补肺养阴汤辅助治疗耐多药肺结核的疗效观察
于菁菁 胡雪


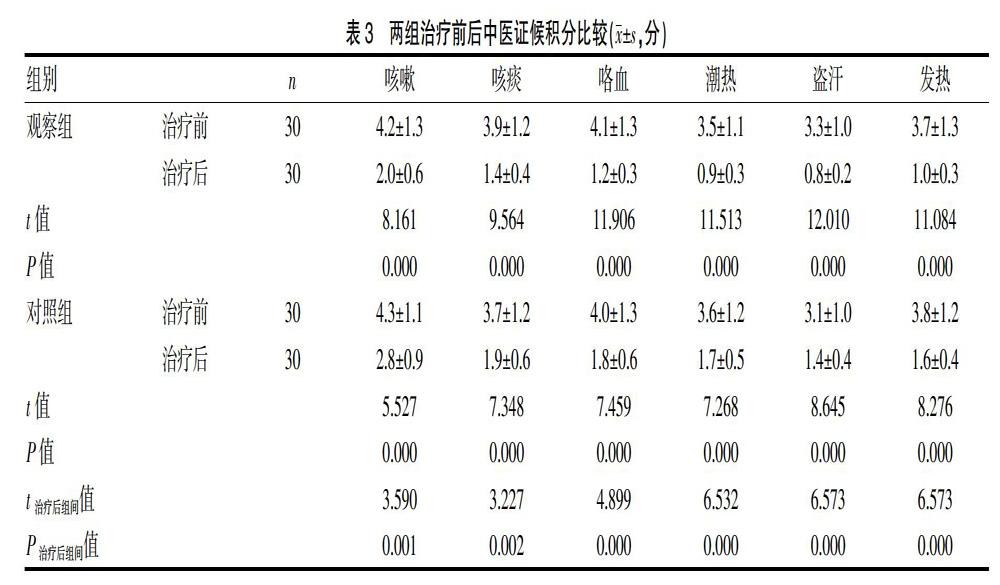
[摘要] 目的 探討补肺养阴汤辅助治疗耐多药肺结核的临床疗效及对患者免疫功能的影响。 方法 选择2017年1~12月在医院诊断治疗的耐多药肺结核患者60例为研究对象,随机分为两组,观察组30例,对照组30例。两组均给予常规西药治疗,观察组在此基础上加用补肺养阴汤治疗。比较两组临床疗效、痰结核菌培养转阴率、CT影像结果好转率、外周血T细胞水平及中医证候积分。 结果 观察组总有效率显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后,两组中医证候积分显著下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后观察组中医证候积分得分显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组治疗3个月与6个月,痰结合菌培养转阴率均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后3个月、6个月,观察组影像好转率均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后,观察组CD3+、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+水平显著高于治疗前及对照组治疗后,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);CD8+水平显著低于治疗前及对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核能显著改善患者免疫功能,提高临床疗效,提高痰结核菌转阴率。
[关键词] 中西医结合;耐多药;肺结核;免疫功能;咳嗽;咯血
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy of Bufei Yangyin Decoction in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and its effect on immune function. Methods 60 patients with multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosed and treated in the hospital from January to December 2017 were randomly divided into two groups including the observation group (n=30) and the control group(n=30). Both groups were treated with conventional western medicine, and the observation group was treated with Bufei Yangyin decoction based on the above treatment. The clinical efficacy, the negative conversion ratio of sputum tuberculosis culture, the CT image improvement rate, the peripheral blood T cell level and the TCM syndrome scores of the two groups were compared. Results The total effective rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). After treatment, the scores of TCM syndromes in the two groups decreased significantly, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). After treatment, the scores of TCM syndromes in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The negative conversion ratio of sputum tuberculosis culture in the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group after 3 months and 6 months of treatment, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). At 3 months and 6 months after treatment, the image improvement rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). After treatment, the levels of CD3+, CD4+, CD4+/CD8+ in the observation group were significantly higher than those before treatment and those in the control group after treatment(P<0.05). The level of CD8+ in the observation group after treatment was significantly lower than that before treatment and that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Integrated Chinese and Western medicine treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis can significantly improve the immune function of patients, improve clinical efficacy, and improve the negative conversion ratio of sputum tuberculosis.
综上所述,中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核能显著改善患者免疫功能,提高临床疗效,提高痰结核菌转阴率。
[参考文献]
[1] 刘晓方.2011-2017年徐州市活動性肺结核流行病学分析[J].江苏预防医学,2018,29(3):295-297.
[2] 米春存.肺结核中医辨证论治的探讨[J].光明中医,2017,32(22):3203-3205.
[3] 郑丽华.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核的疗效观察[J].中国医药科学,2015,5(12):43-45,48.
[4] 黄华,胡克.养阴补肺中药治疗耐多药肺结核疗效及对免疫功能的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(9):941-943,947.
[5] 余旭良,金菊仙,陆军,等.134例耐多药肺结核耐药情况分析[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2018,28(9):1114-1116, 1119.
[6] 王燕敏.化学治疗联合免疫药物治疗耐多药肺结核临床疗效[J].海峡药学,2018,30(7):197-199.
[7] 杨安文,周亮,徐祖辉,等.湖南省肺结核四种一线抗结核药物耐药特征及影响因素研究[J].中国人兽共患病学报,2018,34(5):396-403.
[8] 张宏,邝浩斌,覃红娟,等.利奈唑胺所致47例耐多药肺结核患者不良反应分析[J].中国防痨杂志,2018,40(1):73-79.
[9] 郭晓燕,张惠勇,马子风,等.740例耐多药肺结核中医病性证候要素分布规律[J].中医杂志,2018,59(7):603-606.
[10] 李志强,刘凤新,何玉霞,等.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核的疗效及对患者免疫功能的影响[J].世界中医药,2018,13(7):1605-1608.
[11] 古丽巴哈尔·阿不拉合买提,夏衣扎提·库尔曼.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核50例疗效观察[J].中国社区医师,2017,33(7):99-100.
[12] 尹柯,谢和宾,杨励,等.中西医结合治疗对耐多药肺结核患者T淋巴细胞亚群影响的Meta分析[J].新中医,2017,49(7):164-167.
[13] 徐向前,鹿振辉,陆城华,等.中医药治疗耐多药肺结核的研究近况[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,5(4):1653-1655.
[14] 卫芳征.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核50例临床分析[J].黑龙江医药,2017,30(5):1078-1079.
[15] 李悦琳,汪洋,刘勇,等.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核病临床研究[J].亚太传统医药,2016,12(16):107-108.
[16] 梁强.中西医结合治疗耐多药肺结核疗效分析[J].中医临床研究,2016,8(13):68-69.
[17] 刘晓,吴雪琼.中药治疗耐多药肺结核的研究进展[J].中国防痨杂志,2016,38(1):53-56.
[18] 张尊敬,刘忠达,郭净.耐多药肺结核中医证候分布规律及相关因素研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,3(11):4147-4148.
[19] 欧阳兵,汪亚玲,李练,等.耐药性肺结核中医证候系统综述[J].实用中医内科杂志,2017,31(3):1-2.
[20] 周玲霞,黄金鹏,楼敏.中西医联合治疗耐多药肺结核病的临床疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊,2013,31(4):942-944.
[21] 刘艳芬.养阴补肺法治疗耐多药肺结核的疗效观察[J].当代医学,2018,25(27):165-166.
(收稿日期:2019-04-11)

