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical College, Qiqihar, Heilongjiang Province, 161006 China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of PLGA/collagen fiber scaffold on the proliferation and tendon differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (mBMSCs) under hypoxic environment. Methods Thirty groups of PLGA/collagen fiber scaffolds were fabricated by electrospinning technology. The mBMSCs cultured under normal conditions served as the normal control group; the hypoxia model of cells was established with 3% O2, 5% CO2, and 92% N2, under hypoxia environment cultivated mBMSCs served as the hypoxic control group, and mBMSCs planted on PLGA/collagen fiber scaffolds served as the hypoxic scaffold experimental group. Each group was subjected to tendon differentiation induction experiments for 14 d. CCK-8 experiment was used to detect the absorbance value of mBMSCs proliferation in each group on 3 d, 5 d, 7 d, and the content of Tenomodulin and Scleraxis in the supernatant of mBMSCs in each group was detected by ELISA. Results Within the observation points of 3, 5, and 7 d, the absorbance values of mBMSCs in the normal control group, hypoxia control group, and hypoxia stent experimental group were significantly different (P<0.05). On the 3rd, 5th, and 7th day, in the observation point, the absorbance values of mBMSCs in the hypoxic control group were all higher than those of the normal control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.01); compared with the hypoxic control group, the absorbance A values of the hypoxic stent experimental group were increased at 3, 5, and 7 d respectively,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.01). In the hypoxic environment, the contents of Tenomodulin protein (4.526±0.002) μmol/L and Scleraxis protein (3.752±0.004) μmol/L in the hypoxic stent experimental group were higher than those in the hypoxia control group Tenomodulin protein (2.831±0.023)μmol/L And Scleraxis protein (2.457±0.032)μmol/L, the hypoxic control group Tenomodulin protein (2.831±0.023)μmol/L and Scleraxis protein (2.457±0.032)μmol/L content were higher than the normal control group Tenomodulin protein (1.542±0.071)μmol/L and Scleraxis protein (1.136±0.056)μmol/L, the difference between the three groups was statistically significant (P<0.01). Conclusion The PLGA/collagen fiber scaffold can effectively promote the proliferation and tendon differentiation of mBMSCs under hypoxia.
综上所述,在低氧环境下PLGA/胶原纤维支架材料与间充质干细胞有良好的相容性,支架材料促进间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,在体外实验模拟机体微环境为肌腱损伤修复提供给一个有力的实验依据。但在低氧环境下PLGA/胶原纤维支架材料促进间充质干细胞分化肌腱细胞生物化机制不明确,还需要深入研究探索,今后将研究低氧环境下详细细胞信号通路,為干细胞组织工程加速修复损伤肌腱,为临床上再生和修复肌腱奠定实验研究基础。
[参考文献]
[1] 杨健,葛建忠.修复运动性肌腱损伤组织工程化肌腱及种子细胞和支架材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8333-8337.
[2] 胡静,李章华.干细胞治疗闭合性不完全肌腱损伤的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(25):32-36,48.
[3] 李丹,郭杏,谭美云.低氧环境对脂肪源性间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].西南医科大学学报,2017,40(2):202-205.
[4] 郭劲书. 腱-骨愈合用硅磷酸钙复合材料的设计、制备及性能研究[D].中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所),2019.
[5] 罗芸,马俊,钱前,等.不同低氧浓度对人脐带间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的影响[J].解放军医药杂志,2019,31(8):6-11.
[6] Ju X, Xue D, Wang T, et al. Catalpol Promotes the Survival and VEGF Secretion of Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells and Their Role in Myocardial Repair After Myocardial Infarction in Rats [J].Cardiovasc Toxicol,2018,18(5): 471-481.
[7] Song F,Jiang D,Wang T, et al. Mechanical Loading Improves Tendon-Bone Healing in a Rabbit Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Model by Promoting Proliferation and Matrix Formation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Tendon Cells [J].Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 41(3): 875-889.
[8] Teng C, Zhou C, Xu D, et al. Combination of platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances tendon-bone healing in a rabbit model of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction[J].J Orthop Surg Res,2016,11(1): 96.
[9] Yang X, Li Y, Liu X, et al. Incorporation of silica nanoparticles to PLGA electrospun fibers for osteogenic differentiation of humanosteoblast-like cells[J].Regen Biomater, 2018, 5(4): 229-238.
[10] 姜杨,李永涛,徐桂清,等.低氧环境下SDF-1对间充质干细胞迁移影响的初探[J].系统医学,2018,3(15):13-15.
[11] 杨晓鹏.壳聚糖-胶原支架引导牙周骨组织再生的实验研究[J].中国民康医学,2018, 30 (4):68-69,72.
[12] 田晓红,张彬,房艳,等.大鼠脂肪源性干细胞与三维打印明胶支架的相容性[J].解剖学报,2017,48(2):209-215.
[13] 贾岩波,梁子红,任逸众,等.同种异体肌腱移植重建治疗膝关节前交叉韧带断裂:中期随访评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(42):6764-6769.
[14] 张新涛,江华基,梁祖儒,等.骨碎补总黄酮通过激活mTOR信号通路促进大鼠腱骨愈合的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(3):248-253.
[15] 冯鹏飞,王继宏,冀云涛,等.肌腱组织工程材料在肌腱损伤的应用特点及前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(18):2940-2945.
[16] 袁晓伟. 载CS-nHA/zein-SIM微球复合明胶支架的制备及其促进腱骨愈合的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2019.
[17] 汪晶晶. 牛脂肪间充质干细胞生物学特性及治疗小鼠肌腱损伤模型的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨体育学院,2018.
[18] Kwak S, Haider A, Gupta KC, et al. Micro/Nano Multilayered Scaffolds of PLGA and Collagen by Alternately Electrospinning for Bone Tissue Engineering[J].Nanoscale Res Lett, 2016, 11(1): 323.
[19] 陈娇,舒莉萍,李轩泽,等.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物负载人骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(26):4109-4114.
[20] 陈凤浩. 间充质干细胞治疗单板U型场地运动员肌腱损伤动物模型的建立研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨体育学院,2017.
(收稿日期:2020-08-01)
[基金项目] 齐齐哈尔医学院院内科研基金项目(QY2016M-03)。
[作者简介] 姜杨(1981-),女,硕士,讲师,研究方向为组织工程肌组织与肌腱。
[通信作者] 沈雷(1975-),男,博士,教授,研究方向为组织工程肌组织与肌腱,E-mail:shenleiby@126.com。

