分数阶霍顿渗透模型及其应用
漆勇方,黄祖峰,欧阳慧敏
分数阶霍顿渗透模型及其应用
漆勇方1,黄祖峰2,欧阳慧敏3
(1. 萍乡学院 工程与管理学院;2. 芦溪县大安中学;3. 萍乡市第七中学,江西 萍乡 337000)
文章研究了Riemann-Liouville 分数阶和Caputo分数阶霍顿渗透模型,得到了分数阶霍顿下渗公式。首先利用分数阶微积分相关理论知识,构建了Riemann-Liouville分数阶和Caputo分数阶霍顿渗透模型。其次,利用分数阶线性微分方程的求解公式,对分数阶霍顿渗透模型进行求解,得到了分数阶霍顿下渗公式。研究结果可运用到城市雨水累积入渗量问题中。
分数阶;霍顿;下渗;柯西问题
引言
近几年,城市内涝成为了公众普遍关心的问题。为了缓解城市内涝灾害,2015年开始,国家着手海绵城市建设并公布了第一批海绵城市名单。经过几年的发展,我国在海绵城市建设方面积累了一些的经验。海绵城市建设过程中,大家最关注的是雨水下渗问题。一直以来,霍顿下渗公式被广泛运用,成为研究城市水文化的有力工具。
1941年,霍顿构建了一阶微分系统,并对其进行了求解,得到了雨水下渗速度和时间的函数关系式,也就是霍顿下渗公式,霍顿下渗公式生动地描述了下降渗透能力从最大容量到最小容量的过程[1]。1982年,Verma对霍顿方程进行了改善,模型考虑了雨水达到稳定下渗速度以后,下渗函数值的变化情况[2]。
利用霍顿下渗方程研究城市地表的降雨径流行为是一个重要的科学和实践问题。Redfern Thomas W等研究了一种复杂的水文行为,其入渗速率比通常假设的要大,其构造的水文模型有助于进一步了解城市表面和水文行为之间的联系[3]。Leandro J等人揭示了一种考虑建筑类型变异性和地表空间异质性的方法,该方法依赖于开放式街道地图(OSM)的蓄水能力有限的城市地区。研究结果表明:城市特征的空间异质性对估计的陆上洪水深度具有中等到高度的影响;由于模型模拟的动态效应,多个城市特征的添加具有更高的累积效应;将建筑物的径流连接到下水道有助于在地表洪水深度上观察到的非线性效应;OSM数据有助于确定冲击区域和可渗透自然地表水流路径[4]。Steffen Davidsen等人利用霍顿下渗方程,在给定城市透水表面的初始条件的情况下估计入渗能力。研究表明,对于典型的大暴雨,一般来说,前期条件会降低砂土和黏性土的入渗能力1~10年以上的重现期有大量径流[5]。
一直以来,霍顿微分系统得到了广泛的应用,但在实际运用过程中,难免产生误差。为了尽可能地减小误差,本文引进分数阶微积分相关知识,构造分数阶霍顿微分系统,并将研究结果运用到城市雨水累积入渗量问题中。
1 基本概念和有用的引理
本小节主要介绍Riemann-Liouville分数阶微积分以及Caputo 分数阶微积分相关的定义和性质,为后面的研究奠定基础。





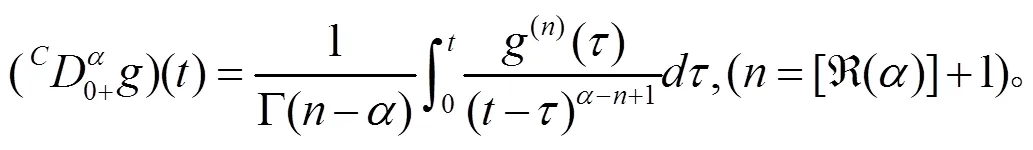
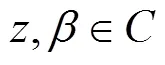
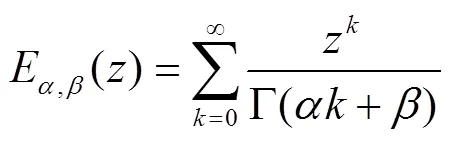
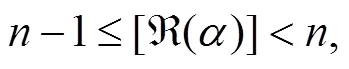

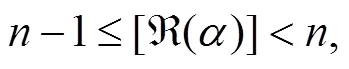
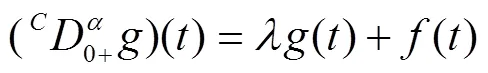
2 主要结果
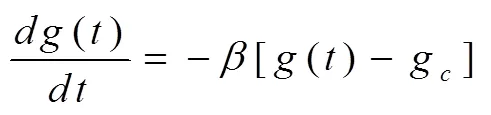
利用常数变异法,或者直接用一阶线性微分方程的求解公式,不难得到霍顿下渗公式:

分数阶微分系统能够准确地描述复杂的物理现象和自然现象。很多用整数阶微分方程无法解决的实际问题,借助分数阶微分微积分的相关理论,都能得到圆满地解决。分数阶微积分在近20年的时间里,取得了突飞猛进的发展,为其他学科的创新与发展提供了理论依据。本小节将在已有的研究成果基础上,研究分数阶霍顿下渗系统及其应用。




的解为

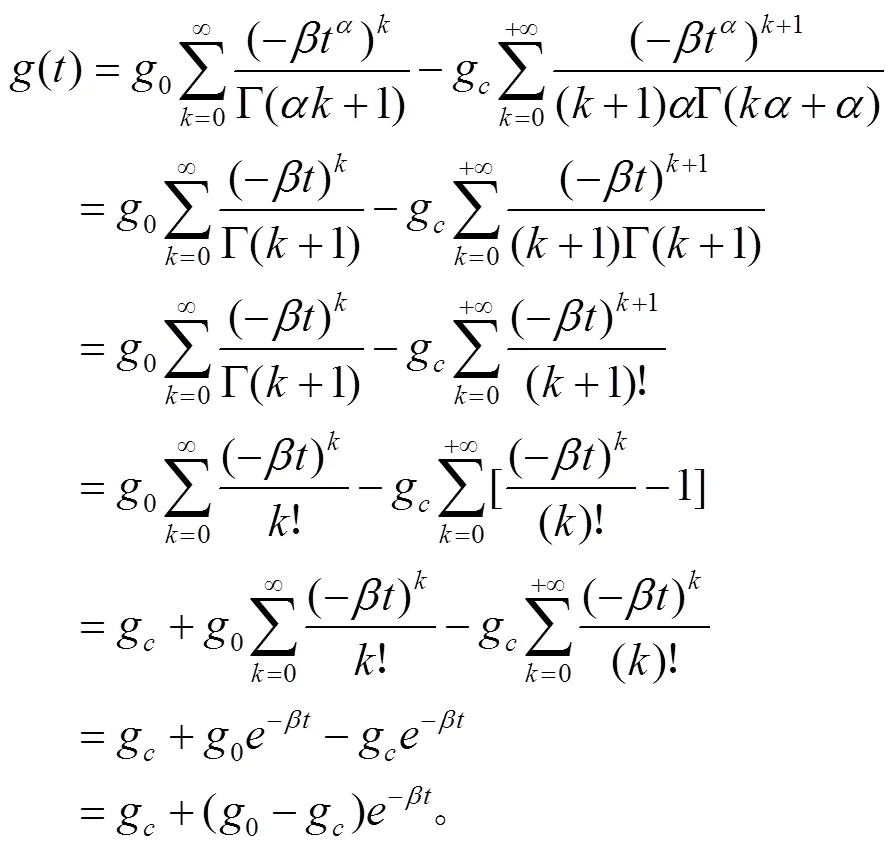
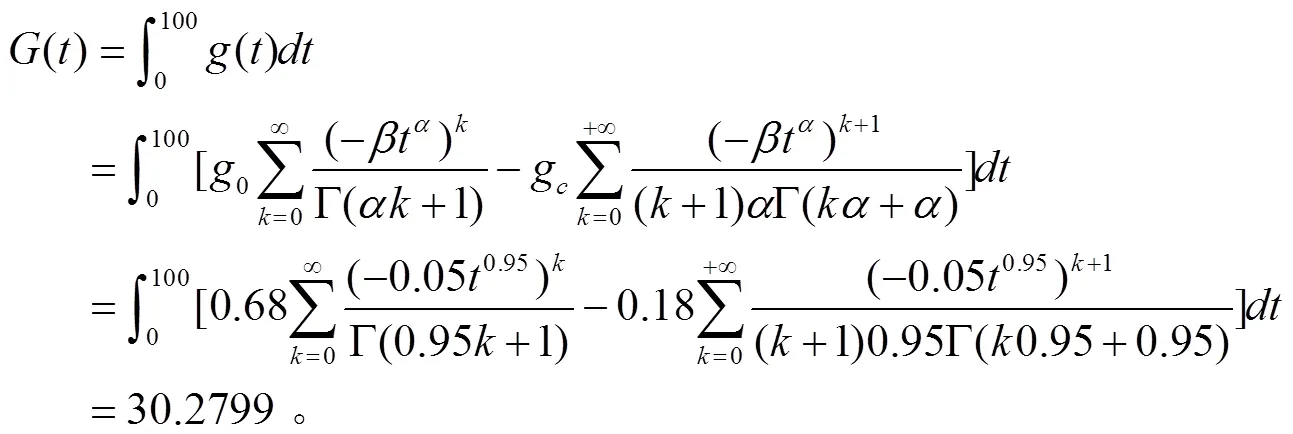
结论

[1] Horton, R. E. An approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration-capacity[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1941, 5(C): 399~400.
[2] Verma, S. C.Modified Horton’s infiltration equation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1982,58: 383~388.
[3] Redfern, T. W., Macdonald, N., Kjeldsen, T. R., etal. Current understanding of hydrological processes on common urban surfaces[J]. Progress in Physical Geography, 2016, 40(5): 699~713.
[4] Leandro J., Schumann A. , Pfister, A. A step towards considering the spatial heterogeneity of urban key features in urban hydrology flood modelling[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 535: 356~365.
[5] Steffen D, Roland L, Nanna H.R., etal. Initial conditions of urban permeable surfaces in rainfall-runoff models using Horton’s infifiltration[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2018, 77(3): 662~669.
[6] Kilbas Anatoly A., Srivastava Hari M., Trujillo Juan J. Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Ltd, 2006: 69~91.
[7] Barrett, J.H. Differential equations of non-integer order[J]. Canad. J. Math., 1954, 6(4): 529~541.
[8] Luchko, Y. F. and GORENFLO, R., An operational method for solving fractional differential equations with the Caputo derivatives[J]. Ada Math. Vietnam., 1999, 24(2): 207~233.
Fractional Horton Infiltration Model and Its Application
QI Yong-fang1, HUANG Zu-feng2, OUYANG Hui-min3
(1. School of Management and Engineering, Pingxiang University, Pingxiang Jiangxi 337000; 2. Da’an Middle School, Pingxiang Jiangxi 337000; 3. Pingxiang No.7 Middle School, Pingxiang Jiangxi 337000, China)
The Riemann Liouville fractional and Caputo fractional Horton infiltration models are studied, and the fractional Horton infiltration formula is obtained. Firstly, the Riemann Liouville fractional order and Caputo fractional order Horton penetration models are constructed by using the relevant theoretical knowledge of fractional calculus. Secondly, the fractional Horton infiltration model is solved by using the solution formula of fractional linear differential equation, and the fractional Horton infiltration formula is obtained. The research results are applied to the problem of accumulated infiltration of rainwater in the region.
fractional; Horton; infiltration; Cauchy type problem
2020-03-07
萍乡市科技计划项目(2019C0104);江西省教育厅科技项目(GJJ191146)
漆勇方(1984—),男,江西萍乡人,讲师,硕士,研究方向:定性理论。
O211
A
2095-9249(2020)03-0013-05
〔责任编校:吴侃民〕

