肿瘤标志物联合多b值DWIMR多期动态增强成像对肝脏肿瘤的诊断价值
蔡彩云 刘建成 陈文锦
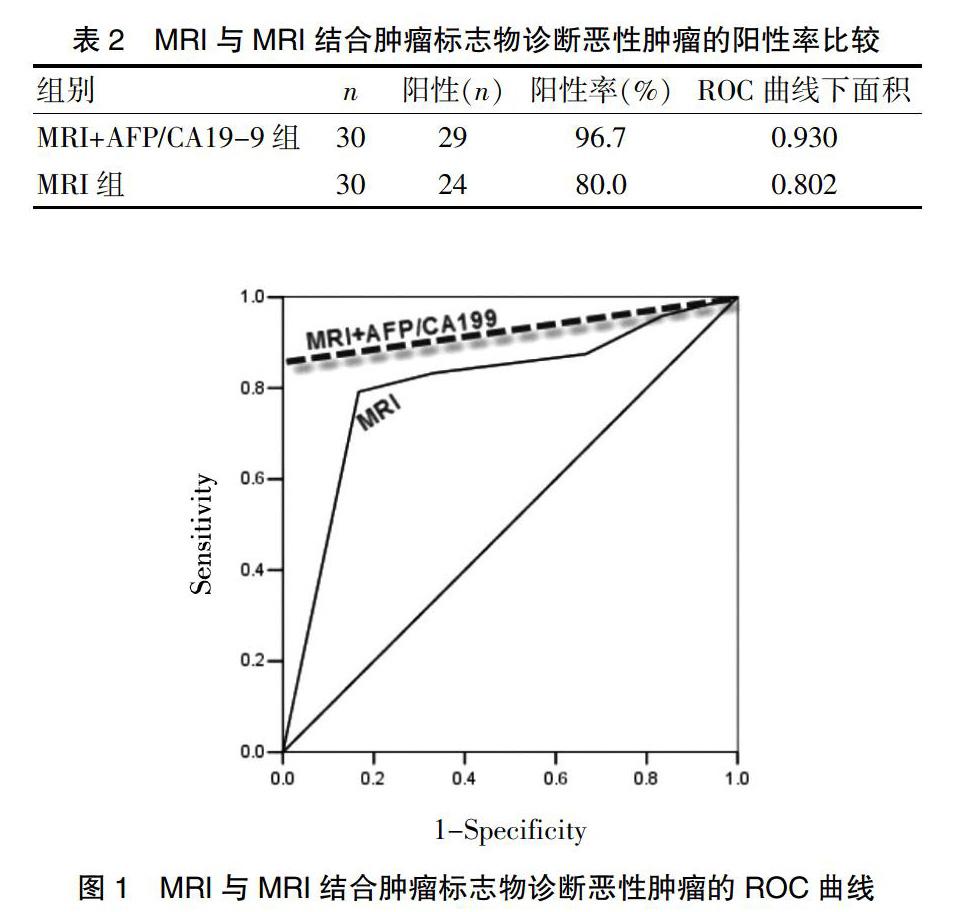
[摘要] 目的 探讨肿瘤标志物联合多b值弥散加权成像(DWI)MR多期动态增强成像对肝脏肿瘤的定性诊断价值。 方法 选取2018年1月~2020年1月在我院确诊的肝脏肿瘤患者为研究对象,根据肿瘤性质分为良性肿瘤组和恶性肿瘤组,均常规行多b值DWI MR多期动态增强成像扫描,结合血清肿瘤标志物水平进行综合分析。结果 低b值时,肝脏良、恶性肿瘤的ADC值间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);高b值时,肝脏良、恶性肿瘤的ADC值间比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。肿瘤标志物联合多b值DWI MR多期动态增强成像对恶性肝脏肿瘤的阳性诊断率为96.7%,而仅单独采用MRI的诊断阳性率为80.0%,差异有统计意义(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析进一步证实MRI联合肿瘤标志物对恶性肿瘤诊断价值较高(ROC曲线下面积为0.930,P=0.021)。 结论 肿瘤标志物联合多b值DWI MRI多期动态增强扫描有利于提高肝脏恶性肿瘤的诊断阳性率,可以作为肝脏恶性肿瘤诊断的有效工具。
[关键词] 核磁共振成像;弥散加权成像;肿瘤标志物;肝脏肿瘤
[中图分类号] R445.2 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)29-0125-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the value of tumor markers combined with multi-b value diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) MR multi-phase dynamic enhanced imaging in the qualitative diagnosis of liver tumors. Methods The patients with liver tumor who were diagnosed in our hospital from January 2018 to January 2020 were selected as the study subjects. According to the nature of the tumor, the patients were divided into a benign tumor group and a malignant tumor group. MRI multi-b value DWI multi-phase dynamic enhancement scans were performed routinely. A comprehensive analysis was carried out on the basis of the serum tumor marker levels. Results When the b value was low, there was no statistically significant difference between the ADC values of benign and malignant tumors of the liver (P>0.05); when the value of b was high, the difference between ADC values of benign and malignant tumors of the liver was statistically significant (P<0.05). The positive rate of tumor markers combined with MRI multi-b value DWI multi-phase dynamic enhancement scan for malignant liver tumors was 96.7%. The positive rate of MRI diagnosis alone was 80.0%, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). ROC curve analysis also further confirmed that MRI combined with tumor markers was of great value in the diagnosis of malignant tumors(the area under the ROC curve was 0.930, P=0.021). Conclusion The combination of tumor markers and multi-b value DWI MRI multi-phase dynamic enhancement scan is conducive to improving the positive diagnosis rate of liver malignant tumors, and can be used as an effective tool for the diagnosis of liver malignant tumors.
[Key words] Magnetic resonance imaging; Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI); Tumor markers; Liver tumor
肝臟恶性肿瘤位居世界恶性肿瘤死亡率的第三位,我国每年约有50万人确诊[1]。早期诊断和治疗对肝脏肿瘤的预后意义重大。资料显示,42.0%的肝脏肿瘤早期局限于单一肝段。局灶性肝脏肿瘤患者五年生存率接近30.0%[2-3]。因此,有效区分恶性与良性肝脏结节对患者的治疗规划和预后具有十分重要的意义。
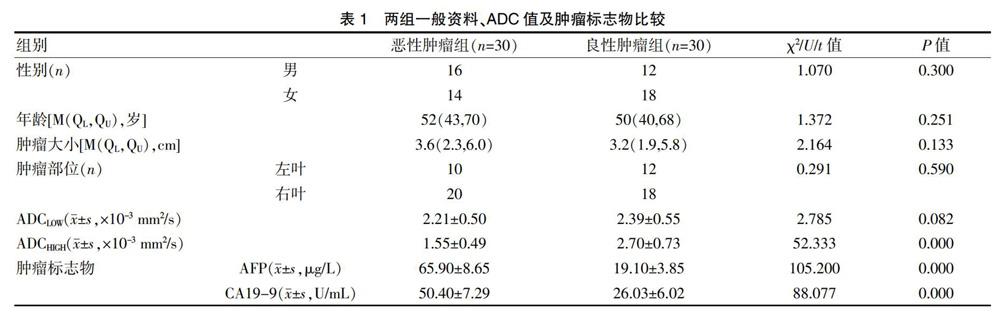
ADC值受b值和感兴趣区域选择的影响,且对直径<2 cm结节的诊断存在假阳性可能[12],因此本研究尝试结合其他检查以提高肝脏恶性肿瘤的诊断阳性率。近年来众多文献报道了多种肝癌有关的血清标志物,包括AFP、CA19-9、高尔基体蛋白73(GP73)、甲胎蛋白异质体、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)、血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)、异常凝血酶原(DCP)等。而其中诊断特异性和灵敏度最高的是AFP和CA19-9[7,13]。AFP主要针对肝细胞肝癌,每隔半年检测1次,其对肝癌筛查及预后判断均具有较大的临床价值。然而有研究显示,部分肝癌患者(如胆管细胞癌等)的AFP并不升高,建议采用影像学联合血清AFP检查的方法,可以降低肝癌漏诊率[14]。CA19-9作为一种非特异性肿瘤相关抗原,在健康人群体内处于低水平,而在消化道恶性肿瘤患者中存在异常增高现象。CA19-9检测有利于发现AFP阴性的肝癌患者,提高肝癌诊断阳性率[15]。本研究结果显示,恶性肿瘤组血AFP、CA19-9浓度分别为(65.90±8.65)μg/L、(50.40±7.29)U/mL,显著高于良性肿瘤组的(19.10±3.85)μg/L、(26.03±6.02)U/mL,两组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),因此本研究同时选用AFP和CA19-9两个肿瘤标志物。通过比较分析单独MRI检测和MRI联合AFP/CA19-9检测对肝脏恶性肿瘤的诊断阳性率,结果显示多b值DWI MR多期动态增强成像与肿瘤标志物联合检测对恶性肿瘤的阳性诊断率为96.7%,而仅依靠MRI的阳性诊断率为80.0%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析也进一步证实,MRI联合肿瘤标志物对恶性肿瘤的诊断价值较单独MRI检测更高(ROC曲线下面积为0.930,P=0.021)。
综上所述,肿瘤标志物联合多b值DWI MRI多期动态增强扫描有利于提高肝脏恶性肿瘤的诊断阳性率,对临床鉴别肝脏良、恶性肿瘤具有一定的实际价值。
[参考文献]
[1] An L,Zeng HM,Zheng RS,et al.Liver cancer epidemiology in China,2015[J].Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi,2019,41(10):721-727.
[2] Ji M,Liu Z,Chang ET,et al.Mass screening for liver cancer:Results from a demonstration screening project in Zhongshan City,China[J].Sci Rep,2018,8(1):12 787-12 795.
[3] Qu CF,Chen TY,Wang YT,et al.Primary prevention model of liver cancer in rural China[J].Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi,2018,40(7):481-489.
[4] Li J,Yang Y.Clinical study of diffusion-weighted imaging in the diagnosis of liver focal lesion[J].J Med Syst,2019,43(3):43-48.
[5] Mürtz P,Sprinkart AM,ReickM,et al.Accurate IVIM model-based liver lesion characterisation can be achieved with only three b-value DWI[J].Eur Radiol,2018,28(10):4418-4428.
[6] Wu LF,Rao SX,Xu PJ.Pre-TACE kurtosis of ADC(total) derived from histogram analysis for diffusion-weighted imaging is the best independent predictor of prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Eur Radiol,2019,29(1):213-223.
[7] Ma B,Liu X,Yu Z.The effect of high intensity focused ultrasound on the treatment of liver cancer and patients' immunity[J].Cancer Biomark,2019,24(1):85-90.
[8] Li S,Shi S,Li A,et al.Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of primary liver cancer after HIFU treatment[J].J Coll Physicians Surg Pak,2019,29(4):305-308.
[9] Stein D,Goldberg N,Domachevsky L,et al.Quantitative biomarkers for liver metastases:Comparison of MRI diffusion-weighted imaging heterogeneity index and fluorine-18-fluoro-deoxyglucose standardised uptake value in hybrid PET/MR[J].Clin Radiol,2018,73(9):832.e17-832.e22.
[10] 王殿峰,張凤翔,卢东霞,等.多b值DWI对肝脏占位性病变的诊断价值[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2017,15(3):315-317.
[11] 刘岩.多b值DWI联合MRI动态增强扫描对诊断肝细胞癌的价值探讨[J].中国现代医生杂志,2018,56(24):119-122.
[12] 于洪远,刘淑明,李兵.AFP、AFU、TSGF联合检测在早期肝癌中的诊断效能[J].癌症进展,2019,15(2):10-14.
[13] 梁美妹,林秋艳,柯振符.肿瘤特异性生长因子与AFP、CEA联合检测在原发性肝癌早期诊断的意义[J].现代诊断与治疗,2018,12(22):3652-3654.
[14] 杨绍蕊.血清肿瘤标志物联合血常规指标检测在原发性肝癌诊断中的应用效果分析[J].世界复合医学,2019, 5(8):145-147.
[15] Kudo M,Ikeda M,Ueshima K.Response evaluation criteria in cancer of the liver version 5(RECICL 2019 revised version)[J].Hepatol Res,2019,49(9):981-989.
(收稿日期:2020-04-14)

