钢轨横垂双向Pinned-pinned振动抑制研究
纪忠辉,文永蓬,翁琳,邹钰
钢轨横垂双向Pinned-pinned振动抑制研究
纪忠辉,文永蓬,翁琳,邹钰
(上海工程技术大学 城市轨道交通学院,上海 201620)
为抑制钢轨的横向和垂向Pinned-pinned振动,建立含横向与垂向双向振动的轨道系统动力学模型,对钢轨横垂双向振动的特性进行分析,提出将吸振器安装在轨腰两侧用以抑制钢轨横垂双向振动的方法。利用提出的Pinned-pinned振动数值评价指标,设计了钢轨吸振器的参数,分别对横垂双向钢轨吸振器的有效性进行验证。研究结果表明:轨枕离散支撑的作用使钢轨产生横垂双向的Pinned-pinned振动。柔度比指标根据轨道不同位置的动柔度差异建立,可以反映Pinned-pinned振动的频率与大小,从而有效指导钢轨吸振器的设计。在钢轨两侧分别附加设计频率为145 Hz与270 Hz的横向与垂向钢轨吸振器,可以有效降低钢轨不同位置的动柔度差异,提高钢轨振动衰减能力,对横向、垂向的Pinned-pinned振动抑制效果分别达到90%与91%。研究成果对钢轨双向Pinned-pinned振动抑制以及钢轨吸振器的参数设计具有重要的参考价值。
横向振动;钢轨动柔度;Pinned-pinned振动;双向吸振器;振动衰减率
由于钢轨受到不连续支撑,城市轨道交通的轨道系统出现Pinned-pinned振动,加剧钢轨波磨的发展,造成轨道−车辆系统的振动加剧,不仅降低乘客的乘坐舒适性,而且影响车辆与轨道部件的使用寿命[1−2]。由质量、刚度和阻尼构成的钢轨吸振器,因其具有结构简单、易于实施、减振效果好等优点,成为轨道交通领域振动控制的有效手段之一[3−4]。近年来,针对钢轨的Pinned-pinned振动以及钢轨吸振器的抑振方法,国内外学者开展了大量的研究工作。谷永磊等[5]通过建立无砟轨道有限元模型,获得了钢轨垂向与横向Pinned-pinned振动的频率以及直观的振动模态。李伟等[6]通过对广州地铁轨道系统进行力锤敲击测试得到钢轨位移导纳,发现垂向Pinned-pinned振动在1 030 Hz左右,横向Pinned-pinned振动在468 Hz左右。张攀等[7]通过有限元模型研究了支撑的刚度、阻尼与间距参数对垂向与横向Pinned-pinned振动的影响,为振动的抑制提供了思路。LI等[8]研究了Euler-Bernoulli梁与Timoshenko梁2种钢轨条件下的Pinned-pinned振动特性,为后续的减振研究提供了良好基础。WU等[9]发现钢轨在Pinned-pinned振动形式下辐射的噪声在轮轨滚动噪声中占主导地位。钢轨吸振器是将包含质量与刚度因素的调谐质量阻尼器黏贴在钢轨轨腰两侧,用以抑制钢轨的振动,降低轨道系统振动带来的危害。刘卫丰等[10]通过现场试验分析发现,在北京地铁剪切型减振器扣件区段,将钢轨减振器安装于轨腰处这一做法可以使钢轨横垂双向频响曲线均趋于平缓,提高钢轨的振动衰减率,显著抑制了此频段内钢轨双向的振动。TAM等[11]提出了在轨道上安装质量−弹簧组成的钢轨吸振器方法,并通过有限元分析与现场测试研究证明,该方法可以有效治理轨道的横垂双向Pinned-pinned共振。赵悦等[12]通过改变吸振器的质量、刚度和阻尼参数,研究了吸振器在轨道垂向振动模型中对钢轨的减振效果,结果表明:吸振器可以有效提高钢轨的振动衰减率,抑制钢轨振动,并且在一定范围内对吸振器参数合理组合可以产生显著的吸振效果。综上,目前对于钢轨吸振器抑制Pinned-pinned振动的研究,多以垂向振动为主,研究方法多采用有限元分析,结合实验测试,尚缺少钢轨吸振器同时抑制轨道垂向与横向振动的方法。因此,本文对钢轨横向和垂向双向振动特性进行分析,建立Pinned-pinned振动数值评价指标,提出并验证将吸振器安装在轨腰两侧用以抑制钢轨横垂双向振动的方法,依据指标设计吸振器的优化参数,从而有效地抑制轨道系统的振动,降低影响车辆行驶的不利因素。
1 轨道系统动力学模型
图1为轨道系统动力学模型,假设横向振动与垂向振动具有正交性。模型中包含钢轨、轨枕、路基以及附加的钢轨吸振器,将其全部简化为质量体,用垂向与横向弹簧表示接触关系。
模型中,钢轨吸振器采用左右同质量双振子结构,左侧钢轨吸振器通过垂向弹簧连接钢轨,用以抑制钢轨垂向振动;右侧钢轨吸振器通过横向弹簧连接钢轨,用以抑制钢轨横向振动。选用等截面的无限长Timoshenko梁代替钢轨,并在两相邻轨枕的中间位置安装钢轨吸振器[13],随轨枕一同周期性离散分布。将轮轨作用力简化为垂向与横向上的单位简谐力。轨道系统动力学模型的参数如表1所示。

图1 轨道系统动力学模型

表1 某地铁轨道系统动力学模型的参数
根据图1建立的轨道系统动力学模型与钢轨简化的Timoshenko梁特性,得到经变换后钢轨垂向与横向振动微分方程,可分别表示如下。
垂向振动:


横向振动:


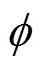
轨道系统中,轨枕和钢轨吸振器的运动方程分别表示为:



利用动柔度概念以及线性叠加理论[13],钢轨振动位移是由外部激励力和内部弹性恢复力共同影响。因此,钢轨的垂向与横向振动位移可分别表 示为:
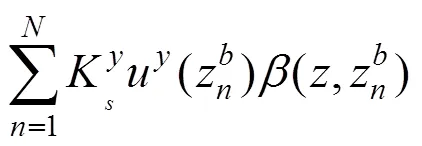
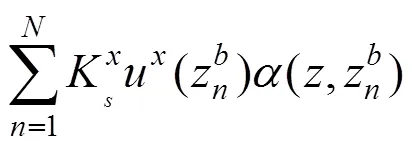
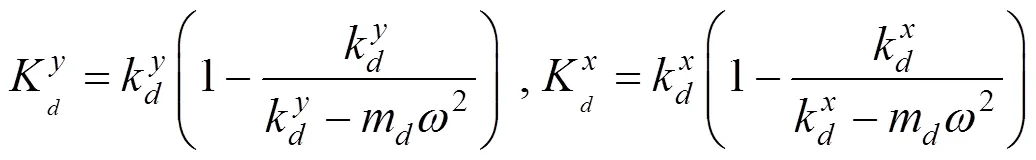

当=0时,(0)即为钢轨受激励处的振动位移响应,则有:

2 钢轨振动特性分析
根据轨道系统动力学模型,选取轨道上具有代表性的典型位置,即轨枕跨度中间位置与轨枕支撑处位置。图2为轨道典型位置的钢轨垂向与横向动柔度。
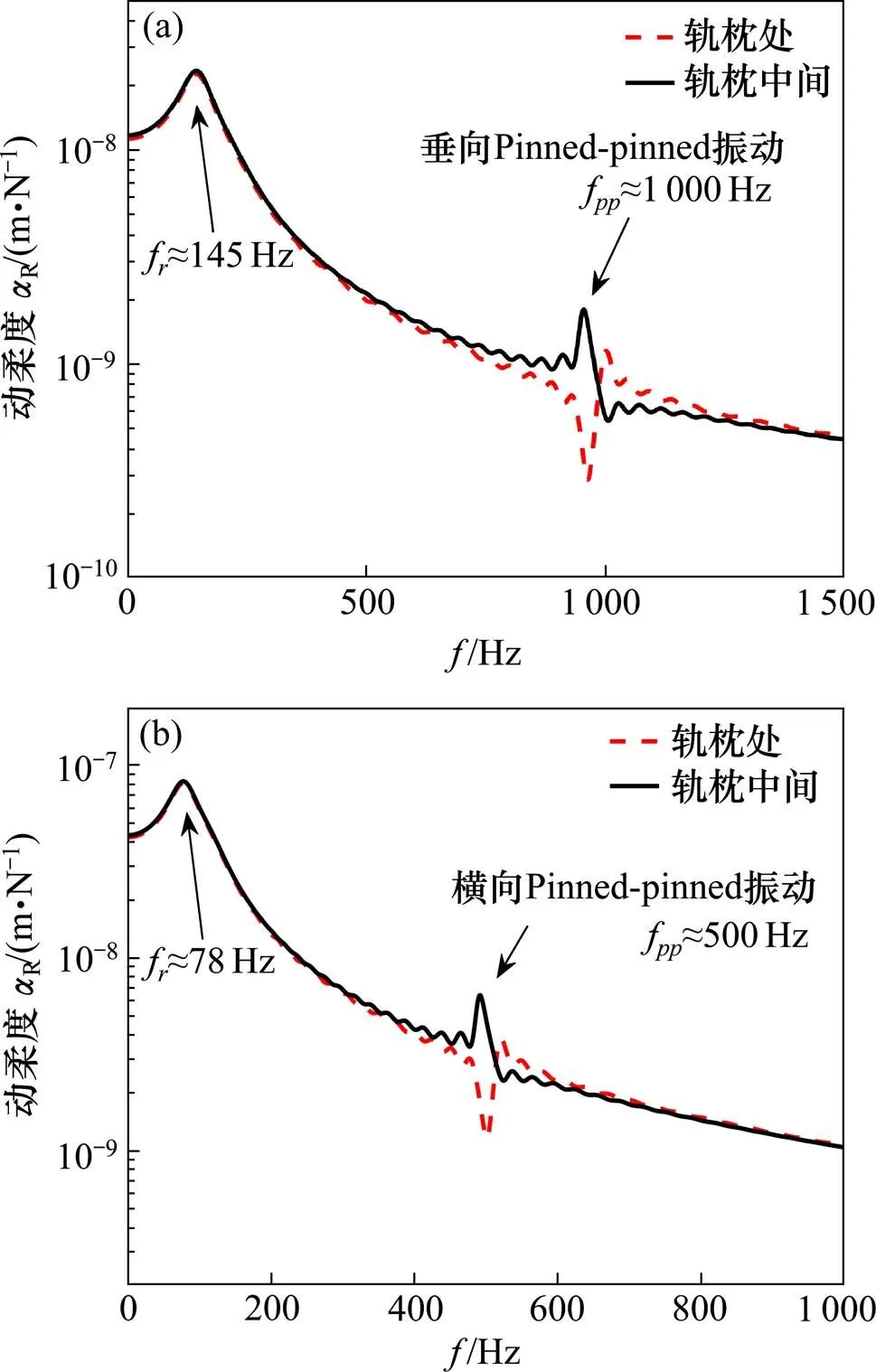
(a) 垂向;(b) 横向
由图2(a)可知:钢轨垂向动柔度在f≈145 Hz处产生第1处峰值。这是由于钢轨通过扣件连接轨枕时,产生了钢轨整体相对于轨枕垂向振动的模态振型,在钢轨的不同位置振动没有明显区别,145 Hz为钢轨与扣件组成系统的固有频率。而在f=1 000 Hz左右钢轨垂向动柔度发生变化,在轨道上不同位置体现为不同形式:在轨枕位置处动柔度出现谷值,振动位移出现极小值;在轨枕中间位置处动柔度出现峰值,振动位移出现极大值。这是由于轨下离散支撑轨枕对钢轨的影响,使钢轨呈现了特殊的垂向Pinned-pinned振动[14],振动模态体现为类似于正弦波的钢轨多段弯曲垂向弹性振动,以轨枕位置为波形的驻节点,如图3(a)所示。
由图2(b)可知:钢轨横向动柔度在78 Hz体现出钢轨整体横向的振动,在500 Hz左右出现钢轨横向Pinned-pinned振动,振动形式与垂向Pinned-pinned振动类似,振动模态如图3(b)所示。
由图2可知:钢轨横垂双向Pinned-pinned振动体现形式近似,振动频率分别为垂向1 000 Hz,横向500 Hz左右。动柔度在轨道不同位置产生较大差异,在轨枕位置处产生谷值,在轨枕跨度中间位置处产生峰值。
3 钢轨吸振器参数设计
根据钢轨的振动特性分析可知,不同位置上的动柔度在Pinned-pinned振动频段产生较大差异,因此论文用两典型位置的钢轨动柔度的差异衡量Pinned-pinned振动的大小。
定义柔度比指标为:

式中:为轨枕跨度中间位置的钢轨动柔度;为轨枕处位置的钢轨动柔度。该指标反映了轨道不同位置在各个频率上的动柔度差异程度,数值越接近0,动柔度差异越小。图4为初始钢轨柔度比情况。
由图4可知:钢轨的垂向与横向柔度比基本保持为0左右,垂向柔度比在959 Hz附近处产生峰值与谷值,横向柔度比在498 Hz附近处产生峰值与谷值,分别对应着垂向与横向的Pinned-pinned振动频率。由此可知,柔度比指标可以基本反应钢轨Pinned-pinned振动的对应频率及量化大小,其绝对值越大,Pinned-pinned振动越激烈,可以依靠此指标来设计钢轨吸振器,达到抑制双向Pinned-pinned振动的目的。
采用在钢轨两侧安装不同方向的钢轨吸振器,来抑制双向的Pinned-pinned振动。钢轨吸振器的各参数变化对减振效果的影响,文献[12]已经作过详细研究。为简化计算,首先选用其结论明确钢轨吸振器的参数,于是令m=12 kg,=0.3。
钢轨吸振器的设计频率design是选取钢轨吸振器参数的关键所在,可表示为[15]:

钢轨吸振器参数的优化可以影响轨道系统的钢轨动柔度,从而降低钢轨动柔度的差异,达到抑制Pinned-pinned振动的目的。
由于振子的质量m确定,因此,下文通过改变刚度k来确定钢轨吸振器的设计频率。在1~500 Hz频率范围内,以1 Hz为区间遍历设计频率design,共500组钢轨吸振器设计方案。图5为每组钢轨吸振器对应的柔度比的最大绝对值,以此观察钢轨吸振器对于Pinned-pinned振动的抑制情况。

图5 钢轨吸振器设计频率对柔度比的影响

图6 钢轨吸振器影响下的钢轨动柔度
由图5可知:随着钢轨吸振器设计频率的增大,柔度比先降低后增大,垂向与横向钢轨吸振器分别在270 Hz与145 Hz达到最优设计频率。2种优化设计使得柔度比最小,意味着此时钢轨动柔度随位置的差异最小。横向、垂向钢轨吸振器对于Pinned- pinned振动的抑制效果分别达到91%与90%。远离优化频率的钢轨吸振器设计方案都会使得对Pinned-pinned振动的抑制效果变差。
将图5中获得的优化设计方案输入模型,获得优化后的钢轨垂向以及横向动柔度,如图6所示。
由图6可知:当钢轨吸振器选用优化设计频率即垂向270 Hz,横向145 Hz时,动柔度在Pinned- pinned振动频段上体现的峰值与谷值得到较好抑制。轨道不同位置体现出的动柔度差异也近乎消失,动柔度曲线变得平滑。这说明钢轨吸振器对双向Pinned-pinned振动都起到了良好的抑制左右,使用柔度比指标进行钢轨吸振器的设计也是有效可行的。
4 验证
为了验证钢轨吸振器的减振效果,采用振动衰减率进行进一步研究。振动衰减率常被国内外学者用来体现振动沿钢轨方向的衰减能力[10, 16],在某一段频率范围内,振动衰减率的数值越大,表明钢轨吸振器的减振效果越明显。
钢轨振动衰减率可以通过轨道上2个位置的位移响应关系求解,具体表示为:
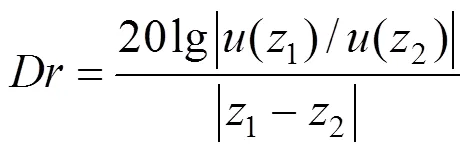
由图7和图8可知:在钢轨的典型位置处,原本在Pinned-pinned振动频段很低的振动衰减率,在附加钢轨吸振器均有所提高。初始很难衰减的Pinned-pinned振动钢轨吸振器的积极作用下变得容易消散。此外,在吸振器设计频率附近的振动衰减率,在附加钢轨吸振器后也有所增长。由此可知,钢轨吸振器可以有效地提高2个频段上的钢轨振动衰减率,有利于轨道系统的振动抑制。

(a) 轨枕位置处;(b) 轨枕跨度中间位置处

(a) 轨枕位置处;(b) 轨枕跨度中间位置处
5 结论
1) 钢轨受到轨枕离散支撑的影响,产生特殊的垂向与横向双向Pinned-pinned振动。Pinned-pinned振动使轨道不同位置的钢轨动柔度产生较大差异,即在轨枕处位置产生谷值,在轨枕跨度中间位置产生峰值。
2) 观察轨道轨枕跨度中间位置与轨枕处位置钢轨动柔度比值的差异,建立柔度比指标,能够反映双向Pinned-pinned的对应频率和量化大小,对钢轨吸振器的抑振参数设计方面具有一定指导作用。
3) 在钢轨两侧分别附加设计频率为145 Hz的横向钢轨吸振器与设计频率为270 Hz的垂向钢轨吸振器,可以使不同位置的钢轨双向动柔度差异减小,对横向、垂向Pinned-pinned振动的抑制效果分别达到90%与91%。在轨道系统中附加钢轨吸振器还可以提高2个频段上的振动衰减率,使轨道振动能量更易消散,从而降低轨道振动带给车辆行驶的不利影响。
[1] 于淼, 王卫东, 刘金朝. 钢轨波磨区段高速轮轨瞬态滚动接触高频动态特性[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2018, 39(5): 58−66. YU Miao, WANG Weidong, LIU Jinzhao. High frequency dynamic characteristics of high-speed wheel- rail transient rolling contact in rail corrugation section[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(5): 58−66.
[2] LI Q, Thompson D J, Toward M G R. Estimation of track parameters and wheel–rail combined roughness from rail vibration[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2018, 232(4): 1149−1167.
[3] Basili M, Casini P, Morelli L, et al. A hysteretic absorber to mitigate vibrations of rail noise barriers[C]// Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2019, 1264(1): 012033.
[4] WU Tianxing. Effects on short pitch rail corrugation growth of a rail vibration absorber/damper[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(1−2): 339−348.
[5] 谷永磊, 赵国堂, 王衡禹, 等. 轨道振动特性对高速铁路钢轨波磨的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2016, 37(4): 42−47. GU Yonglei, ZHAO Guotang, WANG Hengyu, et al. Effect of track vibration characteristics on rail corrugation of high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2016, 37(4): 42−47.
[6] 李伟, 温泽峰, 王衡禹, 等. 地铁钢轨波磨演化过程中的特性分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(4): 70−78. LI Wei, WEN Zefeng, WANG Hengyu, et al. Analysis on the evolution characteristics of rail corrugation on a metro[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(4): 70−78.
[7] 张攀, 王安斌, 王志强, 等. 轨道参数对钢轨Pinned- pinned振动的影响[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2016, 19(12): 72−76, 82. ZHANG Pan, WANG Anbin, WANG Zhiqiang, et al. Influence of track parameters on rail Pinned-pinned vibration[J]. Journal of Urban Rail Transit Research, 2016, 19(12): 72−76, 82.
[8] LI Peng, WANG Ying. Free vibrations of timoshenko beams on viscoelastic foundation[C]// 2018 7th International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 2018). Atlantis Press, 2018.
[9] WU Tianxing, LIU Haiping. Reducing the rail component of rolling noise by vibration absorber: theoretical prediction[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2009, 223(5): 473−483.
[10] 刘卫丰, 张厚贵, 孟磊, 等. 北京地铁采用调频式钢轨减振器抑制钢轨振动的试验研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2016, 29(1): 105−111. LIU Weifeng, ZHANG Hougui, MENG Lei, et al. A test of suppressing rail vibration by tuned rail damper for Beijing metro[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2016, 29(1): 105−111.
[11] TAM P, LEUNG C, MAK C, et al. Development of orthogonal resilient materials for tuned mass dampers[M]. Noise and Vibration Mitigation for Rail Transportation Systems, Springer, Cham, 2018: 585−593.
[12] 赵悦, 肖新标, 韩健, 等. 高速有砟轨道钢轨动力吸振器垂向吸振特性及其参数影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(16):17−25.ZHAO Yue, XIAO Xinbiao, HAN Jian, et al. Vertical characteristic and its parameter effect of rail vibration absorber used in high-speed ballasted track[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(16): 17−25.
[13] WU Tianxing. On the railway track dynamics with rail vibration absorber for noise reduction[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 309(3−5): 739−755.
[14] 吴海涛, 李伟, 温泽峰, 等. 地铁线路轨道中高频动态特性研究[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2017, 37(4): 138−143, 196. WU Haitao, LI Wei, WEN Zefeng, et al. Study on medium/high frequency dynamic characteristics of subway tracks[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2017, 37(4):138−143, 196.
[15] WEN Yongpeng, SUN Qian, ZOU Yu, et al. Study on the vibration suppression of a flexible carbody for urban railway vehicles with a magneto rheological elastomer- based dynamic vibration absorber[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2020, 234(7):749−764.
[16] 王绍华, 韦凯, 杨敏婕, 等. 扣件胶垫频变动力性能对钢轨垂向振动特性影响分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2019, 16(4): 892−899. WANG Shaohua, WEI Kai, YANG Minjie, et al. Influence of frequency-dependent dynamic properties of rail pad on vertical vibration characteristics of rail[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(4): 892−899.
Study on the lateral and vertical two-direction Pinned-pinned vibration suppression of rails
JI Zhonghui, WEN Yongpeng, WENG Lin, ZOU Yu
(School of Urban Railway Transportation, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China)
To suppress the lateral and vertical Pinned-pinned vibration of the rail, a dynamic model of the rail system with lateral and vertical two-direction vibration was established. The characteristics of the lateral and vertical two-direction vibration of the rail were analyzed. A method of installing the vibration absorber on both sides of the rail waist to suppress the two directions rail vibration was proposed. Based on the proposed Pinned-pinned vibration numerical evaluation index, the parameters of the rail vibration absorber were designed, and the effectiveness of the lateral and vertical two-direction rail vibration absorber was verified. The results show that the effect of the discrete support of the sleeper makes the rail produce the lateral and vertical Pinned-pinned vibration. The flexibility ratio index was established according to the difference of dynamic flexibility at different positions of the track, which can reflect the frequency and magnitude of the Pinned-pinned vibration, thus effectively guiding the design of the rail vibration absorber. Lateral and vertical rail shock absorbers with a design frequency of 270 Hz and 145 Hz were added to both sides of the rail, which can effectively reduce the difference in rail dynamic flexibility at different positions and improve the rail vibration decay ability. The Pinned-pinned vibration suppression effect of the vertical and lateral direction is 90% and 91%,respectively. The research work has important reference value for the suppression of the Pinned-pinned vibration of the two-direction rail and the parameter design of the rail vibration absorber.
lateral vibration; rail dynamic flexibility; Pinned-pinned vibration; two-direction vibration absorber; vibration decay rate

U211.3
A
1672 − 7029(2020)08 − 1935 − 08
10.19713/j.cnki.43−1423/u.T20190925
2019−10−21
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11472176,51701118);上海市自然科学基金资助项目(15ZR1419200)
文永蓬(1979−),男,江西永新人,副教授,博士,从事城市轨道车辆振动与控制、城市轨道车辆轮轨磨损、城市轨道车辆关键结构优化设计方面研究;E−mail:yp_wen@163.com
(编辑 涂鹏)

