急诊医学教学中急性中毒模拟情景式教学的研究
王凯飞 王舒 李治延 段鹏 屈慧 杜俊凯
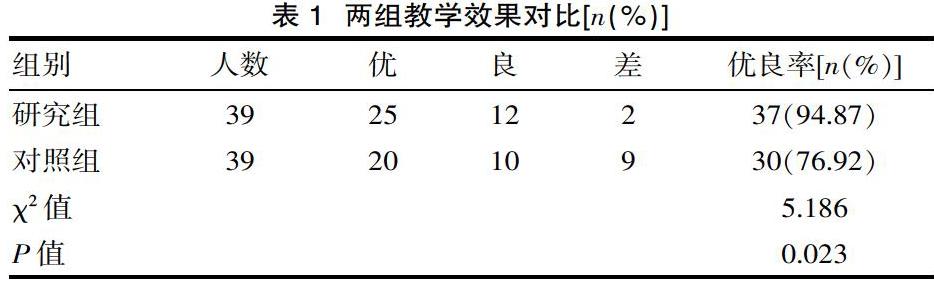
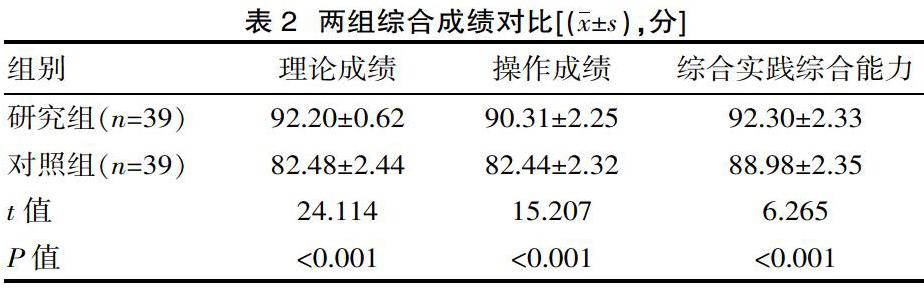

[摘要] 目的 探讨急诊医学教学中急性中毒模拟情景式教学的效果。方法 选取该院2018年9月—2019年9月入学的78名医学生作为研究对象,按照硬币两面法分为研究组(n=39)与对照组(n=39),研究组急诊医学教学中采用急性中毒模拟情景式教学,对照组急诊医学教学中采用常规模式教学,比较两组教学效果、学生综合成绩及教学质量。结果 教学效果:研究组教学效果优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。学生综合成绩:研究组理论成绩、操作成绩及综合实践能力均明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。教学质量:研究组基本操作、临床操作及教学满意度相较对照组明显偏高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 急诊医学教学中采用急性中毒模拟情景式教学,既能促进教学效果,又能提高学生综合成绩,确保教学质量,应被大力推广及应用。
[关键词] 急诊;医学教学;急性中毒;模拟情景式教学;教学效果
[中图分类号] R587 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-5654(2020)09(a)-0153-03
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of simulated situational teaching of acute poisoning in emergency medicine teaching. Methods A total of 78 medical students who enrolled in the hospital from September 2018 to September 2019 were selected as the research objects. According to the two-sided method of the coin, they were divided into a study group (n=39) and a control group (n=39). The study group in the emergency department of acute poisoning simulated situational teaching was used in medical teaching, while the control group used conventional mode of teaching in emergency medicine teaching. The teaching effect, students' comprehensive performance and teaching quality were compared between the two groups. Results Teaching effect: The teaching effect of the study group was better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Students' comprehensive scores: the theoretical scores, operational scores and comprehensive practical ability of the study group were significantly higher than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Teaching quality: the basic operation, clinical operation and teaching satisfaction of the study group were significantly higher than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The use of acute poisoning simulation scene teaching in emergency medicine teaching can not only promote the teaching effect, but also improve the students' overall performance and ensure the quality of teaching. It should be promoted and applied.
[Key words] Emergency department; Medical teaching; Acute poisoning; Simulated situational teaching; Teaching effect
近幾年,随着人们生活水平不断提高,要求临床医生不但需要具备丰富的理论知识,还需要娴熟的临床操作技能及正确应对实际临床问题的能力,因此,培养优秀临床医生是目前医学教育事业所面临的重点问题[1-2]。急诊医学属于临床操作性较强的学科,临床医生除了要处理患者的抢救问题,还需要应对患者及家属因疾病产生的不良情绪。目前,对于急诊医学教学中使用的教学方式大多以理论知识为主,学生很难有实际操作的机会。针对这一现状,急诊医学教学中推出了急性中毒模拟情景式教学,该教学方式自被提出以来,就取得了显著的教学效果。故该次研究将2018年9月—2019年9月入学的78名医学生作为研究对象,给予学生急性中毒模拟情景式教学,随后对比两组教学效果、学生综合成绩及教学质量,现报道如下。
[4] 周榆然,胡系意,袁策,等.不同评分系统对急性中毒预后评估价值的比较[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2018,36(11):808-812.
[5] Lidia Martinez Sanchez,Victoria Trenchs Sainz de la Maza, Beatriz Azkunaga Santibanez,et al.Impact of quality-indicator-based measures to improve the treatment of acute poisoning in pediatric emergency patients[J].Emergencias,2016,28(1):31-37.
[6] 王洪梅,吴君,陈莲花,等.改良早期预警评分在预测急性中毒患者预后中的应用[J].海南医学,2016,27(16):2740-2741.
[7] 杨艺,丛小玲,李璐寰,等."院前-急诊科-ICU"情景模拟教学对护生急救思维能力的影响[J].中华现代护理杂志,2019,25(10):1309-1312.
[8] Kaya H, Cokun A,Beton O,et al.COHgb levels predict the long-term development of acute myocardial infarction in CO poisoning[J].Am J Emerg Med,2016,34(5):840-844.
[9] 謝言虎,章敏,柴小青.医学模拟教学在麻醉科危急诊事件的应用[J].安徽医学,2016,37(6):773-775.
[10] 邝素华,谢少波,翁丽芳,等.情景模拟教学在低年资外科住院医师心肺复苏培训中的应用[J].中华医学教育探索杂志,2019,18(6):636-640.
[11] 胡增艳,赵洁,潘曙明,等.在高年级医学生中开展情境模拟训练营的尝试和体会[J].中华医学教育探索杂志, 2016,15(12):1220-1225.
[12] 王静,金晓晴,刘瑞宁,等.强化训练联合实时反馈装置的CPR培训对教学效果影响的研究[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2019,28(2):199-202.
(收稿日期:2020-06-04)

